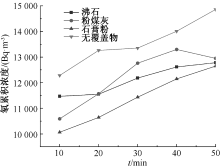
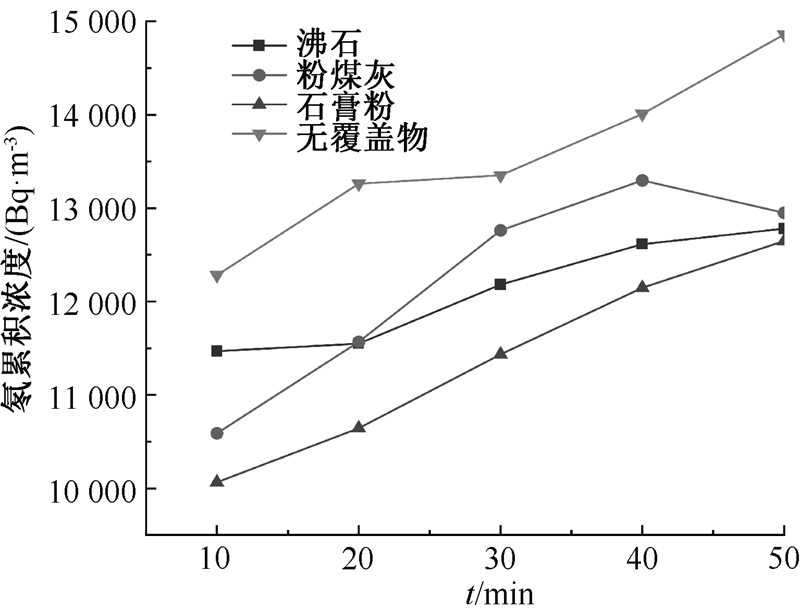
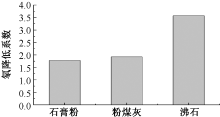
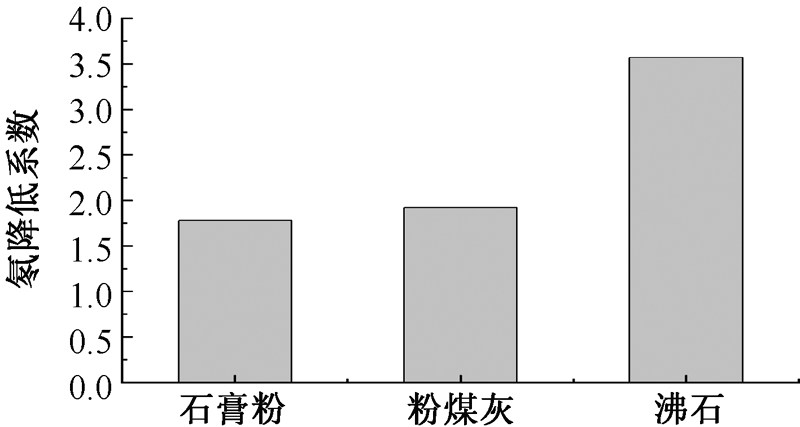
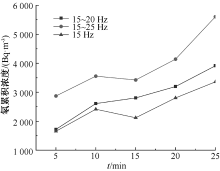
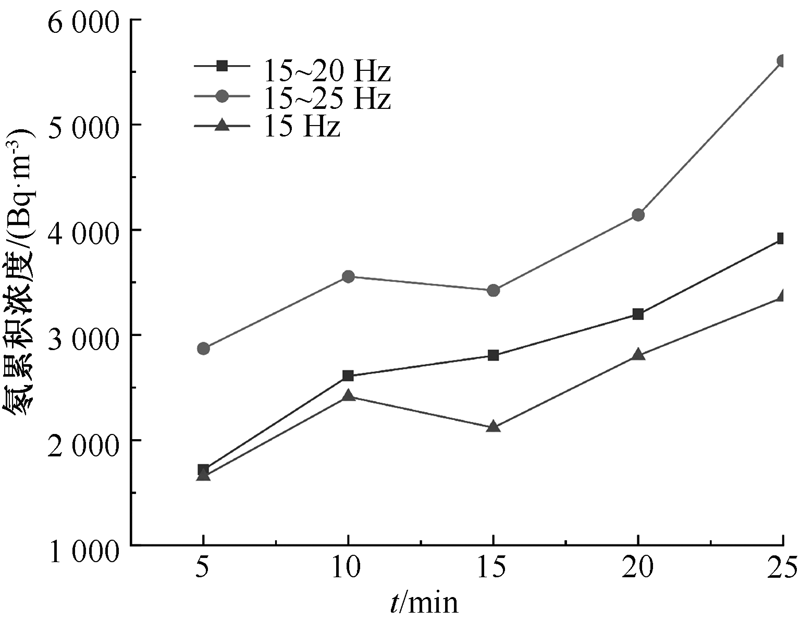
| [1] |
GB18306—2015,中国地震动参数区划图[S].
