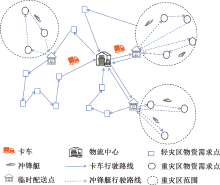
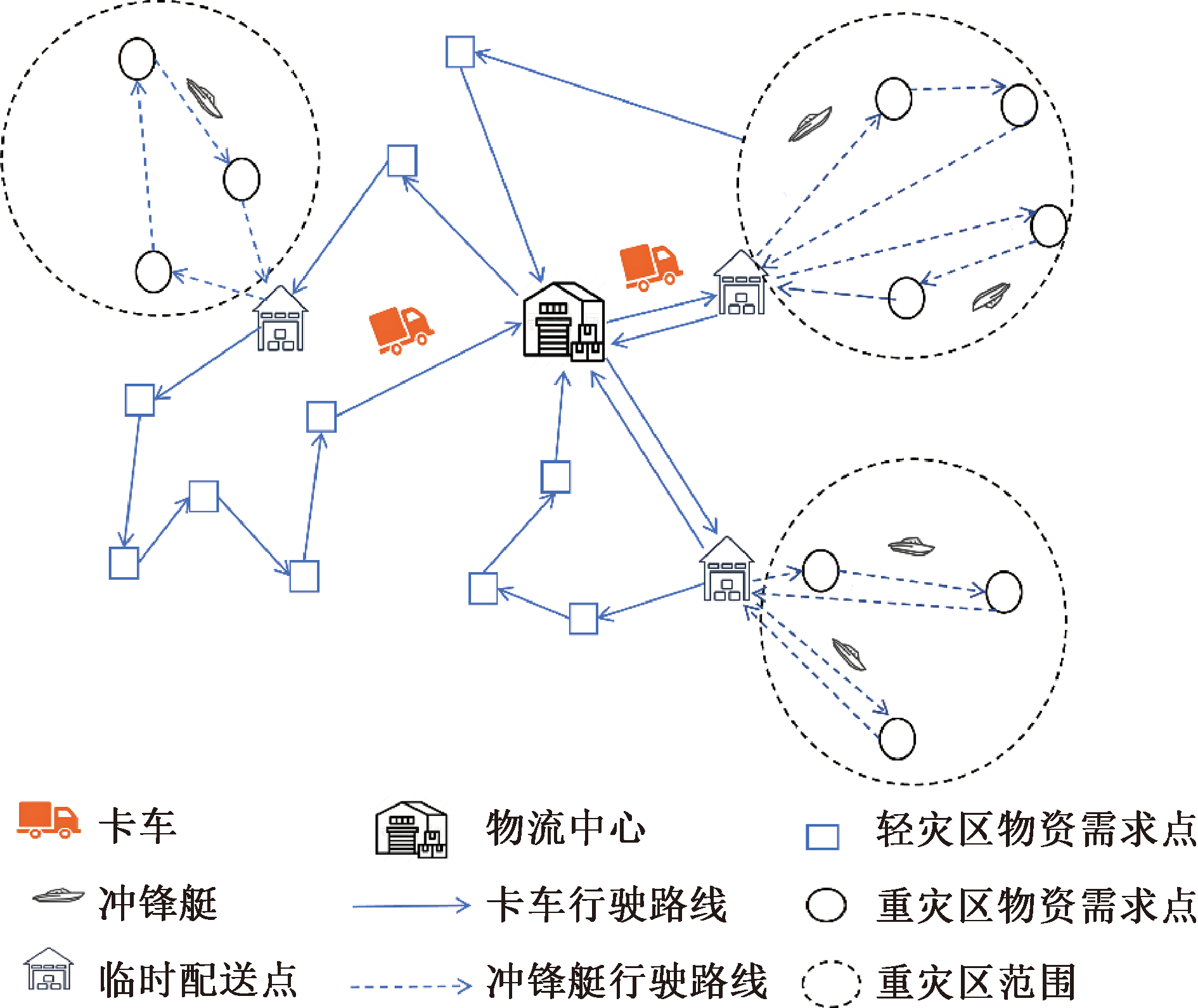
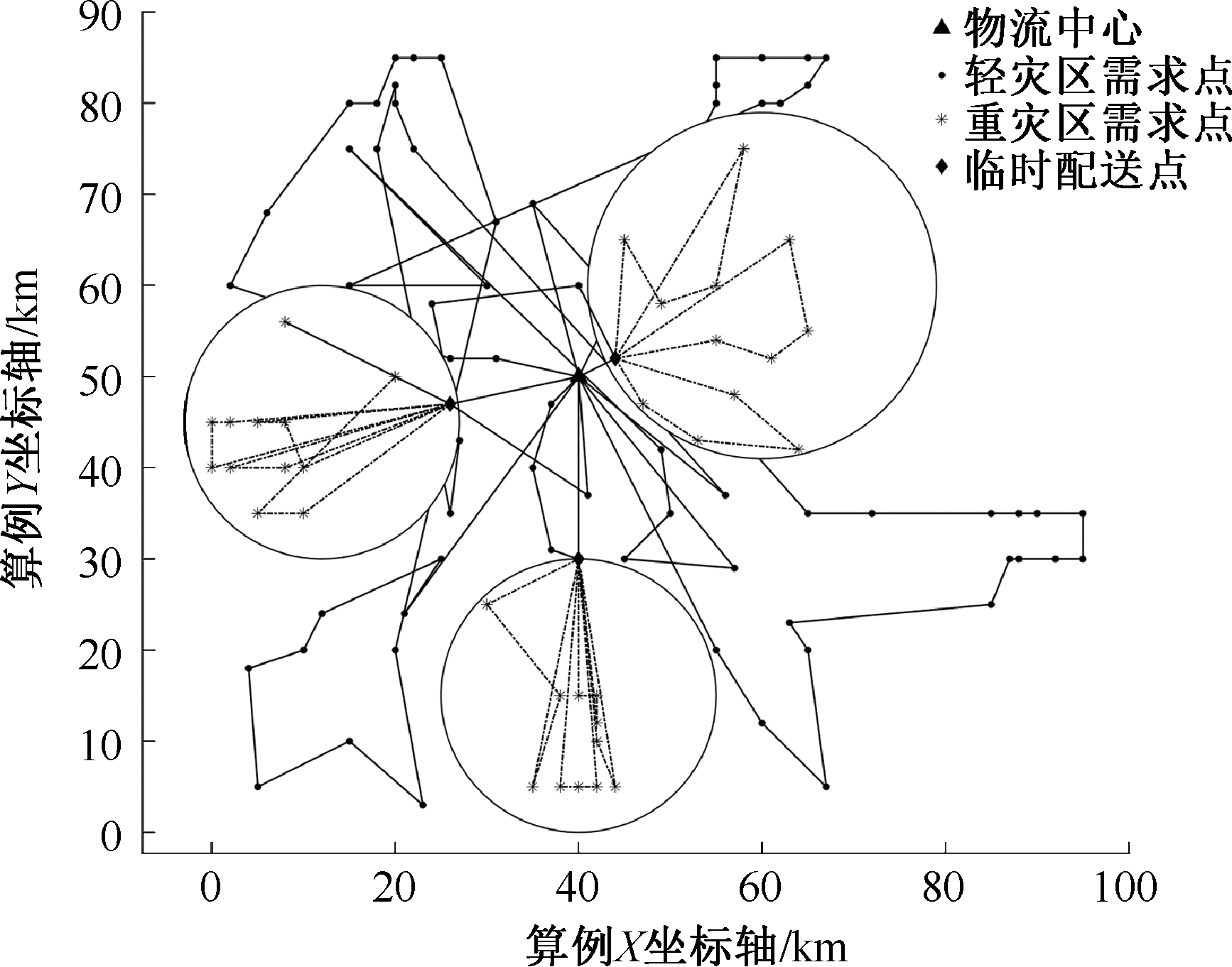
| [1] |
龚英, 涂熳熳, 周愉峰. 卡车-无人机协同的洪灾应急选址-路径鲁棒优化问题[J]. 计算机工程与应用, 2025, 61(14):307-321.
