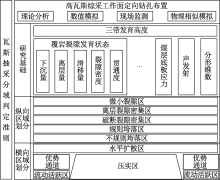
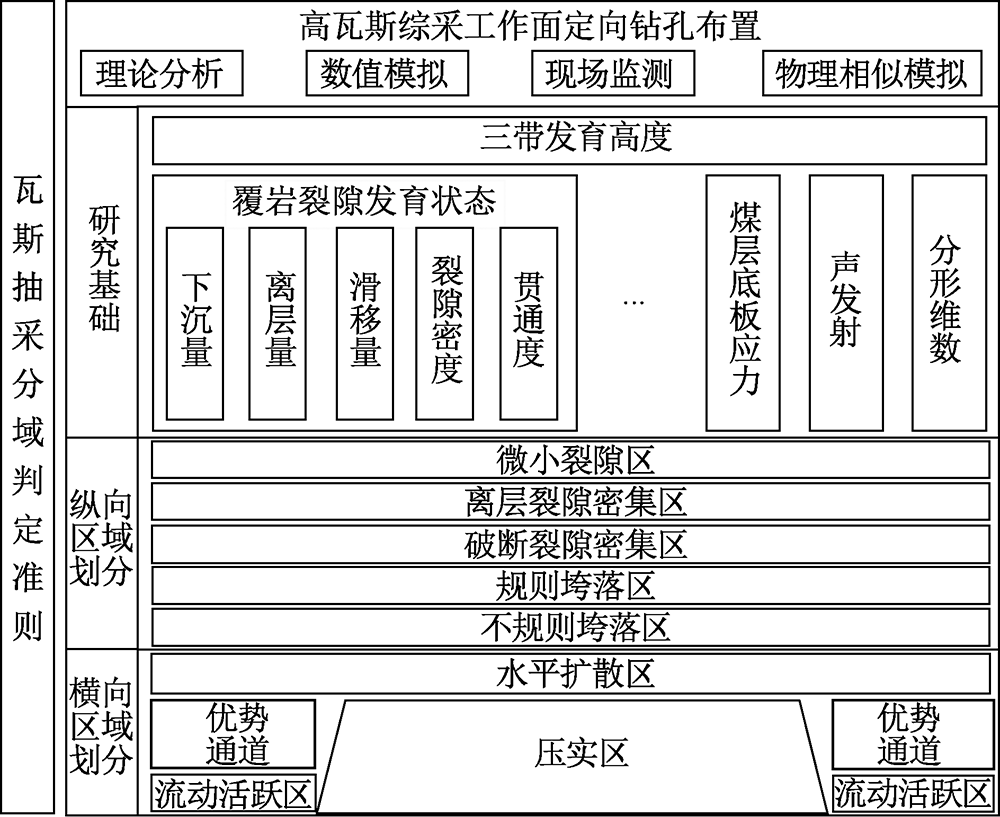
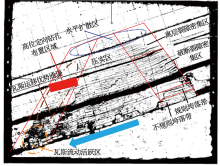
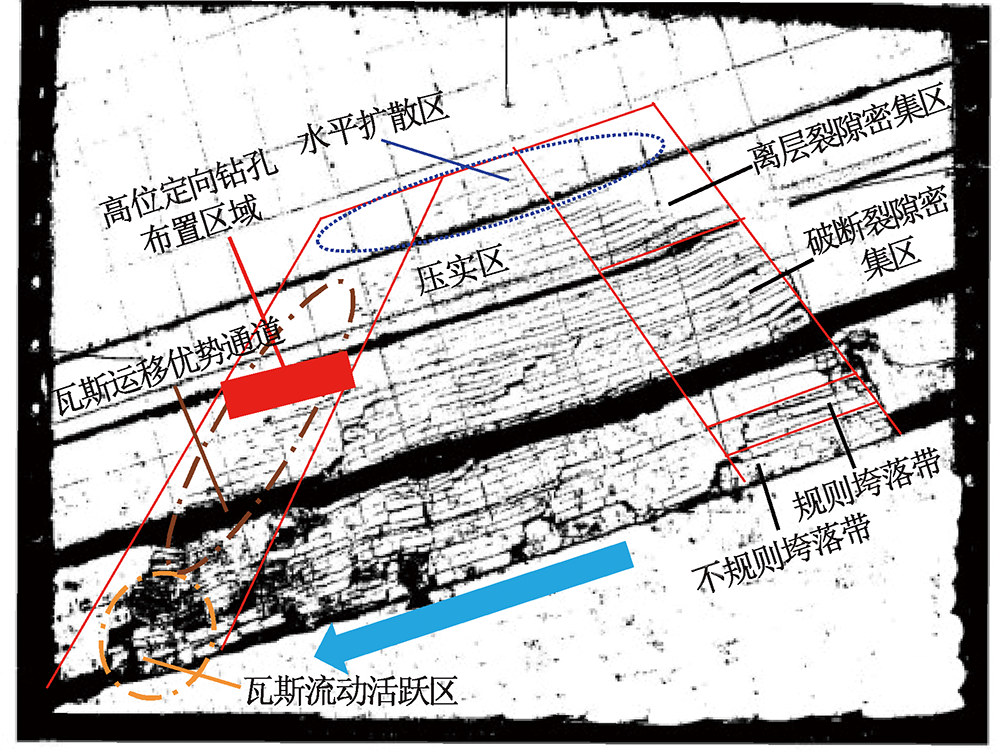
| [1] |
张庆贺, 袁亮, 杨科, 等. 深井煤岩动力灾害的连续卸压开采防治机理[J]. 采矿与安全工程学报, 2019, 36(1): 84-90, 106.
|
|
ZHANG Qinghe, YUAN Liang, YANG Ke, et al. Mechanism analysis on continuous stress-relief mining for preventing coal and rock dynamic disasters in deep coal mines[J]. Journal of Mining and Safety Engineering, 2019, 36(1): 84-90, 106.
|
| [2] |
高魁, 乔国栋, 刘健, 等. 构造复杂矿区煤与瓦斯突出瓦斯地质分析[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2019, 29(1):119-124.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2019.01.020
|
|
GAO Kui, QIAO Guodong, LIU Jian, et al. Gas-geology action analysis of coal-gas outburst in complicated geological structure coal mine[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2019, 29(1): 119-124.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2019.01.020
|
| [3] |
汪腾蛟, 聂朝刚, 杨小彬, 等. 考虑温度变化的采空区瓦斯抽采数值模拟[J]. 煤炭科学技术, 2021, 49(7):85-94.
|
|
WANG Tengjiao, NIE Chaogang, YANG Xiaobin, et al. Numerical simulation of gas drainage in gob considering temperature change[J]. Coal Science and Technology, 2021, 49(7): 85-94.
|
| [4] |
杨正凯, 程志恒, 刘彦青, 等. 突出煤层群多次采动对底板穿层钻孔瓦斯抽采的影响[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2020, 30(5):66-73.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2020.05.011
