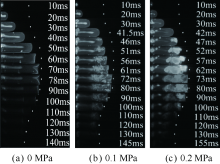
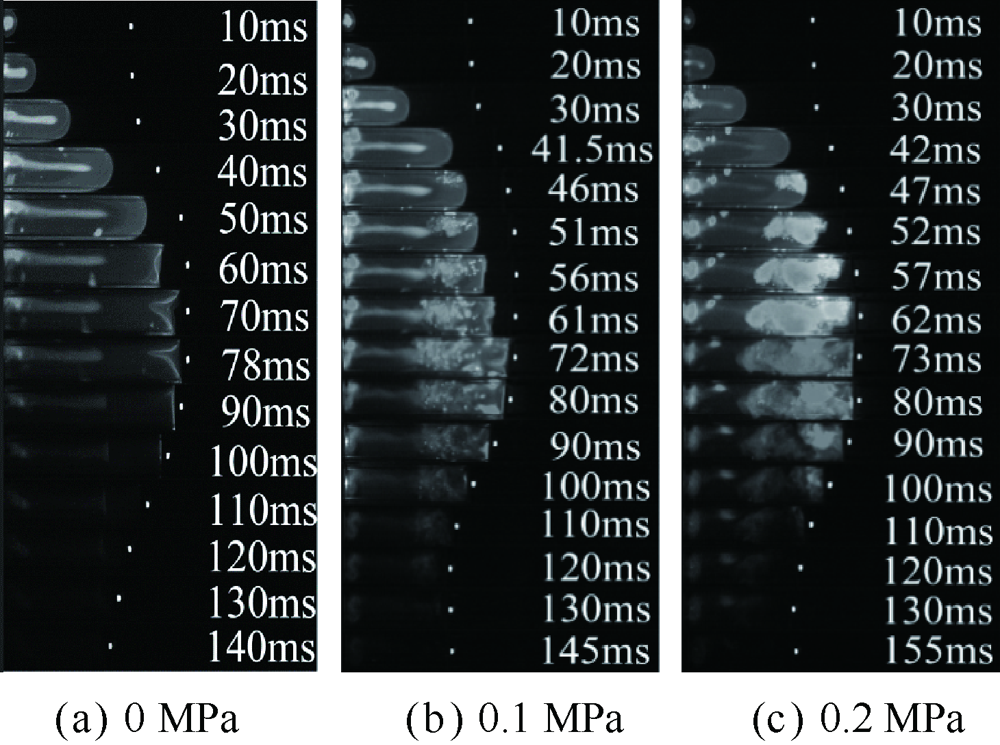
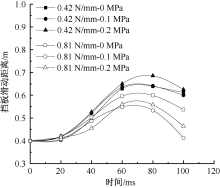
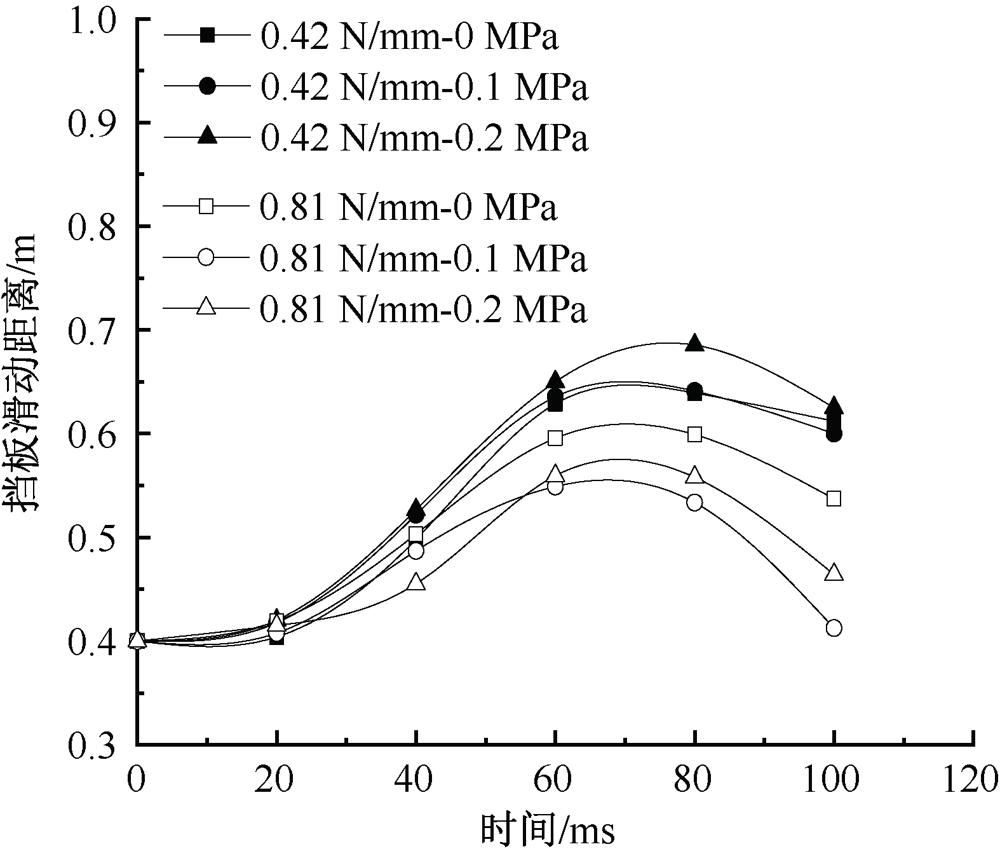
| [1] |
钱海林, 王志荣, 蒋军成. N2/CO2混合气体对甲烷爆炸的影响[J]. 爆炸与冲击, 2012, 32(4):445-448.
|
|
QIAN Hailin, WANG Zhirong, JIANG Juncheng. Influence of N2/CO2 mixture on methane explosion[J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 2012, 32(4): 445-448.
|
| [2] |
曲忠伟, 颜事龙, 李学超. 惰性介质对甲烷/空气预混气体爆炸极限的影响[J]. 爆破器材, 2016, 45(2):11-15.
|
|
QU Zhongwei, YAN Shilong, LI Xuechao. Effect of inert gas to gas explosion limits of methane/air premixed[J]. Explosive Materials, 2016, 45(2): 11-15.
|
| [3] |
INGRAM J M, AUERILL A F, BATTERSBY P N, et al. Suppression of hydrogen-oxygen-nitrogen explosions by fine water mist: part 1. burning velocity[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2012, 37(24):19250-19 257.
doi: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2011.09.070
|
| [4] |
WANG Mengming, WEN Xiaoping, ZHANG Sumei, et al. Effect of metal foam mesh on flame propagation of biomass-derived gas in a half-open duct[J]. ACS Omega, 2020: DOI: 10.1021/acsomega.0c03055.
doi: 10.1021/acsomega.0c03055
|
| [5] |
王亚磊, 郑立刚, 于水军, 等. NaHCO3分散状况对其抑制甲烷爆炸的影响研究[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2018, 28(11):80-85.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2018.11.013
|
|
WANG Yalei, ZHENG Ligang, YU Shuijun, et al. Effect of dispersion condition of NaHCO3 on inhibiting methane-air mixture explosion[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2018, 28(11): 80-85.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2018.11.013
|
| [6] |
何昆. 初始温度对氮气抑爆性能影响的实验研究[J]. 消防科学与技术, 2014, 33(11):1247-1250.
|
|
HE Kun. Experimental study on effect of explosion suppression of nitrogen at different initial temperatures[J]. Fire Science and Technology, 2014, 33(11): 1247-1250.
|
| [7] |
陈金健, 胡双启, 曹雄. 多元惰气对瓦斯爆炸特性影响的实验研究[J]. 煤炭技术, 2015, 34(8):161-164.
|
|
CHEN Jinjian, HU Shuangqi, CAO Xiong. Experimental research on influence of gas explosion characteristics by multiple inert gas[J]. Coal Technology, 2015, 34(8): 161-164.
