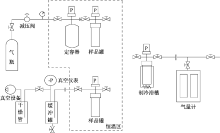
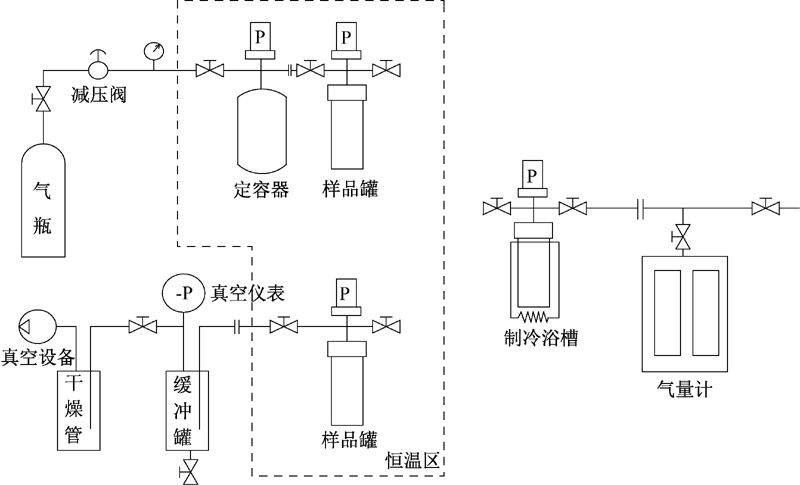
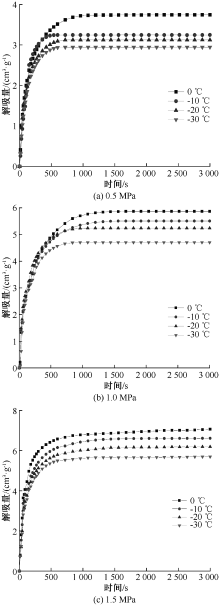
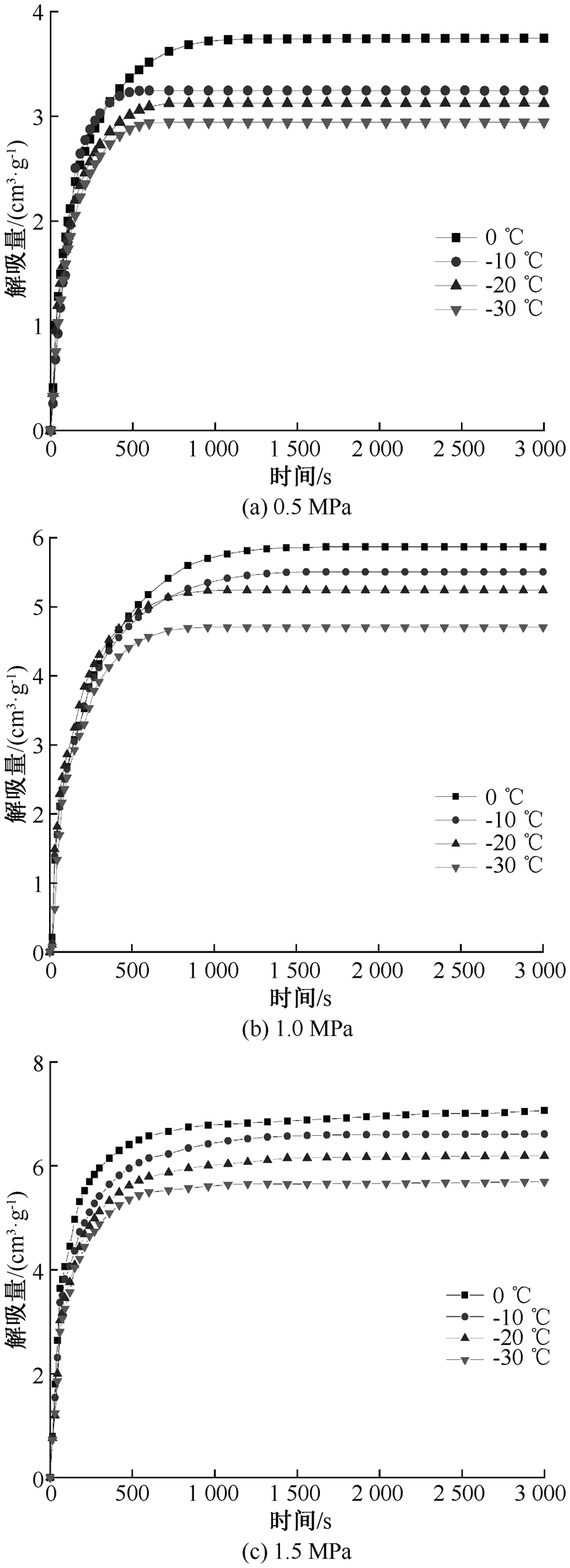
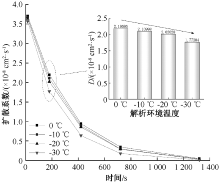
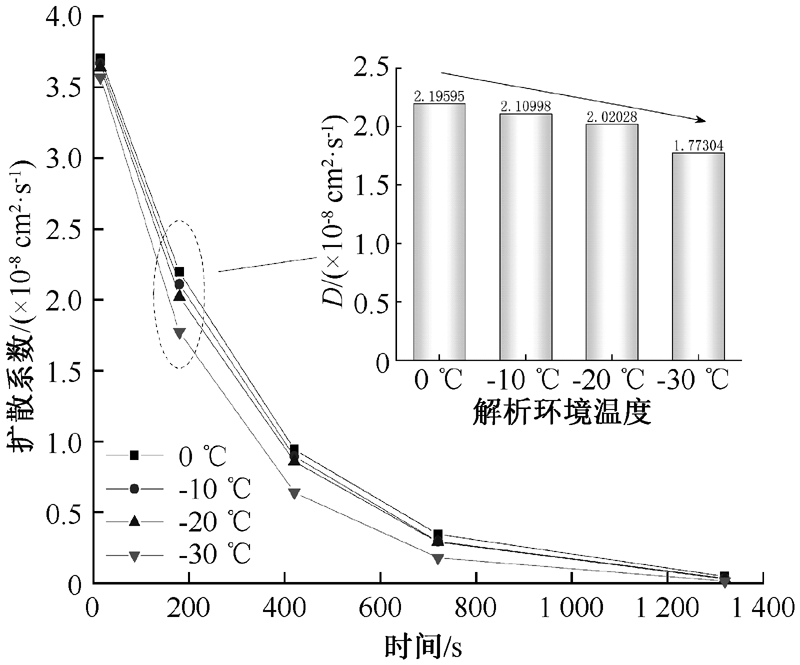
| [1] |
WANG Zhaofeng, TANG Xu, YUE Gaowei, et al. Physical simulation of temperature influence on methane sorption and kinetics in coal: benefits of temperature under 273.15 K[J]. Fuel, 2015, 158:207-216.
doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2015.05.011
|
| [2] |
YUE Jiwei, YUE Gaowei, WANG Zhaofeng, et al. Freezing method for rock cross-cut coal uncovering I: mechanical properties of a frozen coal seam for preventing outburst[J]. Scientific Reports, 2019, 9(1):96-101.
doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-36471-4
|
| [3] |
WANG Long, WANG Zhaofeng, QI Chenjun, et al. Physical simulation of temperature and pressure evolvement in coal by different refrigeration modes for freezing coring[J]. ACS Omega, 2019, 4(11):152-161.
|
| [4] |
王兆丰, 王龙, 董家昕, 等. 冷冻取芯过程含瓦斯煤样温度场演化规律模拟研究[J]. 煤炭学报, 2021, 46(1):199-210.
|
|
WANG Zhaofeng, WANG Long, DONG Jiaxin, et al. Simulation on the temperature evolution law of coal containing gas in the freezing coring process[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2021, 46(1):199-210.
|
| [5] |
岳高伟, 王兆丰, 康博. 低温环境煤的瓦斯扩散系数时变特性[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2014, 24(2):107-112.
|
|
YUE Gaowei, WANG Zhaofeng, KANG Bo. Time-varying characteristics of gas diffusion coefficient in low temperature environment[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2014, 24(2):107-112.
|
| [6] |
张宪尚. 扩散时间对经典模型扩散系数影响研究[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2020, 30(2):60-65.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2020.02.010
|
|
ZHANG Xianshang. Influence of time factor on diffusion coefficient based on classical model[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2020, 30(2):60-65.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2020.02.010
|
| [7] |
贾宏福, 安丰华, 彭信山. 巴雷尔法计算煤瓦斯扩散系数的局限性分析[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2020, 30(2):73-78.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2020.02.012
|
|
JIA Hongfu, AN Fenghua, PENG Xinshan. Limitation of Barrell formula in calculating gas diffusion coefficient of coal[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2020, 30(2):73-78.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2020.02.012
|
| [8] |
史广山, 白鹏飞, 张玉贵. 不同条件煤粒瓦斯瞬时扩散系数变化特征试验[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2017, 27(8):102-107.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2017.08.018
|
|
SHI Guangshan, BAI Pengfei, ZHANG Yugui. Variation characteristics of instantaneous diffusion coefficient of gas through coal particles under different conditions[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2017, 27(8):102-107.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2017.08.018
|
| [9] |
聂百胜, 何学秋, 王恩元. 瓦斯气体在煤层中的扩散机理及模式[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2000, 20(6):27-31.
|
|
NIE Baisheng, HE Xueqiu, WANG Enyuan. Mechanism and modes of gas diffusion in coal seams[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2000, 20(6):27-31.
|
| [10] |
林晨. 煤粒甲烷扩散系数幂函数模型研究[D]. 焦作: 河南理工大学,2018.
|
|
LIN Chen. Research on power function model of coal particle methane diffusion coefficient[D]. Jiaozuo: Henan Polytechnic University, 2018.
|
| [11] |
王宝俊, 章丽娜, 凌丽霞, 等. 煤分子结构对煤层气吸附与扩散行为的影响[J]. 化工学报, 2016, 67(6):2548-2557.
|
|
WANG Baojun, ZHANG Li'na, LING Lixia, et al. Effects of coal molecular structure on adsorption and diffusion behaviors of coalbed methane[J]. CIESC Journal, 2016, 67(6):2548-2557.
|
| [12] |
李志强, 刘勇, 许彦鹏, 等. 煤粒多尺度孔隙中瓦斯扩散机理及动扩散系数新模型[J]. 煤炭学报, 2016, 41(3):633-643.
|
|
LI Zhiqiang, LIU Yong, XU Yanpeng, et al. Gas diffusion mechanism in multi-scale pores of coal particles and new diffusion model of dynamic diffusion coefficient[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2016, 41(3):633-643.
|
| [13] |
贾宏福. 基于浓度差测定方法的扩散系数影响因素空模型研究[D]. 焦作: 河南理工大学,2021.
|
|
JIA Hongfu. Research on the influence factor and model of diffusion coefficient based on the method of concentration difference measurement[D]. Jiaozuo: Henan Polytechnic University,2021.
|
| [14] |
谈慕华, 黄蕴元. 表面物理化学[M]. 北京: 中国建筑工业出版社,1985:27.
|
| [15] |
周世宁, 林伯泉. 煤层瓦斯赋存与流动理论[M]. 北京: 煤炭工业出版社,1997:50-53.
|