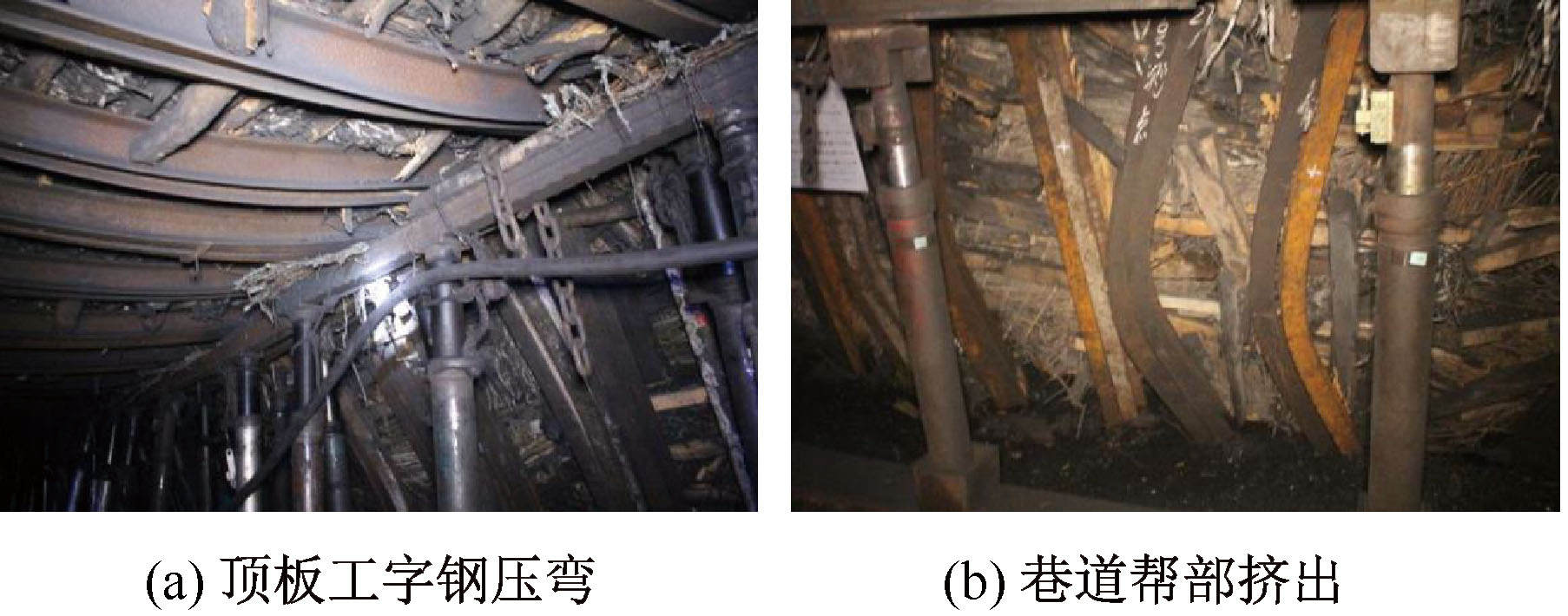
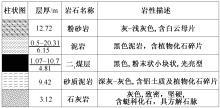
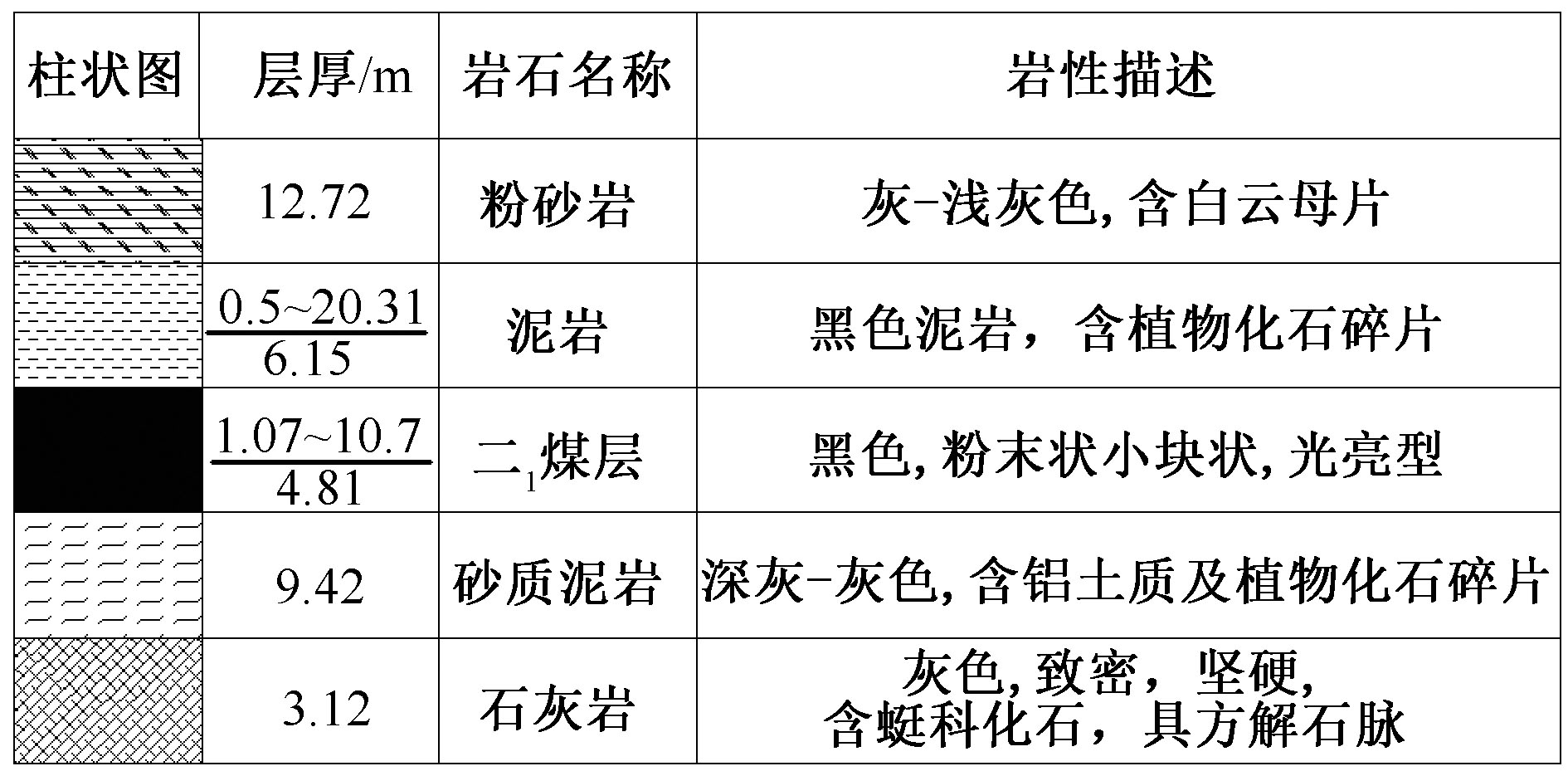
