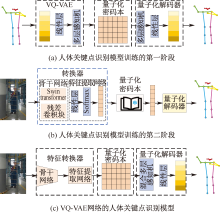
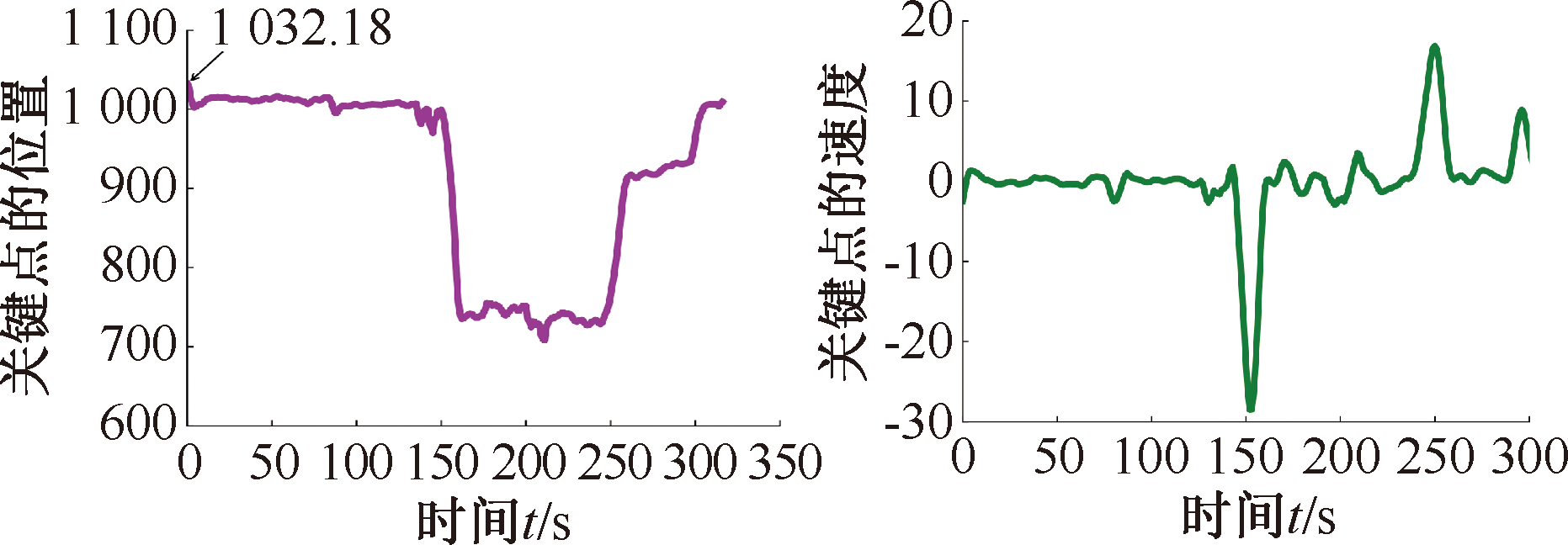
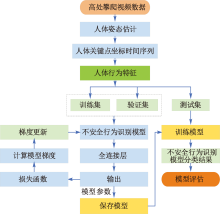
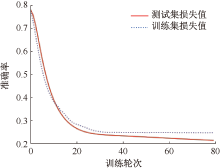
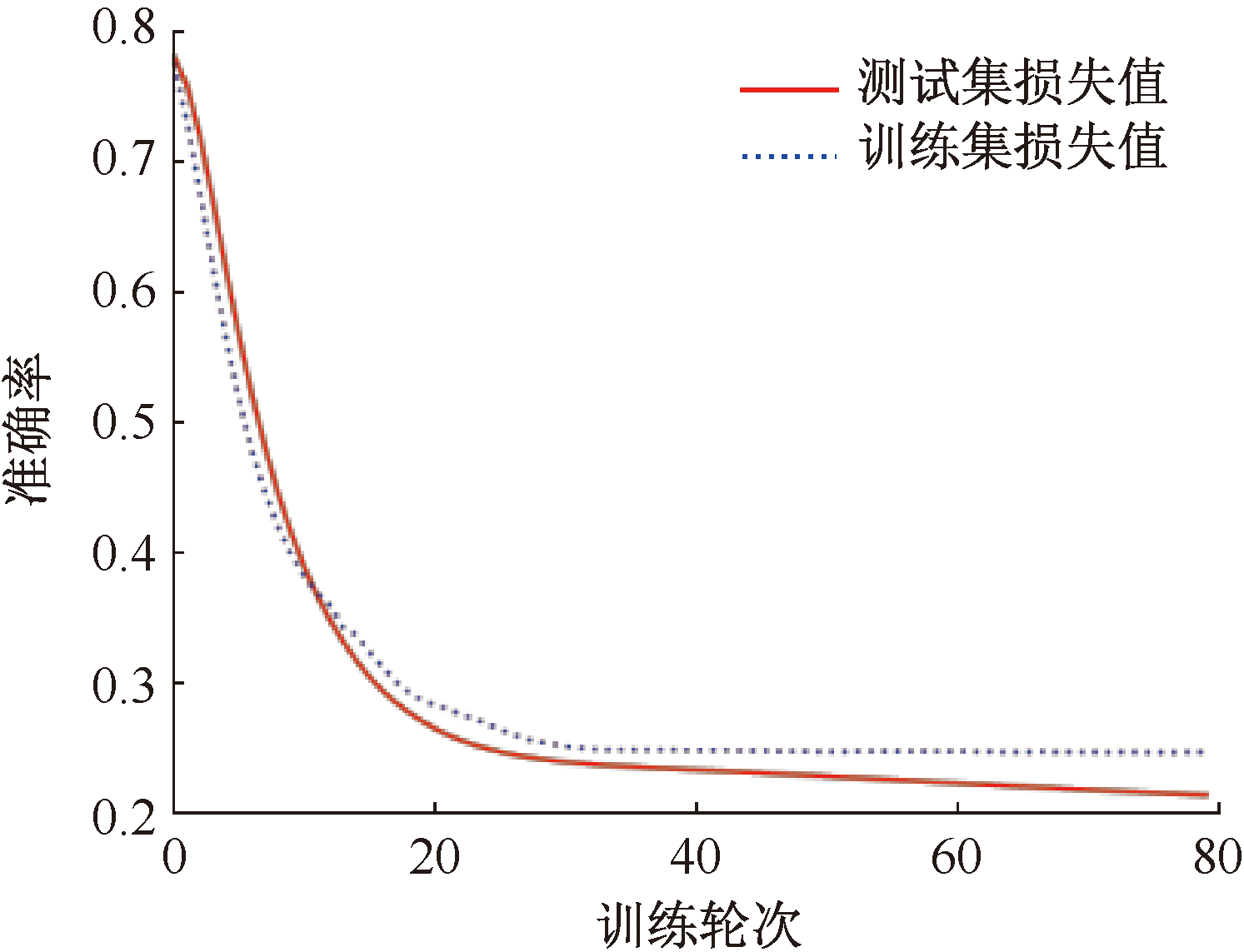
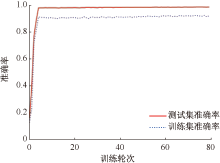
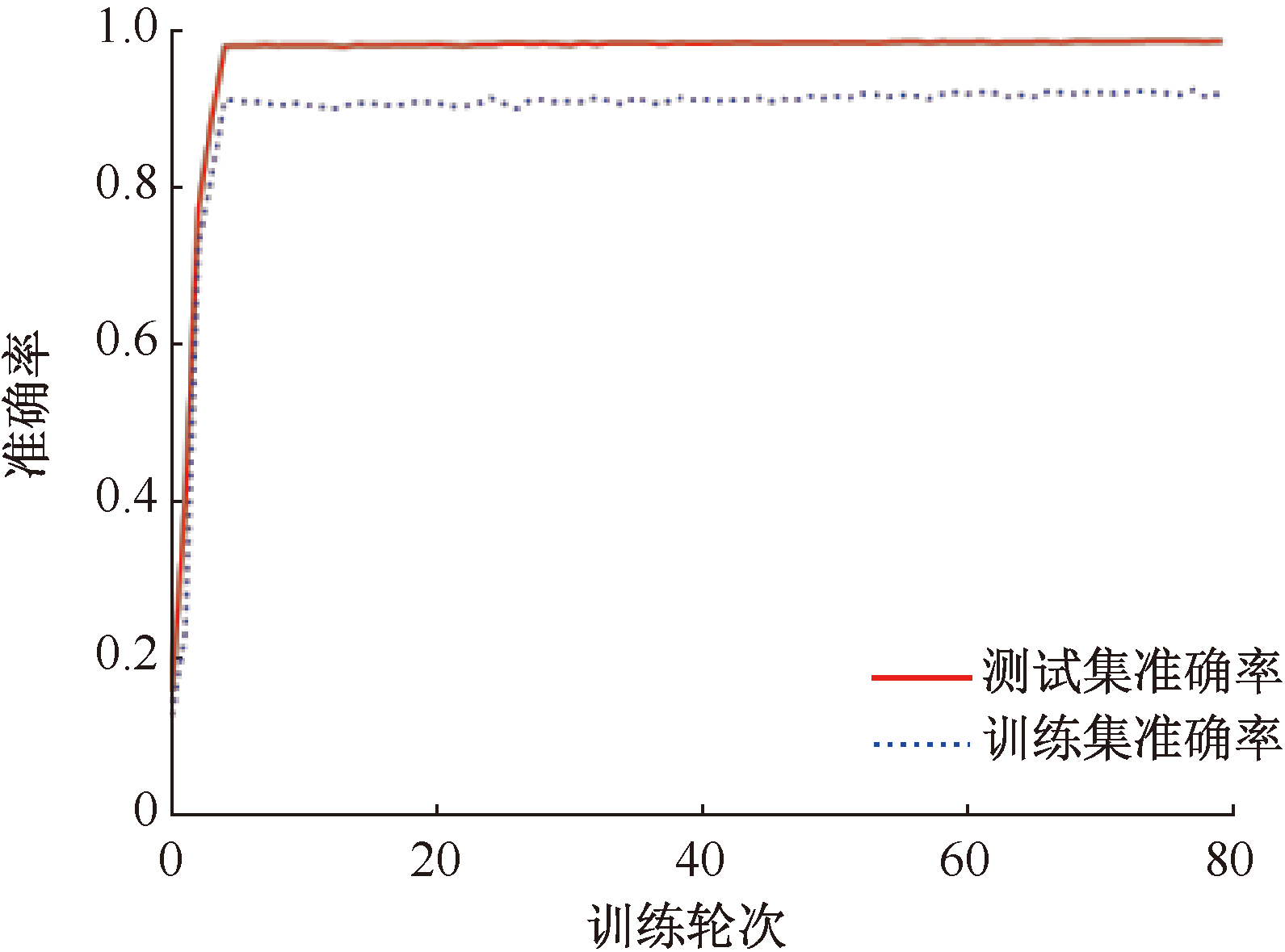
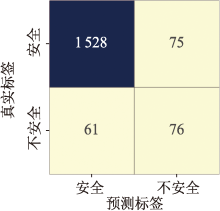
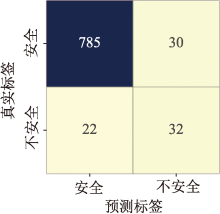
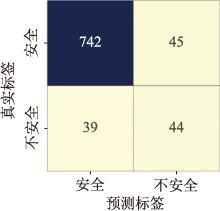
| [1] |
国家统计局. 中华人民共和国2023年国民经济和社会发展统计公报[EB/OL].(2024-02-29). https://www.stats.gov.cn/xxgk/sjfb/tjgb2020/202402/t20240229_1947923.html.
|
| [2] |
