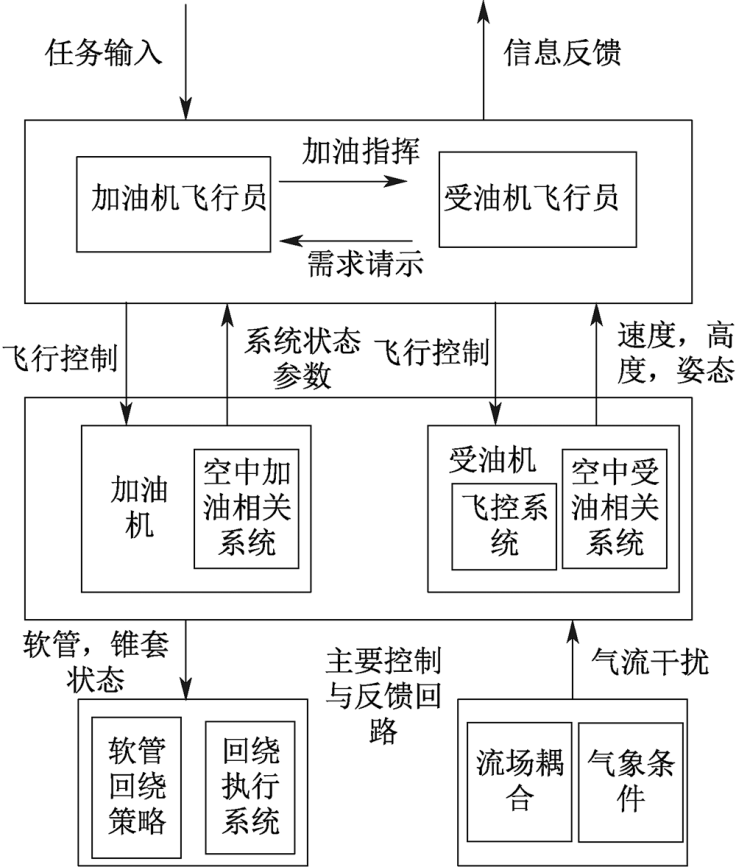
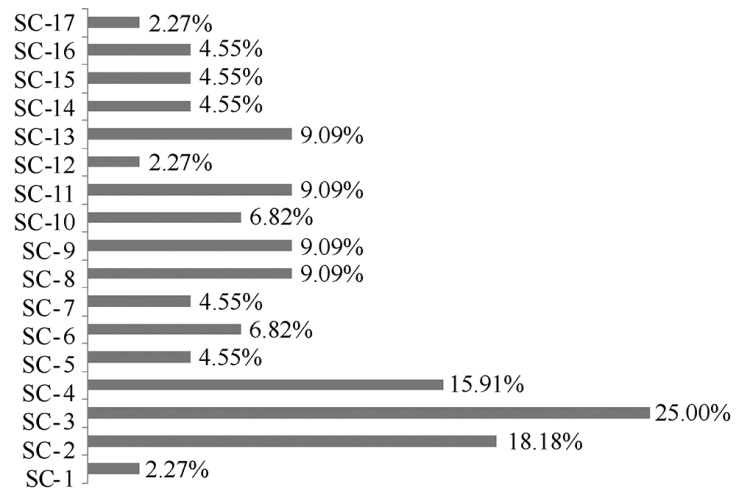
| [1] |
董新民, 徐跃鉴, 陈博. 自动空中加油技术研究进展与关键问题[J]. 空军工程大学学报:自然科学版, 2008, 9(6): 1-5.
|
|
DONG Xinmin, XU Yuejian, CHEN Bo. Progress and challenges in automatic aerial refueling[J]. Journal of Air Force Engineering University: Natural Science Edition, 2008, 9(6): 1-5.
|
| [2] |
全权, 魏子博, 高俊, 等. 软管式自主空中加油对接阶段中的建模与控制综述[J]. 航空学报, 2014, 35(9):2390-2410.
doi: 10.7527/S1000-6893.2014.0092
|
|
QUAN Quan, WEI Zibo, GAO Jun, et al. A survey on modeling and control problems for probe & drogue autonomous aerial docking[J]. Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica, 2014, 35(9):2390-2410.
doi: 10.7527/S1000-6893.2014.0092
|
| [3] |
ZHU Zhenghong, MEGUID S A. Elastodynamic analysis of aerial refueling hose using curved beam element[J]. AIAA Journal, 2006, 44(6):1317-1324.
doi: 10.2514/1.17311
|
| [4] |
王海涛, 董新民, 郭军, 等. 空中加油软管锥套组合体甩鞭现象动力学建模与分析[J]. 航空学报, 2015, 36(9):3116-3127.
