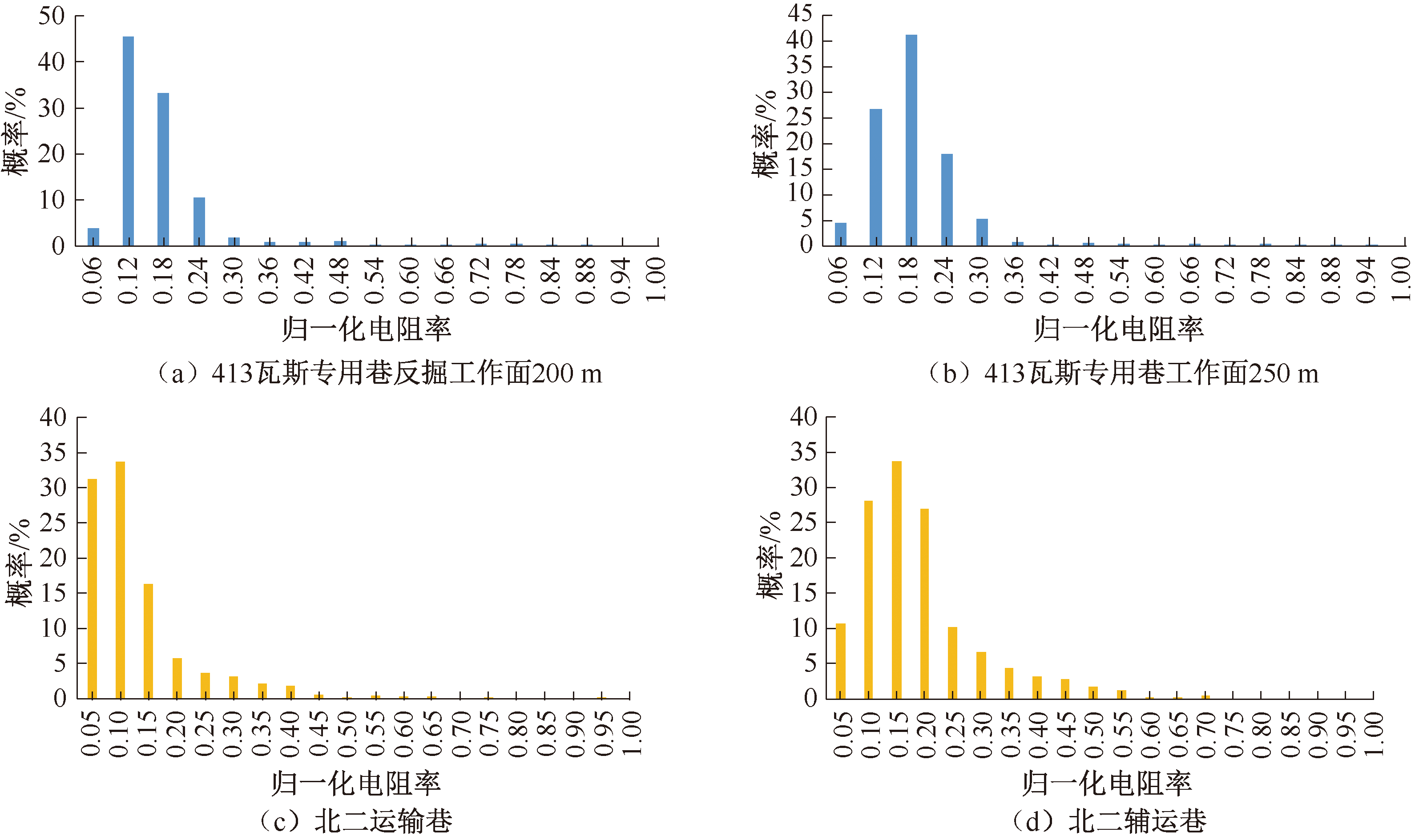
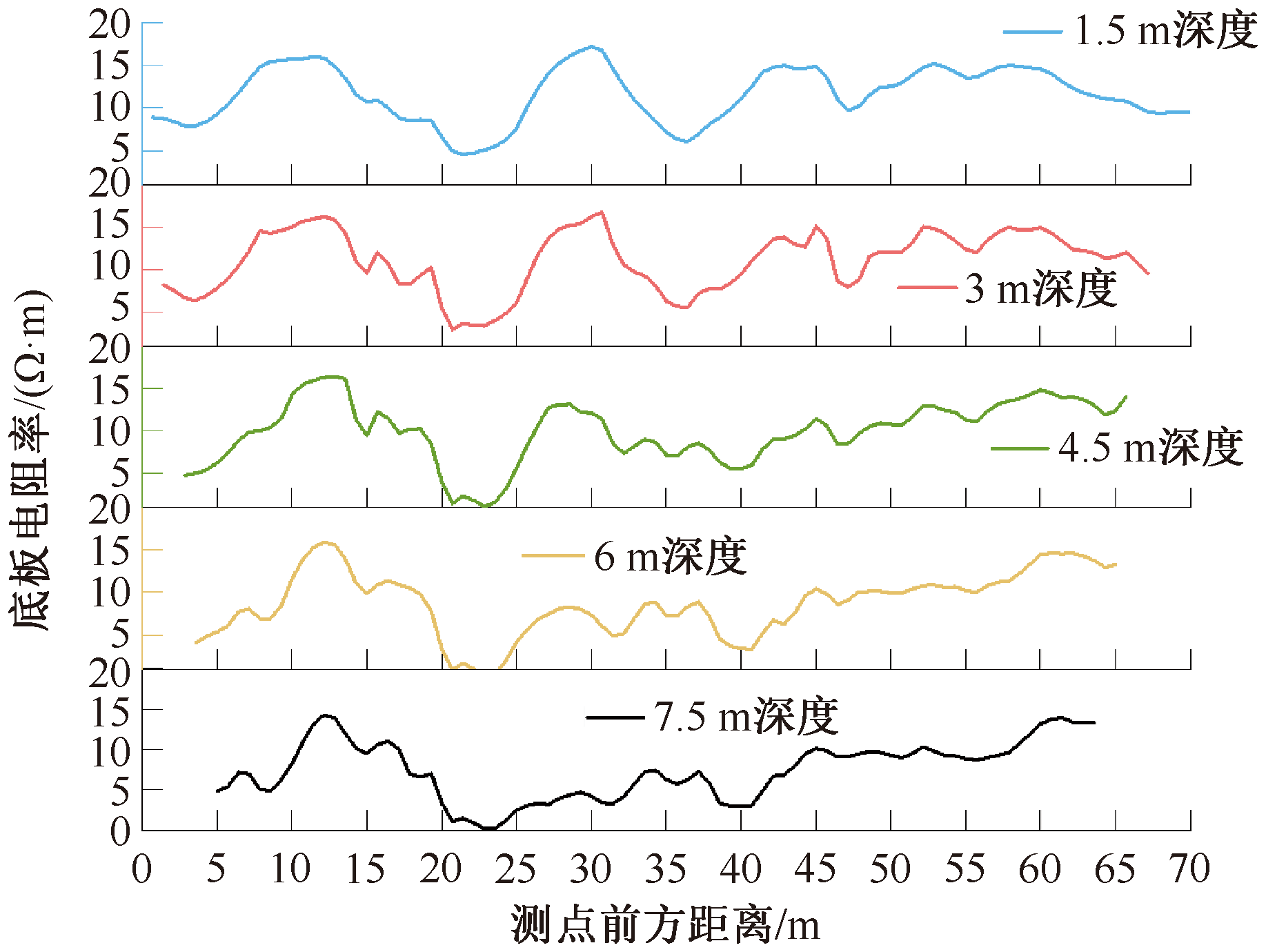
| [1] |
赵继展, 张群, 郑凯歌, 等. 黄陵矿区煤矿井下围岩喷涌气体致灾机理及防治措施[J]. 天然气工业, 2018, 38(11): 114-121.
|
|
ZHAO Jizhan, ZHANG Qun, ZHENG Kaige, et al. Disaster-causing mechanism of surrounding rock gas flowing underground in the Huangling mining area and prevention measures[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2018, 38(11): 114-121.
|
| [2] |
方祖康, 庞雄奇, 高春文. 煤型气和油型气的概念及其类型划分[J]. 天然气工业, 1988, 8(1): 13-17.
|
|
FANG Zukang, PANG Xiongqi, GAO Chunwen. Idea of coll-formed gas and oil-related gas and their classification[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 1988, 8(1): 13-17.
|
| [3] |
韩中喜, 李剑, 严启团, 等. 天然气汞含量作为煤型气与油型气判识指标的探讨[J]. 石油学报, 2013, 34(2): 323-327.
doi: 10.7623/syxb201302014
|
|
