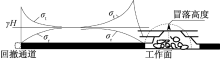
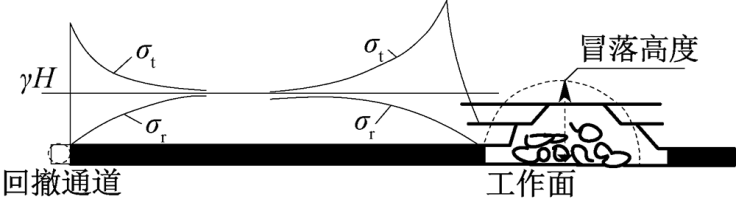
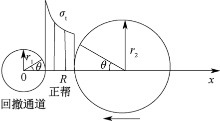
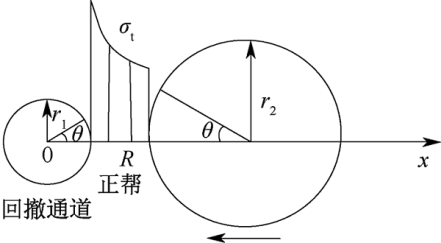
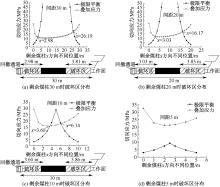
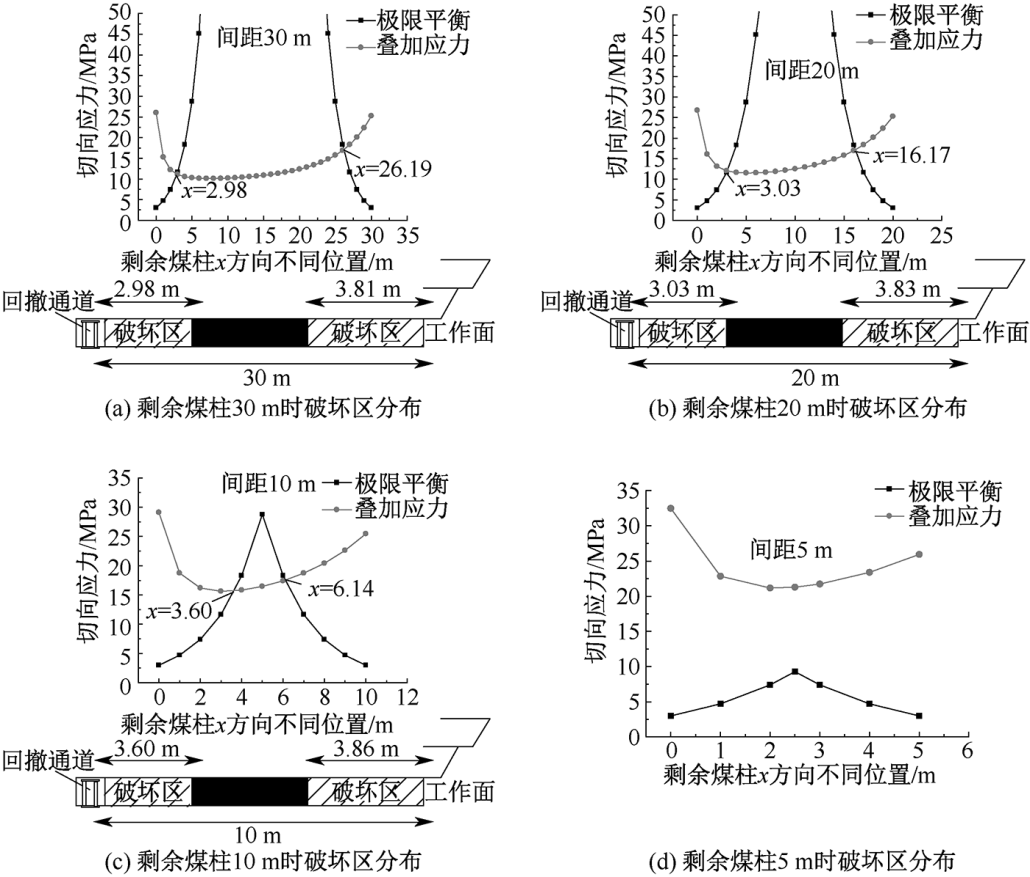
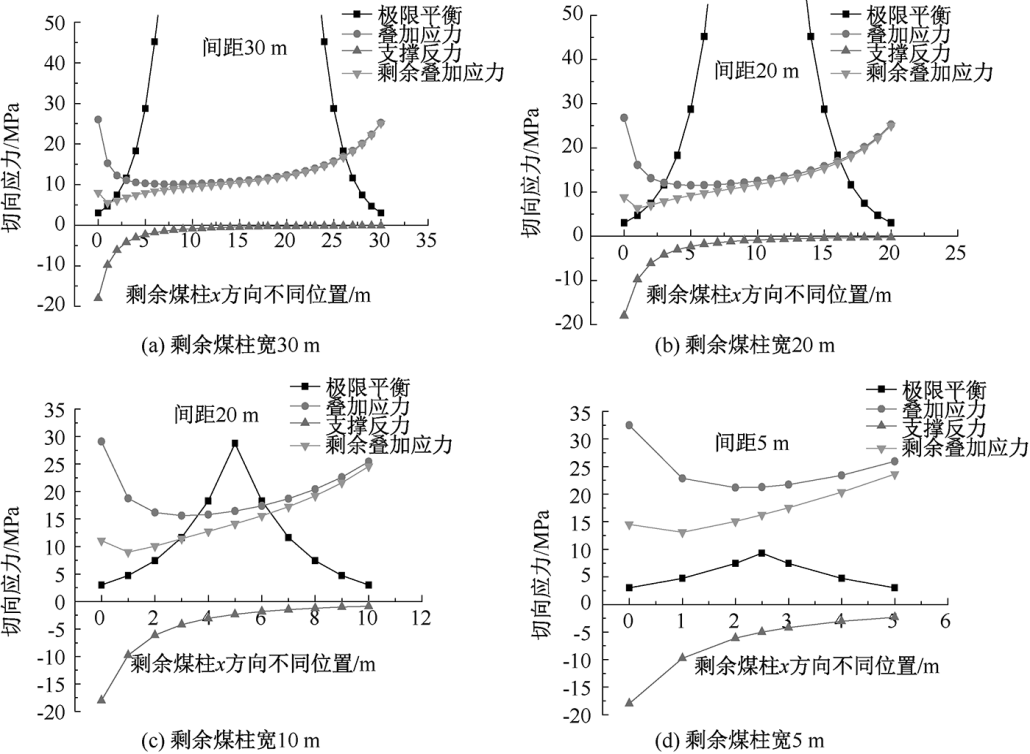
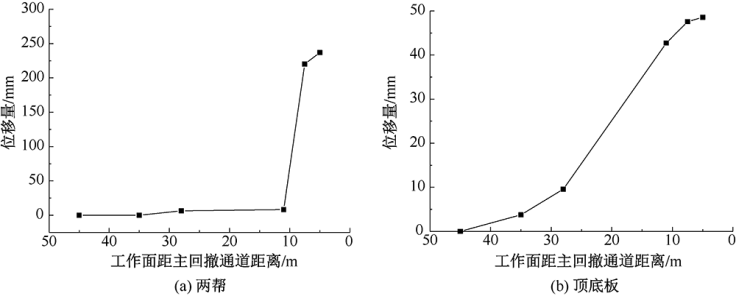
| [1] |
谷拴成, 王博楠, 李金华, 等. 回撤通道保护煤柱应力分布及其影响因素分析[J]. 中国煤炭, 2017, 43(3):36-40,52.
|
|
GU Shuancheng, WANG Bonan, LI Jinhua, et al. Research on stress distribution and impact paarameters of protective coal pillar at retracement channel[J]. China Coal, 2017, 43(3):36-40,52.
|
| [2] |
杨仁树, 李永亮, 朱晔, 等. 特殊条件下大采高工作面回撤通道稳定性控制研究[J]. 煤炭科学技术, 2017, 45(1):10-15.
|
|
YANG Renshu, LI Yongliang, ZHU Ye, et al. Study on the stability control of removal channel for high cutting mining face under special condition[J]. Coal Science and Technology, 2017, 45(1):10-15.
|
| [3] |
吕坤, 赵志超, 赵志强. 特厚煤层综放工作面回撤通道支护技术研究[J]. 煤炭科学技术, 2018, 46(3):39-43.
|