|
|
YANG Zhengkai, CHENG Zhiheng, LIU Yanqing, et al. Influence of multiple mining of outburst coal seam group on gas extraction of cross-layer borehole[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2020, 30(5): 66-73.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2020.05.011
|
| [5] |
张智渊, 朱传杰, 刘思远, 等. 复合储层层间窜流对瓦斯抽采的影响机制研究[J]. 煤矿安全, 2022, 53(2): 1-8.
|
|
ZHANG Zhiyuan, ZHU Chuanjie, LIU Siyuan, et al. Influence of interlayer channeling of composite reservoir on gas drainage[J]. Safety in Coal Mines, 2022, 53(2): 1-8.
|
| [6] |
年军, 高巍, 李润芝, 等. 以孔代巷瓦斯抽采布孔间距模拟及试验研究[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2019, 29(5): 117-123.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2019.05.020
|
|
NIAN Jun, GAO Wei, LI Runzhi, et al. Simulation and experimental study on space between boreholes for gas drainage instead of roadway[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2019, 29(5): 117-123.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2019.05.020
|
| [7] |
KARMIS M, TRIPLETT T, HAYCOCKS C, et al. Mining subsidence and its prediction in appalachian coalfield[C]. Rock Mechanics: Theory, Experiment, Practice. Proceedings, Process 24th US Symp. Rock Mechanics, 1983:665-675.
