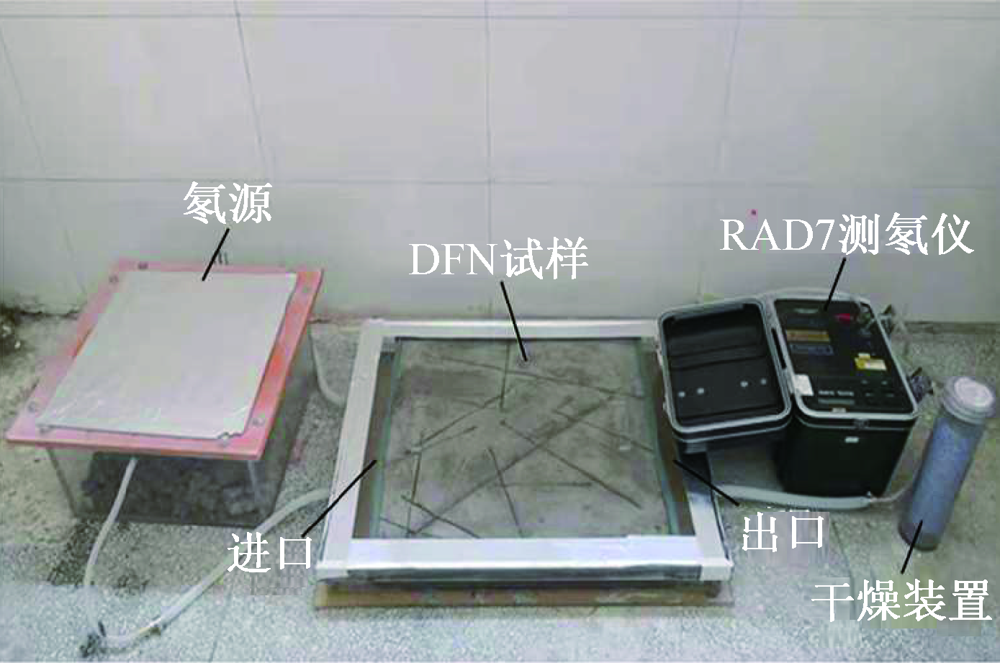
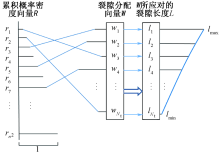
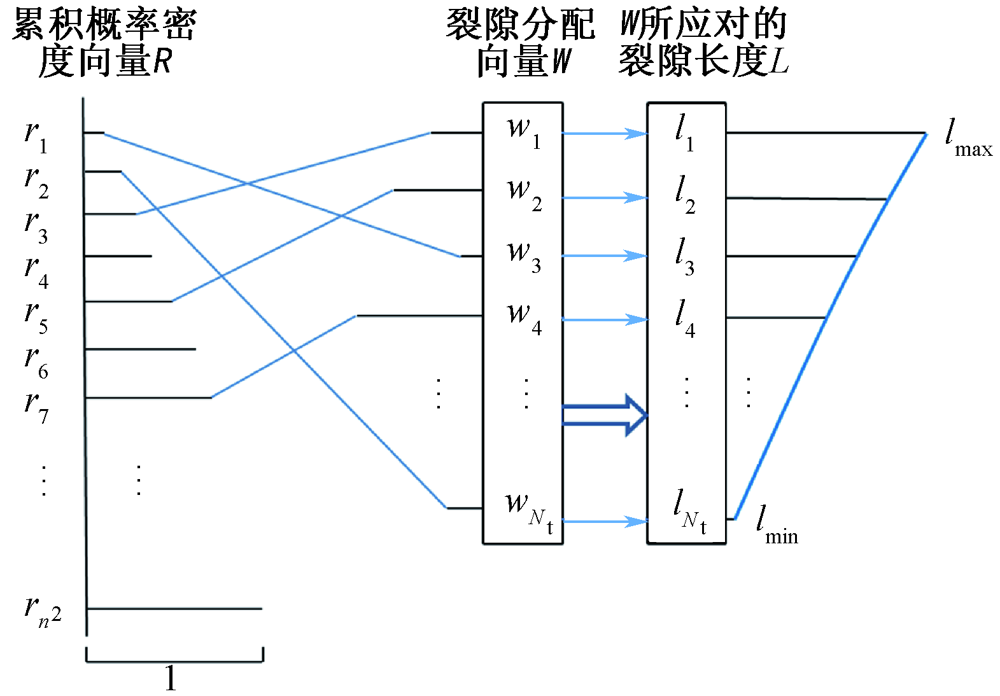