doi: 10.3778/j.issn.1002-8331.2410-0289
|
|
GONG Ying, TU Manman, ZHOU Yufeng. Truck-drone collaborated location-routing robust optimization problem for flood emergency response[J]. Computer Engineering and Applications, 2025, 61(14):307-321.
doi: 10.3778/j.issn.1002-8331.2410-0289
|
| [2] |
刘长石, 罗亮, 周鲜成, 等. 震后初期应急物资分配-运输的协同决策:公平与效率兼顾[J]. 控制与决策, 2018, 33(11):2057-2063.
|
|
LIU Changshi, LUO Liang, ZHOU Xiancheng, et al. Collaborative decision-making of relief allocation-transportation in early post-earthquake: considering both fairness and efficiency[J]. Control and Decision, 2018, 33(11):2057-2063.
|
| [3] |
GHARIB Z, BOZORGI-AMIRI A, TAVAKKOLI-MOGHADDAM R, et al. A cluster-based emergency vehicle routing problem in disaster with reliability[J]. Scientia Iranica, 2018, 25(4):2312-2330.
|
| [4] |
HAGHI M, GHOMI S M T F, JOLAI F. Developing a robust multi-objective model for pre/post disaster times under uncertainty in demand and resource[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2017, 154:188-202.
doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2017.03.102
|
| [5] |
WENG Xun, DUAN Shuyao, ZHANG Jingtian, et al. A material allocation model for public health emergency under a multimodal transportation network by considering the demand priority and psychological pain[J]. Mathematics, 2024, 12(3):DOI: 10.3390/math12030489.
|
| [6] |
张艳萍, 崔娜, 张波. 基于多式联运的应急物资供应多目标优化研究[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2023, 33(7):230-238.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2023.07.1427
|
|
ZHANG Yanping, CUI Na, ZHANG Bo. Multi-objective optimization strategy of emergency material supply based on multi-mode transportation[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2023, 33(7):230-238.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2023.07.1427
|
| [7] |
刘长石, 寇纲, 刘导波. 震后应急物资多方式供应的模糊动态LRP[J]. 管理科学学报, 2016, 19(10):61-72.
|
|
LIU Changshi, KOU Gang, LIU Daobo. Fuzzy dynamic LRP for post-earthquake multimodal relief delivery[J]. Journal of Management Sciences in China, 2016, 19(10):61-72.
|
| [8] |
MAGHFIROH M F N, HANAOKA S. Multi-modal relief distribution model for disaster response operations[J]. Progress in Disaster Science, 2020, 6:DOI: 10.1016/j.pdisas.2020.100095.
|
| [9] |
刘松, 邵毅明, 彭勇, 等. 应急救援物资多式联运路径优化[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2019, 29(12):152-157.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2019.12.024
|
|
LIU Song, SHAO Yiming, PENG Yong, et al. Multi-modal transport route optimization of emergency relief materials[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2019, 29(12): 152-157.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2019.12.024
|
| [10] |
宋英华, 王莉芳, 杜丽敬, 等. 模糊条件下应急物资配送选址-多模式运输问题[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2017, 27(7):169-174.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2017.07.030
|
|
SONG Yinghua, WANG Lifang, DU Lijing, et al. Location-multimodal transportation problem for relief distribution in emergency logistics under fuzzy conditions[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2017, 27(7):169-174.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2017.07.030
|
| [11] |
高鹏飞, 刘方翔, 黄建华, 等. 考虑灾民心理痛苦的震后应急物资调配问题研究[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2022, 32(11):200-207.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2022.11.1392
|
|
GAO Pengfei, LIU Fangxiang, HUANG Jianhua, et al. Research on post-earthquake emergency material allocation considering psychological pain of victims[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2022, 32(11):200-207.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2022.11.1392
|
| [12] |
吕伟, 李志红, 冯满满, 等. 考虑资源和时间窗约束的应急物资调配模型[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2019, 29(12):137-143.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2019.12.022
|
|
LYU Wei, LI Zhihong, FENG Manman, et al. Emergency material allocation in consideration of resource and time window constraints[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2019, 29(12):137-143.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2019.12.022
|
| [13] |
曲冲冲, 王晶, 黄钧, 等. 考虑时效与公平性的震后应急物资动态配送优化研究[J]. 中国管理科学, 2018, 26(6):178-187.