|
| [8] |
BAI Mao, ELSWORTH D. Some aspects of mining under aquifers in China[J]. Mining Science and Technology, 1990, 10(1): 81-91.
doi: 10.1016/0167-9031(90)90878-V
|
| [9] |
PAL-CHIK V. Influence of physical characteristics of weak rock mass on height of caved zone over abandoned subsurface coal mines[J]. Environmental Geology, 2002, 42(1): 92-101.
doi: 10.1007/s00254-002-0542-y
|
| [10] |
刘天泉. 矿山岩体采动影响与控制工程学及其应用[J]. 煤炭学报, 1995, 20(1):1-5.
|
|
LIU Tianquan. Influence of mining activities on mine rockmass and control engineering[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 1995, 20(1): 1-5.
|
| [11] |
ABBAS Majdi. Prediction of the height of destressed zone above the mined panel roof in longwall coal mining[J]. International Journal of Coal Geology, 2012, 98: 62-72.
doi: 10.1016/j.coal.2012.04.005
|
| [12] |
李树刚, 林海飞, 赵鹏翔, 等. 采动裂隙椭抛带动态演化及煤与甲烷共采[J]. 煤炭学报, 2014, 39(8): 1455-1462.
|
|
LI Shugang, LIN Haifei, ZHAO Pengxiang, et al. Dynamic evolution of mining fissure elliptic paraboloid zone extraction coal and gas[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2014, 39(8): 1455-1462.
|
| [13] |
杨科, 谢广祥. 综放开采采动裂隙分布及其演化特征分析[J]. 矿业安全与环保, 2009, 36(4):1-3, 91.
|
|
YANG Ke, XIE Guangxiang. Distribution of mining fissures induced by fully mechanized caving mining and analysis on their evolvement characteristics[J]. Mining Safety and Environmental Protection, 2009, 36(4): 1-3, 91.
|
| [14] |
LIN Haifei, LI Shugang, CHENG Lianhua. Studies on distribution features and internal methane concentration distribution laws of mining-induced fracture zone[C]. Progress in Safety Science and Technology, 2006: 1680-1685.
|
| [15] |
常聚才, 谢广祥, 张学会. 特厚煤层大采高综放工作面煤壁片帮机制分析[J]. 岩土力学, 2015, 36(6): 803-808.
|
|
CHANG Jucai, XIE Guangxiang, ZHANG Xuehui. Analysis of rib spalling mechanism of fully-mechanized top-coal caving face with great mining height in extra-thick coal seam[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2015, 36 (6): 803-808.
|
| [16] |
郭寿松. 大采高工作面煤壁片帮观测及其控制措施[J]. 矿业安全与环保, 2017, 44(3): 62-64.
|
|
GUO Shousong. Observation of coal wall spalling in coal face with large mining height and its control measures[J]. Mining Safety and Environmental Protection, 2017, 44(3): 62-64.
|
| [17] |
贾毅超, 刘萍, 韩森, 等. 近距离煤层群采空区高位定向钻孔布置优化研究[J]. 矿业研究与开发, 2022, 42(2): 18-23.
|
|
JIA Yichao, LIU Ping, HAN Sen, et al. Optimization study on high directional borehole layout in goaf of close distance coal seam group[J]. Mining Research and Development, 2022, 42(2): 18-23.
|
| [18] |
李卫龙, 汪青, 刘欣, 等. 煤矿瓦斯抽采智能系统设计[J]. 煤矿机械, 2021, 42(8): 14-17.
|
|
LI Weilong, WANG Qing, LIU Xin, et al. Design of intelligent system for gas extraction in coal mine[J]. Coal Mine Machinery, 2021, 42(8): 14-17.
|
| [19] |
丁洋, 朱冰, 李树刚, 等. 高突矿井采空区卸压瓦斯精准辨识及高效抽采[J]. 煤炭学报, 2021, 46(11):3565-3577.
|
|
DING Yang, ZHU Bing, LI Shugang, et al. Accurate and efficient drainage of relieved methane in goaf of high outburst mine[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2021, 46(11): 3565-3577.
