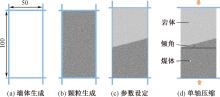
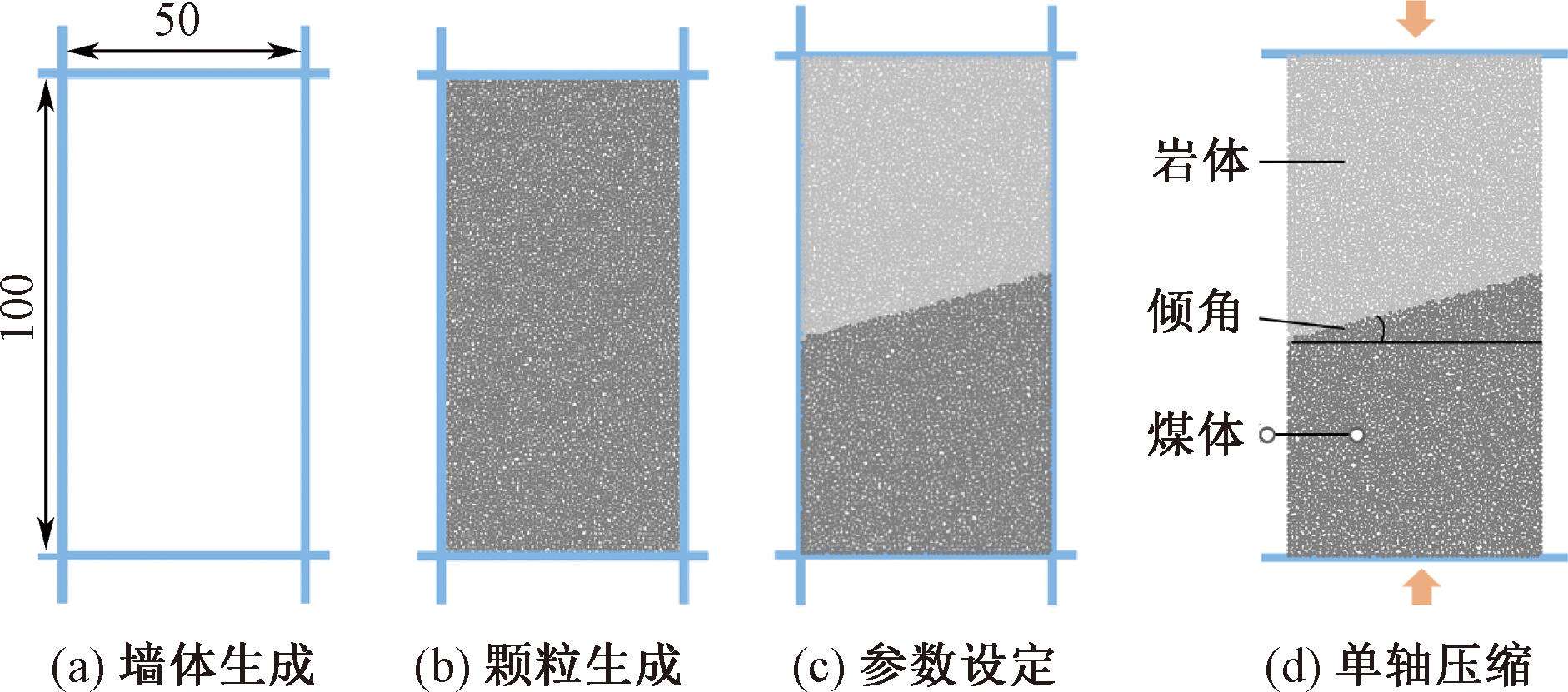
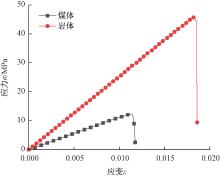
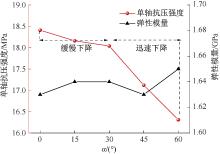
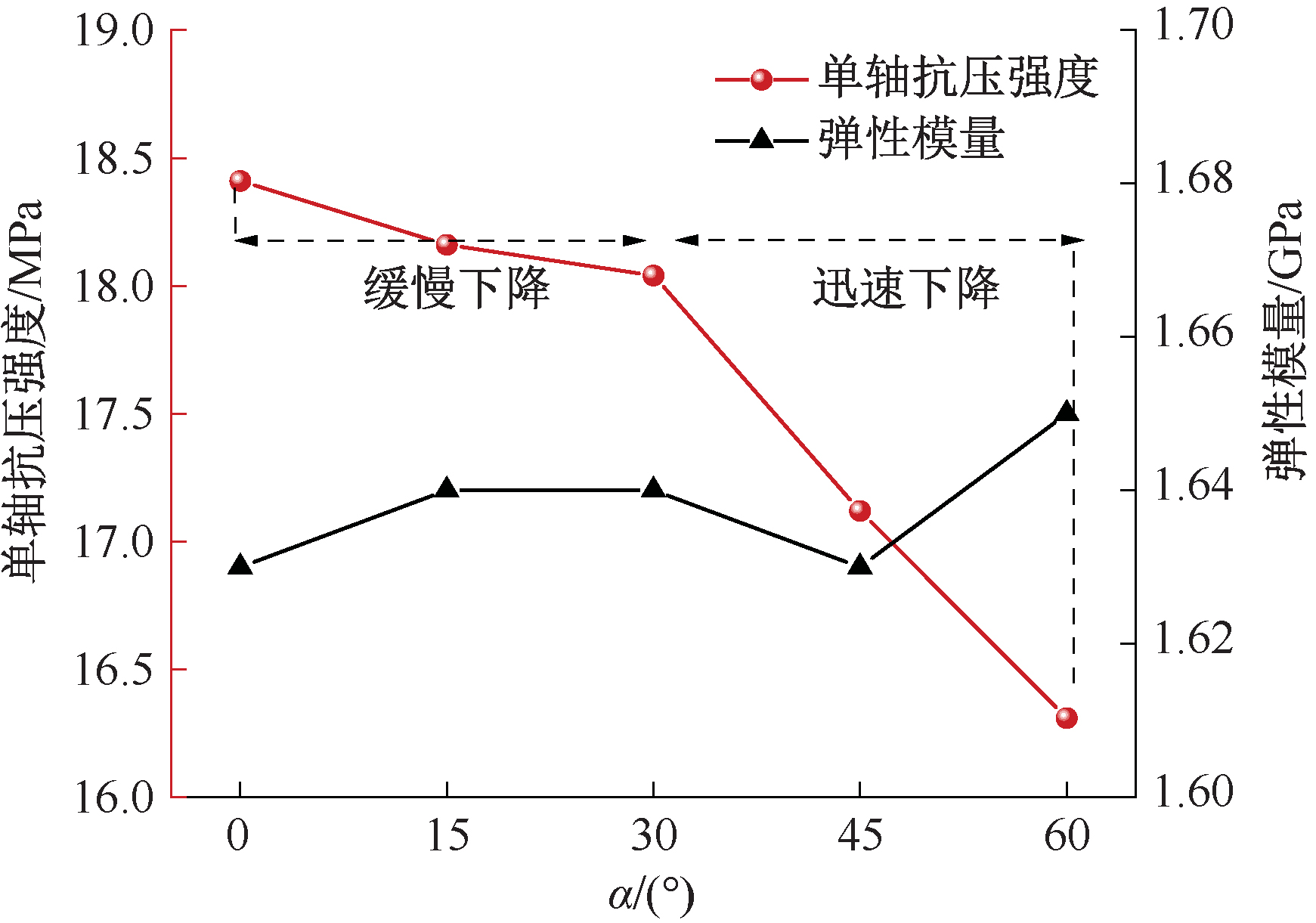
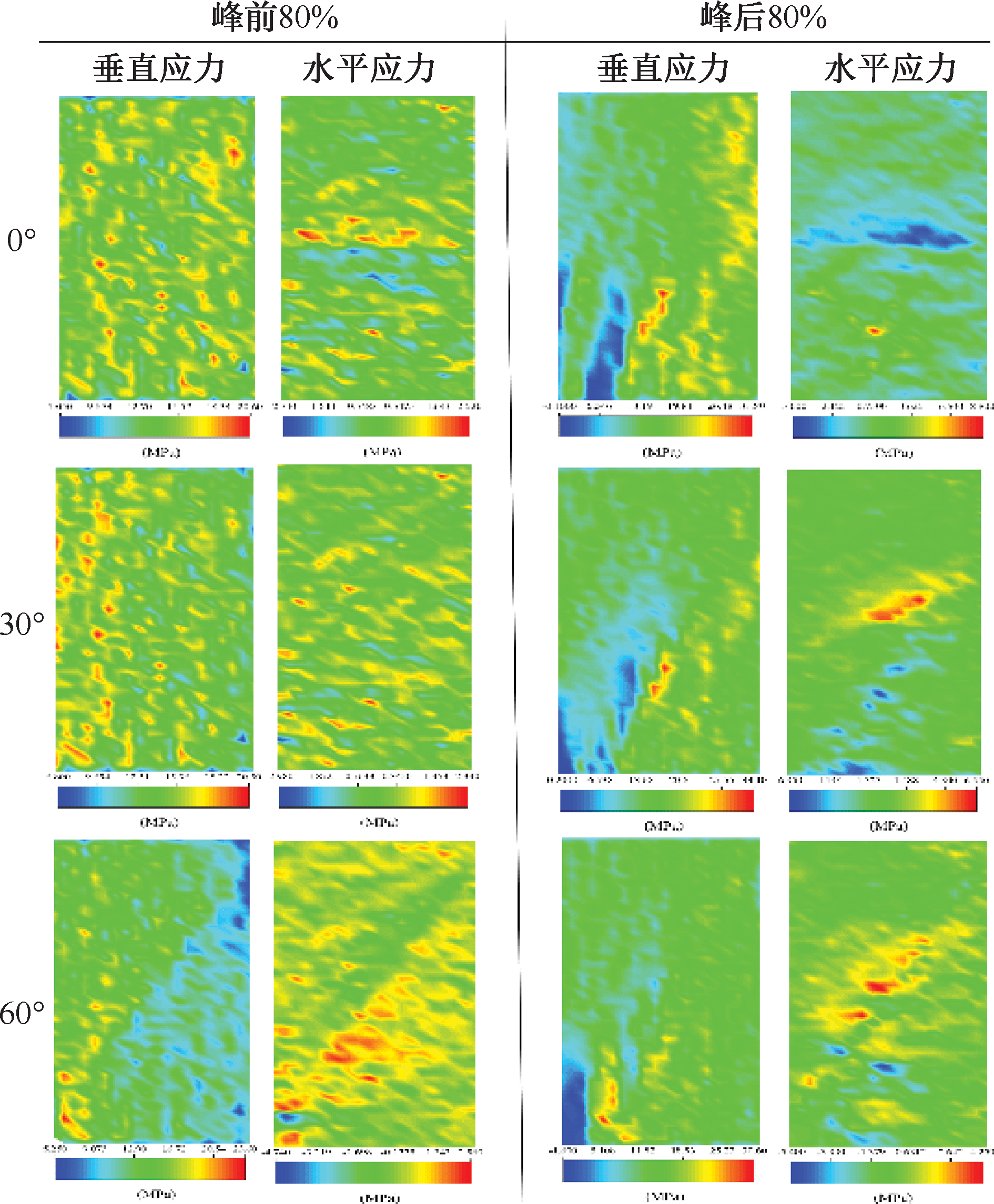
| [1] |
王凯, 郭阳阳, 王刚, 等. 真三轴路径下含瓦斯复合煤岩体渗流及力学破坏特性[J]. 煤炭学报, 2023, 48(1):226-237.
|
|
WANG Kai, GUO Yangyang, WANG Gang, et al. Seepage and mechanical failure characteristics of gas-bearing composite coal-rock under true triaxial path[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2023, 48(1):226-237.
|
| [2] |
刘玉冰, 王恩元, 张东明, 等. 真三轴应力条件下破断煤体力学响应及渗流特性试验研究[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2023, 33(6):105-113.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2023.06.1428
