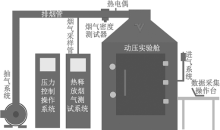
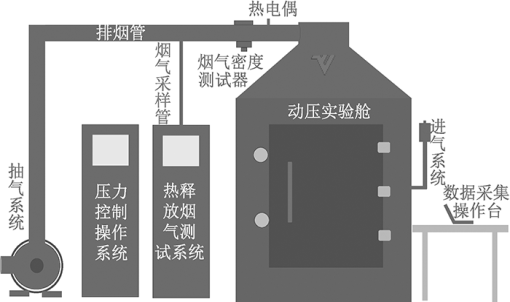
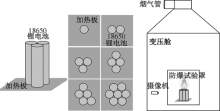
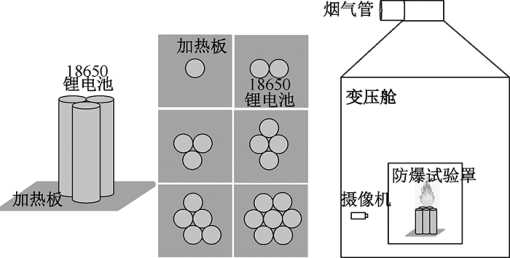
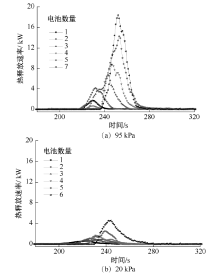
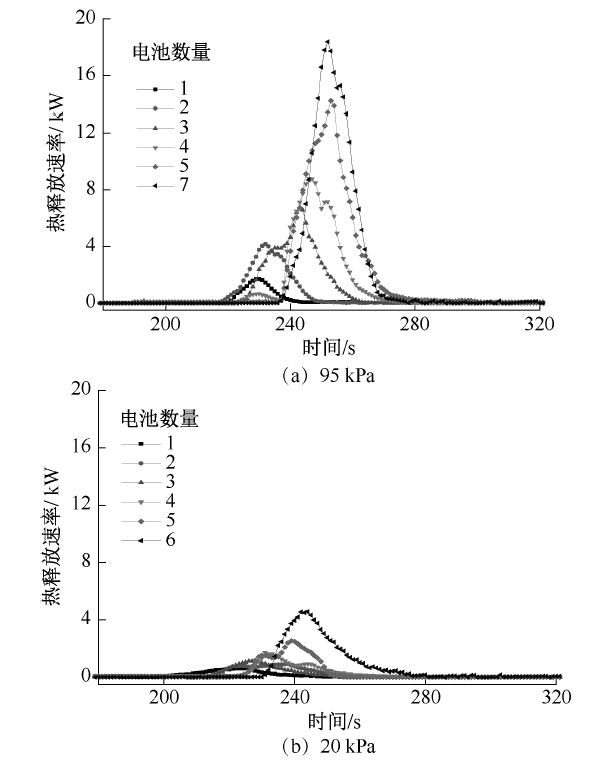
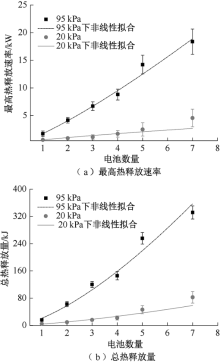
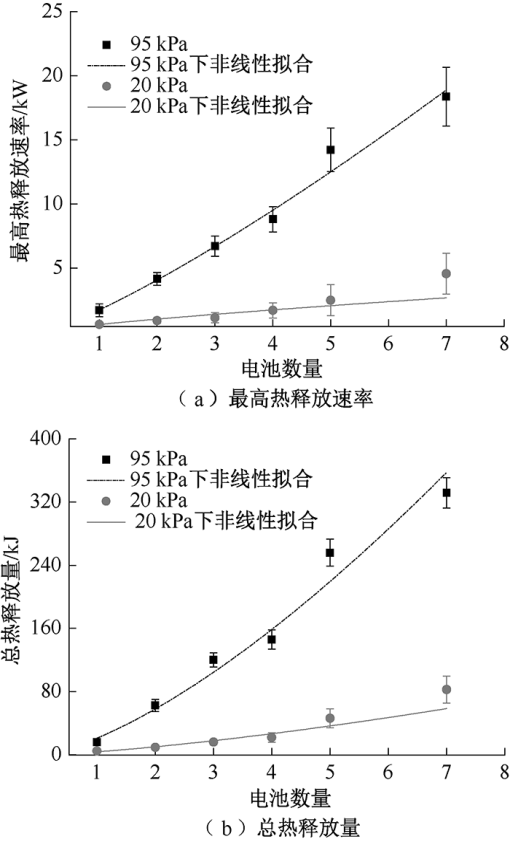