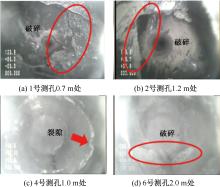
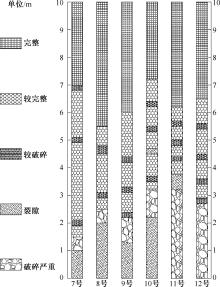
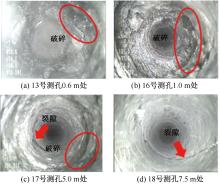
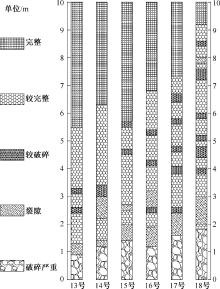
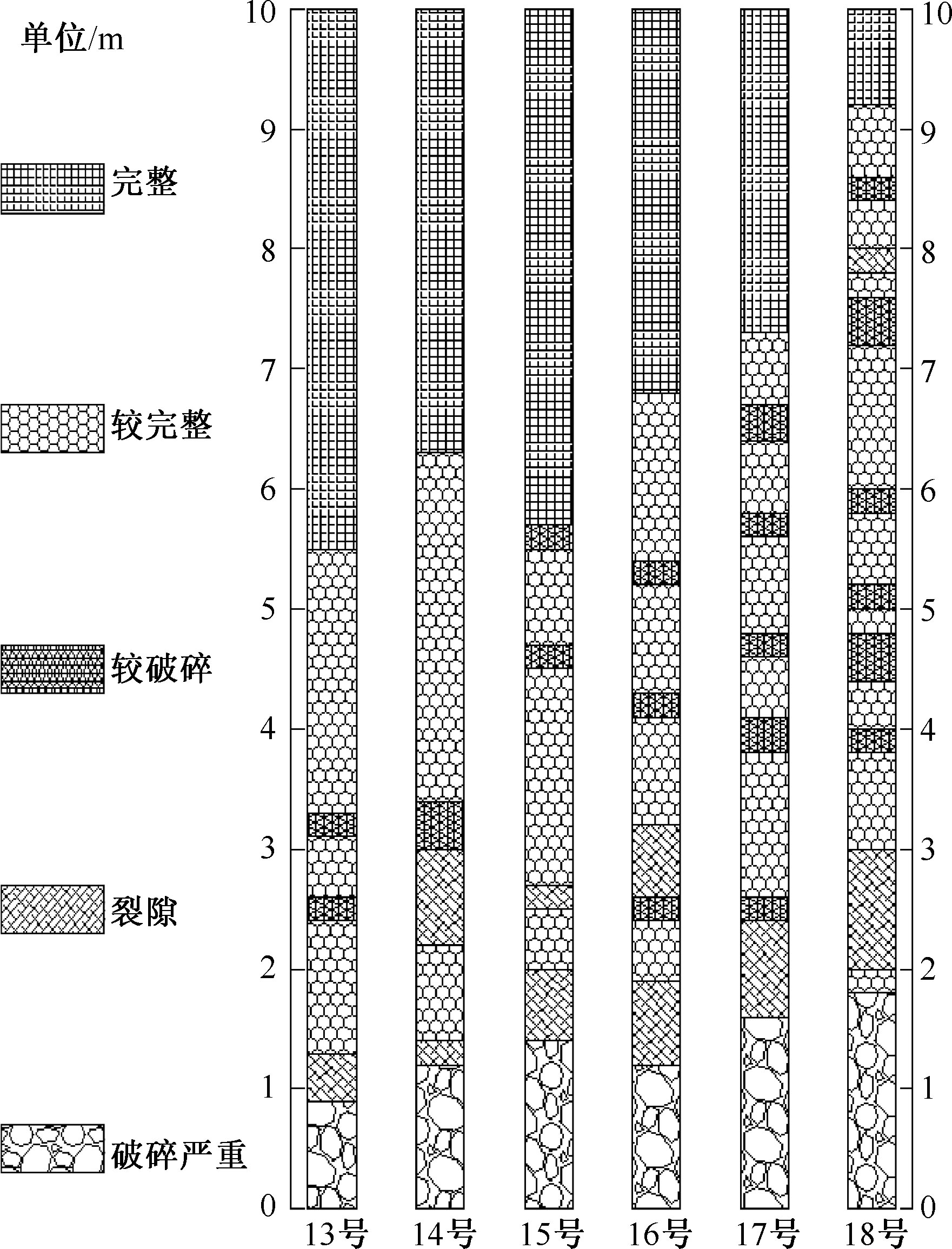
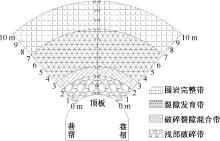
