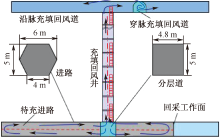
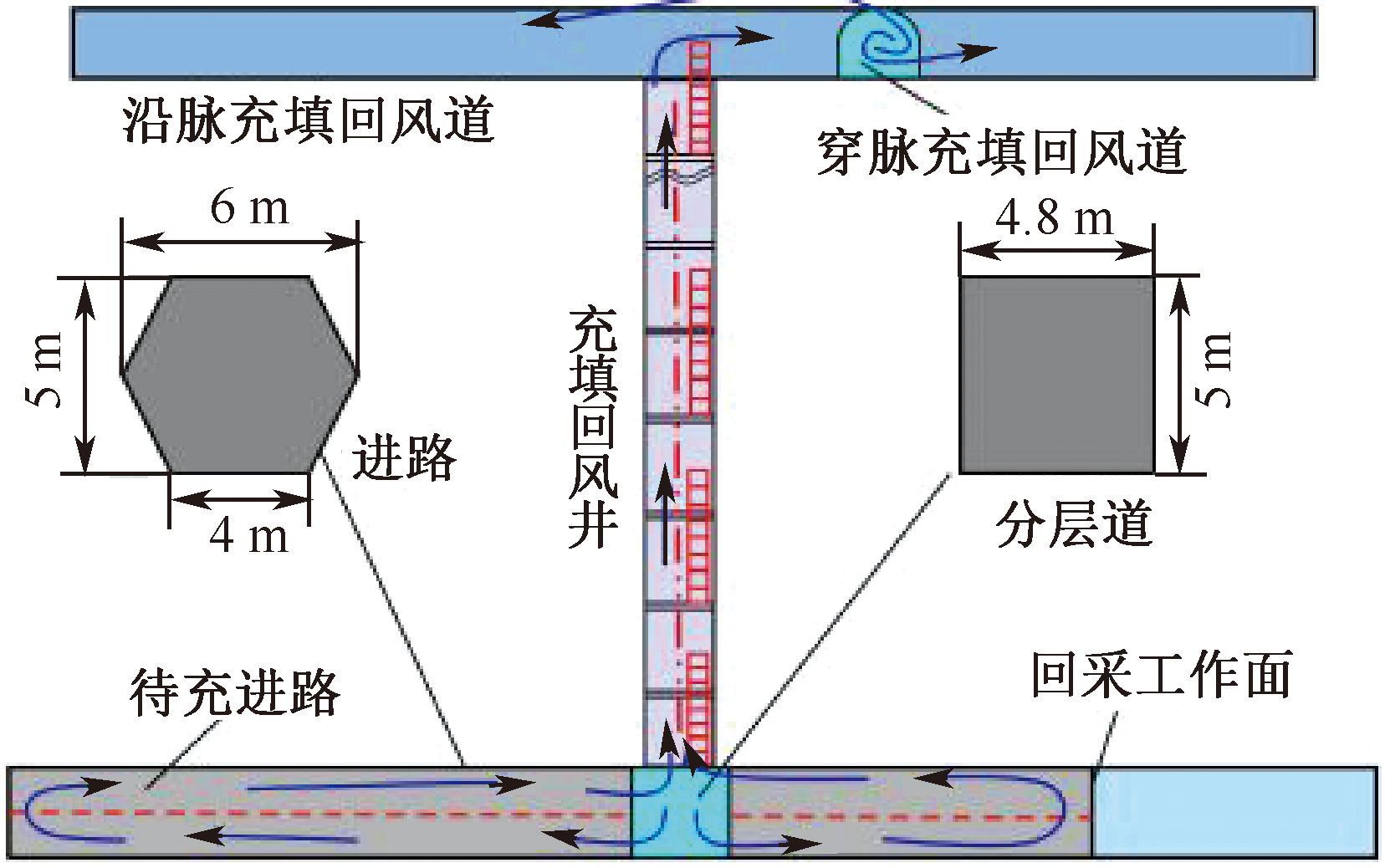
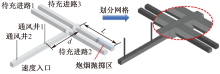
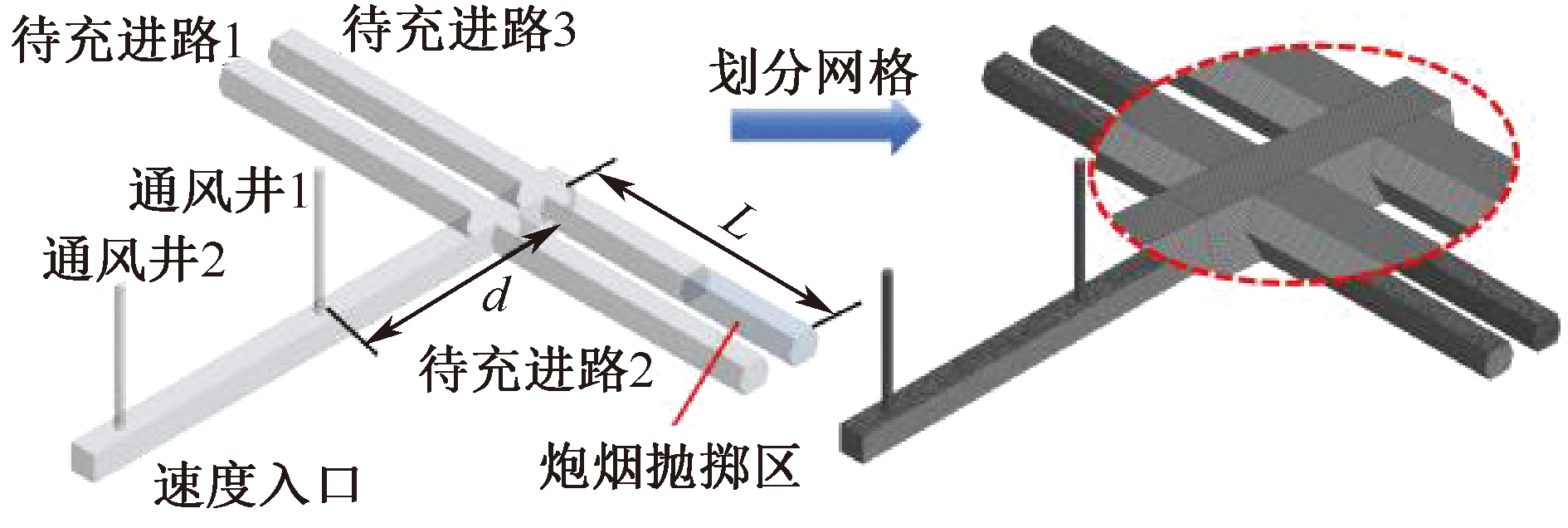
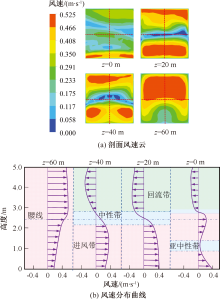
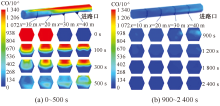
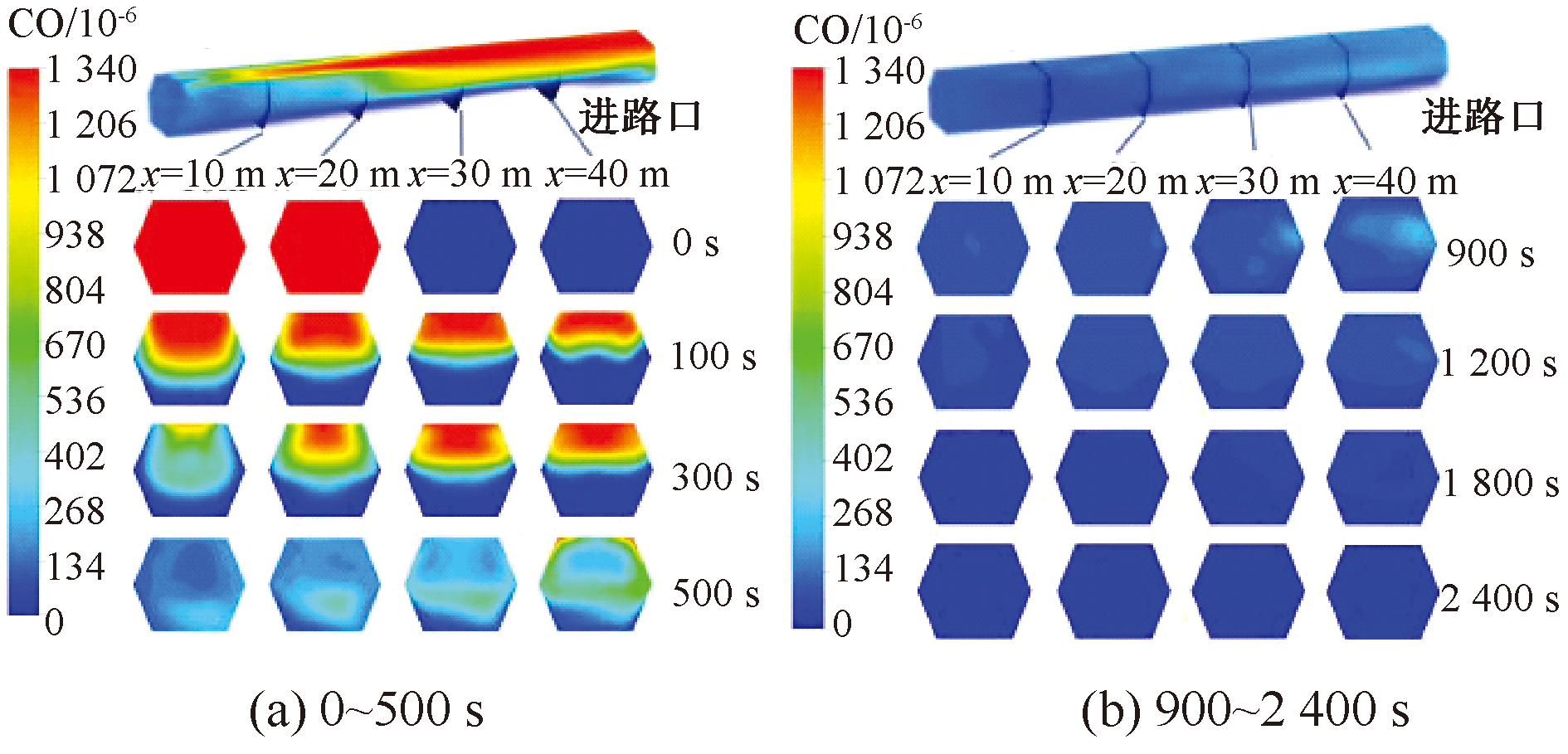
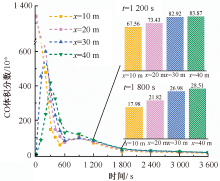
| [1] |
薛希龙, 孙鹏程, 武拴军, 等. 粗骨料纤维充填体的力学特性与能量损伤演变规律[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2024, 34(7): 2476-2490.
|
|
XUE Xilong, SUN Pengcheng, WU Shuanjun, et al. Mechanical properties and energy damage evolution law of coarse aggregate fiber backfill[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2024, 34(7): 2476-2490.
|
| [2] |
金龙哲, 郭敬中, 李刚, 等. 金属矿山采场爆破尘毒防控技术研究进展及展望[J]. 金属矿山, 2021(1): 120-134.
|
|
JIN Longzhe, GUO Jingzhong, LI Gang, et al. Study progress and prospect on prevention and control technology of blasting dust and poison in metal mine stope[J]. Metal Mine, 2021(1): 120-134.
|
| [3] |
陈赞成, 杨鹏, 吕文生, 等. 高寒矿井穿脉巷道掘进炮烟扩散规律的数值模拟[J]. 北京科技大学学报, 2011, 33(5): 521-525.
