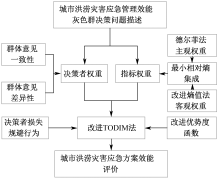
| [1] |
李海辰, 冯文文, 张少恺, 等. 城市洪涝灾害防御中的前沿信息技术应用[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2022, 32(9): 137-143.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2022.09.2707
|
|
LI Haichen, FENG Wenwen, ZHANG Shaokai, et al. Review on application of cutting-edge information technology in urban flood prevention system[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2022, 32(9):137-143.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2022.09.2707
|
| [2] |
王永明, 郑姗姗. 地方政府应急管理效能提升的多重困境与优化路径:基于“河南郑州‘7·20’特大暴雨灾害”的案例分析[J]. 管理世界, 2023, 39(3):83-96.
|
|
WANG Yongming, ZHENG Shanshan. Multiple dilemmas and optimization path for improving the efficiency of local government emergency management: case analysis based on henan zhengzhou torrential rain-caused disaster on July 20[J]. Management Word, 2023, 39(3):83-96.
|
| [3] |
CHEN Ning, LIU Wenjing, BAI Ruizhen, et al. Application of computational intelligence technologies in emergency management: a literature review[J]. Artificial Intelligence Review, 2019, 52: 2131-2168.
doi: 10.1007/s10462-017-9589-8
|
| [4] |
EMERGENCY R. Federal emergency management agency[J]. Federal Register, 1996, 61(90):20944-20 970.
|
| [5] |
OZGUVEN E E, OZBAY K. An RFID-based inventory management framework for emergency relief operations[J]. Transportation Research Part C: Emerging Technologies, 2015, 57: 166-187.
|
| [6] |
CHEN Peng, ZHANG Jiquan, SUN Yingyue. Research on emergency rescue of urban flood disaster based on wargame simulation[J]. Journal of the Indian Society of Remote Sensing, 2018, 46(10): 1677-1687.
|
| [7] |
宋英华, 韩保帅, 郭晨. 考虑洪涝灾害风险的县域应急避难场所选址模型[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2024, 34(4): 191-198.
|
|
SONG Yinghua, HAN Baoshuai, GUO Chen. Location selection model of emergency shelter considering risk of flood disaster in county[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2024, 34(4): 191-198.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2024.04.6850
|
| [8] |
ZHANG Yang, SHANG Kejian. Cloud model assessment of urban flood resilience based on PSR model and game theory[J]. International Journal of Disaster Risk Reduction, 2023, 97: DOI: 10.1016/j.ijdrr.2023.104050.
|
| [9] |
MEHRYAR S, SURMINSKI S. Investigating flood resilience perceptions and supporting collective decision-making through fuzzy cognitive mapping[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2022, 837:DOI: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.155854.
|
| [10] |
LI Guangxu, KOU Gang, PENG Yi. Heterogeneous large-scale group decision making using fuzzy cluster analysis and its application to emergency response plan selection[J]. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics: Systems, 2021, 52(6): 3391-3403.
|
| [11] |
YIN Xuanpeng, XU Xuanhua, PAN Bin. Selection of strategy for large group emergency decision-making based on risk measurement[J]. Reliability Engineering & System Safety, 2021, 208: DOI: 10.1016/j.ress.2020.107325.
|
| [12] |
SUN Huifang, MAO Wenxin, DANG Yaoguo, et al. Optimum path for overcoming barriers of green construction supply chain management: a grey possibility DEMATEL-NK approach[J]. Computers & Industrial Engineering, 2022, 164: DOI: 10.1016/j.cie.2021.107833.
|
| [13] |
XIE Xudong, HU Mingli, YANG Yingjie, et al. Grey target group decision model based on expected intervals of experts[J]. The Journal of Grey System, 2020, 32(4): 77-89.
|
| [14] |
孙慧芳, 党耀国, 毛文鑫. 基于前景理论的风险型多阶段灰靶决策方法[J]. 统计与决策, 2020, 36(7):183-188.
|
|
SUN Huifang, DANG Yaoguo, MAO Wenxin. Risk based multistage grey target decision making method based on prospect theory[J]. Statistics and Decision Making, 2020, 36 (7): 183-188.
|
| [15] |
姜雨茹, 刘焱, 叶国菊. 基于专家动态赋权的离散模糊语言群决策方法[J]. 西华大学学报:自然科学版, 2024, 43(5): 124-130.
|
|
JIANG Yuru, LIU Yan, YE Guoju. Discrete fuzzy language group decision making method based on expert dynamic weighting[J]. Journal of Xihua University:Natural Science Edition, 2024, 43 (5): 124-130.
|
| [16] |
SUN Huifang, DANG Yaoguo, MAO Wenxin. Identifying key factors of regional agricultural drought vulnerability using a panel data grey combined method[J]. Natural Hazards, 2019, 98(2): 621-642.
doi: 10.1007/s11069-019-03722-0
|
| [17] |
LIU Sifeng, YANG Yingjie, FORREST J. Grey data analysis[M]. Singapore: Springer Singapore, 2017: 234-239.
|
| [18] |
KAHNEMAN D, TVERSKY A. Prospect theory: an analysis of decision under risk[M]. Singapore: Handbook of the Fundamentals of Financial Decision Making: Part I. 2013: 99-127.
|
| [19] |
闫书丽. 灰靶决策方法及应用研究[D]. 南京: 南京航空航天大学, 2014.
|
|
YAN Shuli. Grey target decision method and its application[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2014.
|