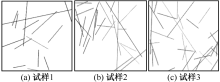
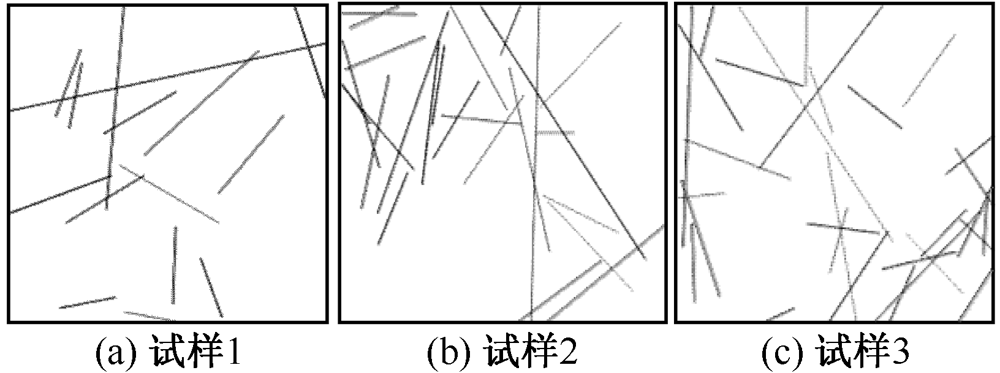
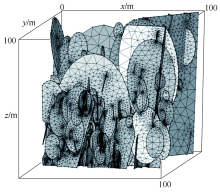
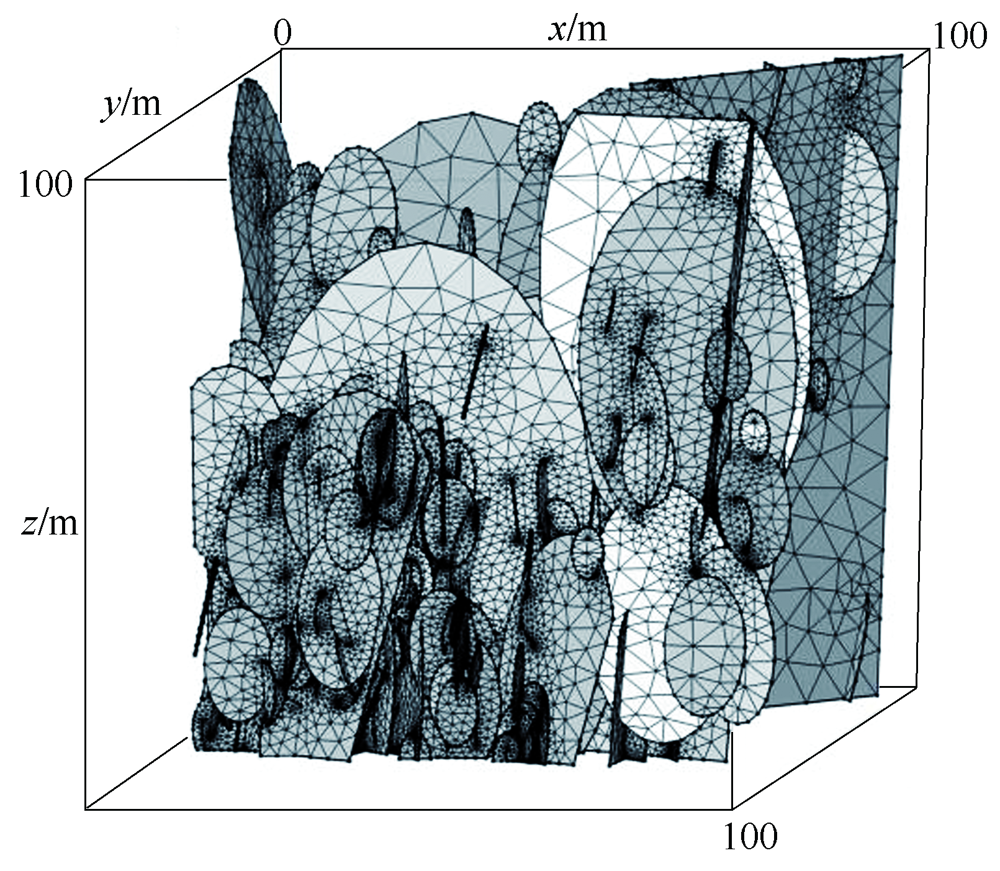
