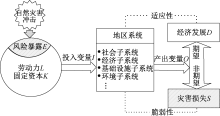
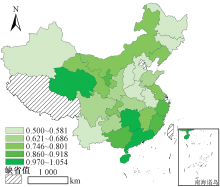
| [1] |
PARSONS M, GLAVAC S, HASTINGS P, et al. Top-down assessment of disaster a conceptual framework using coping and adaptive capacities[J]. International Journal of Disaster Risk Reduction, 2016, 19:1-11.
doi: 10.1016/j.ijdrr.2016.07.005
|
| [2] |
许兆丰, 田杰芳, 张靖. 防灾视角下城市韧性评价体系及优化策略[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2019, 29(3):1-7.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2019.03.001
|
|
XU Zhaofeng, TIAN Jiefang, ZHANG Jing. Urban resilience evaluation system and optimization strategy from perspective of disaster prevention[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2019, 29(3):1-7.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2019.03.001
|
| [3] |
李梦杰, 刘德林. 中原城市群城市灾害韧性时空演变及障碍因子研究[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2022, 32(9):144-151.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2022.09.2072
|
|
LI Mengjie, LIU Delin. Spatial-temporal evolution and obstacle factors of urban disaster resilience in Zhongyuan urban agglomeration[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2022, 32(9):144-151.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2022.09.2072
|
| [4] |
USTUN A K. Evaluating Istanbul' s disaster resilience capacity by data envelopment analysis[J]. Natural Hazards, 2016, 80(3): 1603-1623.
doi: 10.1007/s11069-015-2041-y
|
| [5] |
周侃, 刘宝印, 樊杰. 汶川Ms 8.0地震极重灾区的经济韧性测度及恢复效率[J]. 地理学报, 2019, 74(10):2078-2091.
doi: 10.11821/dlxb201910009
|
|
ZHOU Kan, LIU Baoyin, FAN Jie. Economic resilience and recovery efficiency in the severely affected area of Ms 8.0 Wenchuan earthquake[J]. Acta Geographica Sinica, 2019, 74(10):2078-2091.
doi: 10.11821/dlxb201910009
|
| [6] |
YANG Yuying, GUO Haixiang, WANG Deyun, et al. Flood vulnerability and resilience assessment in China based on super-efficiency DEA and SBM-DEA methods[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 2021, 600:DOI: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2021.126470.
doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2021.126470
|
| [7] |
LI Ying, CEN Hongyi, LIN Taiyu, et al. Undesirable epsilon-based model dea application for chinese natural disaster mitigation efficiency[J]. Sage Open, 2021, 11(3):DOI: 10.1177/21582440211040776.
|
| [8] |
LIU Yang, WEI Jiuchang, XU Jia, et al. Evaluation of the moderate earthquake resilience of counties in China based on a three-stage DEA model[J]. Natural Hazards, 2018, 91(2):587-609.
doi: 10.1007/s11069-017-3142-6
|
| [9] |
VILLANO R A, MAGCALE-MACANDOG D B, ACOSTA L A, et al. Measuring disaster resilience in the Philippines: evidence using network data envelopment analysis[J]. Climate and Development, 2020, 12(1):67-79.
doi: 10.1080/17565529.2019.1599317
|
| [10] |
LI Ying, CHIU Yungho, LIN Taiyu, et al. Evaluation of natural disaster treatment efficiency in 27 Chinese provinces[J]. Natural Resources Forum, 2021, 45(3):256-288.
doi: 10.1111/narf.v45.3
|
| [11] |
CUTTER S L, BARNES L, BERRY M, et al. A place-based model for understanding community resilience to natural disasters[J]. Global Environmental Change-Human and Policy Dimensions, 2008, 18(4):598-606.
doi: 10.1016/j.gloenvcha.2008.07.013
|
| [12] |
LAM N S N, QIANG Y, ARENAS H, et al. Mapping and assessing coastal resilience in the Caribbean region[J]. Cartography and Geographic Information Science, 2015, 42(4):315-322.
doi: 10.1080/15230406.2015.1040999
|
| [13] |
LIU Wenbin, ZHOU Zhongbao, MA Chaoqun, et al. Two-stage DEA models with undesirable input-intermediate-outputs[J]. Omega, 2015, 56:74-87.
doi: 10.1016/j.omega.2015.03.009
|
| [14] |
LIU Wenbin, MENG Wei, LI Xiangtang, et al. DEA models with undesirable inputs and outputs[J]. Annals of Operations Research, 2010, 173(1):177-194.
doi: 10.1007/s10479-009-0587-3
|
| [15] |
ASSARKHANIKI Z, RAJABIFARD A, SABRI S. The conceptualisation of resilience dimensions and comprehensive quantification of the associated indicators: a systematic approach[J]. International Journal of Disaster Risk Reduction, 2020, 51(2):DOI: 10.1016/j.ijdrr.2020.101840.
doi: 10.1016/j.ijdrr.2020.101840
|
| [16] |
NGUYEN H L, AKERKAR R. Modelling, measuring, and visualising community resilience: a systematic review[J]. Sustainability, 2020, 12(19):DOI:10.3390/su12197896.
|
| [17] |
BEHRENS K, THISSE J F. Regional economics: a new economic geography perspective[J]. Regional Science and Urban Economics, 2007, 37(4):457-465.
doi: 10.1016/j.regsciurbeco.2006.10.001
|