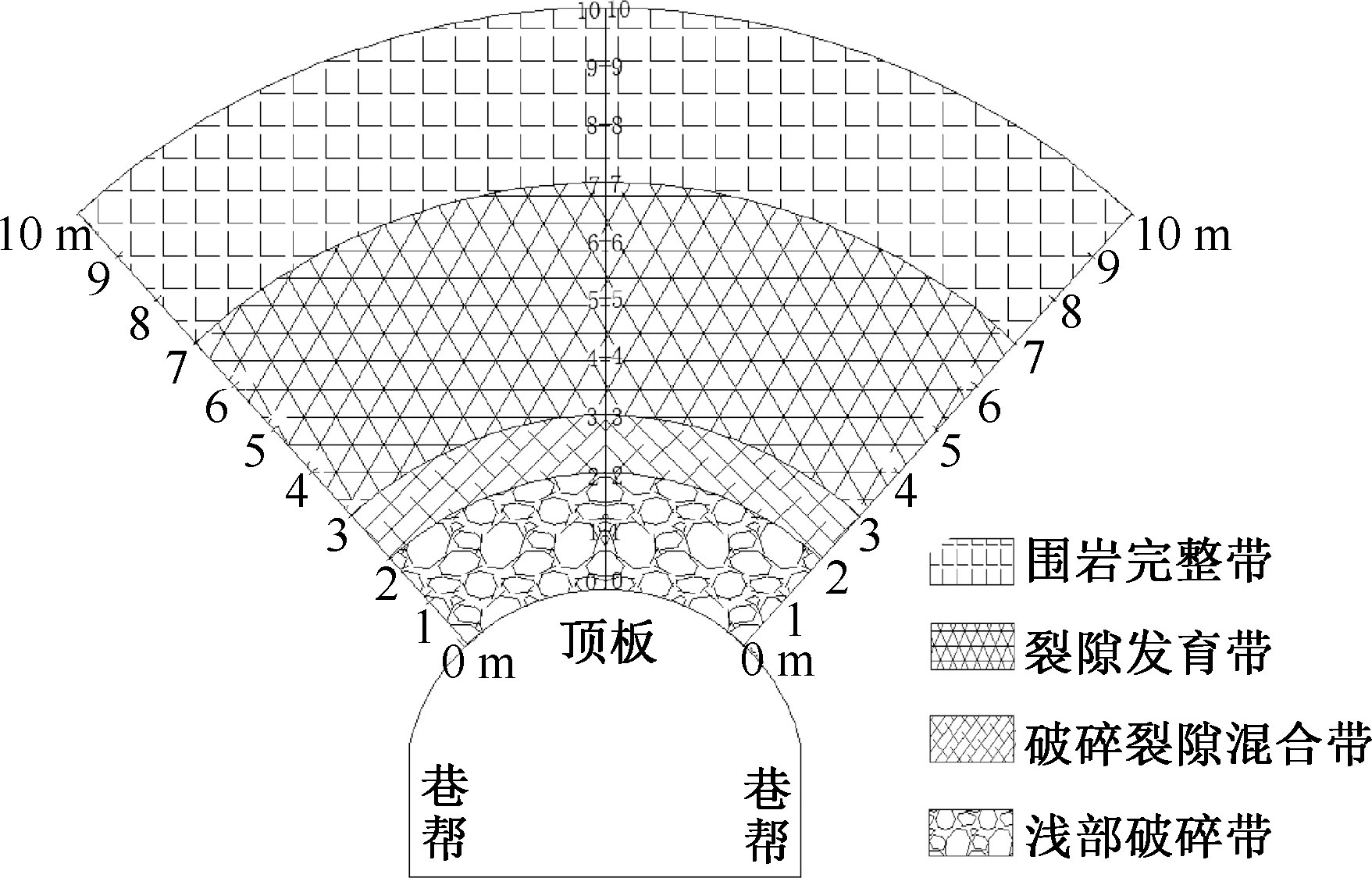
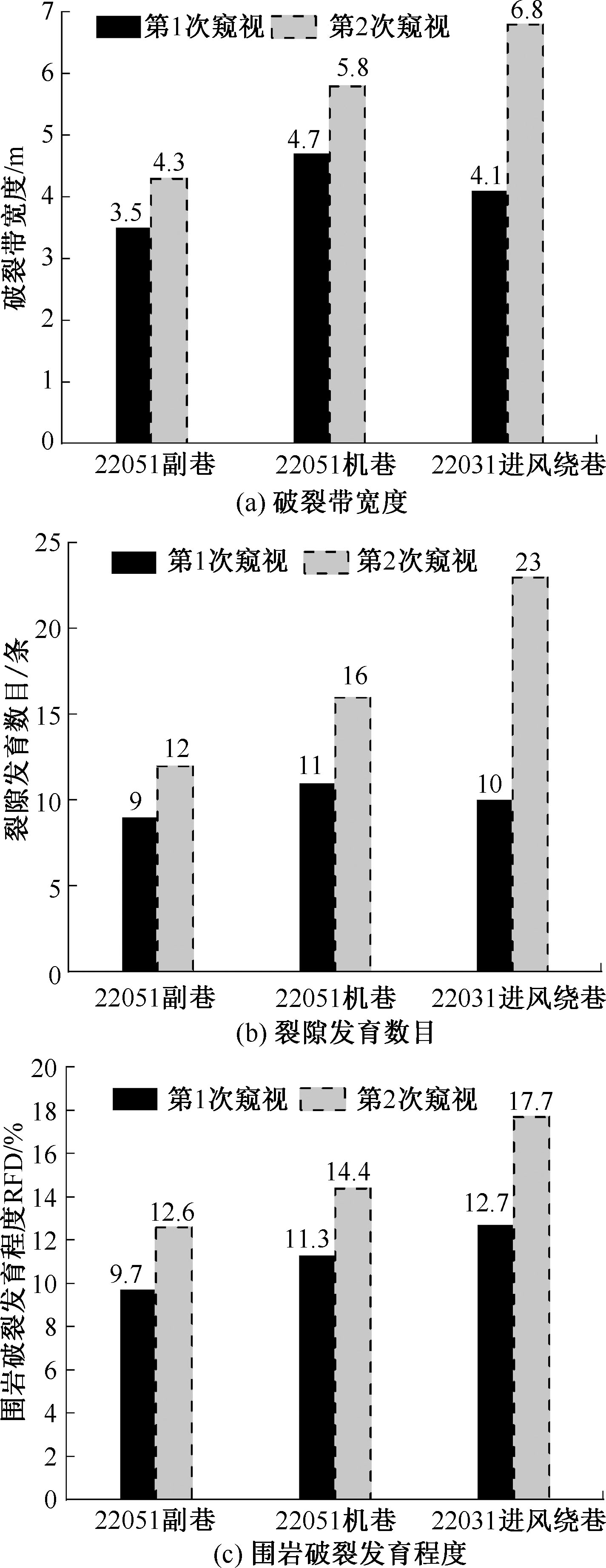
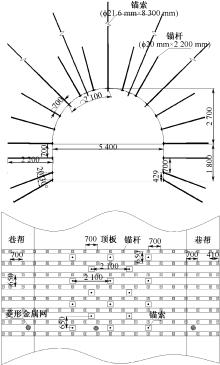
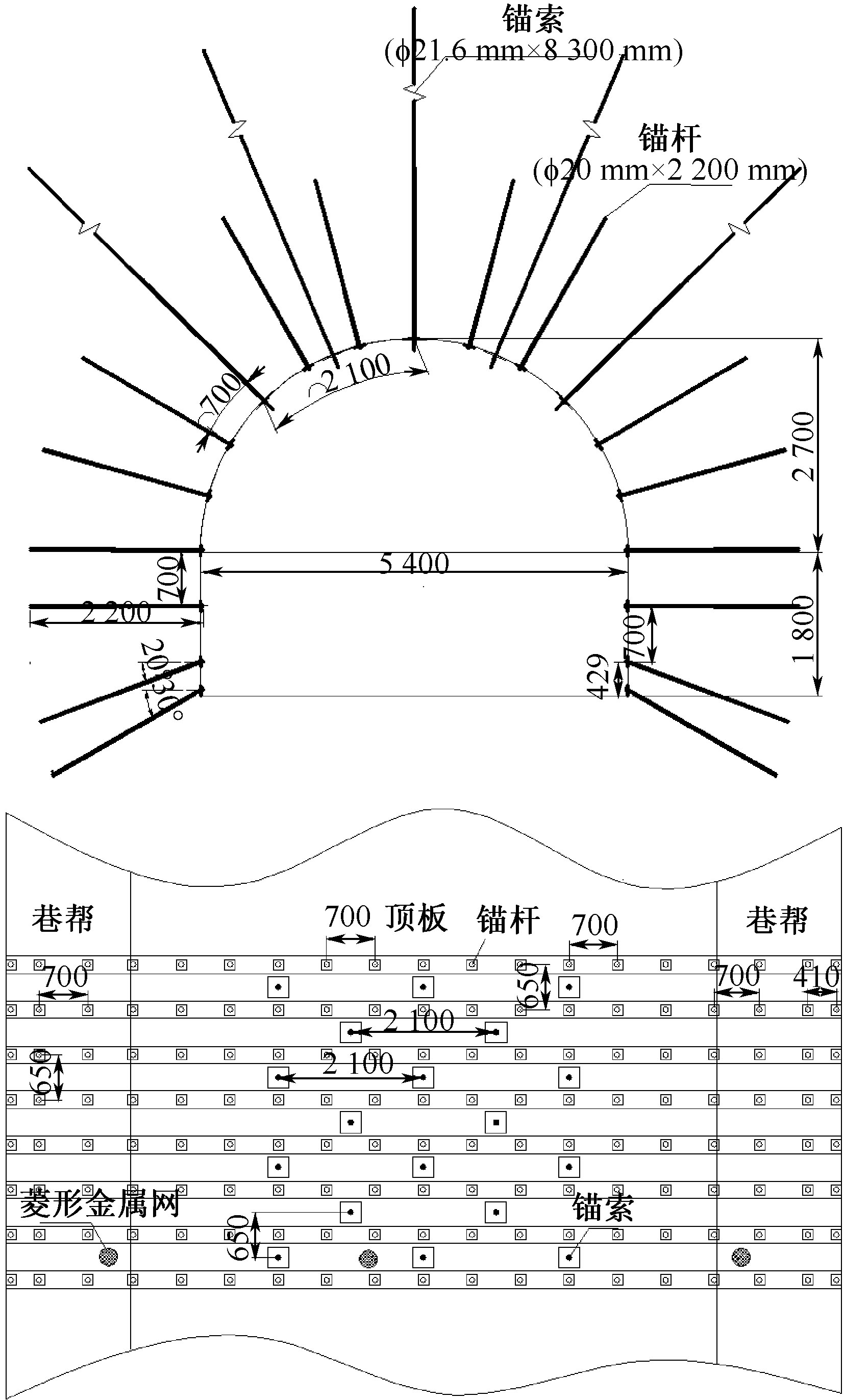