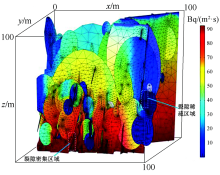
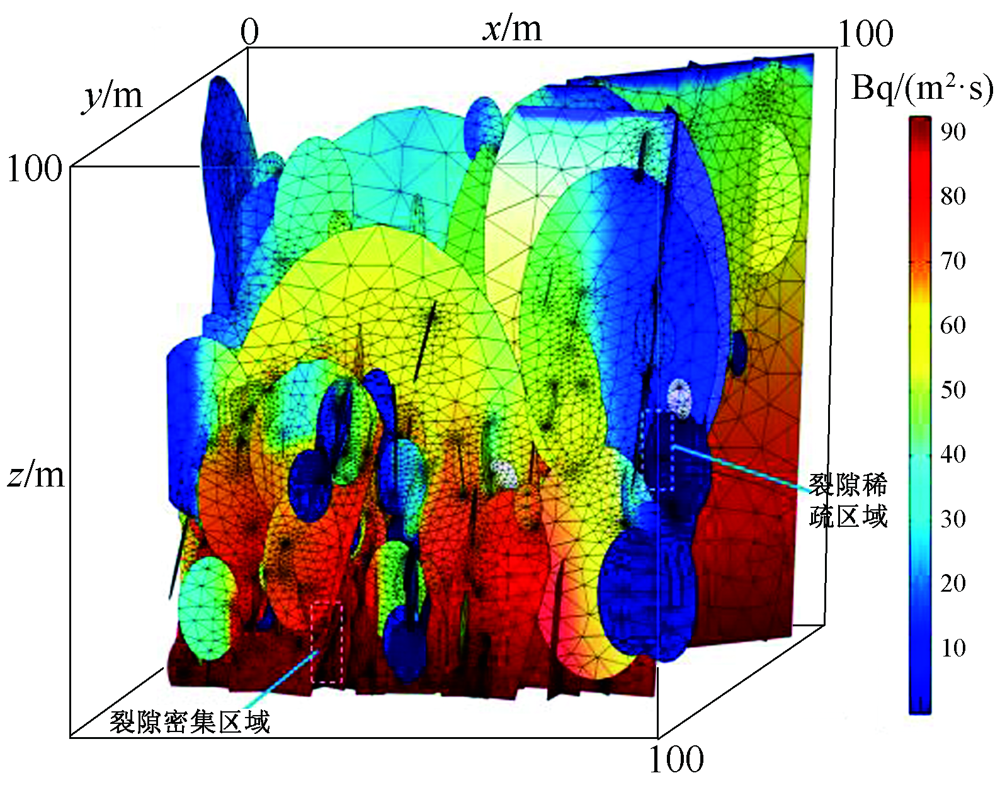
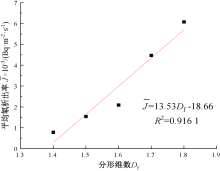