|
| [20] |
张志敏. 不同通风方式下顶板高位定向钻孔瓦斯抽放效果研究[J]. 煤炭与化工, 2021, 44(11): 107-110, 113.
|
|
ZHANG Zhimin. Gas drainage effect of high-level directional drilling in roof under different ventilation modes[J]. Coal and Chemical Industry, 2021, 44(11): 107-110, 113.
|
| [21] |
张朝举, 方俊, 杨亚黎, 等. 祁东煤矿近距离煤层群瓦斯治理顶板拦截定向钻孔试验[J]. 工矿自动化, 2021, 47(11): 112-118.
|
|
ZHANG Chaoju, FANG Jun, YANG Yali, et al. Test of interception directional drilling for close distance coal seam group gas control in Qidong coal mine[J]. Journal of Mine Automation, 2021, 47(11): 112-118.
|
| [22] |
任建平, 王宁. 高位定向长钻孔替代普通倾向孔工程实践[J]. 煤炭技术, 2021, 40(9): 121-125.
|
|
REN Jianping, WANG Ning. Engineering practice of high-level directional long borehole replacing ordinary high-level tendency borehole[J]. Coal Technology, 2021, 40(9): 121-125.
|
| [23] |
林海飞, 杨二豪, 夏保庆, 等. 高瓦斯综采工作面定向钻孔代替尾巷抽采瓦斯技术[J]. 煤炭科学技术, 2020, 48(1):136-143.
|
|
LIN Haifei, YANG Erhao, XIA Baoqing, et al. Directional drilling replacing tailgate gas drainage technology in gassy fully-mechanized coal mining face[J]. Coal Science and Technology, 2020, 48(1): 136-143.
|
| [24] |
李彦明. 基于高位定向长钻孔的上隅角瓦斯治理研究[J]. 煤炭科学技术, 2018, 46(1):215-218.
|
|
LI Yanming. Upper corner gas control based on high level directional long borehole[J]. Coal Science and Technology, 2018, 46(1): 215-218.
|
| [25] |
刘超杰, 高运增, 赵高博, 等. 厚松散层软弱覆岩工作面“三带”发育特征与高度研究[J]. 矿业安全与环保, 2022, 49(1): 53-58.
|
|
LIU Chaojie, GAO Yunzeng, ZHAO Gaobo, et al. Study on the development characteristics and height of "three zones" of the working face covered with thick alluvium and weak overburden[J]. Mining Safety and Environmental Protection, 2022, 49(1): 53-58.
|
| [26] |
侯国培, 郭昆明, 岳茂庄, 等. 高位定向长钻孔瓦斯抽采技术应用[J]. 煤炭工程, 2019, 51(1): 64-67.
|
|
HOU Guopei, GUO Kunming, YUE Maozhuang, et al. Application of gas drainage technology in high-level directional long drilling hole[J]. Coal Engineering, 2019, 51(1): 64-67.
|
| [27] |
黄健丰, 吴璋, 王玉涛, 等. 水库下伏采空区覆岩裂隙探查与综合防治技术[J]. 煤矿安全, 2020, 51(2): 90-96.
|
|
HUANG Jianfeng, WU Zhang, WANG Yutao, et al. Exploration and comprehensive treatment technology of overburden fracture in underlying goaf of reservoir[J]. Safety in Coal Mines, 2020, 51(2): 90-96.
|
| [28] |
郭明杰, 郭文兵, 袁瑞甫, 等. 基于采动裂隙区域分布特征的定向钻孔空间位置研究[J]. 采矿与安全工程学报, 2022, 39(4): 817-826.
|
|
GUO Mingjie, GUO Wenbing, YUAN Ruifu, et al. Spatial location determination of directional boreholes based on regional distribution characteristics of mining-induced overburden fractures[J]. Journal of Mining and Safety Engineering, 2022, 39(4): 817-826.
|
| [29] |
关键, 郭正. 绕翼型低雷诺数流动的数值仿真[J]. 科学技术与工程, 2013, 13(24):7275-7281.
|
|
GUAN Jian, GUO Zheng. Numerical simulations of low-reynolds-number flows over the E387 airfoil[J]. Science Technology and Engineering, 2013, 13(24): 7275- 7281.
|