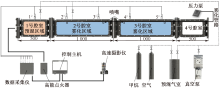
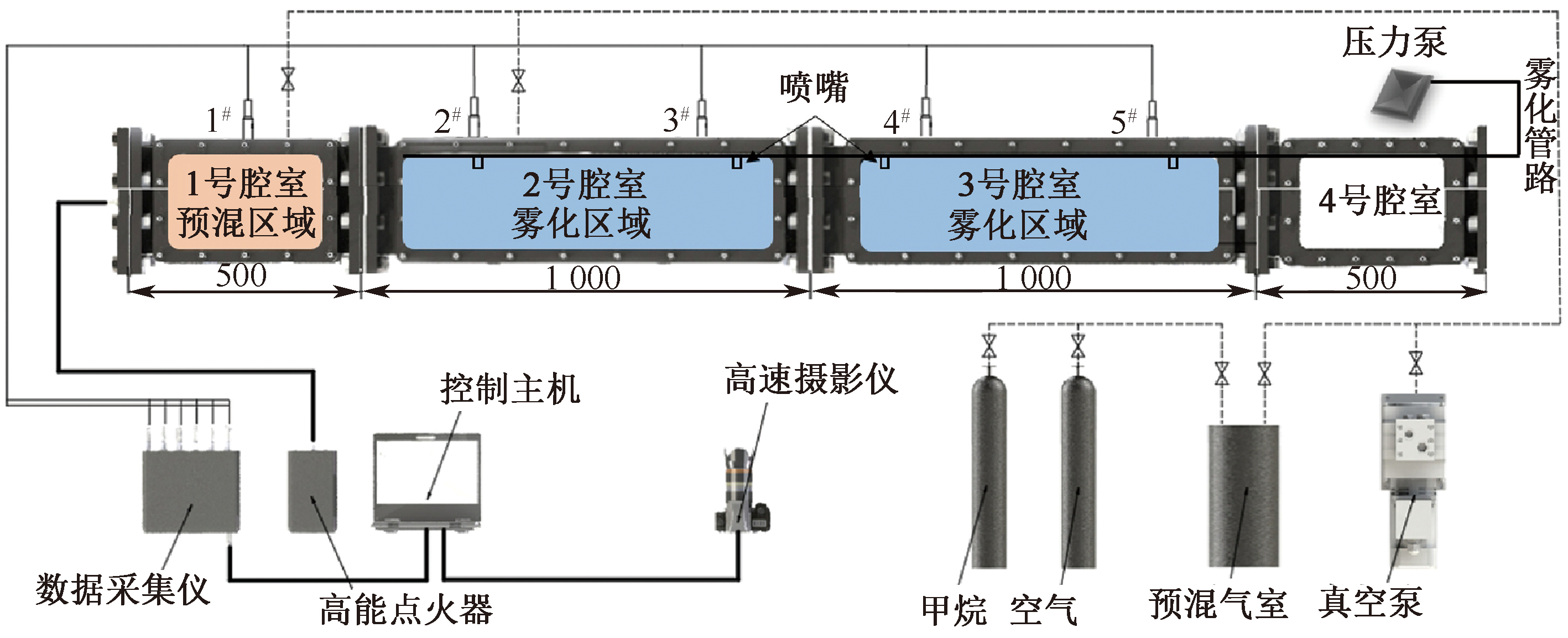
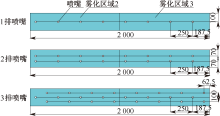
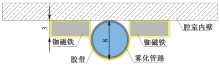
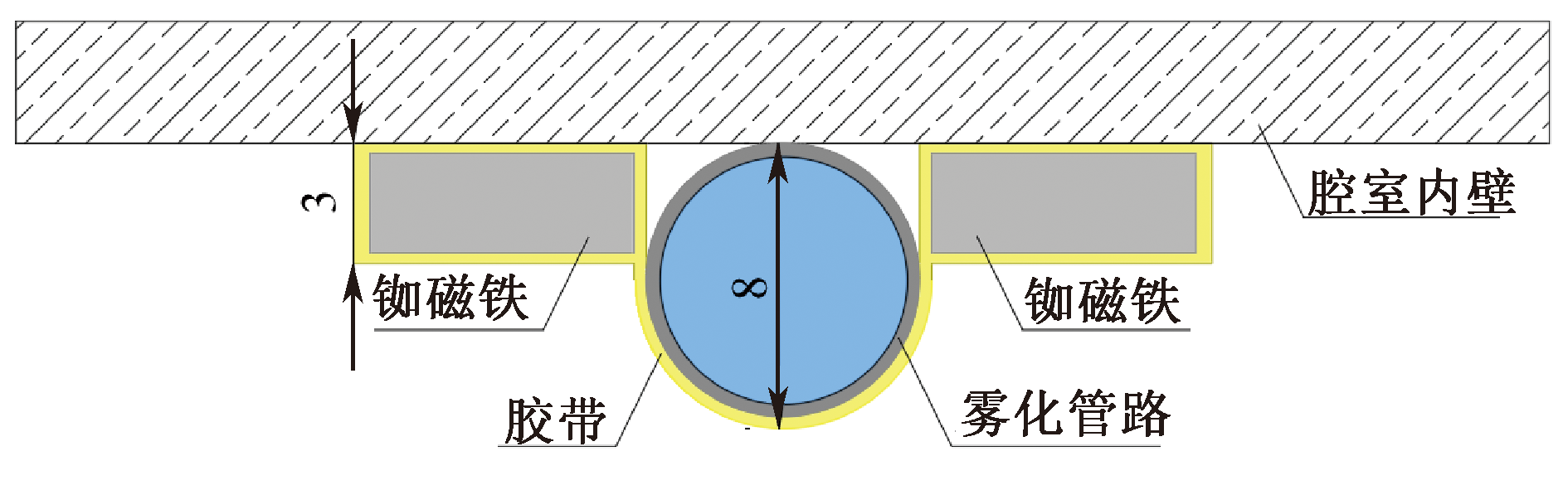
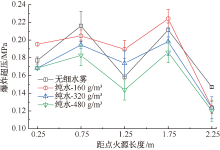
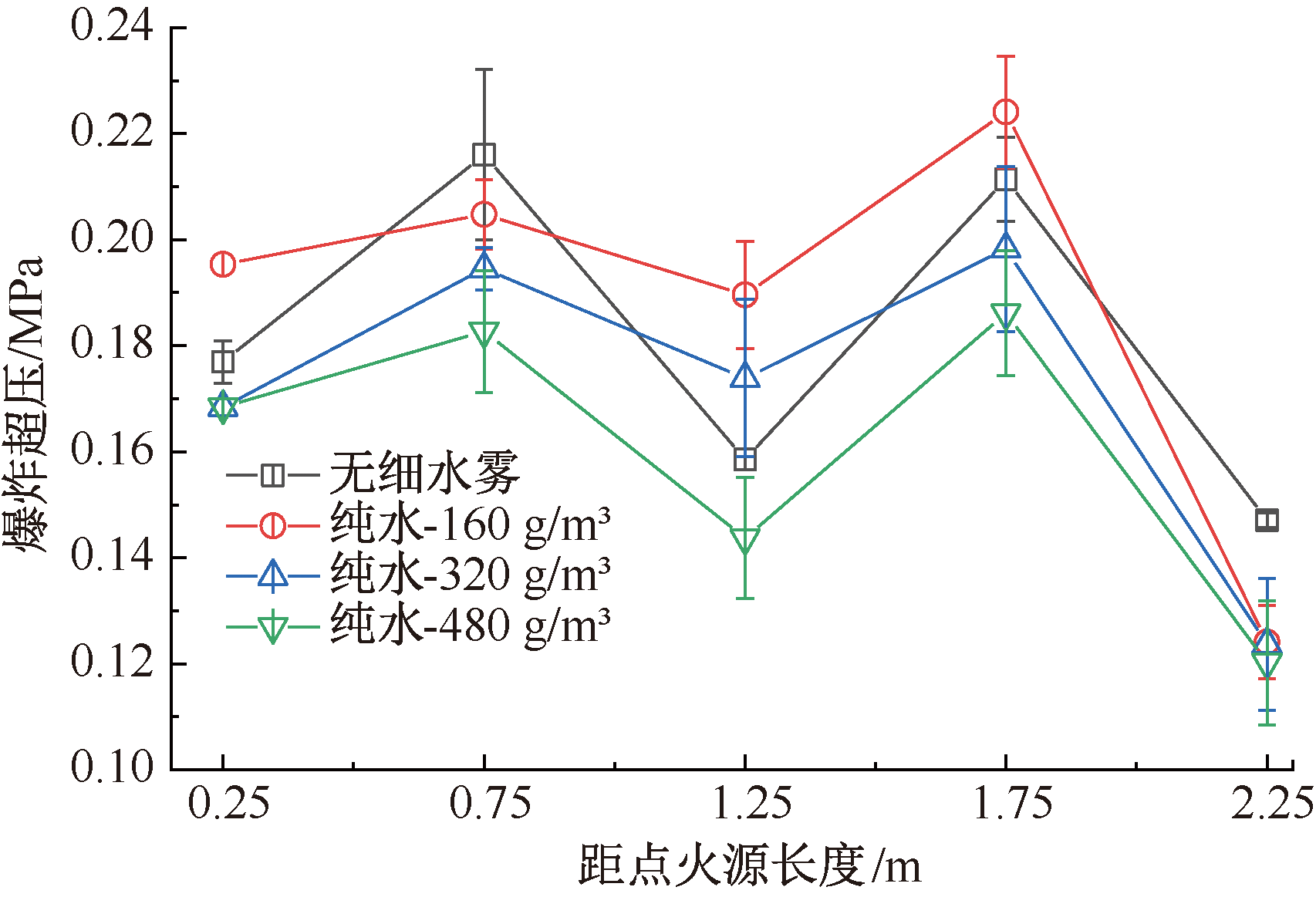
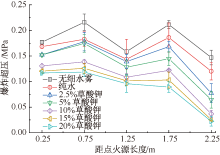
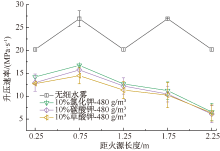
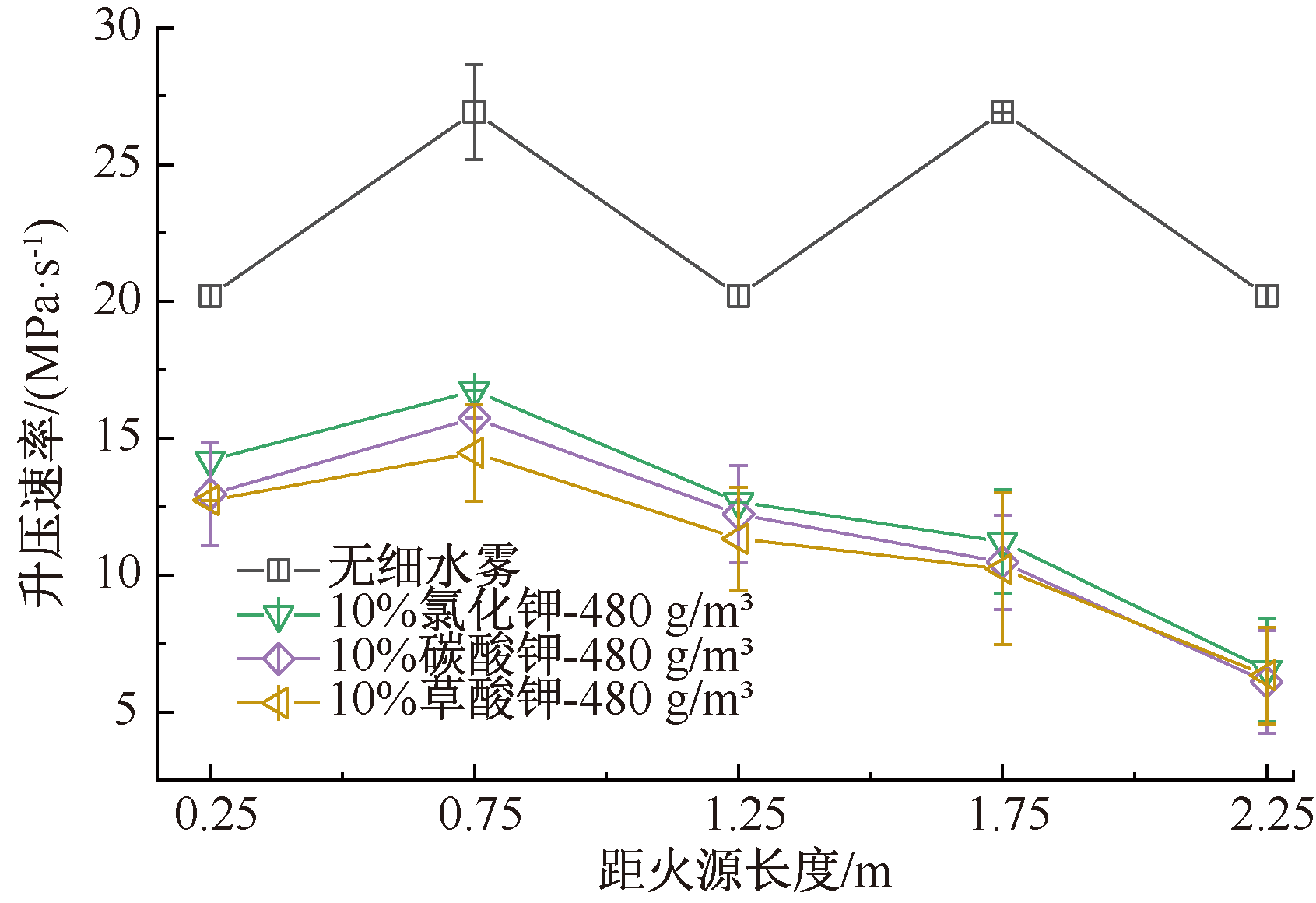
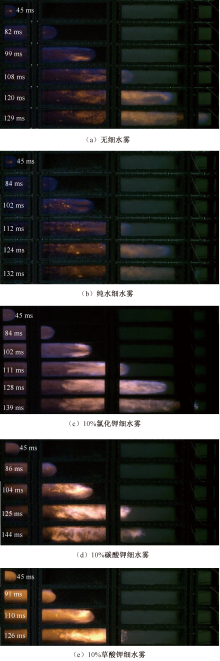