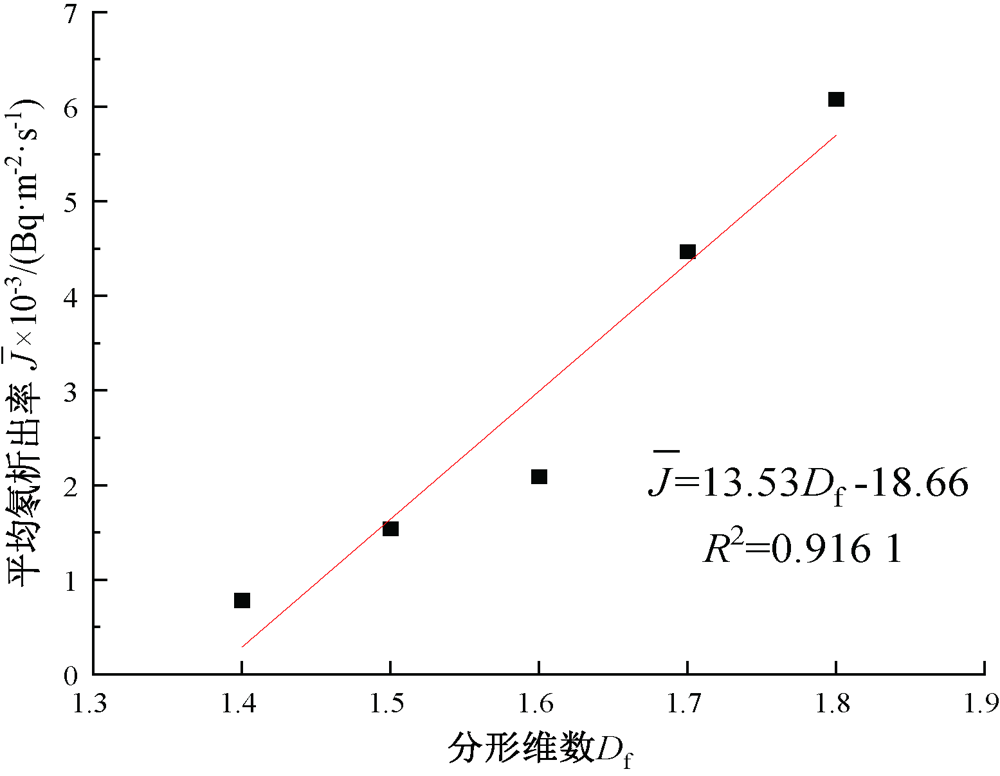
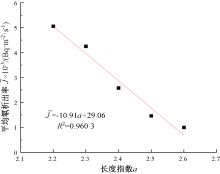
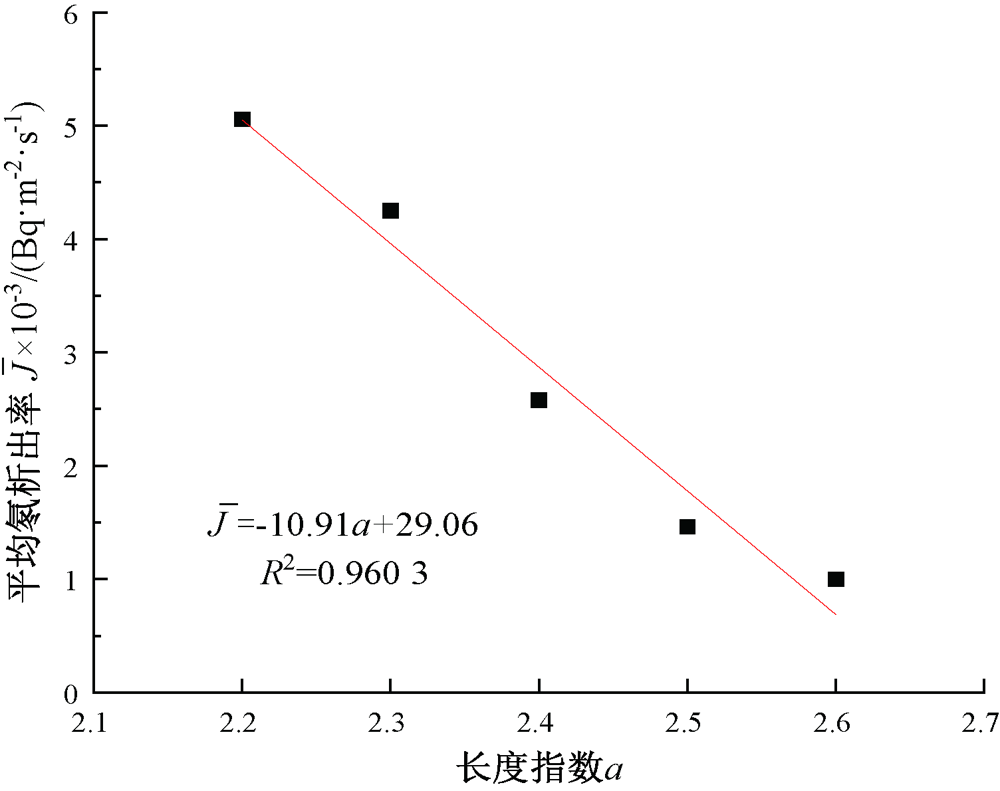
