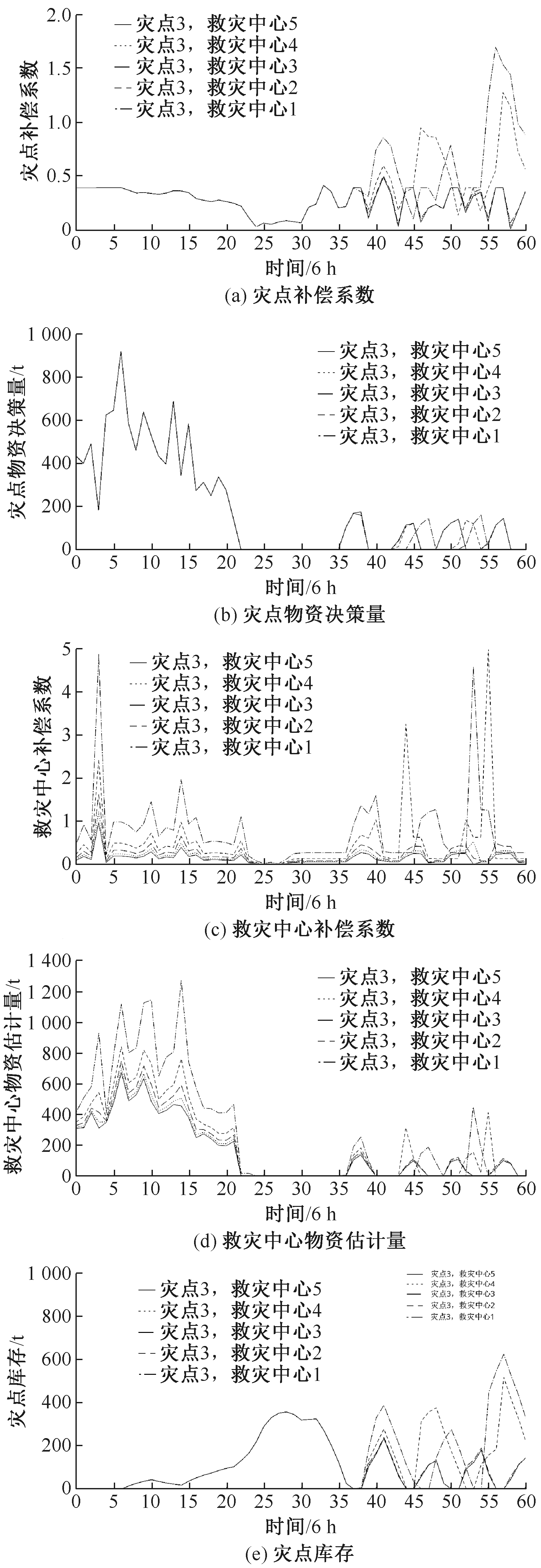
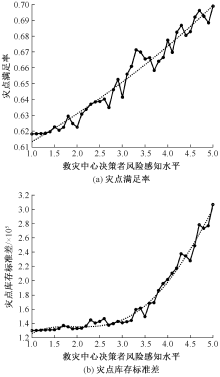
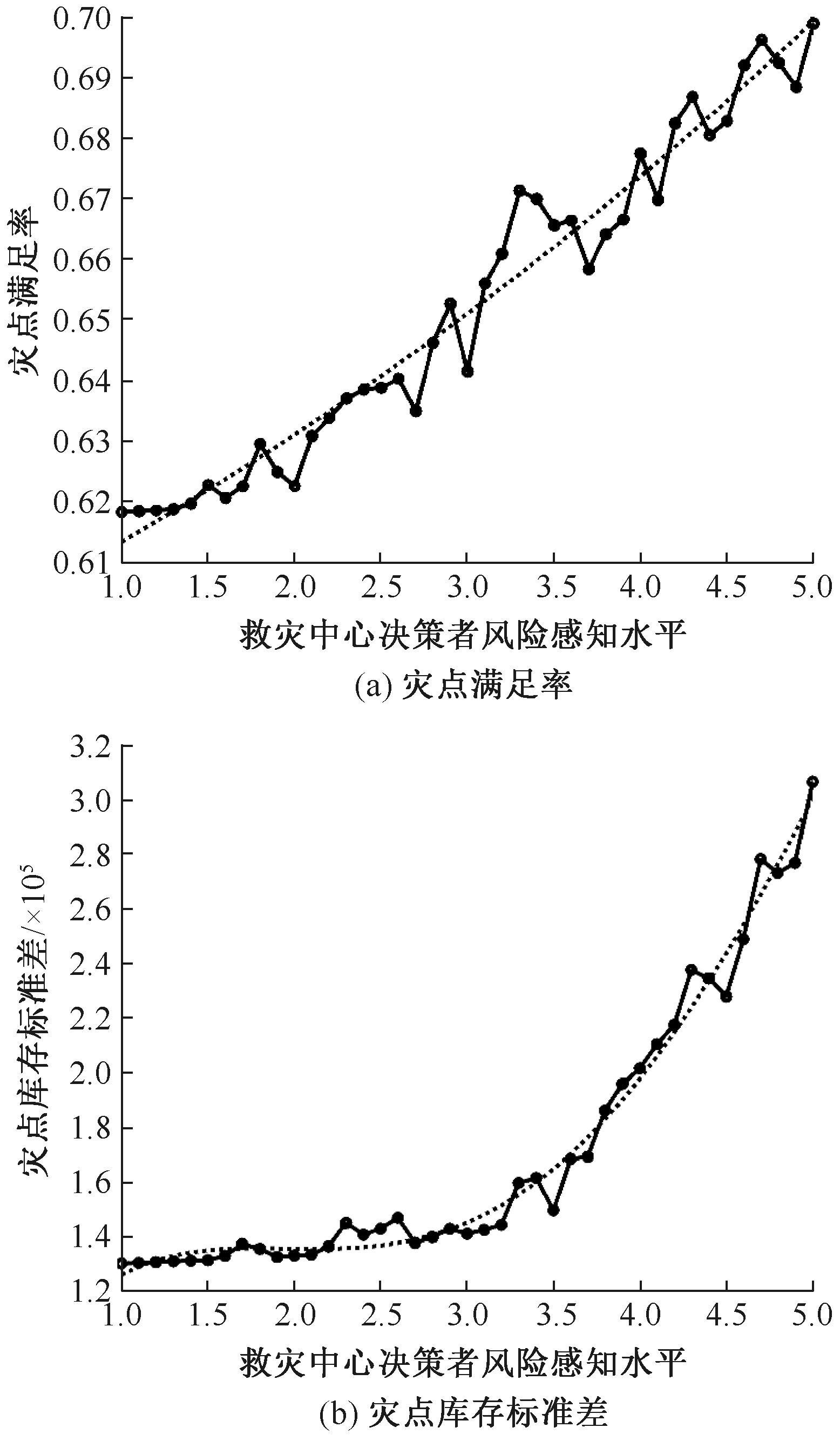
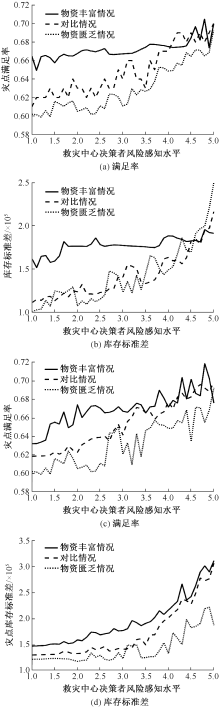
| [1] |
TELLMAN B, SULLIVAN J A, KUHN C. et al. Satellite imaging reveals increased proportion of population exposed to floods[J]. Nature, 2021, 596: 80-86.
doi: 10.1038/s41586-021-03695-w
|
| [2] |
JIANG Ruijie, LU Hui, YANG Kun, et al. Substantial increase in future fluvial flood risk projected in China's major urban agglomerations[J]. Communications Earth & Environment, 2023, 4: DOI: 10.1038/s43247-023-01049-0.
|
| [3] |
李健, 张文文, 白晓昀, 等. 基于系统动力学的应急物资调运速度影响因素研究[J]. 系统工程理论与实践, 2015, 35(3): 661-670.
doi: 10.12011/1000-6788(2015)3-661
|
|
LI Jian, ZHANG Wenwen, BAI Xiaoyun, et al. System-dynamics-based factor analysis for the speed of emergency materials transportation[J]. Systems Engineering-Theory & Practice, 2015, 35(3): 661-670.
