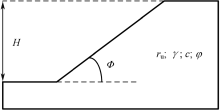
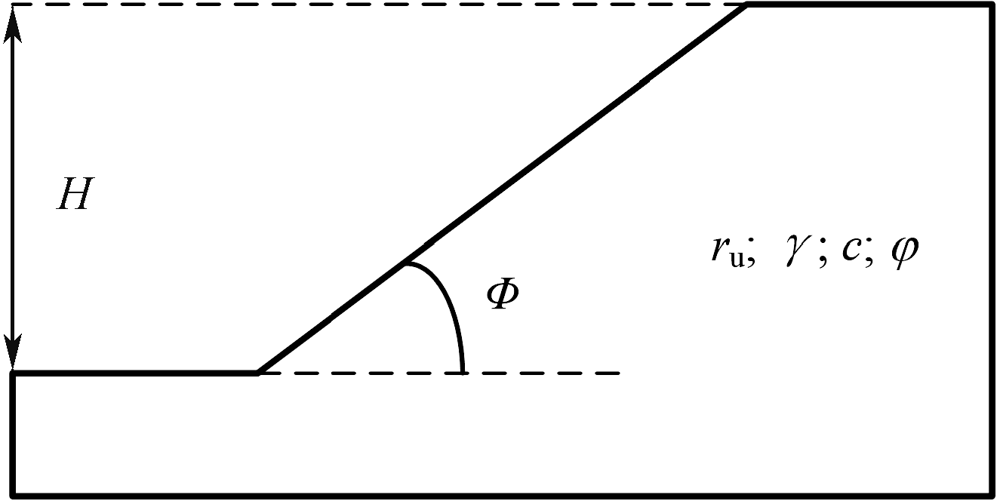
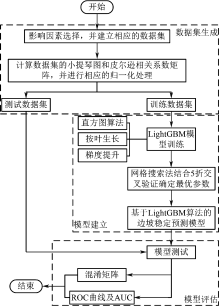
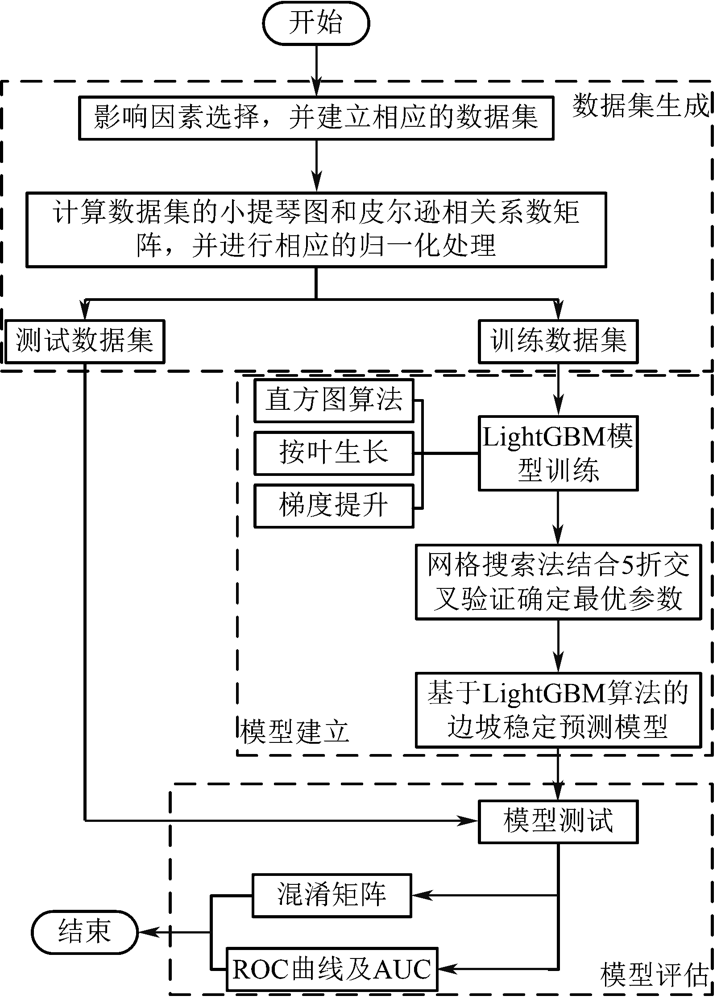
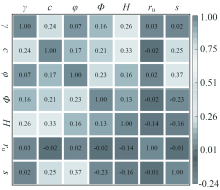
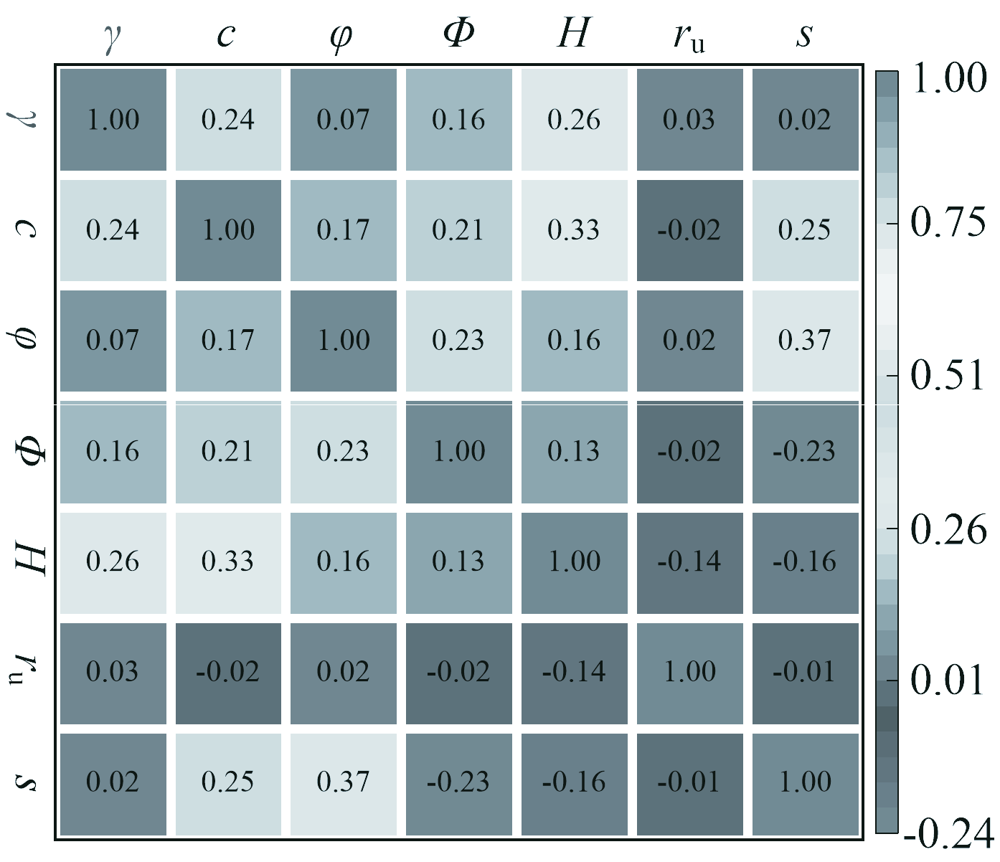
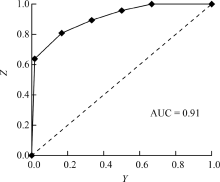
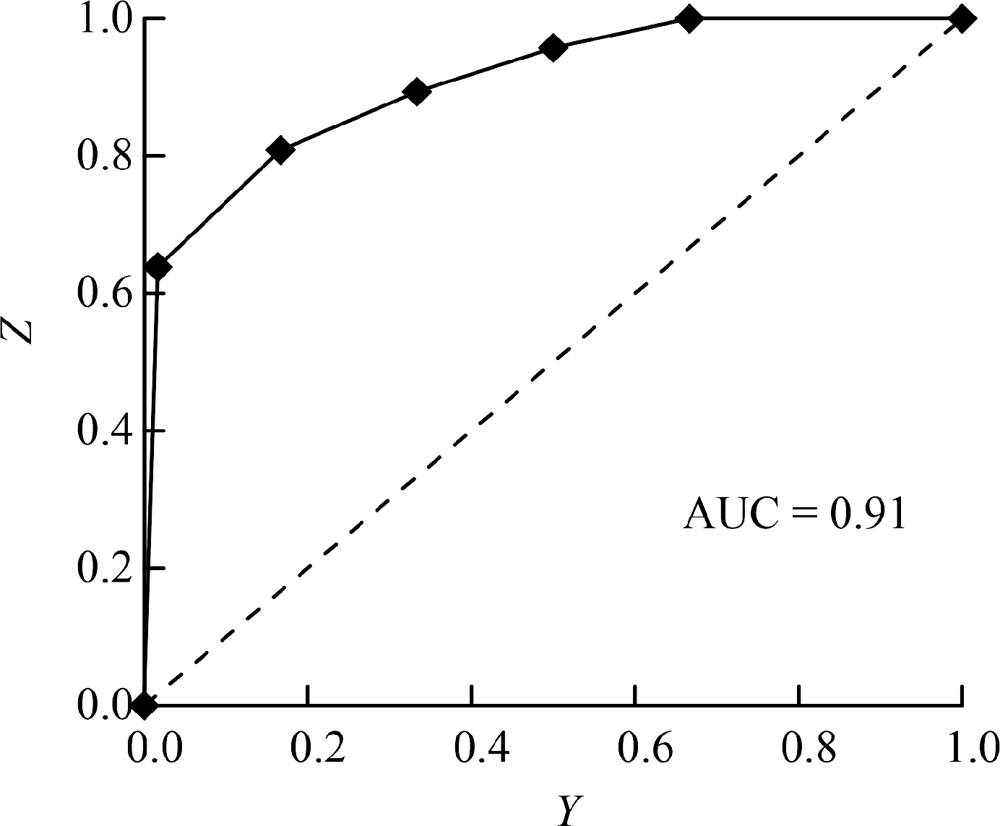
| [1] |
罗亦泳, 姚宜斌, 张立亭, 等. 基于HIOA-MK-TCRVM算法的边坡稳定性估计模型[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2017, 27(1):116-121.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2017.01.021
|
|
LUO Yiyong, YAO Yibin, ZHANG Liting, et al. Slope stability estimation model based on HIOA-MK-TCRVM[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2017, 27(1):116-121.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2017.01.021
|
| [2] |
吴孟龙, 叶义成, 胡南燕, 等. RAGA-PPC云模型在边坡稳定性评价中的应用[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2019, 29(9):57-63.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2019.09.009
|
|