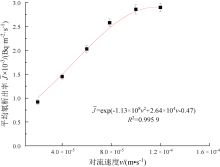
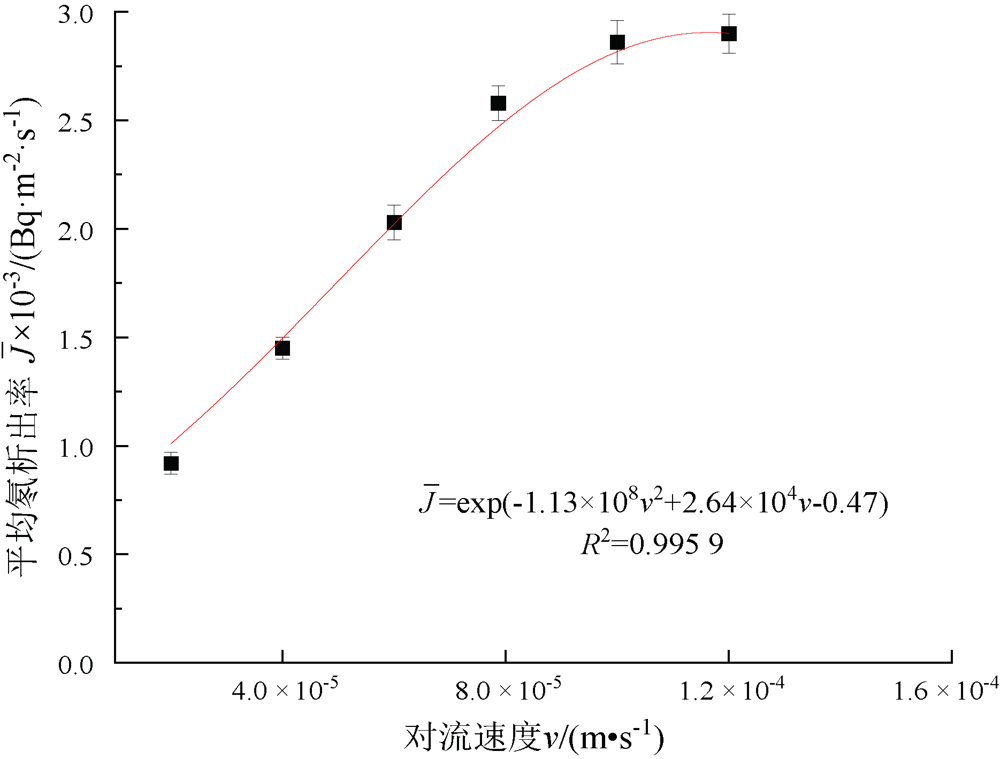
| [1] |
刘耀炜, 任宏微. 汶川8.0级地震氡观测值震后效应特征初步分析[J]. 地震, 2009, 29(1):121-131.
