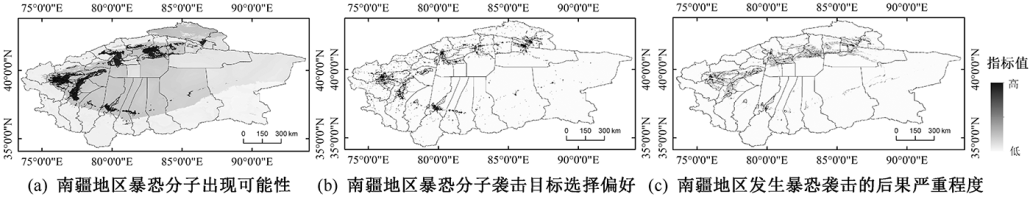
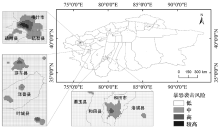
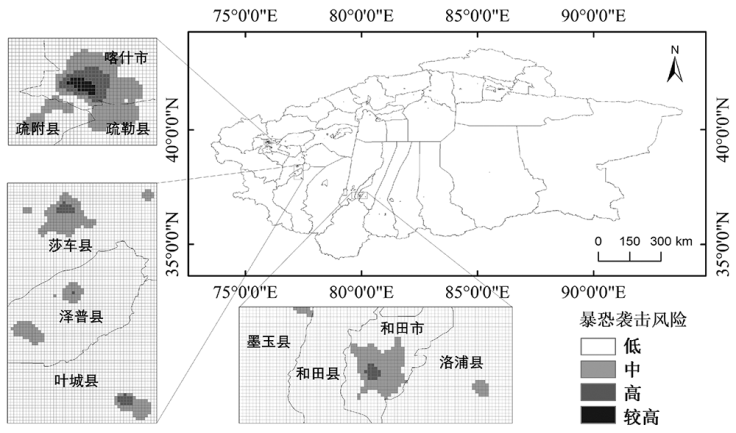
| [1] |
张登国. 我国公共安全体系建构研究[M]. 济南: 山东大学出版社, 2017: 2-3.
|
| [2] |
国务院. 国家突发公共事件总体应急预案[J]. 中国防汛抗旱, 2006(1): 16-19.
|
| [3] |
宋英华, 张哲, 方丹辉. 城市洪涝下承灾体暴露性及行人失稳风险分析[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2020, 30(10):105-111.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn 1003-3033.2020.10.015
|
|
SONG Yinghua, ZHANG Zhe, FANG Danhui. Analysis on exposure of disaster-bearing bodies and pedestrians' instability riskunder urban waterlogging[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2020, 30(10):105-111.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn 1003-3033.2020.10.015
|
| [4] |
ZHENG Zhong, GAO Yanghua, YANG Qingyuan, et al. Predicting forest fire risk based on mining rules with ant-miner algorithm in cloud-rich areas[J]. Ecological Indicators, 2020, 118: DOI: 10.1016/j.ecolind.2020.106772.
doi: 10.1016/j.ecolind.2020.106772
|
| [5] |
KHAKZAD N, KHAN F, PALTRINIERI N. On the application of near accident data to risk analysis of major accidents[J]. Reliability Engineering & System Safety, 2014, 126: 116-125.
doi: 10.1016/j.ress.2014.01.015
|
| [6] |
LIU Yaolong, HUANG Xiaoli, DUAN Jin, et al. The assessment of traffic accident risk based on grey relational analysis and fuzzy comprehensive evaluation method[J]. Natural Hazards, 2017, 88(3): 1409-1422.
doi: 10.1007/s11069-017-2923-2
|
| [7] |
齐先志, 王晓霖, 许学瑞. 成品油管道周边区域社会风险分析[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2019, 29(11): 177-182.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2019.11.028
|
|
QI Xianzhi, WANG Xiaolin, XU Xuerui. Societal risk analysis for vicinity of product oil pipelines[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2019, 29(11): 177-182.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2019.11.028
|
| [8] |
doi: 10.1371/currents.outbreaks.00dd49d24b62731f87f12b0e657aa04c
|
| [9] |
戢晓峰, 吴亚欣, 毛润彩, 等. 突发公共卫生事件下公交暴露风险辨识方法:以深圳应对新型冠状病毒肺炎为例[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2021, 31(2): 89-98.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn 1003-3033.2021.02.013
|
|
JI Xiaofeng, WU Yaxin, MAO Runcai, et al. Identification method of bus exposure risk under public health emergencies: taking Shenzhen's fight against COVID-19 as an example[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2021, 31(2): 89-98.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn 1003-3033.2021.02.013
|
| [10] |
LI Guangquan, HAINING R, RICHARDSON S, et al. Space-time variability in burglary risk: a Bayesian spatio-temporal modelling approach[J]. Spatial Statistics, 2014, 9: 180-191.
