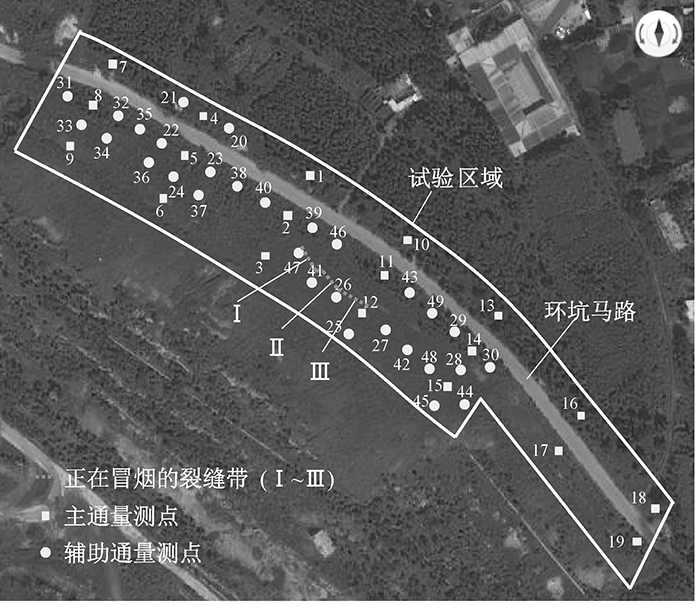
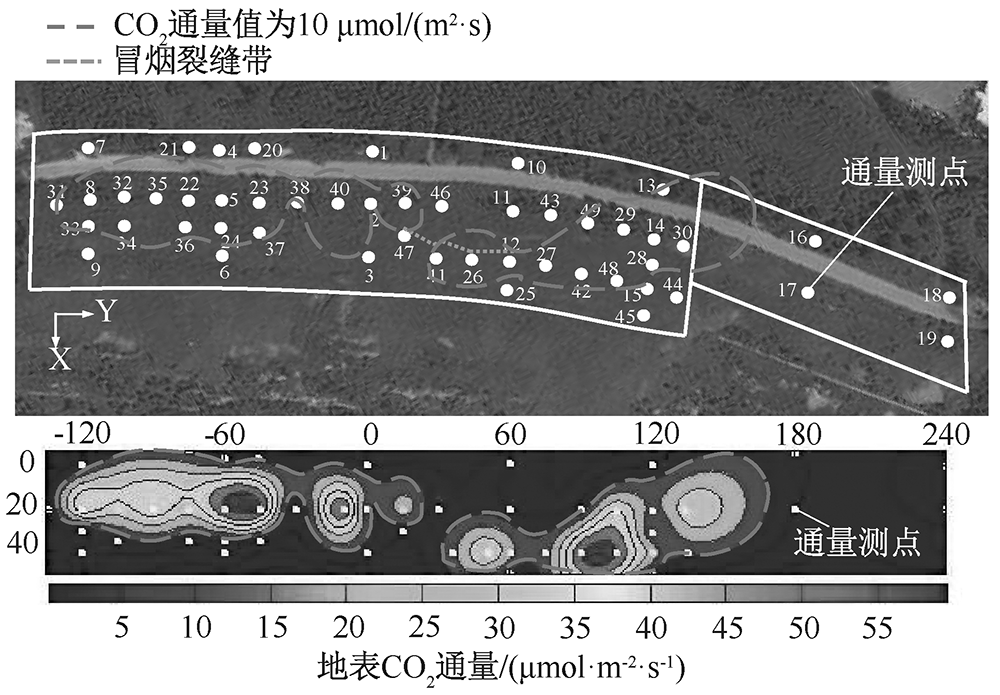
| [1] |
GLENN B S, TAMMY P T. Coal fires burning out of control around the world: thermodynamic recipe for environmental catastrophe[J]. International Journal of Coal Geology, 2003, 59(1): 7-17.
