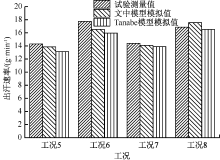
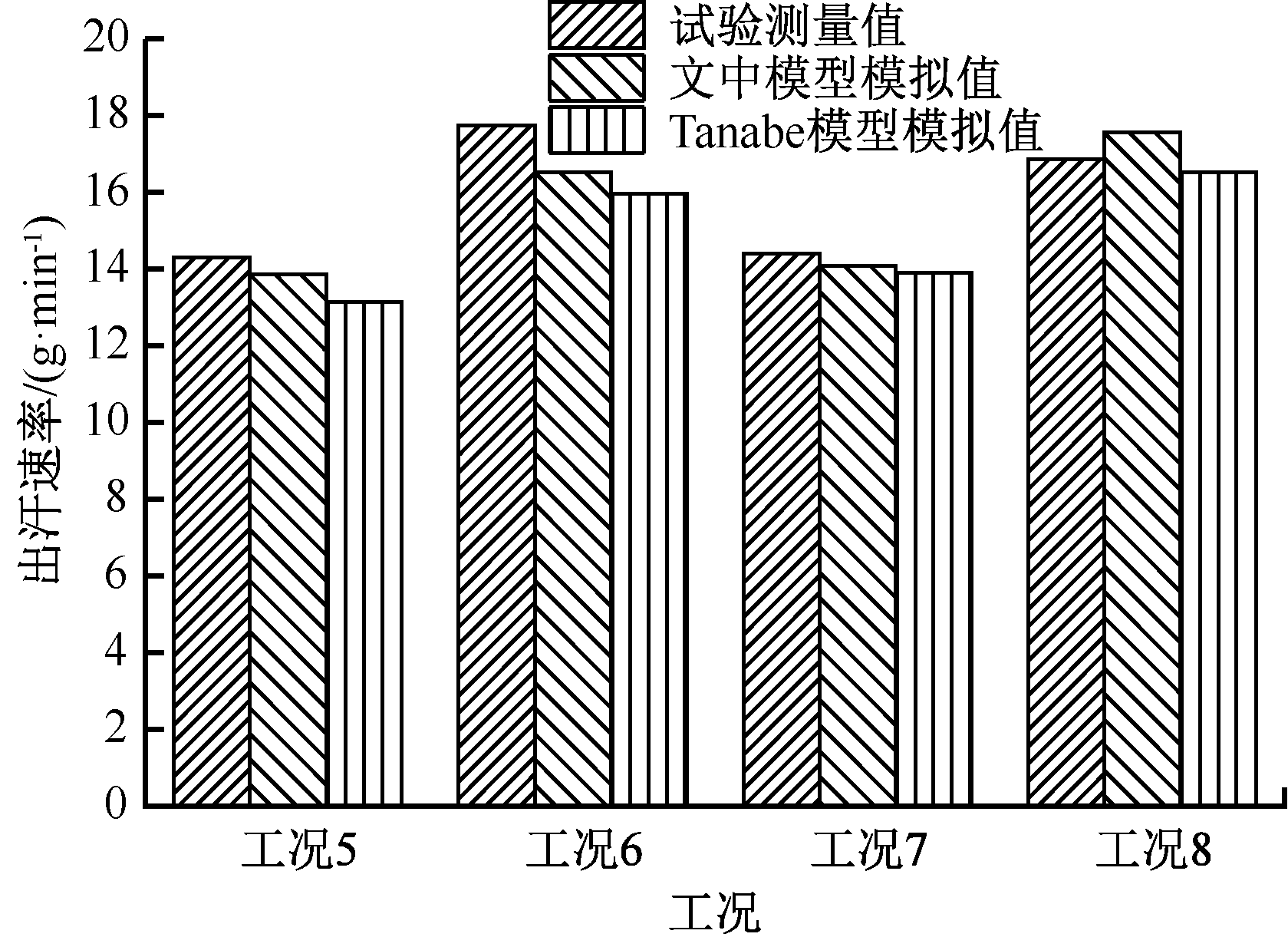
| [1] |
郑国忠, 李珂. 持续高温天气人体生理应激累积效应量化研究[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2019, 29(6):32-36.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2019.06.006
|
|
ZHENG Guozhong, LI Ke. Quantitative study on accumulative effects of continuous high temperature weather on hum physiological stress[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2019, 29(6): 32-36.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2019.06.006
|
| [2] |
GAGGE A P, STOLWIJK J A J, NISHI Y. An effective temperature scale based on a simple model of human physiological regulatory response[J]. ASHRAE Transactions, 1977, 77(1): 21-36.
|
| [3] |
TANABE S, KOBAYASHI K, NAKANO J, et al. Evaluation of thermal comfort using combined multi-node thermoregulation (65 MN) and radiation models and computational fluid dynamics (CFD)[J]. Energy and Buildings, 2002, 34(6): 637-646.