doi: 10.1016/j.spasta.2014.03.006
|
| [11] |
REID A A, FRANK R, IWANSKI N, et al. Uncovering the spatial patterning of crimes: a criminal movement model (CriMM)[J]. Journal of Research in Crime and Delinquency, 2014, 51(2): 230-255.
doi: 10.1177/0022427813483753
|
| [12] |
师维, 孙振雷, 孙卫华, 等. 中国反恐怖主义法研究[M]. 北京: 中国人民公安大学出版社, 2016:12-14.
|
| [13] |
SCHIERMEIER Q. Attempts to predict terrorist attacks hit limits[J]. Nature, 2015, 517:419-420.
doi: 10.1038/517419a
|
| [14] |
滑腾飞, 白玲, 刘大庆. 城市遭受恐怖袭击的风险评估模型研究[J]. 测绘与空间地理信息, 2016, 39(5): 38-40.
|
|
HUA Tengfei, BAI Ling, LIU Daqing. Research on risk evaluation model of urban terrorist attacks[J]. Geomatics & Spatial Information Technology, 2016, 39(5): 38-40.
|
| [15] |
吴文辉, 郭璇, 潘翔, 等. 引入攻防树思想的“软目标”恐怖袭击风险建模[J]. 火力与指挥控制, 2019, 44(7): 79-84.
|
|
WU Wenhui, GUO Xuan, PAN Xiang, et al. "Soft targets" terrorist attacks risk modeling by introduction of attack-defense trees[J]. Fire Control & Command Control, 2019, 44(7): 79-84.
|
| [16] |
陈冲, 庞珣. 非洲恐怖袭击时空规律的大数据分析:基于GIS 技术和分离总体持续期模型[J]. 外交评论:外交学院学报, 2020, 37(2): 121-154.
|
|
CHEN Chong, PANG Xun. Spatial-temporal patterns of terrorist attacks in Africa: a big-data analysis with GIS techniques and split-population duration modeling[J]. Foreign Affairs Review, 2020, 37(2): 121-154.
|
| [17] |
ZHANG Xun, JIN Min, FU Jingying, et al. On the risk assessment of terrorist attacks coupled with multi-source factors[J]. ISPRS International Journal of Geo-Information, 2018, 7(9): DOI: 10.3390/ijgi7090354.
doi: 10.3390/ijgi7090354
|
| [18] |
HAO Mengmeng, JIANG Dong, DING Fangyu, et al. Simulating spatio-temporal patterns of terrorism incidents on the Indochina Peninsula with GIS and the random forest method[J]. ISPRS International Journal of Geo-Information, 2019, 8(3): DOI: 10.3390/ijgi8030133.
doi: 10.3390/ijgi8030133
|
| [19] |
WEISS D J, NELSON A, GIBSON H S, et al. A global map of travel time to cities to assess inequalities in accessibility in 2015[J]. Nature, 2018, 553(7688): 333-336.
doi: 10.1038/nature25181
|
| [20] |
HENGL T. Monthly precipitation in mm at 1 km resolution based on SM2RAIN-ASCAT 2007-2018, IMERGE, CHELSA Climate and WorldClim [DB/OL]. [2020-07-30]. https://zenodo.org/record/3256275.
|
| [21] |
DANIELSON J J, GESCH D B. Global multi-resolution terrain elevation data 2010 (GMTED2010)[R]. US Geological Survey, 2011.
|
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
GONG Peng, LIU Han, ZHANG Meinan, et al. Stable classification with limited sample: transferring a 30-m resolution sample set collected in 2015 to mapping 10-m resolution global land cover in 2017[J]. Science Bulletin, 2019, 64(6): 370-373.
doi: 10.1016/j.scib.2019.03.002
|
| [24] |
SCULLEY D. Web-scale k-means clustering[C]. Proceedings of the 19th International Conference on World Wide Web, 2010: 1177-1178.
|
| [25] |
CALINSKI T, HARABASZ J. A dendrite method for cluster analysis[J]. Communications in Statistics, 1974, 3(1): 1-27.
|
| [26] |
AHMED R. Terrorist ideologies and target selection[J]. Journal of Applied Security Research, 2018, 13(3): 376-389.
doi: 10.1080/19361610.2018.1463140
|
| [27] |
ONAT I. An analysis of spatial correlates of terrorism using risk terrain modeling[J]. Terrorism and Political Violence, 2019, 31(2): 277-298.
doi: 10.1080/09546553.2016.1215309
|
| [28] |
START. Global terrorism database[DB/OL]. [2020-07-19]. https://www.start.umd.edu/gtd/.
|