HAN Zhongxi, LI Jian, YAN Qituan, et al. Discussion on the applicability of mercury content in natural gases as an identification index of coal-type gas and oil-type gas[J]. Acta Petroleum Sinica, 2013, 34(2): 323-327.
|
| [4] |
唐恩贤. 黄陵矿区煤层底板异常涌出气体成因类型[J]. 煤田地质与勘探, 2015, 43(6): 8-11.
|
|
TANG Enxian. Genetic type of abnormal gas emission from coal seam floor in Huangling mining area[J]. Coal Geology & Exploration, 2015, 43(6):8-11.
|
| [5] |
孙四清. 煤油气共存矿井掘进工作面底板油型气涌出机理探讨[J]. 矿业安全与环保, 2017, 44(4): 90-94.
|
|
SUN Siqing. Discussion on oil-type gas emission mechanism from heading face floor in coal-oil-gas coexisting mine[J]. Mining Safety & Environmental Protection, 2017, 44(4): 90-94.
|
| [6] |
孙四清, 陈冬冬, 龙威成, 等. 煤油气共存矿井油型气精准治理技术及工程实践[J]. 煤炭科学技术, 2021, 49(5): 60-66.
|
|
SUN Siqing, CHEN Dongdong, LONG Weicheng, et al. Technology of precise control of oil-type gas and engineering practice in coal mine with coal-oil-gas coexistence[J]. Coal Science and Technology, 2021, 49(5): 60-66.