|
|
CHEN Zancheng, YANG Peng, LYU Wensheng, et al. Numerical simulation on the diffusion law of blasting fume during roadway tunneling across a vein in an alpine mine[J]. Journal of University of Science and Technology Beijing, 2011, 33(5): 521-525.
|
| [4] |
谭香. 巷道型采场通风炮烟运动的数值试验[D]. 南宁: 广西大学, 2012.
|
|
TAN Xiang. Numerical tests on bentilating blasting fume movement in long stope[D]. Nanning: Guangxi University, 2012.
|
| [5] |
WU Bo, ZHAO Rui, MENG Guowang, et al. A numerical study on CO migration after blasting in high-altitude tunnel by inclined shaft[J]. Scientific Reports, 2022, 12: DOI: 10.1038/S41598-022-18995-Y.
|
| [6] |
CHANG Xiaoke, CHAI Junrui, LUO Jipeng, et al. Tunnel ventilation during construction and diffusion of hazardous gases studied by numerical simulations[J]. Building and Environment, 2020, 177: DOI: 10.1016/j.buildenv.2020.106902.
|
| [7] |
LIU Qiang, NIE Wen, HUA Yun, et al. Research on tunnel ventilation systems: dust diffusion and pollution behaviour by air curtains based on CFD technology and field measurement[J]. Building and Environment, 2019, 147: 444-460.
doi: 10.1016/j.buildenv.2018.08.061
|
| [8] |
HUA Yun, NIE Wen, CAI Peng, et al. Pattern characterization concerning spatial and temporal evolution of dust pollution associated with two typical ventilation methods at fully mechanized excavation faces in rock tunnels[J]. Powder Technology, 2018, 334:117-131.
|
| [9] |
曹杨. 金属矿采掘爆破炮烟成分影响因素分析与扩散规律及控制[D]. 北京: 北京科技大学, 2019.
|
|
CAO Yang. Analysis to influence factors to constituents of blasting fume and its dispersion law at stope and heading and control in metal mine[D]. Beijing: University of Science and Technology Beijing, 2019.
|
| [10] |
陶发玉, 陶云波, 黄春云. 基于Fluent模拟的龙首矿下向进路采矿炮烟扩散规律研究[J]. 金属矿山, 2022(8): 232-238.
|
|
TAO Fayu, TAO Yunbo, HUANG Chunyun. Fluent-based simulation of gun smoke diffusion from single-head approach in Longshou mine[J]. Metal Mine, 2022(8): 232-238.
|
| [11] |
FENG Xue, JIANG Zhongan, ZHANG Guoliang, et al. Study on CO diffusion law and concentration distribution function under ventilation after blasting in high-altitude tunnel[J]. Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamics, 2022, 220: DOI: 10.1016/j.jweia.2021.104871.
|
| [12] |
张美长, 祁云, 汪伟, 等. 特厚煤层分层开采的自燃危险区域演化特征[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2024, 34(8): 147-154.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2024.08.0165
|
|
ZHANG Meichang, QI Yun, WANG Wei, et al. Evolution characteristics of spontaneous combustion hazard zone in layered mining of extra thick coal seams[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2024, 34(8): 147-154.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2024.08.0165
|
| [13] |
陈星宇, 吴剑, 任松, 等. 高海拔隧道施工期污染物扩散规律[J]. 浙江大学学报:工学版, 2024, 58(1): 176-187.
|
|
CHEN Xingyu, WU Jian, REN Song, et al. Pollutant diffusion law during high-altitude tunnel construction[J]. Journal of Zhejiang University:Engineering Science, 2024, 58(1): 176-187.
|
| [14] |
HUANG Rui, SHEN Xue, WANG Bing, et al. Migration characteristics of CO under forced ventilation after excavation roadway blasting: a case study in a plateau mine[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2020, 267: DOI: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.122094.
|
| [15] |
拜生学. 龙首矿采场通风方案的研究[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 1998, 8(增1): 124-129.
|
|
BAI Shengxue. Study on the ventilation protecel of down stope in longshou mine[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 1998, 8(S1): 124-129.
|