SABRINA S O, WILLAMES D A S, BIANCA M V. Fatal fall-from-height accidents: statistical treatment using the human factors analysis and classification system-HFACS[J]. Journal of Safety Research, 2023: DOI: 10.1016/j.jsr.2023.05.004.
|
| [3] |
YANG Jingjing, YE Gui, XIANG Qingting, et al. Insights into the mechanism of construction workers' unsafe behaviors from an individual perspective[J]. Safety Science, 2021: DOI: 10.1016/j.ssci.2020.105004.
|
| [4] |
郑霞忠, 王晓宇, 陈述, 等. 高处坠落事故的人因失误与干预策略研究[J]. 中国安全生产科学技术, 2017, 13(6):139-144.
|
|
ZHENG Xiazhong, WANG Xiaoyu, CHEN Shu, et al. Study on human error and intervention strategies of high falling accidents[J]. Journal of Safety Science and Technology, 2017, 13(6):139-144.
|
| [5] |
ZHOU Longfei, ZHANG Lin, KONZ N. Computer vision techniques in manufacturing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics: Systems, 2022, 53(1):105-117.
|
| [6] |
伍麟, 郝鸿宇, 宋友. 基于计算机视觉的工业金属表面缺陷检测综述[J]. 自动化学报, 2024, 50(7):1261-1283.
|
|
WU Lin, HAO Hongyu, SONG You. A review of metal surface defect detection based on computer vision[J]. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2024, 50(7):1261-1283.
|
| [7] |
FANG Weili, DING Lieyun, LOVE P E D, et al. Computer vision applications in construction safety assurance[J]. Automation in Construction, 2020: DOI: 10.1016/j.autcon.2019.103013.