|
| [4] |
|
|
LIU Yang, TIAN Jun, YU Ning, et al. Prepositioning model of emergency supplies and coordination mechanism considering human suffering perception via an option contract[J/OL]. Chinese Journal of Management Science: 1-18.[2025-03-12]. https://doi.org/10.16381/j.cnki.issn1003-207x.2023.0109.
|
| [5] |
朱莉, 曹杰, 顾珺, 等. 公平缓解灾民创伤下的应急物资动态调配研究[J]. 系统工程理论与实践, 2020, 40(9): 2427-2437.
doi: 10.12011/1000-6788-2019-0805-11
|
|
ZHU Li, CAO Jie, GU Jun, et al. Dynamic emergency supply distribution considering fair mitigation of victim suffering[J]. Systems Engineering-Theory & Practice, 2020, 40(9): 2427-2437.
|
| [6] |
PREGNOLATO M, FORD A, WILKINSON S M, et al. The impact of flooding on road transport: a depth-disruption function[J]. Transportation Research Part D: Transport and Environment, 2017, 55: 67-81.
doi: 10.1016/j.trd.2017.06.020
|
| [7] |
GUTJAHR W J, NOLZ P C. Multicriteria optimization in humanitarian aid[J]. European Journal of Operational Research, 2016, 252(2): 351-366.
doi: 10.1016/j.ejor.2015.12.035
|
| [8] |
薛星群, 王旭坪, 韩涛, 等. 考虑通行约束和运力限制的灾后应急物资联合调度优化研究[J]. 中国管理科学, 2020, 28(3): 21-30.
|
|
XUE Xingqun, WANG Xuping, HAN Tao. Study on Joint dispatch optimization of emergency materials considering traffic constraints and capacity[J]. Chinese Journal of Management Science, 2020, 28(3): 21-30.
|
| [9] |
董海, 高秀秀, 魏铭琦. 不确定环境下两阶段应急供应链网络建模与优化求解[J]. 中国管理科学, 2023, 31(12): 107-116.
|
|
DONG Hai, GAO Xiuxiu, WE Mingqi. Modeling and optimization solution of two-stage emergency supply chain under uncertain environment[J]. Chinese Journal of Management Science, 2023, 31(12): 107-116.
|
| [10] |
高鹏飞, 刘方翔, 黄建华, 等. 考虑灾民心理痛苦的震后应急物资调配问题研究[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2022, 32(11): 200-207.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2022.11.1392
|
|
GAO Pengfei, LIU Fangxiang, HUANG Jianhua, et al. Research on post-earthquake emergency material allocation considering psychological pain of victims[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2022, 32(11): 200-207.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2022.11.1392
|
| [11] |
|
|
|
| [12] |
ZHANG Zixin, WANG Liang, WANG Yingming. An emergency decision making method based on prospect theory for different emergency situations[J]. International Journal of Disaster Risk Science, 2018, 9: 407-420.
doi: 10.1007/s13753-018-0173-x
|
| [13] |
蒲国利, 苏秦. 满足救灾需求的灾后救援供应链网络设计[J]. 工业工程与管理, 2015, 20(6): 161-166.
|
|
PU Guoli, SU Qin. Network design of disaster relief supply chain to meet relief demand[J]. Industrial Engineering and Management, 2015, 20(6): 161-166.
|
| [14] |
KAHNEMAN D, TVERSKY A. Prospect theory: an analysis of decision under risk[J]. Econometrica, 1979, 47(2): 363-391.
|
| [15] |
刘娟, 叶然. 基于系统动力学的疏散人员竞争行为仿真分析[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2024, 34(11): 58-65.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2024.11.0182
|
|
LIU Juan, YE Ran. Simulation analysis of evacuees competitive behavior based on system dynamics[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2024, 34(11): 58-68.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2024.11.0182
|
| [16] |
王旭坪, 杨相英, 杨挺, 等. 动态路况下考虑决策者风险感知的地震物资调配动力学模型[J]. 系统管理学报, 2015, 24(2): 174-184.
|
|
WANG Xuping, YANG Xiangying, YANG Ting, et al. System Dynamics model of earthquake material allocation considering decision-makers' psychological risk perception and dynamic traffic[J]. Journal of Systems & Management, 2015, 24(2): 174-184.
|
| [17] |
TVERSKY A, KAHNEMAN D. Advances in prospect theory: cumulative representation of uncertainty[J]. Journal of Risk and Uncertainty, 1992, 5: 297-323.
doi: 10.1007/BF00122574
|