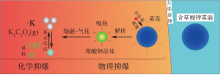
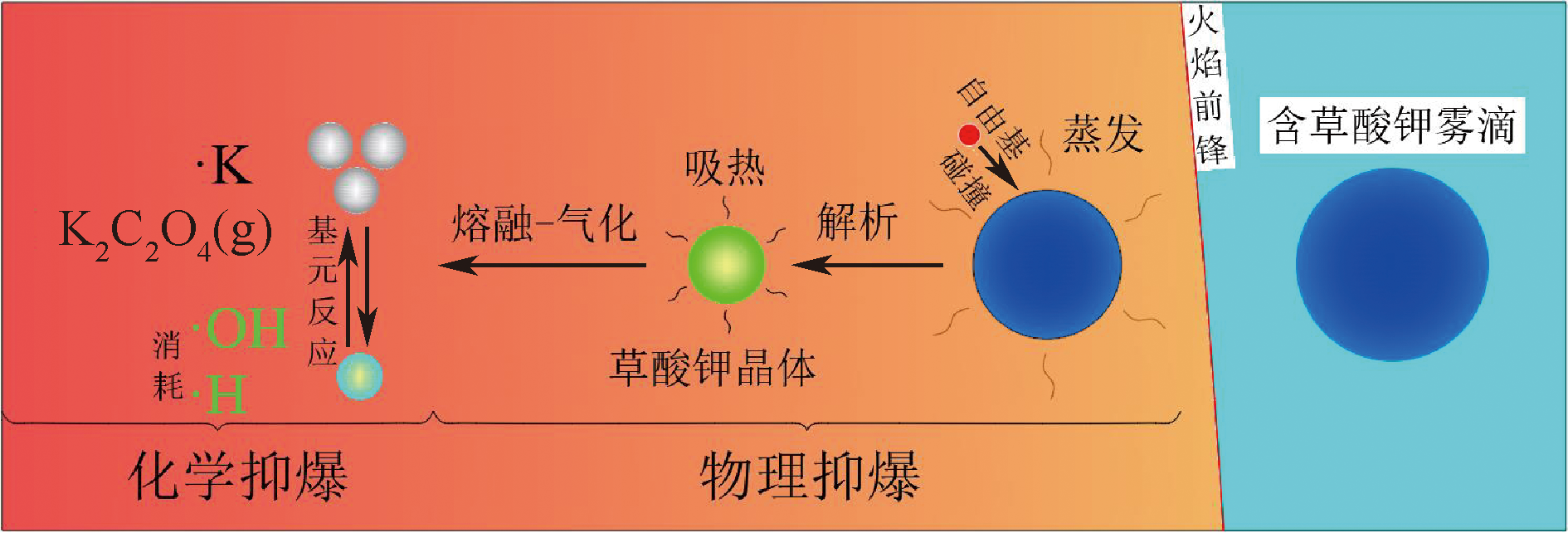
| [1] |
吴建松, 蔡继涛, 赵亦孟, 等. 城市综合管廊燃气爆炸传播特性试验研究[J]. 清华大学学报:自然科学版, 2022, 62(6):1-7.
|
|
WU Jiansong, CAI Jitao, ZHAO Yimeng, et al. Experimental study of the propagation characteristics of gas explosions in urban utility tunnels[J]. Journal of Tsinghua University:Science and Technology, 2022, 62(6):1-7.
|
| [2] |