|
| [8] |
张萌, 韩豫, 刘泽锋. 深度学习下建筑工人高空安全防护装备检测方法[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2022, 32(5):140-146.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2022.05.1141
|
|
ZHANG Meng, HAN Yu, LIU Zefeng. Detection method of high-altitude safety protective equipment for construction workers based on deep learning[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2022, 32(5):140-146.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2022.05.1141
|
| [9] |
程淑红, 马晓菲, 张仕军, 等. 基于多任务分类的吸烟行为检测[J]. 计量学报, 2020, 41(5):538-543.
|
|
CHENG Shuhong, MA Xiaofei, ZHANG Shijun, et al. Smoking detection algorithm based on multitask classification[J]. Acta Metrologica Sinica, 2020, 41(5):538-543.
|
| [10] |
LI Li, ZHONG Boxuan, HUTMACHER J C, et al. Detection of driver manual distraction via image-based hand and ear recognition[J]. Accident Analysis & Prevention, 2020:DOI: 10.1016/j.aap.2020.105432.
|
| [11] |
ZHANG Xiaojun. Application of human motion recognition utilizing deep learning and smart wearable device in sports[J]. International Journal of System Assurance Engineering and Management, 2021, 12(4):835-843.
doi: 10.1007/s13198-021-01118-7
|
| [12] |
XIE Yadong, LI Fan, WU Yue, et al. HearSmoking: smoking detection in driving environment via acoustic sensing on smartphones[J]. IEEE Transactions on Mobile Computing, 2021, 21(8):2847-2860.
|
| [13] |
SHEN Jie, XIONG Xin, LI Ying, et al. Detecting safety helmet wearing on construction sites with bounding-box regression and deep transfer learning[J]. Computer-Aided Civil and Infrastructure Engineering, 2021, 36(2):180-196.
|
| [14] |
SENER A S, INCE I F, BAYDARGIL H B, et al. Deep learning based automatic vertical height adjustment of incorrectly fastened seat belts for driver and passenger safety in fleet vehicles[J]. Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part D: Journal of Automobile Engineering, 2022, 236(4):639-654.
|
| [15] |
GB 30871—2022,危险化学品企业特殊作业安全规范[S].
|
|
GB 30871-2022, Safety specifications of special work in hazardous chemicals enterprises[S].
|
| [16] |
刘勃, 孔韦韦, 肖家钦, 等. 基于RBF神经网络的跌倒检测算法[J]. 计算机技术与发展, 2022, 32(6):167-178.
|
|
LIU Bo, KONG Weiwei, XIAO Jiaqin, et al. Fall detection algorithm based on rbf neural network[J]. Computer Technology and Development, 2022, 32(6):167-178.
|
| [17] |
GENG Zigang, WANG Chunyu, WEI Yixuan, et al. Human pose as compositional tokens[C]. Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2023: DOI: 10.1109/CVPR52729.2023.00071.
|
| [18] |
HU Qiyu, ZHANG Guangyi, QIN Zhijin, et al. Robust semantic communications with masked VQ-VAE enabled codebook[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2023, 22(12):8707-8722.
|
| [19] |
LIU Ze, LIN Yutong, CAO Yue, et al. Swin transformer: hierarchical vision transformer using shifted windows[C]. Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, 2021:DOI: 10.1109/ICCV48922.2021.00986.
|
| [20] |
YU Jianbo, ZHOU Xingkang. One-dimensional residual convolutional autoencoder based feature learning for gearbox fault diagnosis[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2020, 16(10):6347-6358.
|
| [21] |
池毅, 陈光武. 基于一维卷积神经网络的实时道岔故障诊断[J]. 计算机工程与应用, 2022, 58(20):293-299.
doi: 10.3778/j.issn.1002-8331.2103-0348
|
|
CHI Yi, CHEN Guangwu. Real-time turnout fault diagnosis based on one-dimensional convolutional neural network[J]. Computer Engineering and Applications, 2022, 58(20):293-299.
doi: 10.3778/j.issn.1002-8331.2103-0348
|
| [22] |
SONG Yifan, ZHANG Zhang, SHAN Caifeng, et al. Constructing stronger and faster baselines for skeleton-based action recognition[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2022, 45(2):1474-1488.
|
| [23] |
SONG Yifan, ZHANG Zhang, SHAN Caifeng, et al. Richly activated graph convolutional network for robust skeleton-based action recognition[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology, 2020, 31(5):1915-1925.
|
| [24] |
ZHAO Baining, LAN Haijuan, NIU Zhenwen, et al. Detection and location of safety protective wear in power substation operation using wear-enhanced YOLOv3 algorithm[J]. IEEE Access, 2021: DOI: 10.1109/ACCESS.2021.3104731.
|