doi: 10.1016/j.coal.2003.03.002
|
| [2] |
DENIS N P, KIM A A, GLENN B S, et al. The spontaneous combustion of coal and its by products in the witbank and sasolburg coalfields of south africa[J]. International Journal of Coal Geology, 2007, 72(2): 124-140.
doi: 10.1016/j.coal.2007.01.001
|
| [3] |
JENNIFER M K, HENKE K R, HOWER J C, et al. CO2, CO, and Hg emissions from the Truman Shepherd and Ruth Mullins coal fires, Eastern Kentucky, USA[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2010, 408(7): 1628-1633.
doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2009.12.005
|
| [4] |
齐庆杰, 赵尤信, 贾新雷, 等. 深部煤层抽采钻孔自然发火原因分析与防治[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2019, 29(1): 37-42.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2019.01.007
|
|
QI Qingjie, ZHAO Youxin, JIA Xinlei, et al. Cause analysis and prevention of spontaneous combustion in deep coal seam drilling[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2019, 29(1): 37-42.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2019.01.007
|
| [5] |
黄福昌, 崔洪义, 王振平, 等. 兖州矿区矿井通风安全技术[M]. 北京: 煤炭工业出版社, 2001:3-4.
|
| [6] |
陈晓坤, 程方明, 邓军, 等. 煤矿采空区自然发火多参数监测系统研究[J]. 煤矿安全, 2012, 43(增1): 22-25.
|
|
CHEN Xiaokun, CHENG Fangming, DENG Jun, et al. Study on multi-parameter monitoring system of spontaneous combustion in coal mine goaf[J]. Safety in Coal Mines, 2012, 43(S1): 22-25.
|
| [7] |
甘建. 复杂采空区气体检测与温度传感双重融合煤自燃探测技术[J]. 内蒙古煤炭经济, 2018(1): 15-16.
|
| [8] |
邵振鲁. 煤田火灾磁、电异常演变特征及综合探测方法研究[D]. 徐州: 中国矿业大学, 2017.
|
|
SHAO Zhenlu. Magnetic and electrical signature of coal fires and comprehensive detection methodology[D]. Xuzhou: China University of Mining and Technology, 2017.
|
| [9] |
李源辉, 刘鸿福, 张新军, 等. 活性炭测氡法在浅埋煤层火区探测中的应用研究[J]. 煤炭技术, 2016, 35(10): 237-239.
|
|
LI Yuanhui, LIU Hongfu, ZHANG Xinjun, et al. Application research of Rn measurement with active carbon in fire detection of shallow coal seam[J]. Coal Technology, 2016, 35(10): 237-239.
|
| [10] |
ENGLE M A, RADKE L F, HEFFERN E L, et al. Gas emissions, minerals, and tars associated with three coal fires,Powder River Basin,USA[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2012, 420: 146-159.
doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2012.01.037
|
| [11] |
张晓明, 刘礼龙, 王永军, 等. 露天矿遗煤区地表CO2通量变化规律测试分析[J]. 中国安全生产科学技术, 2018, 14(6): 90-96.
|
|
ZHANG Xiaoming, LIU Lilong, WANG Yongjun, et al. Test and analysis of surface CO2 flux variation in opencast coal mining area[J]. Journal of Safety Science and Technology, 2018, 14(6): 90-96.
|
| [12] |
WANG Yongjun, ZHANG Xiaoming, YUICHI S, et al. Field study on correlation between CO2 concentration and surface soil CO2 flux in closed coal mine goaf[J]. ACS Omega, 2019, 4(7): 12 136-12 145.
|
| [13] |
谭波, 胡瑞丽, 高鹏, 等. 煤自燃灾害气体指标的阶段特征试验研究[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2013, 23(2): 51-57.
|
|
TAN Bo, HU Ruili, GAO Peng, et al. Temperature-programmed experimental study on stage characteristics of coal spontaneous combustion disaster gas indicators[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2013, 23(2): 51-57.
|
| [14] |
李璐. 煤中常见化学键的解离及分子结构的量子化学理论研究[D]. 大连: 大连理工大学, 2016.
