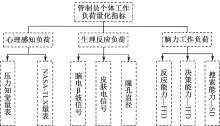
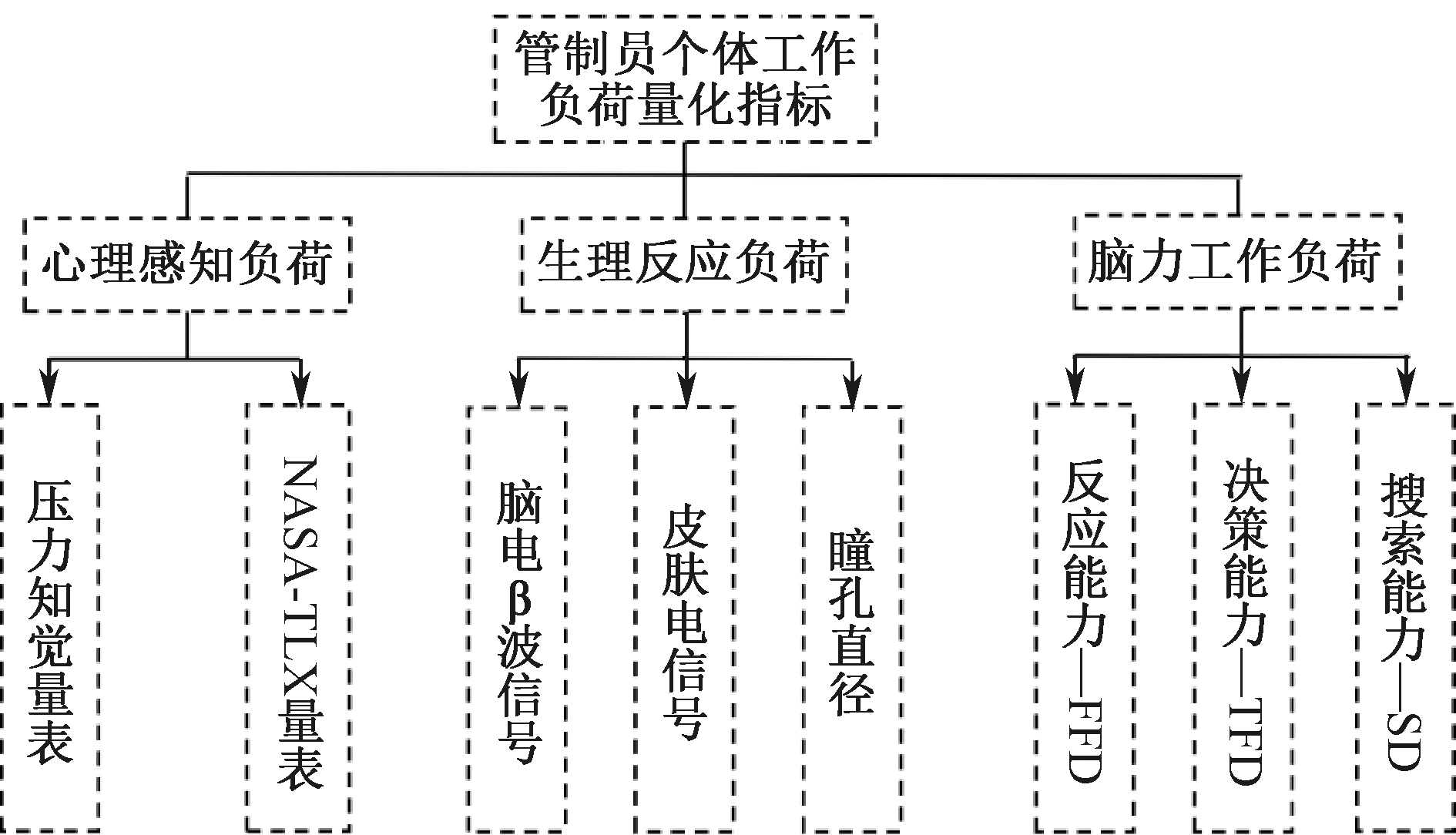
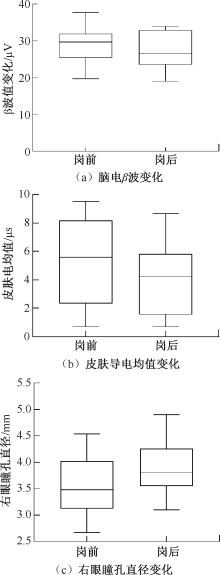
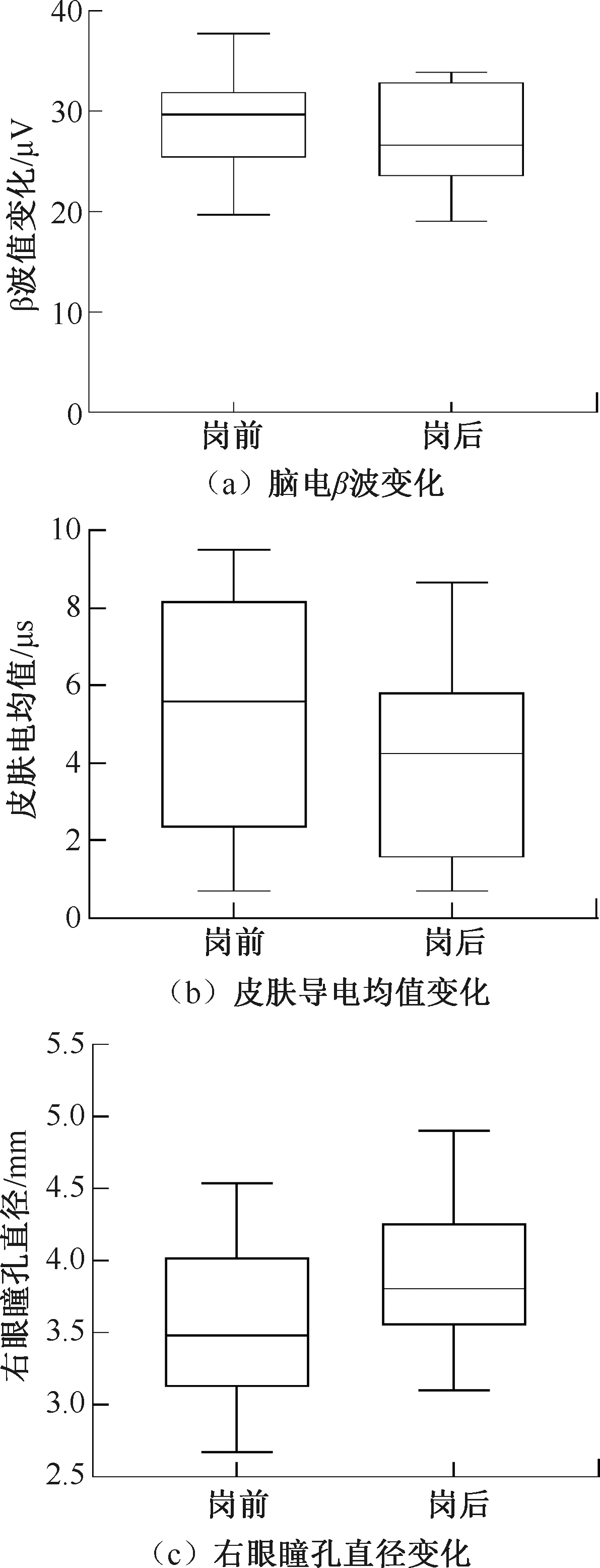
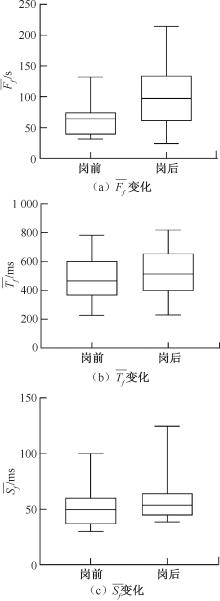
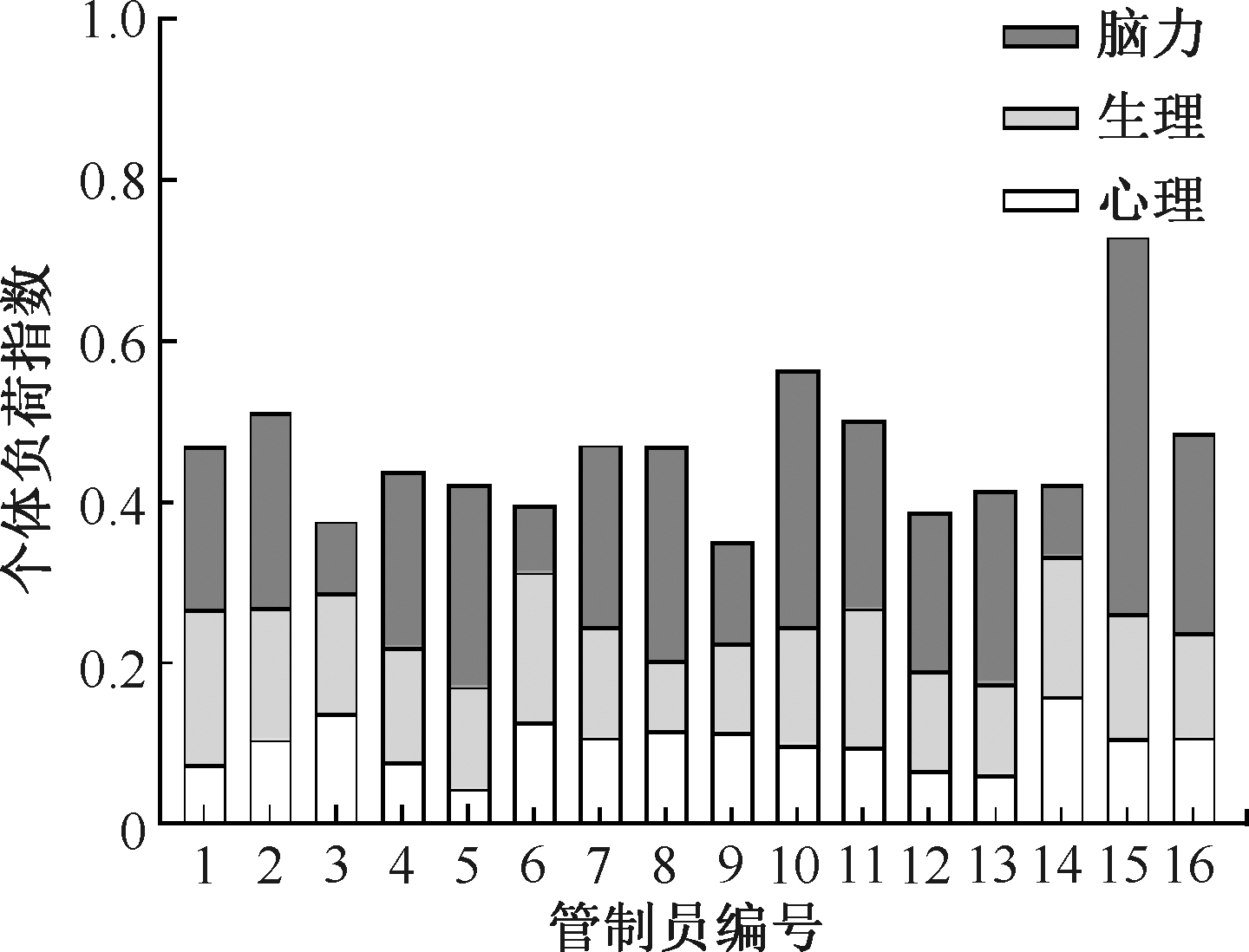
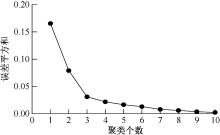
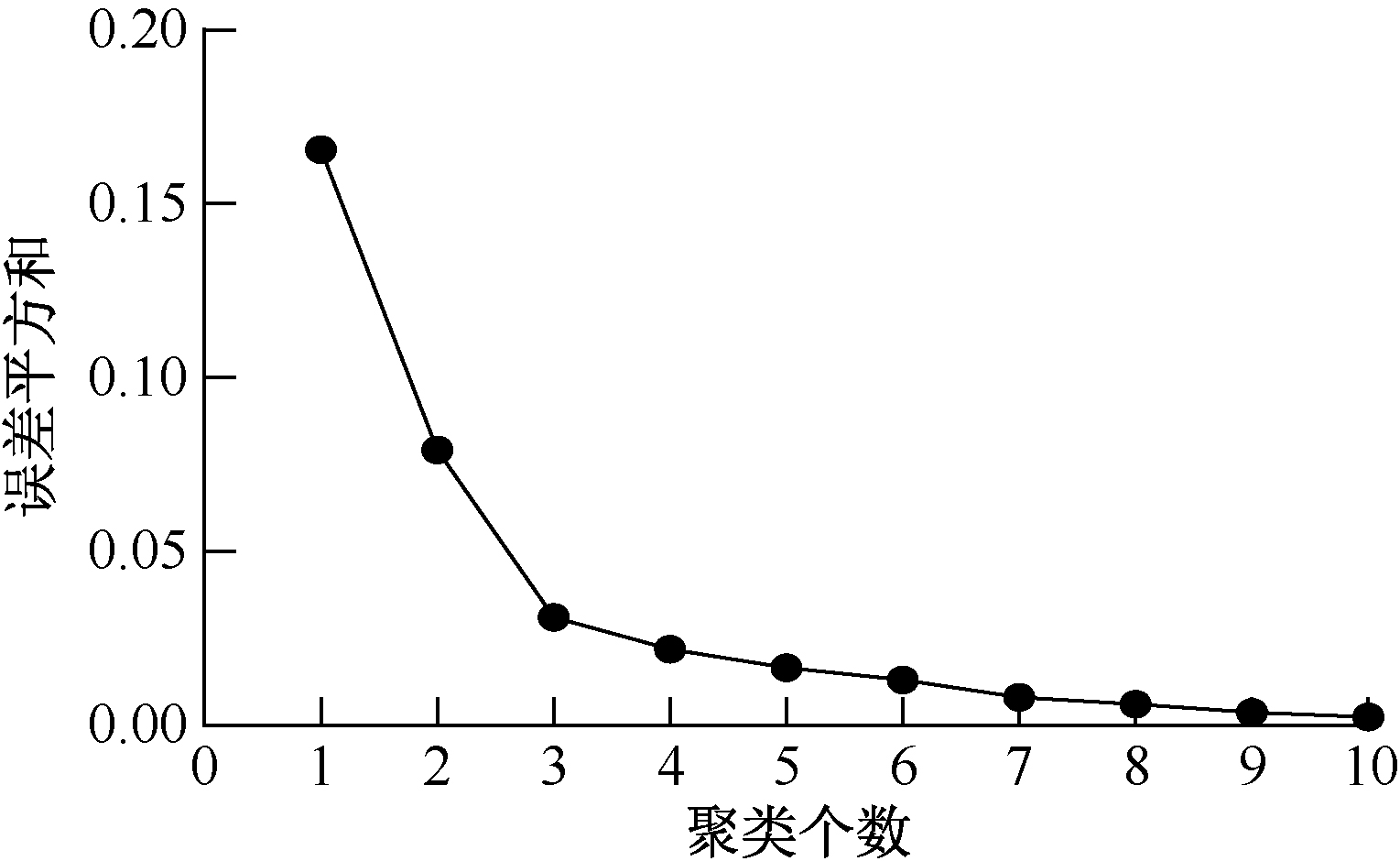
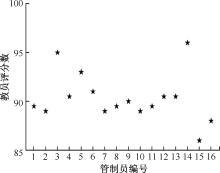
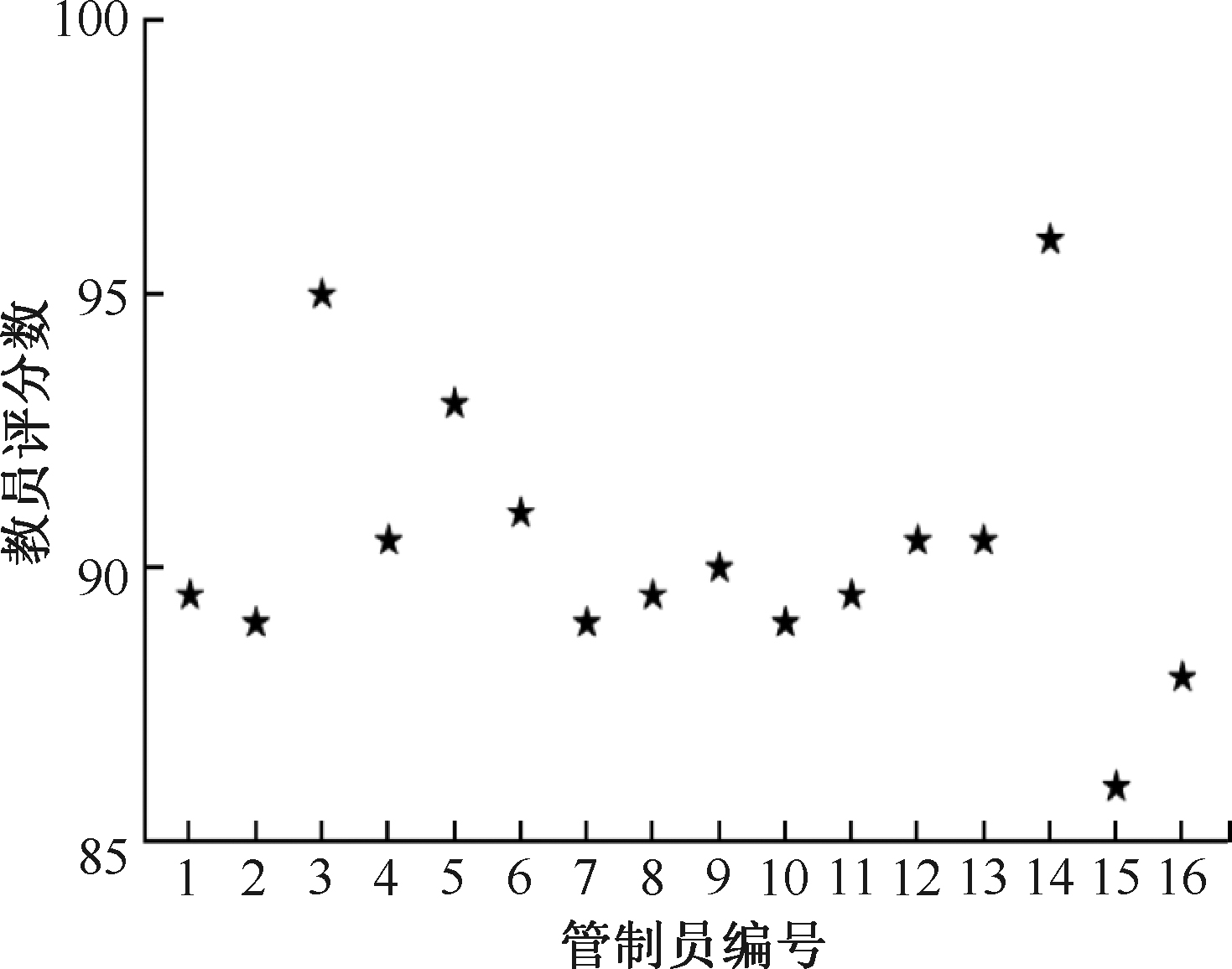
| [1] |
