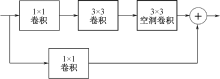
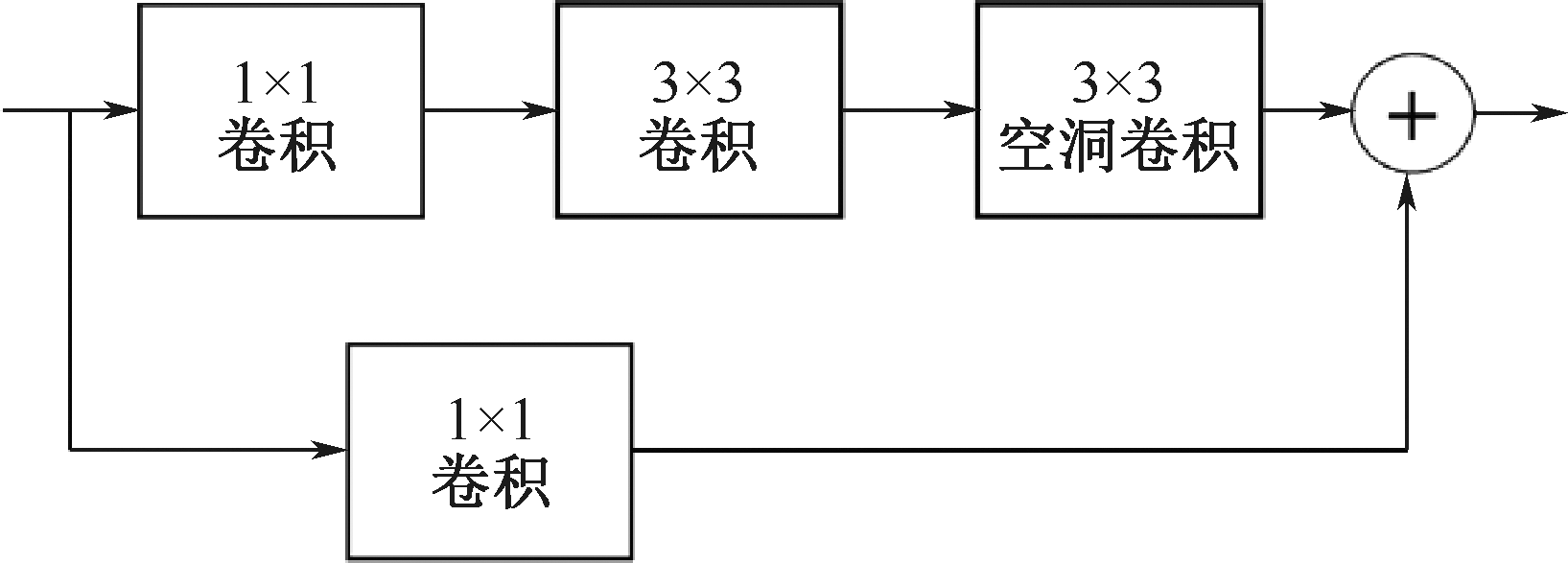
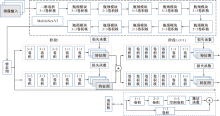
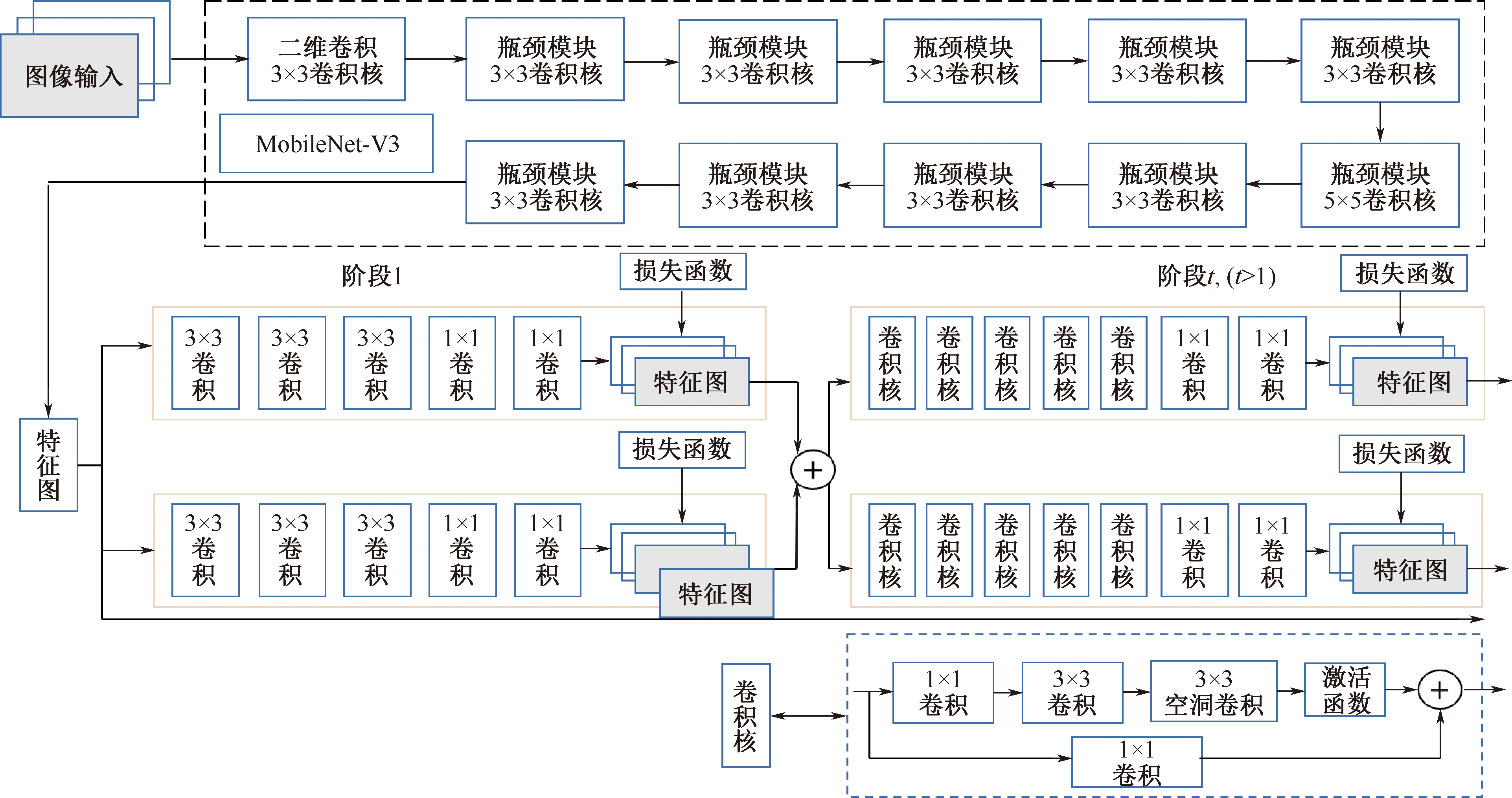
| [1] |
TIAN Shuicheng, WANG Yajuan, LI Hongxia, et al. Analysis of the causes and safety countermeasures of coal mine accidents: a case study of coal mine accidents in China from 2018 to 2022[J]. Process Safety and Environmental Protection, 2024, 187: 864-875.
doi: 10.1016/j.psep.2024.04.137
|
| [2] |
王大龙, 王冰山, 曹睿, 等. 煤矿安全管理行为交互机制与模型[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2025, 35(5):32-38.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2025.05.1094
|
|
WANG Dalong, WANG Bingshan, CAO Rui, et al. Interaction mechanism and model of coal mine safety management behaviors[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2025, 35(5): 32-38.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2025.05.1094
|
| [3] |
HAO Wenchao, JIANG Haiyan, SONG Qinghui, et al. A multi modal fusion coal gangue recognition method based on IBWO-CNN-LSTM[J]. Scientific Reports, 2024, 14: DOI: 10.1038/S41598-024-80811-6.
|
| [4] |
DENG Lujuan, FU Ruochong, SUN Qian, et al. Abnormal behavior recognition based on feature fusion C3D network[J]. Journal of Electronic Imaging, 2023, 32(2): DOI: 10.1117/1.JEI.32.2.021605.
|
| [5] |
CAO Xiangang, ZHANG Chiyu, WANG Peng, et al. Unsafe mining behavior identification method based on an improved ST-GCN[J]. Sustainability, 2023, 15(2): DOI: 10.3390/SU15021041.
|
| [6] |
NAN Yahui, JU Jianguo, HUA Qingyi, et al. A-mobileNet: an approach of facial expression recognition[J]. Alexandria Engineering Journal, 2022, 61(6): 4435-4444.