doi: 10.7527/S1000-6893.2014.0343
|
|
WANG Haitao, DONG Xinmin, GUO Jun, et al. Dynamics modeling and analysis of hose whipping phenomenon of aerial refueling hose-drogue assembly[J]. Acta Aeronautica Et Astronautica Sinica, 2015, 36(9): 3116-3127.
doi: 10.7527/S1000-6893.2014.0343
|
| [5] |
喻振华, 周倩, 李伟. 空中加油电驱动响应技术研究[J]. 航空科学技术, 2016, 27(12):18-22.
|
|
YU Zhenghua, ZHOU Qian, LI Wei. Reasearch on electric drive technology under the response condition of aerial refueling[J]. Aeronautical Science & Technology, 2016, 27(12):18-22.
|
| [6] |
闵强. 空中加油软管甩鞭现象建模与载荷计算[J]. 四川轻化工大学学报:自然科学版, 2020, 33(5):81-87.
|
|
MIN Qiang. Dynamic modeling and load calculation of hose whipping phenomenon of aerial refueling hose-drogue assembly[J]. Journal of Sichuan University of Science & Engineering:Natural Science Edition, 2020, 33(5):81-87.
|
| [7] |
STYUART A, GASTON R, YAMASHIRO H, et al. Numerical simulation of hose whip phenomenon in aerial refueling[C]. AIAA Atmospheric Flight Mechanics Conference,2011: DOI: 10.2514/6.2011-6211.
doi: 10.2514/6.2011-6211
|
| [8] |
胡剑波, 李俊, 郑磊, 等. 复杂系统安全性建模、分析、控制与仿真研究[J]. 火力与指挥控制, 2018, 43(7):1-9.
|
|
HU Jianbo, LI Jun, ZHENG Lei, et al. Research summary on safety model,analysis,control and simulate for complex systems[J]. Fire Control & Command Control, 2018, 43(7):1-9.
|
| [9] |
王洁宁, 李保燊, 冀姗姗. 基于STPA和模糊BN的AIDC移交人误研究[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2019, 29(9): 27-35.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2019.09.005
|
|
WANG Jiening, LI Baoshen, JI Shanshan. Study on human error in AIDC transfer based on STPA and fuzzy BN[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2019, 29(9): 27-35.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2019.09.005
|
| [10] |
李京生, 赵林, 王阳, 等. CRES的危害因素识别方法:以EETD为例[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2019, 29(1): 106-111.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2019.01.018
|
|
LI Jingsheng, ZHAO Lin, WANG Yang, et al. Study on method for identifying hazardous factors in CRES: EETD taken as an example[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2019, 29(1): 106-111.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2019.01.018
|
| [11] |
REJZEK M, HILBES C. Use of STPA as a diverse analysis method for optimization and design verification of digital instrumentation and control systems in nuclear power plants[J]. Nuclear Engineering and Design, 2018, 331: 125-135.
doi: 10.1016/j.nucengdes.2018.02.030
|
| [12] |
王瑛, 郭之俊, 孙贇, 等. 基于IDAC-STPA模型的战机飞行安全性分析与评价[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 2019, 41(5): 1056-1062.
|
|
WANG Ying, GUO Zhijun, SUN Yun, et al. Aircraft flight safety analysis and simulation based on IDAC-STPA model[J]. System Engineering and Electronics, 2019, 41(5): 1056-1062.
|
| [13] |
HU Jianbo, ZHENG Lei, XU Shukui. Safety analysis of wheel brake system based on STAMP/STPA and Monte Carlo simulation[J]. Journal of Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2018, 29(6): 1327-1339.
doi: 10.21629/JSEE.2018.06.20
|
| [14] |
王洁宁, 孙晓萌. 基于STPA空管运行系统安全分析方法研究[J]. 武汉理工大学学报, 2017, 39(12): 54-60.
|
|
WANG Jiening, SUN Xiaomeng. Research on safety analysis of air traffic control system based on STPA[J]. Journal of Wuhan University of Technology, 2017, 39(12): 54-60.
|
| [15] |
KRAUSS S S, REJZEK M, HILBES C. Tool qualification considerations for tools supporting STPA[J]. Procedia Engineering, 2015, 128: 15-24.
doi: 10.1016/j.proeng.2015.11.500
|
| [16] |
LONGJI D A, EMILIA V. System safety assessment based on STPA and model checking[J]. Safety Science, 2018, 109:130-143.
doi: 10.1016/j.ssci.2018.05.009
|
| [17] |
丛继平, 崔利杰, 陈浩然, 等. 空中加油“甩鞭”现象安全性分析与仿真验证[J]. 北京航空航天大学学报, 2020, 46(10):1958-1965.
|
|
CONG Jiping, CUI Lijie, CHEN Haoran, et al. Research on safety analysis and simulation validation of HWP in air refueling[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2020, 46(10):1958-1965.
|