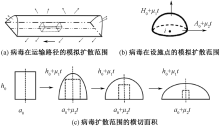
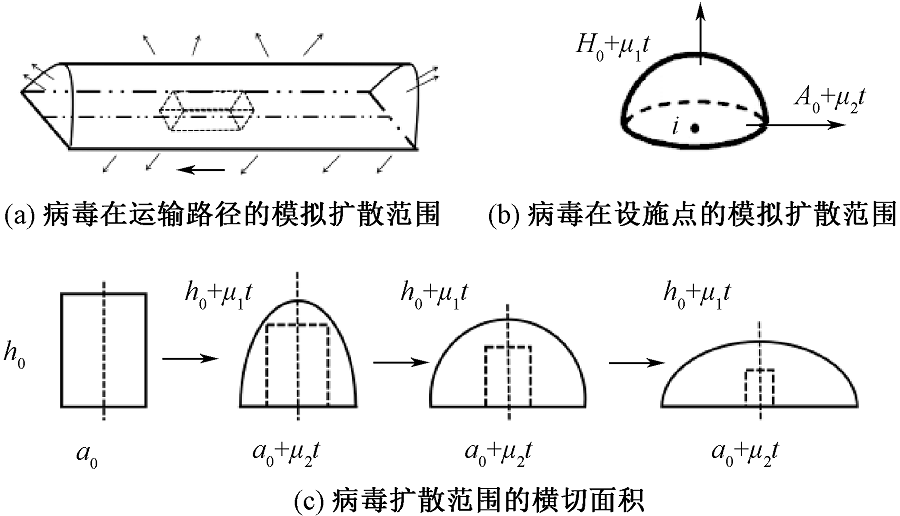
| [1] |
GINGER Y K, ZHANG Huiwen, BOOKBINDER J H. A dual toll policy for maintaining risk equity in hazardous materials transportation with fuzzy incident rate[J]. International Journal of Production Economics, 2020,227: DOI: 10.1016/j.ijpe.2020.107650.
doi: 10.1016/j.ijpe.2020.107650
|
| [2] |
FONTAINE P, CRAINIC T G, GENDREAU M, et al. Population-based risk equilibration for the multimode hazmat transport network design problem[J]. European Journal of Operational Research, 2019, 284(1):188-200.
doi: 10.1016/j.ejor.2019.12.028
|
| [3] |
ZHAO Jiahong, VERTER V. A bi-objective model for the used oil location-routing problem[J]. Computers & Operations Research, 2015, 62:157-168.
doi: 10.1016/j.cor.2014.10.016
|
| [4] |
RONAY A, BAHRAMI M, BOZKAYA B. A time-based model and GIS framework for assessing hazardous materials transportation risk in urban areas[J]. Journal of Transport & Health, 2020, 19: DOI: 10.1016/j.jth.2020.100943.
doi: 10.1016/j.jth.2020.100943
|
| [5] |
杨婷, 帅斌, 黄文成. 基于N-K模型的道路危险品运输系统耦合风险分析[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2019, 29(9):132-137.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2019.09.021
|
|
YANG Ting, SHUAI Bin, HUANG Wencheng. Coupling risk analysis of road dangerous goods transportation system based on N-K model[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2019, 29(9):132-137.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2019.09.021
|
| [6] |
YU Hao, XU Sun, WEI Deng, et al. Reverse logistics network design for effective management of medical waste in epidemic outbreaks: insights from the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) outbreak in Wuhan (China)[J]. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 2020, 17: DOI: 10.3390/ijerph17051770.
doi: 10.3390/ijerph17051770
|
| [7] |
KARGAR S, POURMEHDI M, PAYDAR M M. Reverse logistics network design for medical waste management in the epidemic outbreak of the novel coronavirus (COVID-19)[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2020,746:DOI: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.141183.
doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.141183
|
| [8] |
薛翔, 朱小林. 不确定需求下危险品运输路径问题的多目标优化[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2016, 26(11):93-98.
|
|
XUE Xiang, ZHU Xiaolin. Multi-obiective optimization of hazardous materials transportation route under uncertain demand condition[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2016, 26(11):93-98.
|
| [9] |
TIRKOLAEE E B, ABBASIAN P, WILHELMWEBER G. Sustainable fuzzy multi-trip location-routing problem for medical waste management during the COVID-19 outbreak[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2020, 10: DOI: j.scitotenv.2020.143607.
doi: j.scitotenv.2020.143607
|
| [10] |
李雪, 蒋靖坤, 王东滨, 等. 冠状病毒气溶胶传播及环境影响因素[J]. 环境科学, 2021, 42(7):3091-3098.
|
|
LI Xue, JIANG Jingkun, WANG Dongbin, et al. Transmission of coronavirus via aerosols and influence of environmental conditions on its transmission[J]. Environmental Science, 2021, 42(7):3091-3098.
|
| [11] |
KARGAR S, PAYDAR M, SAFAEI A S. A reverse supply chain for medical waste: a case study in Babol healthcare sector[J]. Waste Management, 2020, 113:197-209.
doi: S0956-053X(20)30302-0
pmid: 32535372
|
| [12] |
YU Chianson, LI Hanlin. A robust optimization model for stochastic logistic problems[J]. International Journal of Production Economics, 2000, 64(1):385-397.
doi: 10.1016/S0925-5273(99)00074-2
|
| [13] |
ZHAO Jiahong, WU Biaohua, GINGER Y K. A bi-objective robust optimization approach for the management of infectious wastes with demand uncertainty during a pandemic[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2021, 314(1):DOI: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2021.127922.
doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2021.127922
|