doi: 10.1016/j.aej.2021.09.066
|
| [7] |
杨奉展, 顾清华, 李少博, 等. 露天矿低能见度下多模态融合障碍物检测[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2025, 35(5):195-203.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2025.05.1654
|
|
YANG Fengzhan, GU Qinghua, LI Shaobo, et al. Multimodal fusion-based obstacle detection in low-visibility open-pit mines[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2025, 35(5):195-203.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2025.05.1654
|
| [8] |
饶天荣, 潘涛, 徐会军. 基于交叉注意力机制的煤矿井下不安全行为识别[J]. 工矿自动化, 2022, 48(10):48-54.
|
|
RAO Tianrong, PAN Tao, XU Huijun. Unsafe action recognition in underground coal mine based on cross-attention mechanism[J]. Journal of Mine Automation, 2022, 48(10): 48-54.
|
| [9] |
马天, 姜梅, 杨嘉怡, 等. 基于多特征融合时差网络的带式输送机区域违规行为识别[J]. 工矿自动化, 2024, 50(7):115-122.
|
|
MA Tian, JIANG Mei, YANG Jiayi, et al. Recognition of violations in belt conveyor area based on multi-feature fusion for time-difference network[J]. Journal of Mine Automation, 2024, 50(7):115-122.
|
| [10] |
王宇, 于春华, 陈晓青, 等. 基于多模态特征融合的井下人员不安全行为识别[J]. 工矿自动化, 2023, 49(11):138-144.
|
|
WANG Yu, YU Chunhua, CHEN Xiaoqing, et al. Recognition of unsafe behaviors of underground personnel based on multi modal feature fusion[J]. Journal of Mine Automation, 2023, 49(11): 138-144.
|
| [11] |
KUEHNE H, JHUANG H, GARROTE E, et al. HMDB: a large video database for human motion recognition[C]. 2011 International Conference on Computer Vision, 2011:2556-2563.
|
| [12] |
SOOMRO K, ZAMIR A R, SHAH M. UCF101: a dataset of 101 human actions classes from videos in the wild[J]. Computer Science, 2012: DOI: 10.48550/arXiv.1212.0402.
|