|
| [8] |
ZAHEDI P, YOUSEFI K. Effects of pressure and carbon dioxide, hydrogen and nitrogen concentration on laminar burning velocities and NO formation of methane-air mixtures[J]. Journal of Mechanical Science & Technology, 2014, 28(1): 377-386.
|
| [9] |
LU Chang, WANG Hongbo, PAN Rongkun, et al. Preventing the propagation of gas explosion in ducts using spurted nitrogen[J]. Process Safety and Environmental Protection, 2019, 123: 11-23.
doi: 10.1016/j.psep.2018.12.028
|
| [10] |
李振峰, 王天政, 安安, 等. 细水雾抑制煤尘与瓦斯爆炸实验[J]. 西安科技大学学报, 2011, 31(6):698-702, 707.
|
|
LI Zhenfeng, WANG Tianzheng, AN An, et al. Experiments on the suppression of coal dust and gas explosion by water mist[J]. Journal of Xi'an University of Science and Technology, 2011, 31(6): 698-702, 707.
|
| [11] |
杨克, 邢志祥, 纪虹, 等. 超细水雾抑制甲烷爆炸的影响因素分析[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2018, 28(11):66-71.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2018.11.011
|
|
YANG Ke, XING Zhixiang, JI Hong, et al. Analysis of factors influencing air-methane explosion suppression by ultrafine water mist[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2018, 28(11): 66-71.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2018.11.011
|
| [12] |
杨春丽, 刘艳, 胡玢, 等. 氮气和水蒸气对瓦斯爆炸基元反应的影响及抑爆机理分析[J]. 高压物理学报, 2017, 31(3):301-308.
|
|
YANG Chunli, LIU Yan, HU Bin, et al. Effect of nitrogen and water vapor on methane-air mixture explosion elementary reaction and suppression mechanism[J]. Chinese Journal of High Pressure Physics, 2017, 31(3): 301-308.
|
| [13] |
PEI Bei, YU Minggao, CHEN Liwei, et al. Experimental study on the synergistic inhibition effect of nitrogen and ultrafine water mist on gas explosion in a vented duct[J]. Journal of Loss Prevention in the Process Industries, 2016, 40: 546-553.
doi: 10.1016/j.jlp.2016.02.005
|
| [14] |
曹兴岩, 任婧杰, 毕明树, 等. 超细水雾雾化方式对甲烷爆炸过程影响的实验研究[J]. 煤炭学报, 2017, 42(7):1795-1802.
|
|
CAO Xingyan, REN Jingjie, BI Mingshu, et al. Experimental study on effect of methane explosion process by atomization method of ultrafine water mist[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2017, 42(7): 1795-1802.
|
| [15] |
DUAN Yulong, YANG Yanling, LI Yuanbing, et al. Influence of initial position of sliding device on premixed methane/air gas explosion flame at driving face in coal mine[J]. Combustion Science and Technology, 2021:DOI: 10.1080/00102202.2021.1932851.
doi: 10.1080/00102202.2021.1932851
|
| [16] |
陈敏剑. 聚甲醛纳米材料的开发及性能研究[D]. 成都: 四川大学, 2005.
|
|
CHEN Minjian. Development and performance research of polyoxymethylene nanomaterials[D]. Chengdu: Sichuan University, 2005.
|
| [17] |
ANANTH R, WILLAUER H D, FARLEY J P, et al. Effects of fine water mist on a confined blast[J]. Fire Technology, 2012, 48(3): 641-675.
doi: 10.1007/s10694-010-0156-y
|
| [18] |
余明高, 杨勇, 裴蓓, 等. N2双流体细水雾抑制管道瓦斯爆炸实验研究[J]. 爆炸与冲击, 2017, 37(2):194-200.
|
|
YU Minggao, YANG Yong, PEI Bei, et al. Experimental study of methane explosion suppression by nitrogen twin-fluid water mist[J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 2017, 37(2): 194-200.
|