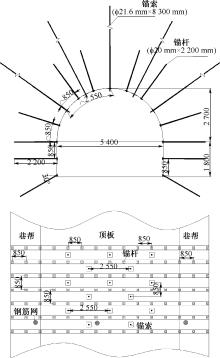
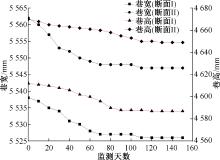
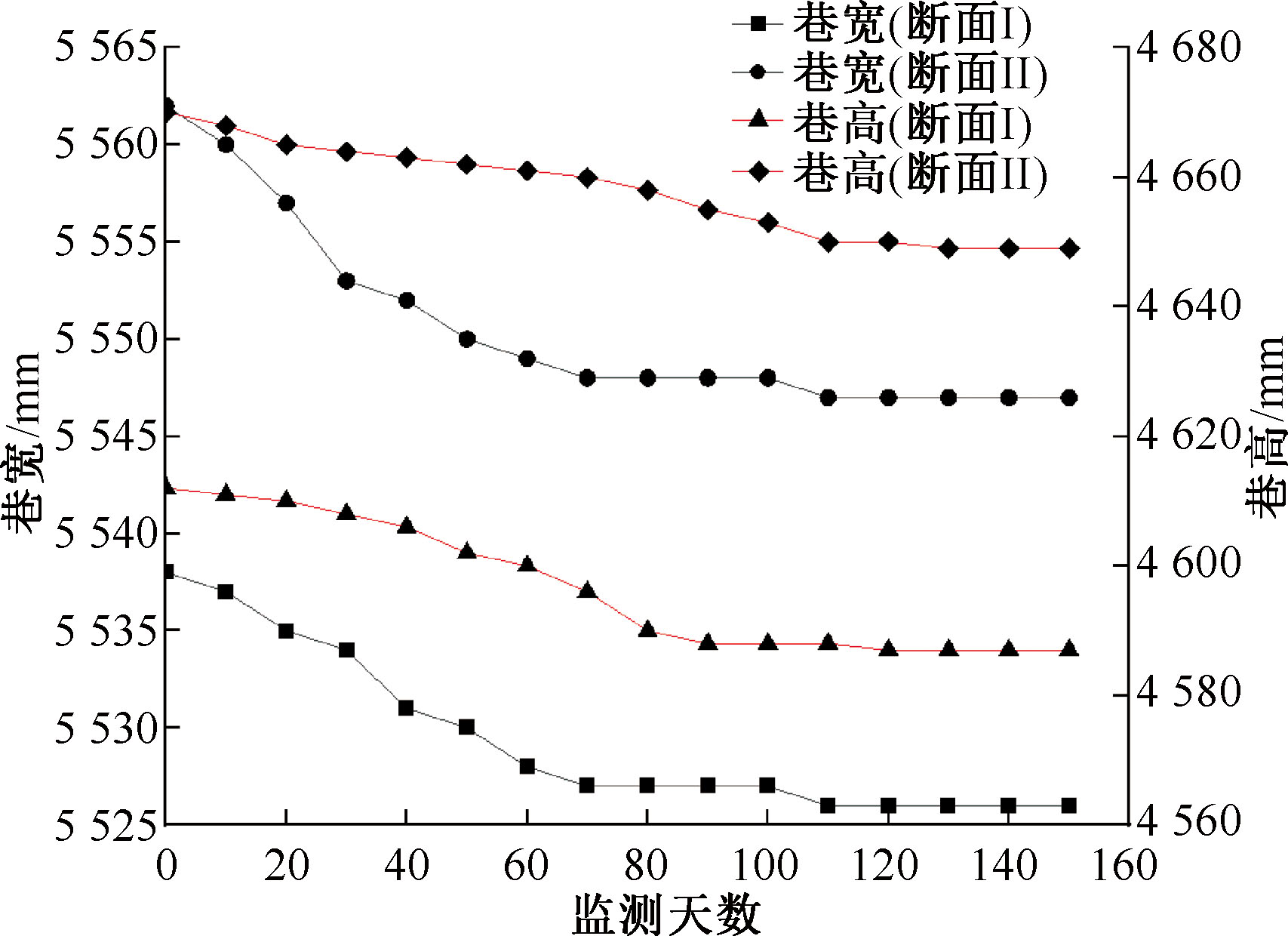
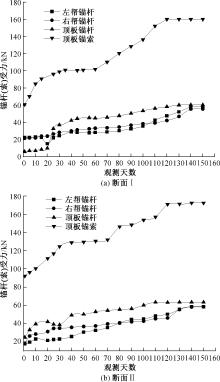
| [1] |
康红普, 徐刚, 王彪谋, 等. 我国煤炭开采与岩层控制技术发展40a及展望[J]. 采矿与岩层控制工程学报, 2019, 1(2):7-39.
