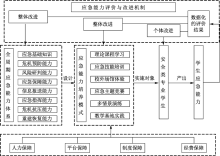
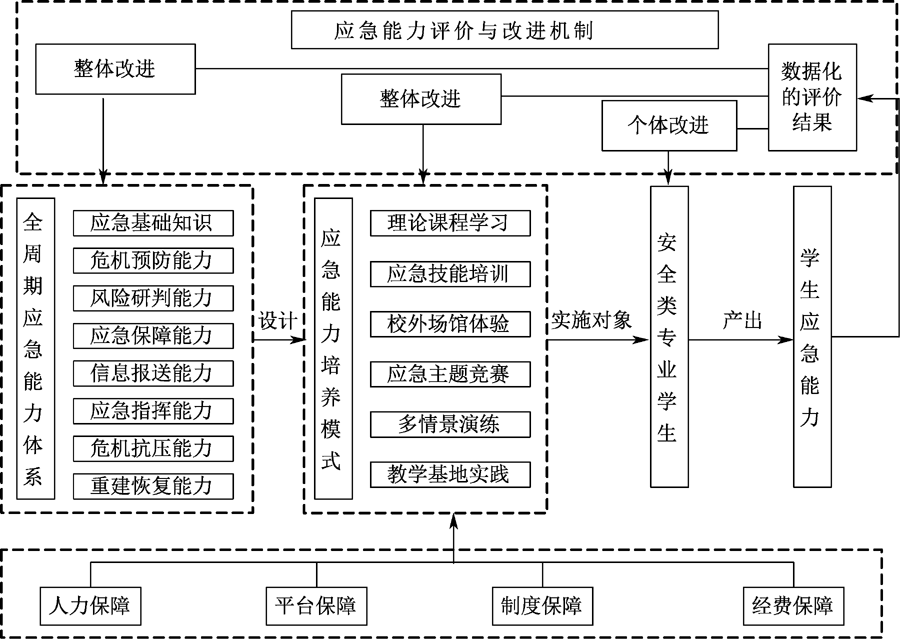
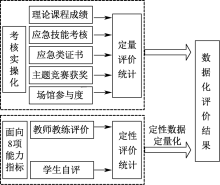
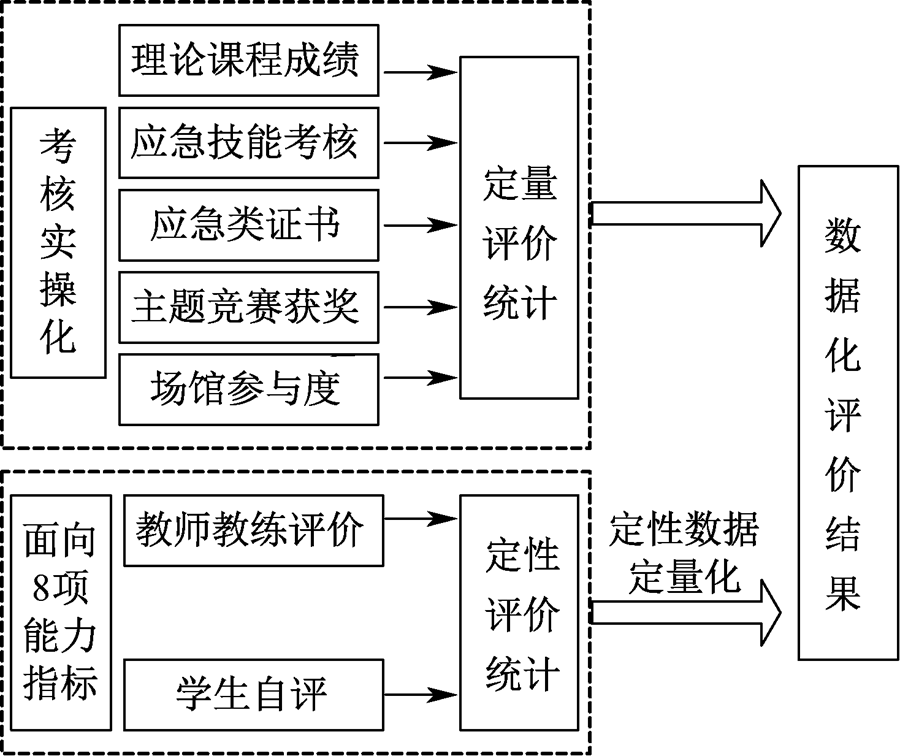
| [1] |
王亮, 孙一伟, 王凯. 安全工程人才多维能力培养体系构建与实践[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2021, 31(5):52-57.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2021.05.008
|
|
WANG Liang, SUN Yiwei, WANG Kai. Construction and practice of multi-dimensional ability training system for safety engineering talents[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2021, 31(5):52-57.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2021.05.008
|
| [2] |
张小良, 梁梵洁, 麻庭光, 等. 安全与应急管理专业学科发展[J]. 中国安全生产科学技术, 2020, 16(12):183-188.
|
|
ZHANG Xiaoliang, LIANG Fanjie, MA Tingguang, et al. Professional and disciplinary development of safety and emergency management[J]. Journal of Safety Science and Technology, 2020, 16(12):183-188.
