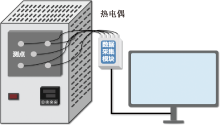
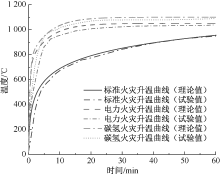
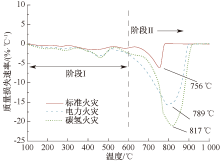
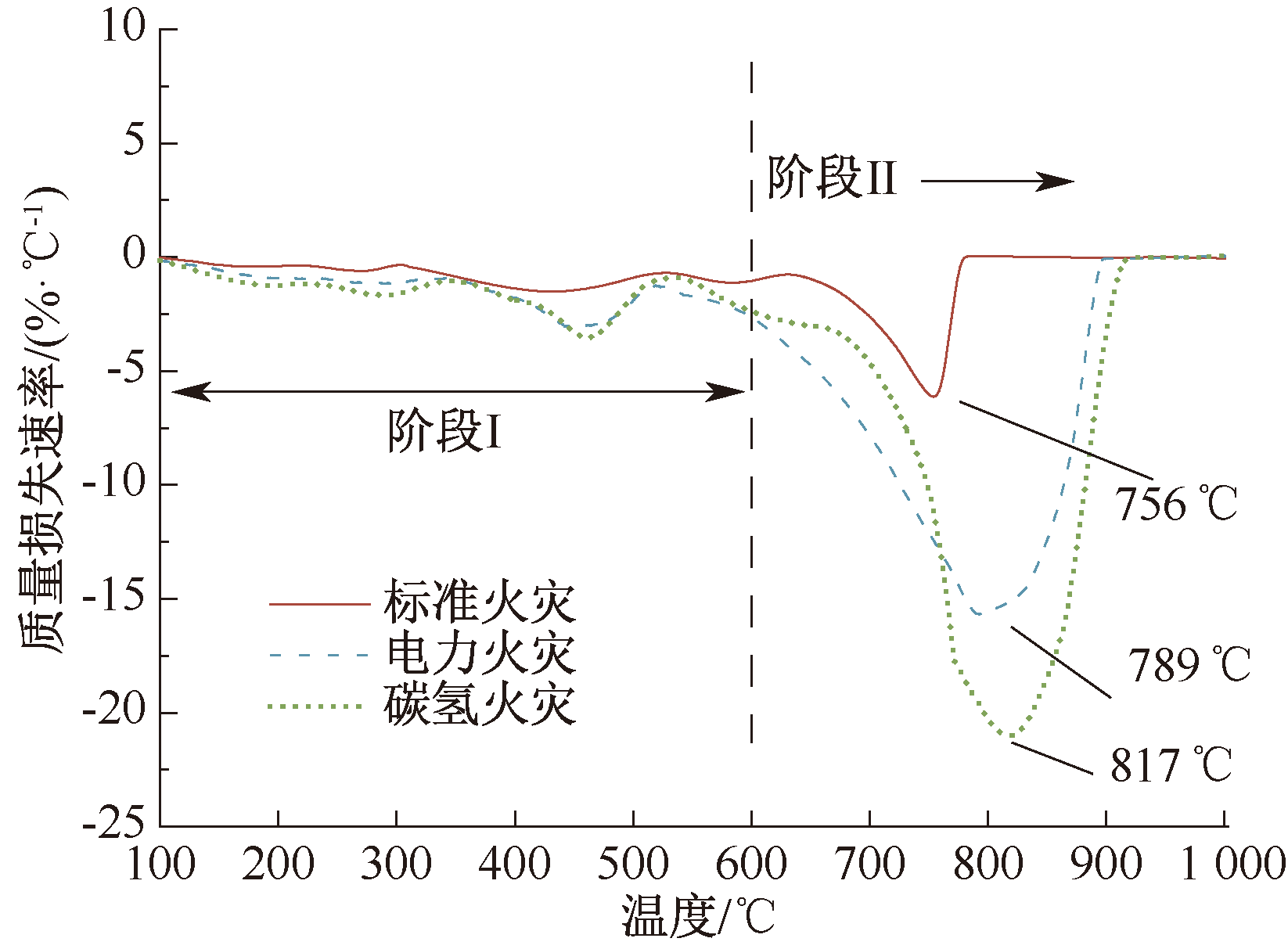
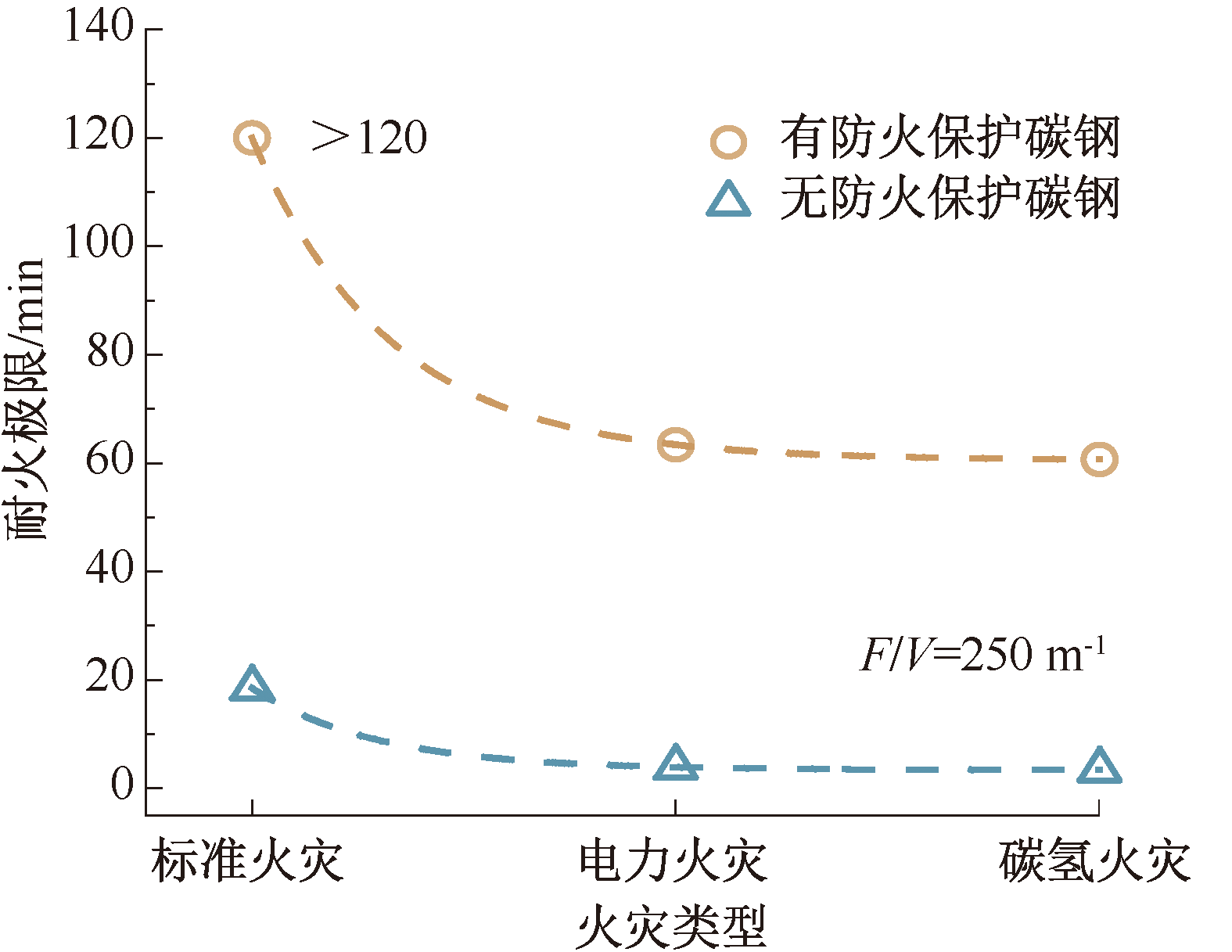
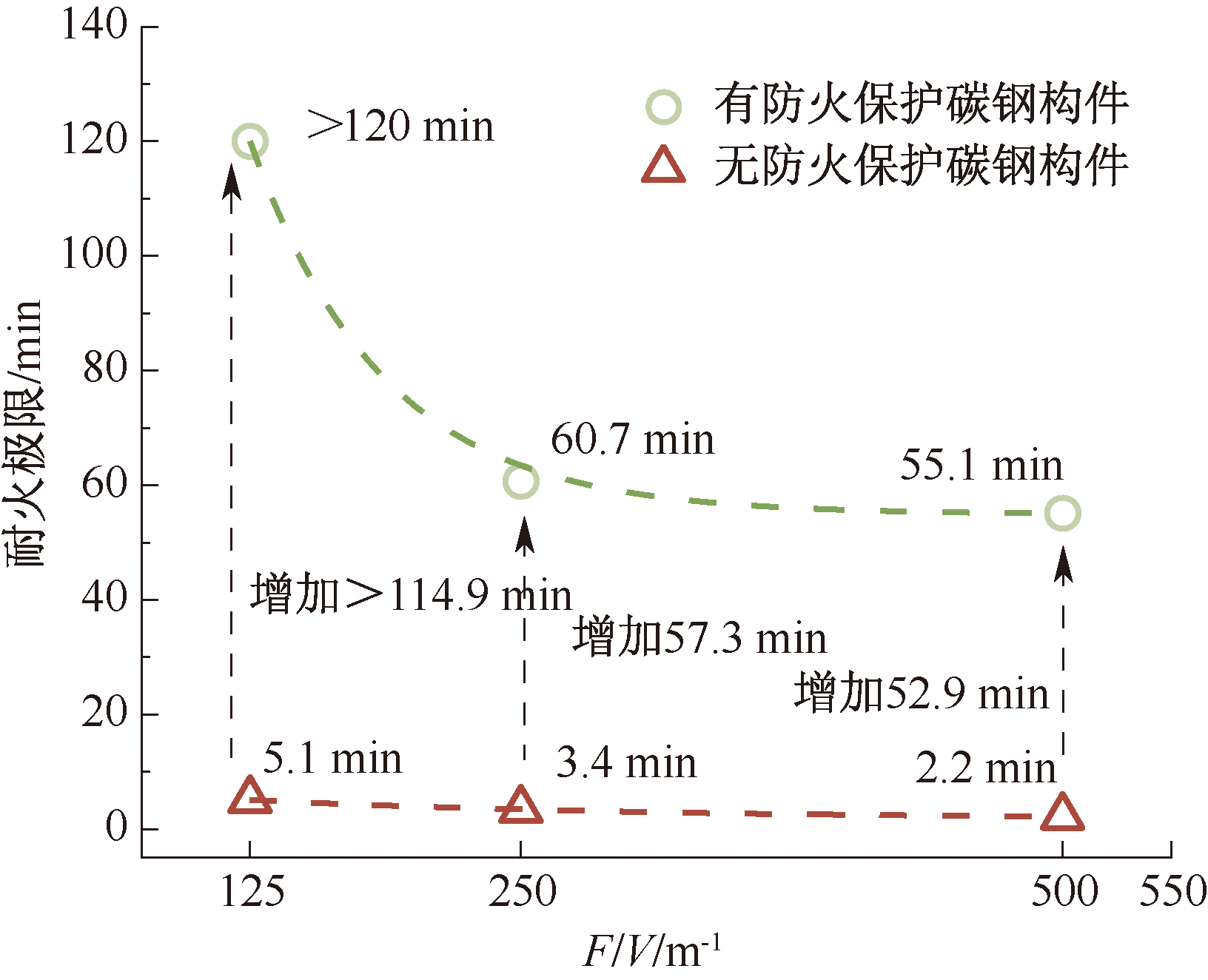
| [1] |
陈德平, 侯柯屹, 王立佳, 等. 超级绝热型防火材料的研究进展及其在城市地下空间的应用展望[J]. 工程科学学报, 2017, 39(6):811-822.
|
|
CHEN Deping, HOU Keyi, WANG Lijia, et al. Status and development of fire protection materials based on super thermal insulator and their application prospect in urban underground space[J]. Chinese Journal of Engineering, 2017, 39(6):811-822.
|
| [2] |
徐志胜, 周寰, 颜龙, 等. 硼酸三聚氰胺在膨胀型防火涂料中的协同作用[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2018, 28(12):40-45.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2018.12.007
|
|
XU Zhisheng, ZHOU Huan, YAN Long, et al. Synergistic effect of melamine borate in intumescent fire-retardant coatings[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2018, 28(12):40-45.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2018.12.007
|
| [3] |
王飞跃, 刘辉, 颜龙. 钨尾矿填料在膨胀型防火涂料中的协效作用[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2021, 31(10): 46-53.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2021.10.007
|
|
WANG Feiyue, LIU Hui, YAN Long. Synergistic effect of tungsten tailing filler in intumescent fire-retardant coatings[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2021, 31(10):46-53.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2021.10.007
|
| [4] |
GB 14907—2018, 钢结构防火涂料[S].
|
|
GB 14907-2018, Fire resistive coating for steel structure[S].
|
| [5] |
王玲玲, 李国强, 徐玉野, 等. 不同火灾下膨胀型钢结构防火涂层的隔热性能[J]. 建筑材料学报, 2016, 19(2):267-273,279.