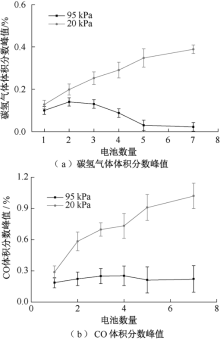
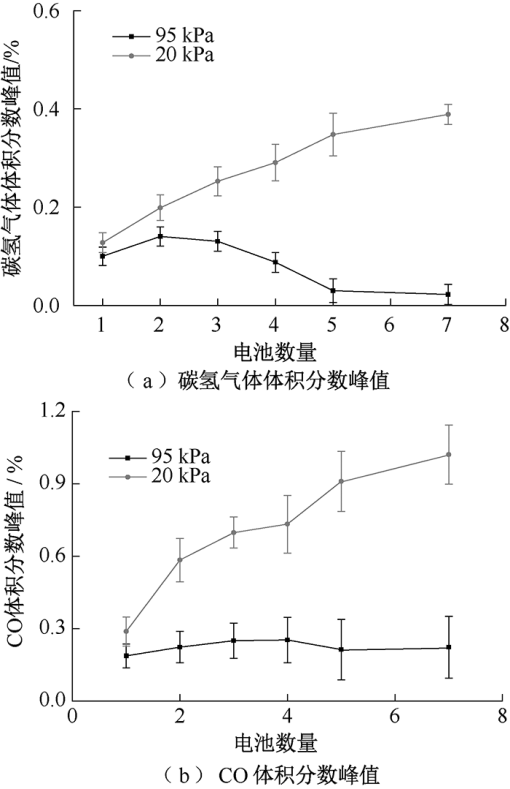
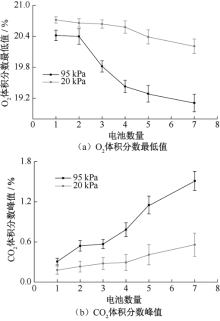
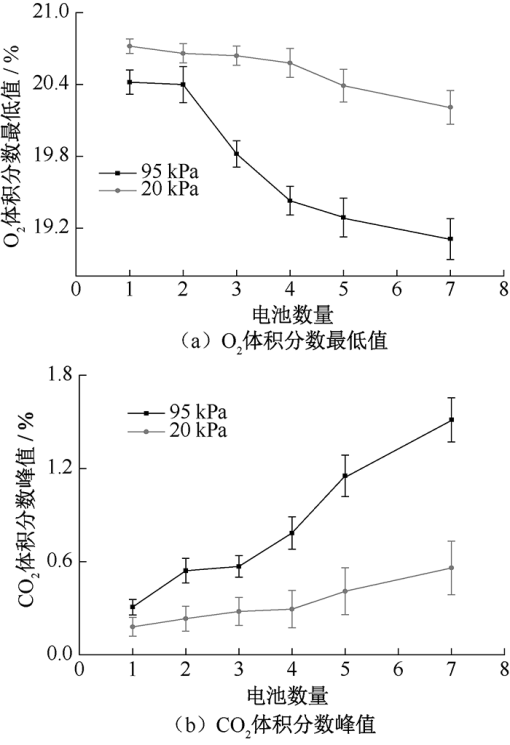
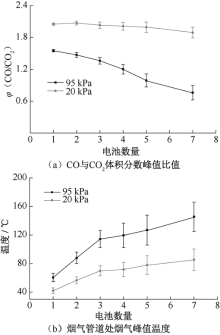
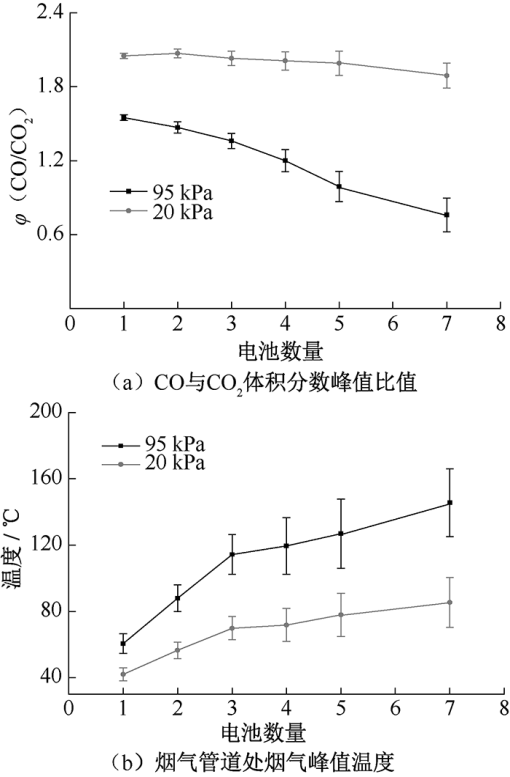
| [1] |
高飞, 杨凯, 李大贺, 等. 锂离子电池组件燃烧性及危险性评价[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2015, 25(8): 62-67.