|
LYU Kun, ZHAO Zhichao, ZHAO Zhiqiang. Study on support technology of equipment removal channel in fully-mechanized top coal caving face in ultra-thick seam[J]. Coal Science and Technology, 2018, 46 (3):39-43.
|
| [4] |
王博. 综采工作面液压支架快速回撤技术初探[J]. 山东煤炭科技, 2017(8):143-145.
|
|
WANG Bo. Preliminary discussion hydraulic support quick recovery technology in fully mechanized face[J]. Shandong Coal Technology, 2017(8):143-145.
|
| [5] |
张丽萍, 武维承. 矿井条件对支架安全快速回撤技术的影响分析[J]. 设备管理与维修, 2018(22):150-152.
|
| [6] |
朱永庆, 艾俊友, 李立军, 等. 综放工作面回撤与安装新工艺在小康矿的应用[J]. 煤矿安全, 2005, 36(2):24-26.
|
| [7] |
王兆会, 孔德中, 王闯, 等. 浅埋高强度采场回撤阶段围岩破断机理及控制[J]. 煤炭工程, 2014, 46(9):76-79.
|
|
WANG Zhaohui, KONG Dezhong, WANG Chuang, et al. Mechanism and control of surrounding rock breakdown at mining equipment withdrawn stage from high intensity coal mining face in shallow depth seam[J]. Coal Engineering, 2014, 46(9):76-79.
|
| [8] |
吴志刚, 田西勇. 大采高工作面回撤通道矿压规律实测[J]. 煤矿开采, 2013, 18(6):78-80.