|
| [7] |
张俭让, 张荃, 董丁稳, 等. 油型气涌出矿井CH4扩散规律数值模拟[J]. 煤炭技术, 2015, 34(10): 136-138.
|
|
ZHANG Jianrang, ZHANG Quan, DONG Dingwen, et al. Law of gas distribution of numerical simulation with oil-type gas emission[J]. Coal Technology, 2015, 34(10): 136-138.
|
| [8] |
张俭让, 张玲洁, 李倩玉. 油型气涌出矿井局部通风排瓦斯优化[J]. 西安科技大学学报, 2017, 37(6): 823-828.
|
|
ZHANG Jianrang, ZHANG Lingjie, LI Qianyu. Gas-exhausting optimization of drivage roadway under the condition of oil-type gas emission[J]. Journal of Xi'an University of Science and Technology, 2017, 37(6): 823-828.
|
| [9] |
司俊鸿, 许敏, 郑凯凯, 等. 黄陇矿区瓦斯-油型气混合气体爆炸特性及预警技术研究[J]. 煤炭科学技术, 2019, 47(8): 251-256.
|
|
SI Junhong, XU Min, ZHENG Kaikai, et al. Characteristics and early warning technology of gas-oil explosion in Huanglong mining area[J]. Coal Science & Technology, 2019, 47(8): 251-256.
|
| [10] |
殷民胜, 刘耀宗. 黄陵二号煤矿底板油型气释放规律及影响因素[J]. 陕西煤炭, 2023, 42(6):24-28.
|
|
YIN Minsheng, LIU Yaozong. Oil-type gas releasing regularity and influential factors of Huangling No.2 coal mine floor[J]. Shaanxi Coal, 2023, 42(6):24-28.
|
| [11] |
郑凯歌, 孙四清, 赵继展, 等. 黄陵矿区围岩气体成因及致灾机理研究[J]. 煤炭科学技术, 2021, 49(8):139-146.
|
|
ZHENG Kaige, SUN Siqing, ZHAO Jizhan, et al. Study on genetic and destructive mechanism of gas from surrounding rock in Huangling mining area[J]. Coal Science and Technology, 2021, 49 (8): 139-146.
|
| [12] |
牟全斌. 煤油气共生矿井底板油型气赋存特征及防治[J]. 能源与环保, 2020, 42(12): 76-80,88.
|
|
MOU Quanbin. Occurrence characteristics and prevention of oil-type gas in coal-gas symbiosis mine floor[J]. China Energy and Environmental Protection, 2020, 42(12): 76-80,88.
|
| [13] |
方林, 龚晟, 王桂林, 等. 基于突变理论的隔水岩体失稳分析及安全厚度计算[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2024, 34(3):76-83.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2024.03.0344
|
|
FANG Lin, GONG Sheng, WANG Guilin, et al. Instability analysis and safe thickness calculation of waterproof rock mass based on mutation theory[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2024, 34(3):76-83.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2024.03.0344
|
| [14] |
李毛飞, 刘树才, 姜志海, 等. 矿井直流电透视底板探测及三维反演解释[J]. 煤炭学报, 2022, 47(7): 2708-2721.
|
|
LI Maofei, LIU Shucai, JIANG Zhihai, et al. Detecting floor geological information by mine DC perspective and 3D inversion[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2022, 47(7): 2708-2721.
|
| [15] |
马进功. 基于变权模糊理论的残煤连采可行性评价研究[J]. 煤炭科学技术, 2021, 49(8): 30-37.
|
|
MA Jingong. Study on feasibility evaluation of continuous mining of residual coal based on variable weight fuzzy theory[J]. Coal Science and Technology, 2021, 49(8): 30-37.
|
| [16] |
江新, 王婧雯, 王耀威, 等. 突变视角下地下深埋隧洞塌方风险耦合演化研究[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2023, 33(5):103-111.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2023.05.1494
|
|
JIANG Xin, WANG Jingwen, WANG Yaowei, et al. Study on coupling evolution of collapse risk of deep underground tunnel from perspective of catastrophe[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2023, 33(5):103-111.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2023.05.1494
|
| [17] |
武强, 李博, 刘守强, 等. 基于分区变权模型的煤层底板突水脆弱性评价:以开滦蔚州典型矿区为例[J]. 煤炭学报, 2013, 38(9): 1516-1521.
|
|
WU Qiang, LI Bo, LIU Shouqiang, et al. Vulnerability assessment of coal floor groundwater burstiong based on zoning variable weight model: a case study int the typical mining region of Kailuan[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2013, 38(9): 1516-1521.
|
| [18] |
马进功, 宋德军. 基于变权模糊理论的掘锚一体机组掘进适用性数学评价[J]. 煤炭学报, 2023, 48(6): 2579-2589.
|
|
MA Jingong, SONG Dejun. Mathematical evaluation on the applicability of bolter miners based on variable weight fuzzy theory[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2023, 48(6): 2579-2589.
|
| [19] |
张金才, 张玉卓, 刘天泉. 岩体渗流与煤层底板突水[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 1997: 20-35.
|