|
|
GAO Fei, YANG Kai, LI Dahe, et al. Combustibility and risk assessment of lithium-ion batteries module[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2015, 25(8): 62-67.
|
| [2] |
孙强, 王海斌, 谢松, 等. 低压环境对锂电池热失控释放温度影响[J]. 中国安全生产科学技术, 2019, 15(11):78-83.
|
|
SUN Qiang, WANG Haibin, XIE Song, et al. Effects of low pressure environment on the thermal runaway release temperature of lithium battery[J]. Journal of Safety Science and Technology, 2019, 15(11):78-83.
|
| [3] |
FENG Xuning, SUN Jing, OUYANG Minggao, et al. Characterization of penetration induced thermal runaway propagation process within a large format lithium ion battery module[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2015, 275:261-273.
doi: 10.1016/j.jpowsour.2014.11.017
|
| [4] |
PING Ping, WANG Qingsong, HUANG Ping, et al. Thermal behaviour analysis of lithium-ion battery at elevated temperature using deconvolution method[J]. Applied Energy, 2014, 129(15):261-273.
doi: 10.1016/j.apenergy.2014.04.092
|
| [5] |
邓康, 张英, 徐伯乐, 等. 磷酸铁锂电池组燃烧特性研究[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2019, 29(11):83-88.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2019.11.014
|
|
DENG Kang, ZHANG Ying, XU Bole, et al. Study on combustion characteristics of lithium iron phosphate battery pack[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2019, 29(11):83-88.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2019.11.014
|
| [6] |
张青松, 郭超超, 秦帅星. 锂离子电池燃爆特征及空运安全性研究[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2016, 26(2):50-55.
|
|
ZHANG Qingsong, GUO Chaochao, QIN Shuaixing. Study on lithium-ion batteries explosive characteristics and aviation transportation safety[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2016, 26(2):50-55.
|
| [7] |
Federal Avaition Administration Office of Security and Hazardous Materials Safety. Events with smoke, fire, exterme heat or explosion involing lithium batteries[R], 2020.
|
| [8] |
FU Yangang, LU Song, SHI Long, et al. Ignition and combustion characteristics of lithium ion batteries under low atmospheric pressure[J]. Energy, 2018, 161:38-45.
doi: 10.1016/j.energy.2018.06.129
|
| [9] |
CHEN Mingyi, LIU Jiahao, LIN Xiao, et al. Combustion characteristics of primary lithium battery at two altitudes[J]. Journal of Thermal Analysis and Calorimetry, 2016, 124(2): 865-870.
doi: 10.1007/s10973-015-5219-3
|
| [10] |
CHEN Mingyi, LIU Jiahao, HE Yaping, et al. Study of the fire hazards of lithium-ion batteries at different pressures[J]. Applied Thermal Engineering, 2017, 125:1061-1074.
doi: 10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2017.06.131
|
| [11] |
XIE Song, REN Lixiang, YANG Xiaoyong, et al. Influence of cycling aging and ambient pressure on the thermal safety features of lithium-ion battery[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2020, 448:1181-1189.
|
| [12] |
XIE Song, REN Lixiang, GONG Yize, et al. Effect of charging/discharging rate on the thermal runaway characteristics of lithium-ion batteries in low pressure[J]. Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 2020, 167(14):234-243.
|
| [13] |
CHEN Xiantao, ZHANG Xu, WANG Haibin, et al. Influence of ambient pressure and heating power on the thermal runaway features of lithium-ion battery[J]. Journal of Electrochemical Energy Conversion and Storage, 2020, 18(2):1-24.
|
| [14] |
刘奕, 邹晓龙, 陈现涛, 等. 高高原环境下锂离子电池热失控烟气特性[J]. 消防科学与技术, 2020, 39(5):704-709.
|
|
LIU Yi, ZOU Xiaolong, CHEN Xiantao, et al. Study on characteristics of gases emission during lithium batteries thermal runaway at high plateau[J]Fire science and Technology, 2020, 39(5):704-709.
|
| [15] |
LYON R E, WALTERS R N. Energetics of lithium-ion battery failure[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2016, 318(15):164-172.
doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2016.06.047
|
| [16] |
QUINTIERE J G. On methods to measure the energetics of a lithium-ion battery in thermal runaway[J]. Fire Safety Journal, 2019, 2(11):111-119.
doi: 10.1016/0379-7112(79)90037-7
|