杨立中, 叶开. 城市综合管廊消防标准及火灾研究综述[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2021, 31(8): 132-140.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2021.08.019
|
|
YANG Lizhong, YE Kai. A review of research on fire safety codes and fire science in urban utility tunnels[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2021, 31(8): 132-140.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2021.08.019
|
| [3] |
余明高, 阳旭峰, 郑凯, 等. 我国煤矿瓦斯爆炸抑爆减灾技术的研究进展及发展趋势[J]. 煤炭学报, 2020, 45(1): 168-188.
|
|
YU Minggao, YANG Xufeng, ZHENG Kai, et al. Progress and development of coal mine gas explosion suppression and disaster reduction technology in China[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2020, 45(1): 168-188.
|
| [4] |
段玉龙, 卜云兵, 龙凤英, 等. 氮气-细水雾-滑移装置对甲烷爆炸特性的影响[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2022, 32(10):83-89.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2022.10.1861
|
|
DUAN Yulong, BU Yunbing, LONG Fengying, et al. Effect of N2-water mist-slip device on methane explosion characteristics[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2022, 32(10):83-89.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2022.10.1861
|
| [5] |
CHELLIAH H K, LAZZARINI A K, WANIGARATHNE P C, et al. Inhibition of premixed and non-premixed flames with fine droplets of water and solutions[J]. Proceedings of the Combustion Institute, 2002, 29(1):369-376.