|
| [4] |
WENG Wenguo, HAN Xiaofeng, FU Ming. An extended multi-segmented human bioheat model for high temperature environments[J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2014, 75: 504-513.
|
| [5] |
YANG Jie, WENG Wenguo, ZHANG Baoting. Experimental and numerical study of physiological responses in hot environments[J]. Journal of Thermal Biology, 2014, 45: 54-61.
doi: 10.1016/j.jtherbio.2014.07.010
pmid: 25436951
|
| [6] |
GENG Jing, GU Yi, WENG Wenguo, et al. A multi-segmented human bioheat model for asymmetric high temperature environments[J]. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 2022, 19(22): DOI: 10.3390/ijerph192215259.
|
| [7] |
杨杰, 翁文国. 基于高温人体热反应模型的生理参数预测[J]. 清华大学学报, 2014, 54(11): 1422-1427.
|
|
YANG Jie, WENG Wenguo. Prediction of human physiological responses by a thermal response model in hot environments[J]. Journal of Tsinghua University, 2014, 54(11): 1422-1427.
|
| [8] |
BLAZEJCZYK K, NILSSON H, HOLMÉR I. Solar heat load on man: review of different methods of estimation[J]. International Journal of Biometeorology, 1993, 37: 125-132.
|
| [9] |
FIALA D, HAVENITH G, BRÖDE P, et al. UTCI-Fiala multi-node model of human heat transfer and temperature regulation[J]. International Journal of Biometeorology, 2012, 56: 429-441.
doi: 10.1007/s00484-011-0424-7
pmid: 21503622
|
| [10] |
JI Yuchen, SONG Jusheng, SHEN Pengyuan. A review of studies and modelling of solar radiation on human thermal comfort in outdoor environment[J]. Building and Environment, 2022, 214: DOI: 10.1016/j.buildenv.2022.108891.
|
| [11] |
WERNER J, BUSE M. Temperature profiles with respect to inhomogeneity and geometry of the human body[J]. Journal of Applied Physiology, 1988, 65(3): 1110-1118.
pmid: 3182480
|
| [12] |
LIU Hisuying, LU Yifa, CHEN Weijao. Predictive equations for basal metabolic rate in Chinese adults: a cross-validation study[J]. Journal of the American Dietetic Association, 1995, 95(12): 1403-1408.
doi: 10.1016/S0002-8223(95)00369-X
pmid: 7594142
|
| [13] |
ZHOU Xing, LIAN Zhiwei, LAN Li. An individualized human thermoregulation model for Chinese adults[J]. Building and Environment, 2013, 70: 257-265.
|
| [14] |
FIALA D, LOMAS K J, STOHRER M. A computer model of human thermoregulation for a wide range of environmental conditions: the passive system[J]. Journal of Applied Physiology, 1999, 87(5): 1957-1972.
doi: 10.1152/jappl.1999.87.5.1957
pmid: 10562642
|
| [15] |
郑国忠, 岳旭辉, 卫常青. 改进HSDA模型的高温天气户外工作者热安全研究[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2023, 33(5):230-235.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2023.05.1418
|
|
ZHENG Guozhong, YUE Xuhui, WEI Changqing. Study on improved HSDA model for thermal safety of outdoor workers in high temperature weather[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2023, 33(5): 230-235.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2023.05.1418
|
| [16] |
ZHANG Huan, YANG Ruiqiao, YOU Shijun. The CPMV index for evaluating indoor thermal comfort in buildings with solar radiation[J]. Building and Environment, 2018, 134: 1-9.
|
| [17] |
叶海. 人体辐射换热的计算方法[C]. 全国暖通空调制冷2002年学术年会资料集,2002:564-567
|
| [18] |
TANABE S, NARITA C, OZEKI Y, et al. Effective radiation area of human body calculated by a numerical simulation[J]. Energy and Buildings, 2000, 32(2): 205-215.
|
| [19] |
刘冬华, 汪海涛, 杨杰, 等. 高温环境下人体热反应模型的建立及验证[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2022, 32(10): 214-221.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2022.10.1664
|
|
LIU Donghua, WANG Haitao, YANG Jie, et al. Development and verification of human thermal response model in high temperature environment[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2022, 32(10): 214-221.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2022.10.1664
|
| [20] |
ISO EN 7730:2005, Ergonomics of the thermal environment-analytical determination and interpretation of thermal comfort using calculation of the PMV and PPD indices and local thermal comfort criteria[S].
|
| [21] |
李志灏. 室外高温环境人体生理应激及缓解措施研究[D]. 北京: 华北电力大学, 2018.
|
|
LI Zhihao. Study on the physiological responses and relieving measures in outdoor high temperature environment[D]. Beijing: North China Electric Power University, 2018.
|
| [22] |
WISSLER E H. A mathematical model of the human thermal system[J]. The Bulletin of Mathematical Biophysics, 1964, 24: 147-166.
|