WU Menglong, YE Yicheng, HU Nanyan, et al. Application of RAGA-PPC cloud model in slope stability evaluation[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2019, 29(9):57-63.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2019.09.009
|
| [3] |
张豪, 罗亦泳. 基于人工免疫算法的边坡稳定性预测模型[J]. 煤炭学报, 2012, 37(6):911-917.
|
|
ZHANG Hao, LUO Yiyong. Prediction model for slope stability based on artificial immune algorithm[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2012, 37(6):911-917.
|
| [4] |
杨杰, 马春辉, 程琳, 等. 高陡边坡变形及其对坝体安全稳定影响研究进展[J]. 岩土力学, 2019, 40(6):2341-2353, 2368.
|
|
YANG Jie, MA Chunhui, CHENG Lin, et al. Research advances in the deformation of high-steep slopes and its influence on dam safety[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2019, 40(6):2341-2353,2368.
|
| [5] |
LIN Yun, ZHOU Keping, LI Jielin. Prediction of slope stability using four supervised learning methods[J]. IEEE Access, 2018, 6:31169-31 179.
|
| [6] |
LI Bo, LI Duanyou, ZHANG Zhijun, et al. Slope stability analysis based on quantum-behaved particle swarm optimization and least squares support vector machine[J]. Applied Mathematical Modelling, 2015, 39(17):5253-5264.
doi: 10.1016/j.apm.2015.03.032
|
| [7] |
胡军, 董建华, 王凯凯, 等. 边坡稳定性的CPSO-BP模型研究[J]. 岩土力学, 2016, 37(增1):577-582,590.
|
|
HU Jun, DONG Jianhua, WANG Kaikai, et al. Research on CPSO-BP model of slope stability[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2016, 37(S1):577-582,590.
|
| [8] |
HOANG N D, PHAM A D. Hybrid artificial intelligence approach based on metaheuristic and machine learning for slope stability assessment: a multinational data analysis[J]. Expert Systems With Applications, 2016, 46:60-68.
doi: 10.1016/j.eswa.2015.10.020
|
| [9] |
QI Chongchong, TANG Xiaolin. Slope stability prediction using integrated metaheuristic and machine learning approaches: a comparative study[J]. Computers & Industrial Engineering, 2018, 118:112-122.
doi: 10.1016/j.cie.2018.02.028
|
| [10] |
张凌凡, 陈忠辉, 周天白, 等. 基于梯度提升决策树的露天矿边坡多源信息融合与稳定性预测[J]. 煤炭学报, 2020, 45(增1):173-180.