|
|
WANG Lingling, LI Guoqiang, XU Yuye, et al. Insulation properties of intumescent coating for steel element under different fire conditions[J]. Journal of Building Materials, 2016, 19(2):267-273, 279.
|
| [6] |
LI Guoqiang, HAN Jun, LOU Guobiao, et al. Predicting intumescent coating protected steel temperature in fire using constant thermal conductivity[J]. Thin-Walled Structures, 2016,98:177-184.
|
| [7] |
王玲玲, 孙毅, 范光明, 等. 升温机制对膨胀型防火涂层隔热性能的影响[J]. 建筑材料学报, 2019, 22(1):101-107.
|
|
WANG Lingling, SUN Yi, FAN Guangming, et al. Effect of heating mechanism on thermal insulation properties of intumescent fire retardant coatings[J]. Journal of Building Materials, 2019, 22(1):101-107.
|
| [8] |
WANG Lingling, DONG Yuli, ZHANG Chao, et al. Experimental study of heat transfer in intumescent coatings exposed to non-standard furnace curves[J]. Fire Technology, 2015, 51(3):627-643.
|
| [9] |
JIMENEZ M, DUQUESNE S, BOURBIGOT S. Characterization of the performance of an intumescent fire protective coating[J]. Surface and Coatings Technology, 2006, 201(3/4):979-987.
|
| [10] |
ANDERSON JR C E, KETCHUM D E, MOUNTAIN W P. Thermal conductivity of intumescent chars[J]. Journal of Fire Sciences, 1988, 6(6):390-410.
|
| [11] |
CIRPICI B K, WANG Yongchang, ROGERS B. Assessment of the thermal conductivity of intumescent coatings in fire[J]. Fire Safety Journal, 2016, 81:74-84.
|
| [12] |
ZHANG Yeqin, WANG Yongchang, BAILEY C G, et al. Global modelling of fire protection performance of intumescent coating under different cone calorimeter heating conditions[J]. Fire Safety Journal, 2012, 50:51-62.
|
| [13] |
GB 51249—2017,建筑钢结构防火技术规范[S].
|
|
GB 51249-2017,Code for fire safety of steel structures in buildings[S].
|
| [14] |
GB/T 26784—2011,建筑构件耐火试验可供选择和附加的试验程序[S].
|
|
GB/T 26784-2011,Fire resistance test for elements of building construction: alternative and additional procedures[S].
|
| [15] |
王朋. 超薄型防火涂料组分间协效作用研究[D]. 北京: 北京化工大学, 2016.
|
|
WANG Peng. Study on the synergistic effects of components in intumescent fire retardant coating[D]. Beijing: Beijing University of Chemical Technology, 2016.
|
| [16] |
袁用文. 超薄型钢结构防火涂料的研制及热解特性研究[D]. 沈阳: 沈阳航空工业学院, 2006.
|
|
YUAN Yongwen. Design of super-thin fire resistant coating for steel structure and study of its characteristic of pyrolysis[D]. Shenyang: Shenyang Institute of Aeronautical Technology, 2006.
|
| [17] |
刘梦洋. 环氧水性超薄钢结构防火涂料的阻燃机理与低烟化研究[D]. 郑州: 郑州大学, 2019.
|
|
LIU Mengyang. Study on flame retardant property and low smoke of epoxy waterborne ultra-thin steel structure fire retardant coatings[D]. Zhengzhou: Zhengzhou University, 2019.
|
| [18] |
郭磊. 膨胀型防火涂料热性能研究[D]. 绵阳: 西南科技大学, 2019.
|
|
GUO Lei. Study on thermal properties of intumescent fire retardant coatings[D]. Mianyang: Southwest University of Science and Technology, 2019.
|
| [19] |
何华俊, 廖定根, 方超. 水性超薄型钢结构防火涂料的研究[J]. 消防科学与技术, 2016, 35(11):1593-1595.
|
|
HE Huajun, LIAO Dinggen, FANG Chao. Study on the aqueous ultra-thin fireproof coating for steel structure[J]. Fire Science and Technology, 2016, 35(11):1593-1595.
|
| [20] |
邢丽萍. 膨胀型防火涂层与钢质基体传热过程影响因素研究[D]. 青岛: 青岛科技大学, 2022.
|
|
XING Liping. Study on influencing factors of heat transfer process between intumescent fire retardant coating and steel substrate[D]. Qingdao: Qingdao University of Science and Technology, 2022.
|