|
|
LI Lu. A quantum chemical study on dissociation behaviour of typical bonds and molecular structural of coal[D]. Dalian: Dalian University of Technology, 2016.
|
| [15] |
邓存宝, 王继仁, 张俭, 等. 煤自燃生成乙烯反应机理[J]. 煤炭学报, 2008, 33(3): 299-303.
|
|
DENG Cunbao, WANG Jiren, ZHANG Jian, et al. Reaction mechanism of ethylene production during spontaneous combustion of coal[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2008, 33(3): 299-303.
|
| [16] |
张晓明, 王永军, 张河猛, 等. 基于F-K理论的大体积煤堆自燃特性试验研究[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2018, 28(2): 57-63.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2018.02.010
|
|
ZHANG Xiaoming, WANG Yongjun, ZHANG Hemeng, et al. Experimental study on spontaneous combustion characteristics of big pile of coal based F-K theory[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2018, 28(2): 57-63.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2018.02.010
|
| [17] |
陈琛. 煤自燃过程中温室气体排放的量化实验研究[D]. 北京: 中国矿业大学(北京), 2016.
|
|
CHEN Chen. The quantitative study of GHG emissions by coal spontaneous combustion[D]. Beijing: China University of Mining and Technology(Beijing), 2016.
|
| [18] |
王俊峰. 煤地下自燃时覆岩中氡气运移规律及应用研究[D]. 太原: 太原理工大学, 2010.
|
|
WANG Junfeng. Radon migration in overlying strata during spontaneous combustion of coal underground and its application[D]. Taiyuan: Taiyuan University of Technology, 2010.
|
| [19] |
刘洪福, 白春明, 舒祥泽, 等. 用测氡技术探测煤矿地下火区的研究[J]. 煤炭学报, 1997, 22(4): 68-71.
|
|
LIU Hongfu, BAI Chunming, SHU Xiangze, et al. A study of detecting underground fire zone applying radon measuring technology[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 1997, 22(4): 68-71.
|
| [20] |
鄢姗姗. 煤矿地下开采中冒落带演变过程模拟方法研究[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2016.
|
|
YAN Shanshan. Numerical simulation method of the evolution of caving zone during underground mining[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences(Beijing), 2016.
|
| [21] |
高英旭, 刘红民, 刘阳, 等. 海州露天矿排土场不同林分土壤理化性质对植被生物量的影响[J]. 中南林业科技大学学报, 2014, 34(1): 78-83.
|
|
GAO Yingxu, LIU Hongmin, LIU Yang, et al. Effects of different forest soil physicochemical properties on vegetation biomass at refuse dump of Haizhou open-pit mine[J]. Journal of Central South University of Forestry & Technology, 2014, 34(1): 78-83.
|
| [22] |
卫万顺, 郑桂森, 栾英波, 等. 常温层温度特征及浅层地温能成因机理研究[J]. 城市地质, 2012, 7(2): 1-5.
|
|
WEI Wanshun, ZHENG Guisen, LUAN Yingbo, et al. Temperature characteristics of the room temperature zone and genetic mechanism of the shallow geothermal energy[J]. Urban Geology, 2012, 7(2): 1-5.
|
| [23] |
陈殿强, 张维正, 郝喆, 等. 海州露天矿矿山地质环境治理理论与技术[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2016:21-23.
|
| [24] |
唐芙蓉. 煤炭地下气化燃空区覆岩裂隙演化及破断规律研究[D]. 徐州: 中国矿业大学, 2013.
|
|
TANG Furong. Fracture evolution and breakage of overlying strata of combustion space area in underground coal gasification[D]. Xuzhou: China University of Mining and Technology, 2013.
|
| [25] |
关笑坤. 二氧化碳在土壤包气带中的运移规律及对环境影响研究[D]. 西安: 长安大学, 2014.
|
|
GUAN Xiaokun. Carbon dioxide transport in the unsaturated soil and its environment impact[D]. Xi'an: Chang'an University, 2014.
|