|
|
ZHANG Lingfan, CHEN Zhonghui, ZHOU Tianbai, et al. Multi-source information fusion and stability prediction of slope based on gradient boosting decision tree[J]. Journal of china coal society, 2020, 45(S1):173-180.
|
| [11] |
KARDANI N, ZHOU Annan, NAZEM M, et al. Improved prediction of slope stability using a hybrid stacking ensemble method based on finite element analysis and field data[J]. Journal of Rock Mechanics and Geotechnical Engineering, 2021, 13(1):188-201.
doi: 10.1016/j.jrmge.2020.05.011
|
| [12] |
KE Guolin, MENG Qi, FINLEY T, et al. LightGBM: a highly efficient gradient boosting decision tree[C]. Proceedings of the 31st International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, 2017:3149-3157.
|
| [13] |
周挺, 杨军, 周强明, 等. 基于改进LightGBM的电力系统暂态稳定评估方法[J]. 电网技术, 2019, 43(6):1931-1940.
|
|
ZHOU Ting, YANG Jun, ZHOU Qiangming, et al. Power system transient stability assessment method based on modified LightGBM[J]. Power System Technology, 2019, 43(6):1931-1940.
|
| [14] |
颜诗旋, 朱平, 刘钊. 基于改进 LightGBM 模型的汽车故障预测方法研究[J]. 汽车工程, 2020, 42(6):815- 819,825.
|
|
YAN Shixuan, ZHU Ping, LIU Zhao. Research on vehicle fault prediction scheme based on improved LightGBM model[J]. Automotive Engineering, 2020, 42(6):815-819,825.
|
| [15] |
CAO Juan, ZHANG Zhao, TAO Fulu, et al. Identifying the contributions of multi-source data for winter wheat yield prediction in China[J]. Remote Sensing, 2020, 12(5):DOI: 10.3390/rs12050750.
doi: 10.3390/rs12050750
|
| [16] |
SUN Yong, LIU Nan, KANG Xuming, et al. Rapid identification of geographical origin of sea cucumbers Apostichopus japonicus using FT-NIR coupled with light gradient boosting machine[J]. Food Control, 2021,124:DOI: 10.1016/j.foodcont.2021.107883.
doi: 10.1016/j.foodcont.2021.107883
|
| [17] |
廖伟涵, 郭创新, 金宇, 等. 基于四阶段预处理与GBDT的油浸式变压器故障诊断方法[J]. 电网技术, 2019, 43(6):2195-2203.
|
|
LIAO Weihan, GUO Chuangxin, JIN Yu, et al. Oil-immersed transformer fault diagnosis method based on four-stage preprocessing and GBDT[J]. Power System Technology, 2019, 43(6):2195-2203.
|
| [18] |
蔡畅, 黄亦翔, 邢宏文. 基于梯度提升树的飞机机身对接状态识别[J]. 浙江大学学报:工学版, 2019, 53(7):1274-1281.
|
|
CAI Chang, HUANG Yixiang, XING Hongwen. State recognition for fuselage join based on gradient boosting tree[J]. Journal of Zhejiang University:Engineering Science, 2019, 53(7):1274-1281.
|
| [19] |
ZENG Ling, BIAN Hanbing, SHI Zhenning, et al. Forming condition of transient saturated zone and its distribution in residual slope under rainfall conditions[J]. Journal of Central South University, 2017, 24(8):1866-1880.
doi: 10.1007/s11771-017-3594-6
|
| [20] |
汪洋, 王俊刚. 基于深度学习算法的铁路列车运行安全检测[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2018, 28(增2):41-45.
|
|
WANG Yang, WANG Jungang. Study on safety inspection of railway train operation based on deep learning algorithm[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2018, 28(S2):41-45.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2018.S2.008
|
| [21] |
吴挡平, 张忠林, 曹婷婷. 基于Stacking策略的稳定性分类器组合模型研究[J]. 小型微型计算机系统, 2019, 40(5):1045-1049.
|
|
WU Dangping, ZHANG Zhonglin, CAO Tingting. Research on stability classifier combination algorithm based on stacking strategy[J]. Journal of Chinese Computer Systems, 2019, 40(5):1045-1049.
|
| [22] |
ZHANG Ke, ZHANG Kai, CAI Chenxi, et al. Displacement prediction of step-like landslides based on feature optimization and VMD-Bi-LSTM: a case study of the Bazimen and Baishuihe landslides in the Three Gorges, China[J]. Bulletin of Engineering Geology and the Environment, 2021, 80(11):8481-8502.
doi: 10.1007/s10064-021-02454-5
|