doi: 10.1016/S1540-7489(02)80049-9
|
| [6] |
罗振敏. 瓦斯爆炸抑制材料的特性及抑爆作用研究[D]. 西安: 西安科技大学, 2009.
|
|
LUO Zhenmin. Study of suppression materials' characteristics and effects on gas explosion[D]. Xi'an: Xi'an University of Science and Technology, 2009.
|
| [7] |
ROOSENDANS D, VAN W K, HOLME M N, et al. Experimental investigation of explosion mitigating properties of aqueous potassium carbonate solutions[J]. Journal of Loss Prevention in the Process Industries, 2017, 46: 209-226.
doi: 10.1016/j.jlp.2017.02.008
|
| [8] |
ZHANG Tianwei, HAO Liu, HAN Zhiyue, et al. Active substances study in fire extinguishing by water mist with potassium salt additives based on thermoanalysis and thermodynamics[J]. Applied Thermal Engineering, 2017, 122:429-438.
doi: 10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2017.05.053
|
| [9] |
杨克, 纪虹, 邢志祥, 等. 含草酸钾的超细水雾抑制甲烷爆炸的特性[J]. 化工学报, 2018, 69(12): 5359-5369.
doi: 10.11949/j.issn.0438-1157.20180671
|
|
YANG Ke, JI Hong, XING Zhixiang, et al. Characteristics on methane explosion suppression by ultrafine water mist containing potassium oxalate[J]. CIESC Journal, 2018, 69(12): 5359-5369.
|
| [10] |
LIU Zhenqi, ZHONG Xiaoxing, ZHANG Qi, et al. Experimental study on using water mist containing potassium compounds to suppress methane/air explosions[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2020, 394:DOI: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.122561.
|
| [11] |
CAO Xingyan, REN Jingjie, BI Mingshu, et al. Experimental research on the characteristics of methane/air explosion affected by ultrafine water mist[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2017, 324: 489-497.
doi: S0304-3894(16)31021-4
pmid: 27843023
|
| [12] |
WANG Quan, LIU Shanghao, SHU Chimin, et al. Influence of different types of obstacles on the propagation of premixed methane-air flames in a half-open tube[J]. Energies, 2017, 10(11): DOI: 10.3390/en10111908.
|
| [13] |
NAINNA A M, PHYLAKTOU H N, ANDREWS G E. Explosion flame acceleration over obstacles: effects of separation distance for a range of scales[J]. Process Safety and Environmental Protection, 2017, 107: 309-316.
doi: 10.1016/j.psep.2017.01.019
|
| [14] |
CHEN Xiaokun, LIN Ying, LUO Zhenmin, et al. Experiment study on controlling gas explosion by water-depressant[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2006, 31(5): 603-606.
|
| [15] |
杨克, 张平, 邢志祥, 等. 含菌-无机盐超细水雾抑制甲烷爆炸试验研究[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2019, 29(1): 62-67.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2019.01.011
|
|
YANG Ke, ZHANG Ping, XING Zhixiang, et al. Experimental study on suppression of methane explosion with ultral-fine water mist containing both optimized methane oxidizing bacteria and inorganic salt[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2019, 29(1): 62-67.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2019.01.011
|
| [16] |
高伟, 周永浩, 李智勇, 等. 障碍物对开敞空间贫燃天然气爆炸特性的影响研究[J]. 安全与环境学报, 2021, 21(4):1539-1544.
|
|
GAO Wei, ZHOU Yonghao, LI Zhiyong, et al. Effect of obstacles on unconfined methane explosion characteristics under lean-fuel conditions[J]. Journal of Safety and Environment, 2021, 21(4):1539-1544.
|
| [17] |
LUO Zhenmin, LIU Litao, CHENG Fangming, et al. Effects of a carbon monoxide-dominant gas mixture on the explosion and flame propagation behaviors of methane in air[J]. Journal of Loss Prevention in the Process Industries, 2019, 58: 8-16.
doi: 10.1016/j.jlp.2019.01.004
|