|
|
LIU Yaowei, REN Hongwei. Preliminary analysis on the characteristics of post-earthquake effect of radon observations in Wenchuan M8.0 earthquake[J]. Earthquake, 2009, 29(1):121-131.
|
| [2] |
BASKARAN M. Radon:a tracer for geological, geophysical and geochemical studies[M]. Basel: Springer International Publishing, 2016:1-14.
|
| [3] |
NIELSON K, ROGERS V. A mathematical model for radon diffusion in earthen materials[R]. Pacific Northwest Laboratory, 1982.
|
| [4] |
ETIOPE G, MARTINELLI G. Migration of carrier and trace gases in the geosphere:an overview[J]. Physics of the Earth and Planetary Interiors, 2002, 129(3/4):185-204.
doi: 10.1016/S0031-9201(01)00292-8
|
| [5] |
AJAYI K M, SHAHBAZI K, TUKKARAJA P, et al. A discrete model for prediction of radon flux from fractured rocks[J]. Journal of Rock Mechanics and Geotechnical Engineering, 2018, 10(5):879-892.
doi: 10.1016/j.jrmge.2018.02.009
|
| [6] |
AJAYI K M, SHAHBAZI K, TUKKARAJA P, et al. Estimation of radon diffusivity tensor for fractured rocks in cave mines using a discrete fracture network model[J]. Journal of Environmental Radioactivity, 2019, 196:104-112.
doi: S0265-931X(17)30583-0
pmid: 30447553
|
| [7] |
ROWBERRY M, MARTÍ X, FRONTERA C, et al. Calculating flux to predict future cave radon concentrations[J]. Journal of Environmental Radioactivity, 2016, 157:16-26.
doi: 10.1016/j.jenvrad.2016.02.023
pmid: 26950394
|
| [8] |
刘波, 金爱兵, 高永涛, 等. 基于分形几何理论的DFN模型构建方法研究[J]. 岩土力学, 2016, 37(增1):625-630,638.
|
|
LIU Bo, JIN Aibing, GAO Yongtao, et al. Construction method research on DFN model based on fractal geometry theory[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2016, 37(S1):625-630,638.
|
| [9] |
任崇鸿, 李波波, 杨康, 等. 考虑分形效应的煤岩损伤模型及渗透率模型[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2019, 29(2):63-68.
|
|
REN Chonghong, LI Bobo, YANG Kang, et al. Research on coal damage model and permeability model considering fractal effect[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2019, 29(2):63-68.
|
| [10] |
FENG Shengyang, WU Yurong, LIU Yong, et al. A fractal analysis of radon migration in discrete fracture network model[J]. Chemosphere, 2021, 266:DOI: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.129010.
doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.129010
|
| [11] |
FENG Shengyang, WANG Hanqing, CUI Yu, et al. Fractal discrete fracture network model for the analysis of radon migration in fractured media[J]. Computers and Geotechnics, 2020, 128:DOI: 10.1016/j.compgeo.2020.103810.
doi: 10.1016/j.compgeo.2020.103810
|
| [12] |
KIM T H. Fracture characterization and estimation of fracture porosity of naturally fractured reservoirs with no matrix porosity using stochastic fractal models[D]. Texas: Texas A&M University, 2007.