|
|
GB18306-2015,Seismic ground motion parameter zoning map of China[S].
|
| [2] |
谭凯旋, 胡寒桥, 刘泽华, 等. 不同覆盖物抑制铀尾矿氡析出的效果[J]. 矿物学报, 2012, 32(2) : 233-237.
|
|
TAN Kaixuan, HU Hanqiao, LIU Zehua, et al. Effect of different mulch on Radon exhalation from uranium tailings[J]. Journal of Mineralogy, 2012, 32(2): 233-237.
|
| [3] |
袁劲帆. 低频振动对干湿混合型铀尾矿库滩面氡析出影响的实验研究[D]. 衡阳: 南华大学,2020.
|
|
YUAN Jinfan. The experimental study on low-frequency vibration of dry-wet mixed uranium tailings pond beach face of radon exhalation effect[D]. Hengyang: University of South China, 2020.
|
| [4] |
李向阳, 朱海, 袁劲帆, 等. TVU耦合作用对砂岩型铀矿岩氡析出影响的试验研究[J]. 铀矿冶, 2019, 38(2):140-145.
|
|
LI Xiangyang, ZHU Hai, YUAN Jinfan, et al. Experimental study on the effect of TVU coupling on Radon exhalation from sandstone-type uranium deposit[J]. Uranium Mining and Metallurgy, 2019, 38(2):140-145.
|
| [5] |
TAREEN A D K, NADEEM M S A, KEARFOTT K J, et al. Descriptive analysis and earthquake prediction using boxplot interpretation of soil radon time series data[J]. Appliedradiation and Isotopes,2019,154:DOI:10.1016/j.apradiso.2019.108861.
|
| [6] |
蔡梓麒, 李向阳, 雷波, 等. 低频振动对高温类铀矿岩氡析出规律的影响研究[J]. 工业安全与环保, 2018, 44(4):22-26.
|
|
CAI Ziqi, LI Xiangyang, LEI Bo, et al. Effect of low frequency vibration on Radon exhalation from high temperature uranium ores[J]. Industrial Safety and Environmental Protection, 2018, 44(4) : 22-26.
|
| [7] |
刘艳, 刘永, 徐正华, 等. 长期高温下铀尾矿库覆土层控氡性能研究[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2020, 30(3): 171-177.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2020.03.026
|
|
LIU Yan, LIU Yong, XU Zhenghua, et al. Research on radon control performance of covering soil in uranium tailings reservoir under long time high temperature[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2020, 30(3): 171-177.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2020.03.026
|
| [8] |
FERRY C, RICHON P, BENEITO A, et al. Evaluation of the effect of a cover layer on radon exhalation from uranium mill tailings:transient radon flux analysis[J]. Journal of Environmental Radioactivity, 2002, 63(1):49-64.
doi: 10.1016/S0265-931X(02)00015-2
|
| [9] |
谢腾飞, 李君利, 王玲. 铀尾矿库覆盖降氡黏土参数优化[J]. 辐射防护, 2013, 33(4):243-248.
|
|
XIE Tengfei, LI Junli, WANG Ling. Optimization of clay parameters for radon reduction by covering uranium tailings reservoir[J]. Radiation Protection, 2013, 33(4) : 243-248.
|
| [10] |
金佳旭, 崔红志, 梁冰, 等. 地震作用下尾矿库溃坝过程模型试验及加固方案[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2017, 27(2): 92-97.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2017.02.017
|
|
JIN Jiaxu, CUI Hongzhi, LIANG Bing, et al. Model-based study on collapse of tailing sreservoir dam under earthquake action and reinforcement scheme[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2017, 27(2):92-97.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2017.02.017
|
| [11] |
潘英杰. 浅谈俄罗斯铀废石场尾矿库退役治理的安全环保标准[J]. 铀矿冶, 2016, 35(2):118-123.
|
|
PAN Yingjie. Expounding ones view's about safe and environmental protection problem as to close and manage of waste-rock piles and tailings pond of uranium in Russia[J]. Uranium Mining and Metallurgy, 2016, 35(2): 118-123.
|
| [12] |
袁劲帆, 李向阳, 洪昌寿, 等. 单向低频振动对铀尾矿库滩面氡析出影响的实验研究[J]. 南华大学学报:自然科学版, 2020, 34(1):9-15.
|
|
YUAN Jinfan, LI Xiangyang, HONG Changshou, et al. The experimental study on single-direction low-frequency vibration of uranium tailings pond beach face of radon exhalation effect[J]. Journal of University of South China:Science and Technology, 2020, 34(1): 9-15.
|