|
| [3] |
佟瑞鹏, 赵旭, 王露露, 等. 高校应急管理人才培养模式探究与展望[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2021, 31(7):1-8.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn 1003-3033.2021.07.001
|
|
TONG Ruipeng, ZHAO Xu, WANG Lulu, et al. Exploration and prospect of training mode of personnel for emergency management in colleges and universities[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2021, 31(7):1-8.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn 1003-3033.2021.07.001
|
| [4] |
邱霈恩. 中国特色应急管理体系建设探略[J]. 上海行政学院学报, 2012, 13(3):78-86.
|
|
QIU Peien. Exploration of construction of emergency management system with China characteristics[J]. The Journal of Shanghai Administration Institute, 2012, 13(3):78-86.
|
| [5] |
邹积亮. 科学统筹规划加快推进国家应急体系建设:2015年应急体系建设规划理论研讨会综述[J]. 行政管理改革, 2015(8):72-75.
|
| [6] |
“十四五”国家应急体系规划[N]. 人民日报, 2022-02-15( 1).
|
| [7] |
纪晶华, 王晨. 大学生应急能力研究与培养[J]. 科技资讯, 2020, 18(23):220-221, 224.
|
|
JI Jinghua, WANG Chen. Research and training of college students' emergency ability[J]. Science and Technology Information, 2020, 18(23):220-221, 224.
|
| [8] |
安红昌. 我国应急领域教育的现状及应急技术与管理专业人才培养多元机制研究[J]. 工业安全与环保, 2022, 48(11):69-74.
|
|
AN Hongchang. Research on current situation of emergency education in China and multimechanism of training emergency technology and management talents[J]. Industrial Safety and Environmental Protection, 2022, 48(11):69-74.
|
| [9] |
王丽, 李玲, 曾坚. 大学生应急防护能力提升的研究及实践[J]. 灾害学, 2018, 33(2):172-176.
|
|
WANG Li, LI Ling, ZENG Jian. Study and practice on the promotion of emergency prevention and protection capability for college students[J]. Journal of Catastrophology, 2018, 33(2):172-176.
|
| [10] |
唐彦东. 应急管理高等教育人才培养对策[J]. 中国应急管理, 2020(2):68-71.
|
| [11] |
李迎, 王雪峰. 高校大学生应急能力研究进展[J]. 消防科学与技术, 2023, 41(2):263-267.
|
|
LI Ying, WANG Xuefeng. Research progress on emergency capability of university students[J]. Fire Science and Technology, 2023, 41(2):263-267.
|
| [12] |
许素睿, 梁梵洁, 谢振华, 等. 高校安全科学与工程类专业一体化建设模式研究[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2021, 31(5):70-76.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2021.05.011
|
|
XU Surui, LIANG Fanjie, XIE Zhenhua, et al. Research on integrated construction model of safety science and engineering majors in universities[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2021, 31(5):70-76.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2021.05.011
|
| [13] |
易玉枚, 董子文, 易灿南, 等. 专业认证背景下安全工程专业课程体系优化探讨[J]. 安全与环境工程, 2020, 27(3):153-156.
|
|
YI Yumei, DONG Ziwen, YI Cannan, et al. Optimization of course system of safety engineering specialty under the background of professional certification[J]. Safety and Environmental Engineering, 2020, 27(3):153-156.
|
| [14] |
佟瑞鹏, 马晓飞, 栗婧, 等. 新工科理念下安全工程专业教学模式与效果评价[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2019, 29(6):140-145.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2019.06.023
|
|
TONG Ruipeng, MA Xiaofei, LI Jing, et al. Teaching model and effect evaluation of safety engineering discipline under idea of new engineering[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2019, 29(6):140-145.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2019.06.023
|
| [15] |
王亮, 王凯, 时国庆, 等. 安全工程专业本科国际化人才培养体系探究[J]. 煤炭高等教育, 2019, 37(3):91-96.
|
|
WANG Liang, WANG Kai, SHl Guoqing, et al. Exploration of international talent training system for safety engineering undergraduates[J]. Meitan Higher Education, 2019, 37(3):91-96.
|
| [16] |
王倩, 史恭龙. 基于高校突发事件的大学生应急能力培养研究[J]. 技术与创新管理, 2019, 40(5):630-633.
|
|
WANG Qian, SHI Gonglong. Research on the cultivation of college students' emergency ability based on college emergencies[J]. Technology and Innovation Management, 2019, 40(5):630-633.
|
| [17] |
郭沛. 我国高校危机教育与大学生应急能力培养研究[J]. 教学研究, 2013, 36(3):19-21.
|
| [18] |
向晋文. 危机管理视域下高校突发事件管理探析[J]. 高教探索, 2017(3):30-34, 40.
|
| [19] |
马国香. 大学生应急能力培养对策研究:以自然灾害应对为视角[J]. 山东农业工程学院学报, 2017, 34(10):73-74.
|
| [20] |
钱洪伟, 郭晶, 尹香菊. 我国现代应急学科体系建设溯源、构想及展望[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2021, 31(5):77-82.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2021.05.012
|
|
QIAN Hongwei, GUO Jing, YIN Xiangju. Traceability, conception and prospect of construction of modern emergency discipline system in China[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2021, 31(5):77-82.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2021.05.012
|