|
| [13] |
DAVY P, SORNETTE A, SORNETTE D. Some consequences of a proposed fractal nature of continental faulting[J]. Nature, 1990, 348(6296):56-58.
doi: 10.1038/348056a0
|
| [14] |
KIM T H, SCHECHTER D S. Estimation of fracture porosity of naturally fractured reservoirs with no matrix porosity using fractal discrete fracture networks[J]. SPE Reservoir Evaluation and Engineering, 2009, 12(2):232-242.
doi: 10.2118/110720-PA
|
| [15] |
BAGHBANAN A, JING Lanru. Hydraulic properties of fractured rock masses with correlated fracture length and aperture[J]. International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences, 2007, 44(5):704-719.
|
| [16] |
ZHANG Liming, QI Ji, ZHANG Kai, et al. Calibrate complex fracture model for subsurface flow based on Bayesian formulation[J]. Petroleum Science, 2019, 16(5):1105-1120.
doi: 10.1007/s12182-019-00357-5
|
| [17] |
DARCEL C, BOUR O, DAVY P, et al. Connectivity properties of two-dimensional fracture networks with stochastic fractal correlation[J]. Water Resources Research, 2003, 39(10):1-13.
|
| [18] |
HARTHONG B, SCHOLTÈS L, DONZÉ F V. Strength characterization of rock masses, using a coupled DEM-DFN model[J]. Geophysical Journal International, 2012, 191(2):467-480.
doi: 10.1111/j.1365-246X.2012.05642.x
|
| [19] |
MOEIN M J A, VALLEY B, EVANS K F. Scaling of fracture patterns in three deep boreholes and implications for constraining fractal discrete fracture network models[J]. Rock Mechanics and Rock Engineering, 2019, 52(6):1723-1743.
doi: 10.1007/s00603-019-1739-7
|
| [20] |
ALGHALANDIS Y F, XU Chaoshui, DOWD P A. A general framework for fracture intersection analysis:algorithms and practical applications[C]. Australian Geothermal Energy Conference, 2011:15-20.
|
| [21] |
KLIMCZAK C, SCHULTZ R A, PARASHAR R, et al. Cubic law with aperture-length correlation:implications for network scale fluid flow[J]. Hydrogeology Journal, 2010, 18(4):851-862.
doi: 10.1007/s10040-009-0572-6
|
| [22] |
PARASHAR R, REEVES D M. On iterative techniques for computing flow in large two-dimensional discrete fracture networks[J]. Journal of Computational and Applied Mathematics, 2012, 236(18):4712-4724.
doi: 10.1016/j.cam.2012.02.038
|
| [23] |
ALGHALANDIS Y F. ADFNE:open source software for discrete fracture network engineering, two and three dimensional applications[J]. Computers & Geosciences, 2017, 102:1-11.
doi: 10.1016/j.cageo.2017.02.002
|
| [24] |
ROGERS V C, NIELSON K K. Correlations for predicting air permeabilities and 222Rn diffusion coefficients of soils[J]. Health Physics, 1991, 61(2):225-230.
doi: 10.1097/00004032-199108000-00006
|
| [25] |
冯胜洋, 崔宇, 许田贵, 等. 铀尾砂膏体充填材料的流动性能研究[J]. 矿冶工程, 2019, 39(2):8-12.
|
|
FENG Shengyang, CUI Yu, XU Tiangui, et al. Flow properties of uranium tailings as paste backfill[J]. Mining and Metallurgical Engineering, 2019, 39(2):8-12.
|
| [26] |
LEE Chenchang, LEE Chenghaw, YEH Hsinfu, et al. Modeling spatial fracture intensity as a control on flow in fractured rock[J]. Environmental Earth Sciences, 2011, 63(6):1199-1211.
doi: 10.1007/s12665-010-0794-x
|