|
|
QU Chongchong, WANG Jing, HUANG Jun, et al. Dynamic emergency materials distribution optimization with timeliness and fairness objective for post-earthquake emergency rescue[J]. Chinese Journal of Management Science, 2018, 26(6):178-187.
|
| [14] |
王慧丽, 乔咏艺. 考虑优先级和时间窗约束的应急物资调配模型[J]. 科学技术与工程, 2024, 24(12):5069-5075.
|
|
WANG Huili, QIAO Yongyi. Emergency material deployment model considering priority and time window constraints[J]. Science Technology and Engineering, 2024, 24(12):5069-5075.
|
| [15] |
曾昭, 罗威, 梁明贤, 等. 银环蛇咬伤致急性呼吸衰竭的治疗及临床观察[J]. 蛇志, 2024, 36(1):34-35,54.
|
|
ZENG Zhao, LUO Wei, LIANG Mingxian, et al. Treatment and clinical observation of acute respiratory failure caused by snake-bite of Bungarus multicinctus[J]. Journal of Snake, 2024, 36(1):34-35,54.
|
| [16] |
王威, 陈泉芳, 巫艳彬, 等. 广西境内两种常见神经毒类毒蛇咬伤中毒的临床特点与院前急救策略分析[J]. 中国全科医学, 2014, 17(14):1671-1673.
|
|
WANG Wei, CHEN Quanfang, WU Yanbin, et al. Clinical features of poisoning from common nerve poison snake bites and its pre-hospital care strategy in Guangxi province[J]. Chinese General Practice, 2014, 17(14):1671-1673.
|
| [17] |
谭晓燕, 毛新华, 周继彪, 等. 考虑多维修队合作策略的灾后路网修复调度与路由联合优化[J]. 控制与决策, 2024, 39(12):4151-4159.
|
|
TAN Xiaoyang, MAO Xinhua, ZHOU Jibiao, et al. Joint optimization of scheduling and routing in post-disaster road network repair considering multi-crew cooperation[J]. Control and Decision, 2024, 39(12):4151-4159.
|
| [18] |
张玲, 高鹏飞, 张琳. 基于剥夺成本的应急疏散与物资调配问题研究[J]. 中国管理科学, 2024, 32(5):187-195.
|
|
ZHANG Ling, GAO Pengfei, ZHANG Lin. Research on emergency evacuation and material allocation based on deprivation cost[J]. Chinese Journal of Management Science, 2024, 32(5):187-195.
|
| [19] |
周鲜成, 余玮瑛, 李松明, 等. 考虑时间依赖和同时取送货的双目标绿色车辆路径问题研究[J]. 系统科学与数学, 2024, 44(9):2798-2815.
doi: 10.12341/jssms23546
|
|
ZHOU Xiancheng, YU Weiying, LI Songming, et al. Research on time dependent dual objective green vehicle routing problem with simultaneous pick-up and delivery[J]. Journal of Systems Science and Mathematical, 2024, 44(9):2798-2815.
|
| [20] |
SOLOMON M. Algorithms for the vehicle routing problem with time windows constraints[J]. Operations Research, 1987, 35(2):254-265.
doi: 10.1287/opre.35.2.254
|
| [21] |
FRAGSSA C. Engineering design driven by models and measures: the case of a rigid inflatable boat[J]. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 2019, 7(1):DOI: 10.3390/jmse7010006.
|
| [22] |
刘长石, 李君宇, 易鲲翔, 等. 分时电价背景下电动车配送-充电/放电路径规划[J]. 控制与决策, 2025, 40(3):794-802.
|
|
LIU Changshi, LI Junyu, YI Kunxiang, et al. Electric vehicle routing with charging/discharging under time-of-use electricity prices[J]. Control and Decision, 2025, 40(3):794-802.
|
| [23] |
AKBARI R, HEDAYATZADEH R, ZIARATI K, et al. A multi-objective artificial bee colony algorithm[J]. Swarm and Evolutionary Computation, 2012, 2:39-52.
doi: 10.1016/j.swevo.2011.08.001
|