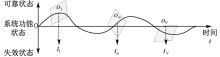
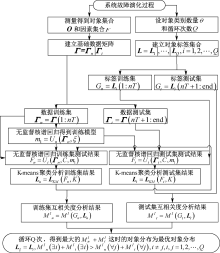
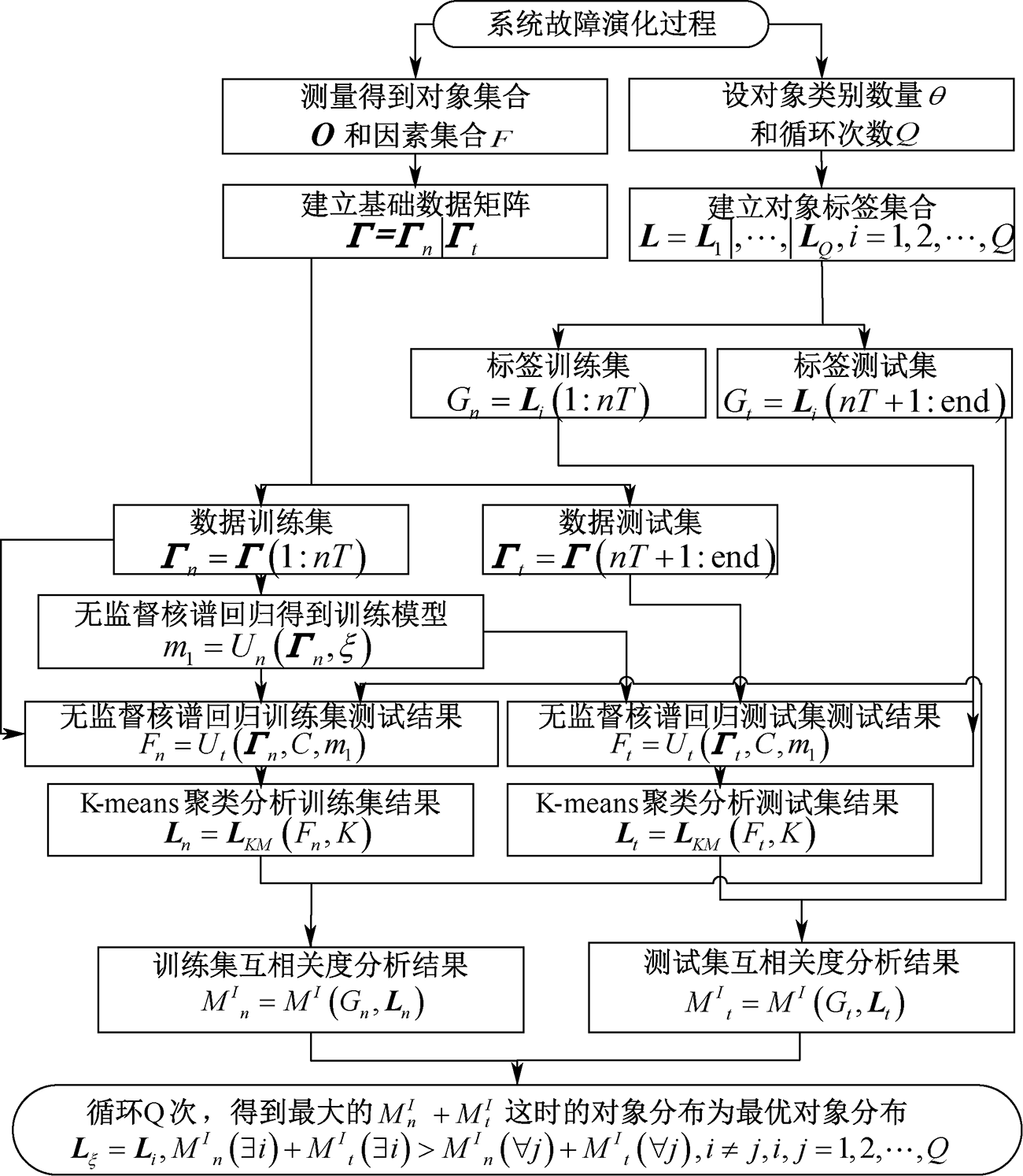
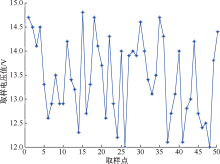
| [1] |
崔铁军, 李莎莎, 朱宝岩. 含有单向环的多向环网络结构及其故障概率计算[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2018, 28(7):19-24.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2018.07.004
|
|
CUI Tiejun, LI Shasha, ZHU Baoyan. Multidirectional ring network structure with one-way ring and its fault probability calculation[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2018, 28(7):19-24.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2018.07.004
|
| [2] |
崔铁军, 李莎莎. 系统故障演化过程最终事件状态及发生概率研究[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2021, 31(8):1-7.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2021.08.001
|
|
CUI Tiejun, LI Shasha. Study on target event state and occurrence probability of system fault evolution process[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2021, 31(8): 1-7.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2021.08.001
|
| [3] |
董缇, 王亦伟, 吴越, 等. 锂离子电池安全故障演化过程热行为分析[J]. 工程热物理学报, 2023, 44(1):175-182.