每日经济新闻. 2023年上半年国内航班量已超2019年同期水平[EB/OL].(2023-07-10). https://baijiahao.baidu.com/s?id=1771017336610393586&wfr=spider&for=pc.
|
| [2] |
PANT R, TAUKARI A, SHARMA K. Cognitive workload of air traffic controllers in area control center of mumbai enroute airspace[J]. Journal of Psychosocial Research, 2012, 7(2):279-284.
|
| [3] |
朱聃, 徐晨, 刘继新. 基于语音识别的管制员工作负荷评估[J]. 计算机应用研究, 2020, 37(增1):24-26,33.
|
|
ZHU Dan, XU Chen, LIU Jixin. Evaluation of air traffic controller workload based on automatic speech recognition[J]. Application Research of Computers, 2020, 37(S1):24-26,33.
|
| [4] |
袁霄, 杨家忠, 吴丹. 基于扇区动态复杂性因素的航空管制员工作负荷计算[J]. 安全与环境学报, 2015, 15(2):108-111.
|
|
YUAN Xiao, YANG Jiazhong, WU Dan. Renovated accounting method for the air traffic controller workload based on the sector division of the dynamic complex factors[J]. Journal of Safety and Environment, 2015, 15(2):108-111.
|
| [5] |
王莉莉, 许凌鹏. 基于眼动数据的管制员注意力特征评价[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2023, 33(2):217-224.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2023.02.2785
|
|
WANG Lili, XU Lingpeng. Evaluation of air traffic controller's attention characteristics based on eye movement data[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2023, 33(2):217-224.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2023.02.2785
|
| [6] |
ORDEN V F K, JUNG T, MAKEIG S. Combined eye activity measures accurately estimate changes in sustained visual task performance[J]. Biological Psychology, 2000, 52(3):221-240.
pmid: 10725565
|
| [7] |
WANG Yanjun, WANG Liwei, LIN Siyuan, et al. Effect of working experience on air traffic controller eye movement[J]. Engineering, 2021, 7:488-494.