|
|
LIU Yubing, WANG Enyuan, ZHANG Dongming, et al. Experimental study on mechanical response and seepage characteristics of broken coal under true triaxial stress conditions[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2023, 33(6):105-113.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2023.06.1428
|
| [3] |
肖晓春, 金晨, 潘一山, 等. 组合煤岩破裂声发射特性和冲击倾向性试验研究[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2016, 26(4):102-107.
|
|
XIAO Xiaochun, WJINU Chen, PAN Yishan, et al. Experimental study on acoustic emission characteristic and outburst-proneness of coal-rock combinations during failure process[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2016, 26(4):102-107.
|
| [4] |
韩军, 崔露郁, 贾冬旭, 等. 坚硬顶板回采巷道冲击地压的卸载滑脱机制[J]. 煤炭学报, 2022, 47(2):711-721.
|
|
HAN Jun, CUI Luyu, JIA Dongxu, et al. Unloading-slippage mechanism of rock burst occurred in longwall roadway[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2022, 47(2):711-721.
|
| [5] |
齐庆新, 史元伟, 刘天泉. 冲击地压粘滑失稳机理的实验研究[J]. 煤炭学报, 1997, 22(2):34-38.
|
|
QI Qingxin, SHI Yuanwei, LIU Tianquan. Mechanism of instability caused by viscous sliding in rock burst[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 1997(2):34-38.
|
| [6] |
谭云亮, 张明, 徐强, 等. 坚硬顶板型冲击地压发生机理及监测预警研究[J]. 煤炭科学技术, 2019, 47(1):166-172.