|
|
WU Zhigang, TIAN Xiyong. Underground pressure rule observation in dismantle roadway of large-mining-height mining face[J]. Coal Mining Technology, 2013, 18(6):78-80.
|
| [9] |
张金虎. 破碎顶板回撤通道围岩运动规律和支护适应性研究[J]. 煤炭科学技术, 2015, 43(12):28-31.
|
|
ZHANG Jinhu. Study on movement law of surrounding rock and support adaptability of the broken roof in return channel[J]. Coal Science and Technology, 2015, 43(12):28-31.
|
| [10] |
吕华文. 预掘回撤通道稳定性机理分析及应用[J]. 煤炭学报, 2014, 39(增1):50-56.
|
|
LYU Huawen. The mechanism of stability of pre-driven rooms and the practical techniques[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2014, 39(S1):50-56.
|
| [11] |
李臣, 郭晓菲, 霍天宏, 等. 预掘双回撤通道煤柱留设及其围岩稳定性控制[J]. 华中科技大学学报:自然科学版, 2021, 49(4):20-25,31.
|
|
LI Chen, GUO Xiaofei, HUO Tianhong, et al. Coal pillar design of pre-excavated double equipment withdrawal channel and its surrounding rock stability control[J]. Huazhong University of Science and Technology:Natural Science Edition, 2021, 49(4):20-25,31.
|
| [12] |
张寅, 赵毅, 李皓. 综采工作面回撤巷强矿压显现机理及控制技术[J]. 煤田地质与勘探, 2021, 49(2):110-116.
|
|
ZHANG Yin, ZHAO Yi, LI Hao. Mechanism and control of strong ground pressure in fully mechanized mining face[J]. Coal Geology & Exploration, 2021, 49(2):110-116.
|
| [13] |
贺艳军, 张金山, 陈凯, 等. 预掘回撤通道末采应力叠加效应及围岩破坏规律分析[J/OL].(2020-11-04). 重庆大学学报. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/50.1044.N.20201102.1743.002.html.
|
|
HE Yanjun, ZHANG Jinshan, CHEN Kai, et al. Analysis on the superposition effect of stress and the failure law of surrounding rock duri ang the last mining period of pre-excavation return channel[J/OL].(2020-11-04). Journal of Chongqing University. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/50.1044.N.20201102.1743.002.html.
|
| [14] |
高林, 王家臣, 孔德中, 等. 动压影响半煤岩上山变形机制及修复技术[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2020, 30(3):67-73.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2020.03.011
|
|
GAO Lin, WANG Jiachen, KONG Dezhong, et al. Deformation mechanism and repairing technology for coal-rock uphill roadway under influence of dynamic pressure[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2020, 30(3):67-73.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2020.03.011
|
| [15] |
李国盛, 张辉, 蒋帅旗. 频繁采动影响巷道围岩强化支护技术及其应用[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2018, 28(7):142-147.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2018.07.023
|
|
LI Guosheng, ZHANG Hui, JIANG Shuaiqi. Technology for enhancing supporting roadway surrounding rock influenced by frequent mining and its application[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2018, 28(7):142-147.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2018.07.023
|
| [16] |
SYD S Peng. Topical areas of research needs in ground control-a state of the art review on coal mine ground control[J]. International Journal of Mining Science and Technology, 2015, 25(1):1-6.
doi: 10.1016/j.ijmst.2014.12.006
|
| [17] |
WANG Hongwei, JIANG Yaodong, XUE Sheng, et al. Assessment of excavation damaged zone around roadways under dynamic pressure induced by an active mining process[J]. International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences, 2015, 77:265-277.
doi: 10.1016/j.ijrmms.2015.03.032
|
| [18] |
彭林军, 岳宁, 李申龙, 等. 超大采高综采工作面回撤通道支护研究[J/OL].(2020-12-17). 煤炭科学技术. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/11.2402.td.20201217.1411.005.html.
|
|
PENG Linjun, YUE Ning, LI Shenlong, et al. Study on support of retractable channel in fully mechanized mining face with super large mining height[J/OL].(2020-12-17). Coal Science and Technology. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/11.2402.td.20201217.1411.005.html.
|
| [19] |
王跃权. 大埋深矿井工作面双回撤通道水力压裂卸压技术[J]. 煤炭科学技术, 2018, 46(增2):90-93.
|
|
WANG Yuequan. Hydraulic fracturing and pressure relief technology of dual return channel in large buried deep mine working face[J]. Coal Science and Technology, 2018, 46(S2):90-93.
|
| [20] |
JIANG Lishuai, KONG Peng, SHU Jiaming, et al. Numerical analysis of support designs based on a case study of a longwall entry[J]. Rock Mechanics and Rock Engineering, 2019, 52(9): 3373-3384.
doi: 10.1007/s00603-018-1728-2
|
| [21] |
李俊平, 连民杰. 矿山岩石力学[M]. 北京: 冶金工业出版社, 2011:184-185.
|