|
| [8] |
AHLSTROM U, FRIEDMAN-BERG F J. Using eye movement activity as a correlate of cognitive workload[J]. International Journal of Industrial Ergonomics, 2006, 36(7):623-636.
|
| [9] |
WEEH J, LYES W, PINHEIRO J P. Real time eye tracking interface for visual monitoring of radar controllers[C]. AIAA Modeling and Simulation Technologies Conference, 2017: DOI: 10.2514/6.2017-1317.
|
| [10] |
PAGNOTTA M, JACOBS DM, DE FRUTOS PL, et al. Task difficulty and physiological measures of mental workload in air traffic control: a scoping review[J]. Ergonomics, 2022, 65(8):1095-1118.
|
| [11] |
PIETRO A, GIANLUCA B, GIANLUCA F D, et al. Reliability over time of EEG-based mental workload evaluation during air traffic management (ATM) tasks[C]. Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, 2015:7242-7245.
|
| [12] |
陈彦峰. 睡意对脑电信号的影响[D]. 兰州: 兰州理工大学, 2013.
|
|
CHEN Yanfeng. The effect of drowsiness on Electroencephalogram[D]. Lanzhou: Lanzhou University of Technology, 2013.
|
| [13] |
陈凤兰. 基于多导生理信号的管制员疲劳分析方法研究[D]. 天津: 中国民航大学, 2018.
|
|
CHEN Fenglan. Research on controller fatigue analysis method based on multi-conductor physiological signals[D]. Tianjin: Civil Aviation University of China, 2018.
|
| [14] |
LEE E H, CHUNG B Y, SUH C H, et al. Korean versions of the perceived stress scale (PSS-14, 10 and 4): psychometric evaluation in patients with chronic disease[J]. Scandinavian Journal of Caring Sciences, 2015, 29(1):183-192.
|
| [15] |
DUNCAN C C, BARRY R J, CONNOLLY J F, et al. Event-related potentials in clinical research:guidelines or eliciting,recording,and quantifying mismatch negativity,P300,and N400[J]. Clinical Neurophysiology, 2009, 120(11):1883-1908.
|
| [16] |
钟铭恩, 吴平东, 彭军强, 等. 基于脑电信号的驾驶员情绪状态识别研究[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2011, 21(9):64-69.
|
|
ZHONG Ming'en, WU Pingdong, PENG Junqiang, et al. Study on an emotional state recognition technology based on drivers' EEGs[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2011, 21(9):64-69.
|
| [17] |
傅根跃, 陈昌凯, 缪伟, 等. 测谎问题中的“情绪成分”对皮肤电反应的影响[J]. 中国临床心理学杂志, 2005, 13(3):321-323.
|
|
FU Genyue, CHEN Changkai, MIAO Wei, et al. The effect of emotionality in lie-detection questions on skin conductance response[J]. Chinese Journal of Clinical Psychology, 2005, 13(3):321-323.
|
| [18] |
中国民用航空局. 雷达管制基础模拟机培训大纲[Z]. 2012.
|
| [19] |
SHIM B J, JOO H S, SHIM S H. The direction and level of dominant eye according to the tests[J]. Journal of Korean Ophthalmic Optics Society, 2015, 20(3):363-368.
|
| [20] |
韩礼博, 门宝辉. 基于组合博弈论法的海河流域水资源承载力评价[J]. 水电能源科学, 2021, 39(11):61-64.
|
|
HAN Libo, MEN Baohui. Evaluation of water resources carrying capacity in haihe riverbasin based on combinatorial game theory[J]. Water Resources and Power, 2021, 39(11):61-64.
|
| [21] |
李敬强, 王蓓, 赵宁, 等. 基于K-Means聚类的管制员注意品质特征研究[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2017, 27(6):13-18.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2017.06.003
|
|
LI Jingqiang, WANG Bei, ZHAO Ning, et al. On characteristics of attention quality of controller based on K-Means clustering[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2017, 27(6):13-18.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2017.06.003
|
| [22] |
杨越, 马博凯, 曹宇轩. 国外空管不安全事件中的人误风险分析[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2022, 32 (12):38-45.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2022.12.2739
|
|
YANG Yue, MA Bokai, CAO Yuxuan. Human error risk analysis base on foreign unsafe events in air traffic management[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2022, 32(12):38-45.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2022.12.2739
|