|
|
TAN Yunliang, ZHANG Ming, XU Qiang, et al. Study on occurrence mechanism and monitoring and early warning of rock burst caused by hard roof[J]. Coal Science and Technology, 2019, 47(1):166-172.
|
| [7] |
何江, 窦林名, 王崧玮, 等. 坚硬顶板诱发冲击矿压机理及类型研究[J]. 采矿与安全工程学报, 2017, 34(6):1122-1127.
|
|
HE Jiang, DOU Linming, WANG Songwei, et al. Study on mechanism and types of hard roof inducing rock burst[J]. Journal of Mining & Safety Engineering, 2017, 34(6):1122-1127.
|
| [8] |
左建平, 谢和平, 吴爱民, 等. 深部煤岩单体及组合体的破坏机制与力学特性研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2011, 30(1):84-92.
|
|
ZUO Jianping, XIE Heping, WU Aimin, et al. Investigation on failure mechanisms and mechanical behaviors of deep coal-rock single body and combined body[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2011, 30(1):84-92.
|
| [9] |
陈光波, 李谭, 杨磊, 等. 不同煤岩比例及组合方式的组合体力学特性及破坏机制[J]. 采矿与岩层控制工程学报, 2021, 3(2):84-94.
|
|
CHEN Guangbo, LI Tan, YANG Lei, et al. Mechanical properties and failure mechanism of combined bodies with different coal-rock ratios and combinations[J]. Journal of Mining And Strata Control Engineering, 2021, 3(2):84-94.
|
| [10] |
刘杰, 王恩元, 宋大钊, 等. 岩石强度对于组合试样力学行为及声发射特性的影响[J]. 煤炭学报, 2014, 39(4):685-691.
|
|
LIU Jie, WANG Enyuan, SONG Dazhao, et al. Effects of rock strength on mechanical behavior and acoustic emission characteristics of samples composed of coal and rock[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2014, 39(4):685-691.
|
| [11] |
刘波, 杨仁树, 郭东明, 等. 孙村煤矿-1100m水平深部煤岩冲击倾向性组合试验研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2004, 23(14):2402-2408.
|
|
LIU Bo, YANG Renshu, GUO Dongming, et al. Burst-prone experiments of coal rock combination at -1100 m level in Suncun coal mine[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2004, 23(14):2402-2408.
|
| [12] |
郭东明, 左建平, 张毅, 等. 不同倾角组合煤岩体的强度与破坏机制研究[J]. 岩土力学, 2011, 32(5):1333-1339.
|
|
GUO Dongming, ZUO Jianping, ZHANG Yi, et al. Research on strength and failure mechanism of deep coal-rock combination bodies of different inclined angles[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2011, 32(5):1333-1339.
|
| [13] |
赵宏林, 赵越. 倾角对煤岩组合体力学及冲击倾向性影响的颗粒流分析[J]. 煤矿安全, 2018, 49(3):198-201.
|
|
ZHAO Honglin, ZHAO Yue. Influence of dip angle of coal and rock combination on outburst tendency based on particle flow code[J]. Safety in Coal Mines, 2018, 49(3):198-201.
|
| [14] |
沈文兵, 余伟健, 潘豹. 不同倾角煤岩组合岩石力学试验及破坏特征[J]. 矿业工程研究, 2021, 36(1):1-8.
|
|
SHEN Wenbing, YU Weijian, PAN Bao. Rock mechanics test and failure characteristics of coal-rock combination with different dip angles[J]. Mineral Engineering Research, 2021, 36(1):1-8.
|
| [15] |
丛宇, 王在泉, 郑颖人, 等. 基于颗粒流原理的岩石类材料细观参数的试验研究[J]. 岩土工程学报, 2015, 37(6):1031-1040.
|
|
CONG Yu, WANG Zaiquan, ZHENG Yingren, et al. Experimental study on microscopic parameters of brittle materials based on particle flow theory[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2015, 37(6):1031-1040.
|
| [16] |
张磊, 刘玥. 基于颗粒离散元模型的煤岩损伤演化及声发射特性分析[J]. 煤矿安全, 2017, 48(11):213-216.
|
|
ZHANG Lei, LIU Yue. Analysis of coal-rock damage evolution and acoustic emission characteristics based on particle discrete element mode[J]. Safety in Coal Mines, 2017, 48(11):213-216.
|
| [17] |
WANG Kai, ZHANG Xiang, DU Feng, et al. Numerical study on damage response and failure mechanism of gas-containing coal-rock combination under confining pressure effect[J]. Fuel, 2023, 349:DOI: 10.1016/j.fuel.2023.128683.
|
| [18] |
李绪强. 兴安煤矿二号煤层群赋存地质特征研究[J]. 黑龙江科技信息, 2013(16):107.
|