|
|
KANG Hongpu, XU Gang, WANG Biaomou, et al. 40a and development of coal mining and rock layer control technology in China[J]. Journal of Mining and Strata Control Engineering, 2019, 1 (2): 7-39.
|
| [2] |
范东林, 王巍. 大采高工作面回风巷道支护参数优化研究[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2022, 32(增2):166-171.
|
|
FAN Donglin, WANG Wei. Study on optimization of supporting parameters of return air roadway in high mining working face[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2022, 32 (S2): 166-171.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2022.S2.0098
|
| [3] |
李京, 胡斌, 刘艳章, 等. 回采巷道锚杆支护效果评判的改进突变级数法[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2021, 31(3):60-65.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2021.03.009
|
|
LI Jing, HU Bin, LIU Yanzhang, et al. Improved mutation series method for the evaluation of anchor bolt support effect in mining roadway[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2021, 31 (3): 60-65.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2021.03.009
|
| [4] |
何峰, 王振伟, 于洋, 等. 复采巷道过破碎顶板区钢梁支护研究[J]. 煤炭科学技术, 2019, 47(7):115-120.
|
|
HE Feng, WANG Zhenwei, YU Yang, et al. Research on steel beam support in overbroken roof area of remining roadway[J]. Coal Science and Technology, 2019, 47 (7): 115-120.
|
| [5] |
张杰, 高守世, 李通, 等. 软岩巷道底板破坏特征及控制研究[J]. 煤炭科学技术, 2023, 51(3):21-28.
|
|
ZHANG Jie, GAO Shoushi, LI Tong, et al. Study on the characteristics and control of roof damage in soft rock roadways[J]. Coal Science and Technology, 2023, 51(3):21-28.
|
| [6] |
王平, 冯涛, 蒋运良, 等. 软弱再生顶板巷道围岩失稳机理及其控制原理与技术[J]. 煤炭学报, 2019, 44(10):2953-2965.
|
|
WANG Ping, FENG Tao, JIANG Yunliang, et al. Mechanism and control principle and technology of surrounding rock instability in weak regenerated roof roadway[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2019, 44 (10): 2953-2965.
|
| [7] |
杨东启, 刘建庄, 王盛川, 等. 深井破碎围岩巷道协同支护技术研究与应用[J]. 煤炭工程, 2023, 55(1):32-36.
doi: 10.11799/ce202301007
|
|
YANG Dongqi, LIU Jianzhuang, WANG Shengchuan, et al. Research and application of collaborative support technology for deep well broken surrounding rock roadway[J]. Coal Engineering, 2023, 55 (1): 32-36.
doi: 10.11799/ce202301007
|
| [8] |
高建成, 张宏伟, 荣海, 等. 高膨胀松软围岩巷道支护技术[J]. 煤矿安全, 2021, 52(1):92-97,102.
|
|
GAO Jiancheng, ZHANG Hongwei, RONG hai, et al. High expansion of soft surrounding rock roadway support technology[J]. Safety in Coal Mines, 2021, 52 (1): 92-97,102.
|
| [9] |
孙广京, 王平, 冯涛, 等. 软弱破碎顶板巷道围岩变形机理及控制技术[J]. 煤炭科学技术, 2020, 48(5):209-215.
|
|
SUN Guangjing, WANG Ping, FENG Tao, et al. Deformation mechanism and control technology of surrounding rock of soft and broken roof roadway[J]. Coal Science and Technology, 2020, 48 (5): 209-215.