|
|
DONG Ti, WANG Yiwei, WU Yue, et al. Thermal behavior analysis of safety faults evolution for li-ion battery[J]. Journal of Engineering Thermophysics, 2023, 44(1): 175-182.
|
| [4] |
段忠峰, 王亚松, 白茂金, 等. 面向互联电网连锁故障安全防控的关键支路辨识[J]. 电力建设, 2023, 44(1):12-20.
doi: 10.12204/j.issn.1000-7229.2023.01.002
|
|
DUAN Zhongfeng, WANG Yasong, BAI Maojin, et al. Identification of key branches for safety prevention and control of cascading failures in interconnected power grids[J]. Electric Power Construction, 2023, 44(1): 12-20.
doi: 10.12204/j.issn.1000-7229.2023.01.002
|
| [5] |
边晓燕, 杨云轶, 黄阮明, 等. 基于机电-电磁混合仿真的交直流混联受端电网连锁故障筛选指标及搜索策略[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2023, 43(17):6614-6628.
|
|
BIAN Xiaoyan, YANG Yunyi, HUANG Ruanming, et al. Screening indices and search strategy for AC-DC hybrid receiving-end power grid sascading failures based on hybrid electromechanical-electromagnetic simulation[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2023, 43(17):6614-6628.
|
| [6] |
李家钰, 秦文萍, 景祥, 等. 台风灾害下考虑连锁故障的电力系统弹性评估[J]. 电力系统及其自动化学报, 2023, 35(1):14-22.
|
|
LI Jiayu, QIN Wenping, JING Xiang, et al. Power system resilience assessment considering cascading failure under typhoon disaster[J]. Proceedings of the CSU-EPSA, 2023, 35(1): 14-22.
|
| [7] |
YIN Min, LI Jince, SHI Yilin, et al. Fusing logic rule-based hybrid variable graph neural network approaches to fault diagnosis of industrial processes[J]. Expert Systems With Applications, 2024,238:DOI: 10.1016/j.eswa.2023.121753.
|
| [8] |
UMANG G, JYOTI R, HARIPRASAD K, et al. A graph embedding based fault detection framework for process systems with multi-variate time-series datasets[J]. Digital Chemical Engineering, 2024,10:DOI: 10.1016/J.DCHE.2023.100135.
|
| [9] |
LIU Yan, XU Zuhua, WANG Kai, et al. Incipient fault detection enhancement based on spatial-temporal multi-mode siamese feature contrast learning for industrial dynamic process[J]. Computers in Industry, 2024,155:DOI: 10.1016/J.COMPIND.2023.104062.
|
| [10] |
崔铁军, 李莎莎. 系统多功能状态表达式构建及其置信度研究[J]. 智能系统学报, 2023, 18(1):124-130.
|
|
CUI Tiejun, LI Shasha. Research on construction of system multi-function state expression and its confidence[J]. CAAI Transactions on Intelligent Systems, 2023, 18(1):124-130.
|
| [11] |
崔铁军, 李莎莎. 系统可靠-失效模型的哲学意义与智能实现[J]. 智能系统学报, 2020, 15(6):1104-1112.
|
|
CUI Tiejun, LI Shasha. Philosophical significance and implementation of an intelligent system based on the system reliability-failure model[J]. CAAI Transactions on Intelligent Systems, 2020, 15(6): 1104-1112.
|
| [12] |
崔铁军, 马云东. 多维空间故障树构建及应用研究[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2013, 23(4):32-37,62.
|
|
CUI Tiejun, MA Yundong. Research on multi-dimensional space fault tree construction and application[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2013, 23(4): 32-37,62.
|
| [13] |
郭嘉嘉, 李占斌, 李鹏, 等. 基于DPSIR模型的陕西省水安全评价及障碍因子诊断[J]. 水土保持研究, 2023, 30(2):149-155.
|
|
GUO Jiajia, LI Zhanbin, LI Peng, et al. Evaluation of water security and obstacle factor diagnosis of Shaanxi province based on DPSIR model[J]. Research of Soil and Water Conservation, 2023, 30(2): 149-155.
|
| [14] |
吕佳朋, 史贤俊, 肖支才. 基于DTW时序距离的故障可诊断性评估方法[J]. 兵工学报, 2024, 45(3):997-1009.
doi: 10.12382/bgxb.2022.0693
|
|
LYU Jiapeng, SHI Xianjun, XIAO Zhicai. Diagnosability evaluation method based on DTW temporal distance[J]. Acta Armamentarii, 2024, 45(3):997-1009.
doi: 10.12382/bgxb.2022.0693
|
| [15] |
CAI Deng. Spectral regression: a regression framework for efficient regularized subspace learning[D]. Urbana: University of Illinois, 2009.
|
| [16] |
CAI Deng, HE Xiaofei, HAN Jiawei. Document clustering using locality preserving indexing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Knowledge and Data Engineering, 2005, 17(12):1624-1637.
|