|
| [10] |
余伟健, 李可, 芦庆和, 等. 裂隙发育岩体巷道围岩工程特征与变形控制[J]. 煤炭学报, 2021, 46(11):3408-3418.
|
|
YU Weijian, LI Ke, LU Qinghe, et al. Engineering characteristics and deformation control of surrounding rock in fissure development[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2021, 46 (11): 3408-3418.
|
| [11] |
孟庆彬, 孙稳, 韩立军, 等. 深井软岩巷道群掘进扰动效应与控制技术研究[J]. 采矿与安全工程学报, 2021, 38(3):496-506.
|
|
MENG Qingbin, SUN Wen, HAN Lijun, et al. Study on the disturbance effect and control technology of deep well soft rock roadway group[J]. Journal of Mining and Strata Control, 2021, 38 (3): 496-506.
|
| [12] |
王卫军, 范磊, 赵志强, 等. 基于塑性区控制的巷道围岩支护理论与技术研究进展[J]. 煤炭学报, 2024, 49(1):320-336.
|
|
WANG Weijun, FAN Lei, ZHAO Zhiqiang, et al. Progress on theory and technology of roadway surrounding rock support based on plastic zone control[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2024, 49 (1): 320-336.
|
| [13] |
范育青, 刘玉成, 赵明洲, 等. 弱胶结软岩巷道围岩应力与位移分布规律及支护技术[J]. 煤炭工程, 2020, 52(4):84-91.
doi: 10.11799/ce202004017
|
|
FAN Yuqing, LIU Yucheng, ZHAO Mingzhou, et al. Law of stress and displacement distribution of surrounding rock of weak cemented soft rock roadway[J]. Coal Engineering, 2020, 52 (4): 84-91.
|
| [14] |
彭文庆, 朱豪, 汪琦. 破碎岩体巷道围岩承载结构应力分布规律[J]. 中南大学学报:自然科学版, 2023, 54(6):2447-2458.
|
|
PENG Wenqing, ZHU Hao, WANG Qi. Stress distribution law of surrounding rock bearing structure in broken rock roadway[J]. Journal of Central South University:Science and Technology, 2023, 54(6):2447-2458.
|
| [15] |
贾后省, 张文彪, 刘少伟, 等. 不稳定厚煤层回采巷道极软顶板破坏规律及分级控制[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2022, 41(增2):3306-3316.
|
|
JIA Housheng, ZHANG Wenbiao, LIU Shaowei, et al. Destruction rule and grading control of extremely soft roof in mining roadway of unstable thick coal seam[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock mechanics and Engineering, 2022, 41 (S2): 3306-3316.
|
| [16] |
王思栋, 朱宗磊, 杨斌. 滨湖矿巷道围岩裂隙演化规律实测研究[J]. 煤矿安全, 2019, 50(10):66-70.
|
|
WANG Sidong, ZHU Zonglei, YANG Bin. Measured study on the evolution law of surrounding rock fissure in lakeside mine roadway[J]. Safety in Coal Mines, 2019, 50 (10): 66-70.
|
| [17] |
芦楠楠, 陈永珩, 马占国, 等. 深部地下巷道围岩结构监测信息化技术研究[J]. 工矿自动化, 2019, 45(6):1-9.
|
|
LU Nannan, CHEN Yongheng, MA Zhanguo, et al. Research on the information technology of monitoring of surrounding rock structure in deep underground roadway[J]. Industry and Mine Automation, 2019, 45 (6): 1-9.
|
| [18] |
李学华, 梁顺, 姚强岭, 等. 泥岩顶板巷道围岩裂隙演化规律与冒顶机理分析[J]. 煤炭学报, 2011, 36(6):903-908.
|
|
LI Xuehua, LIANG Shun, YAO Qiangling, et al. Analysis of the evolution law and roof burst mechanism of surrounding rock fissure in mudstone roof roadway[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2011, 36 (6): 903-908.
|
| [19] |
焦建康, 张镇, 颜立新, 等. 中小型煤矿巷道围岩稳定性定量化评价及分级支护技术[J]. 采矿与安全工程学报, 2022, 39(3):598-606.
|
|
JIAO Jiankang, ZHANG Zhen, YAN Lixin, et al. Quantitative evaluation of surrounding rock stability and grading support technology of small and medium-sized coal mines[J]. Journal of Mining and Strata Control, 2022, 39 (3): 598-606.
|