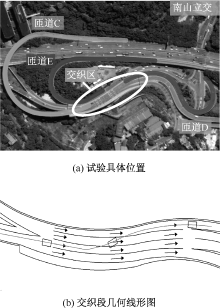
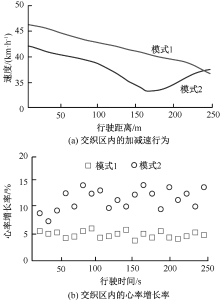
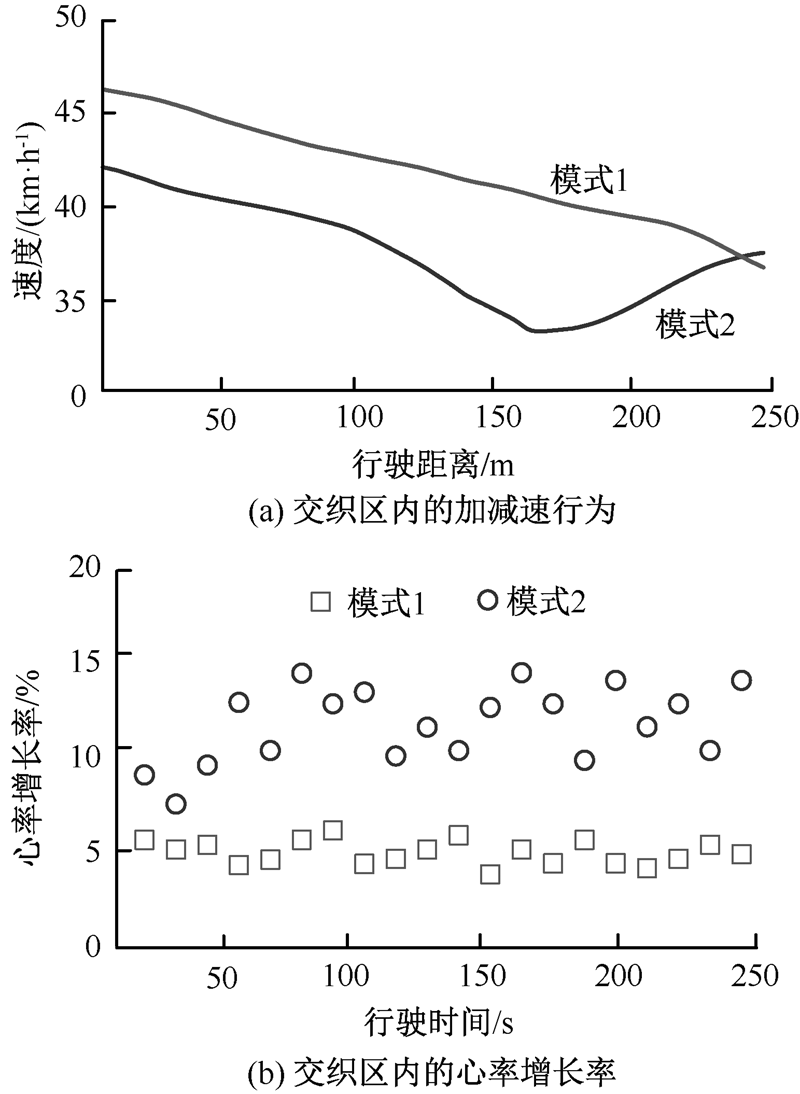
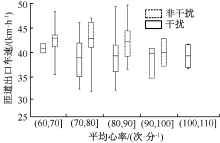
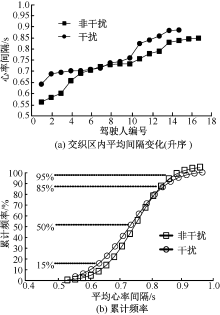
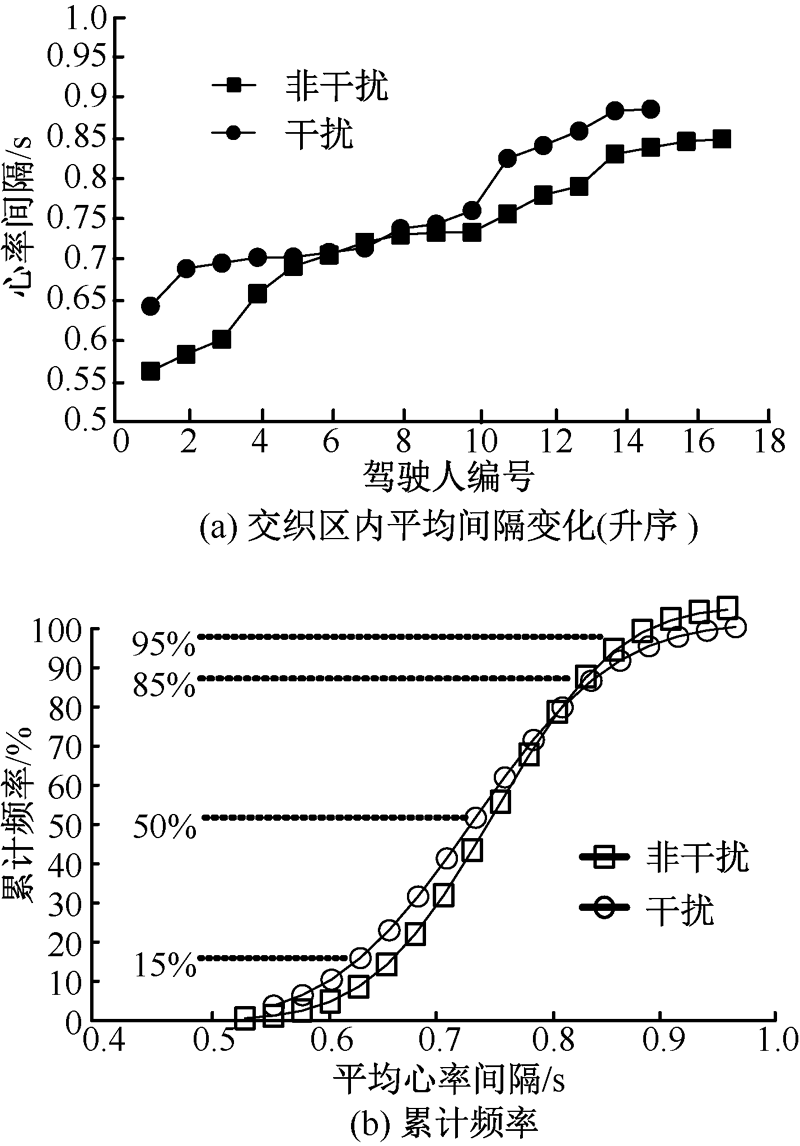
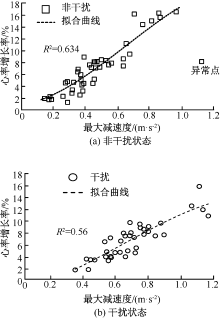
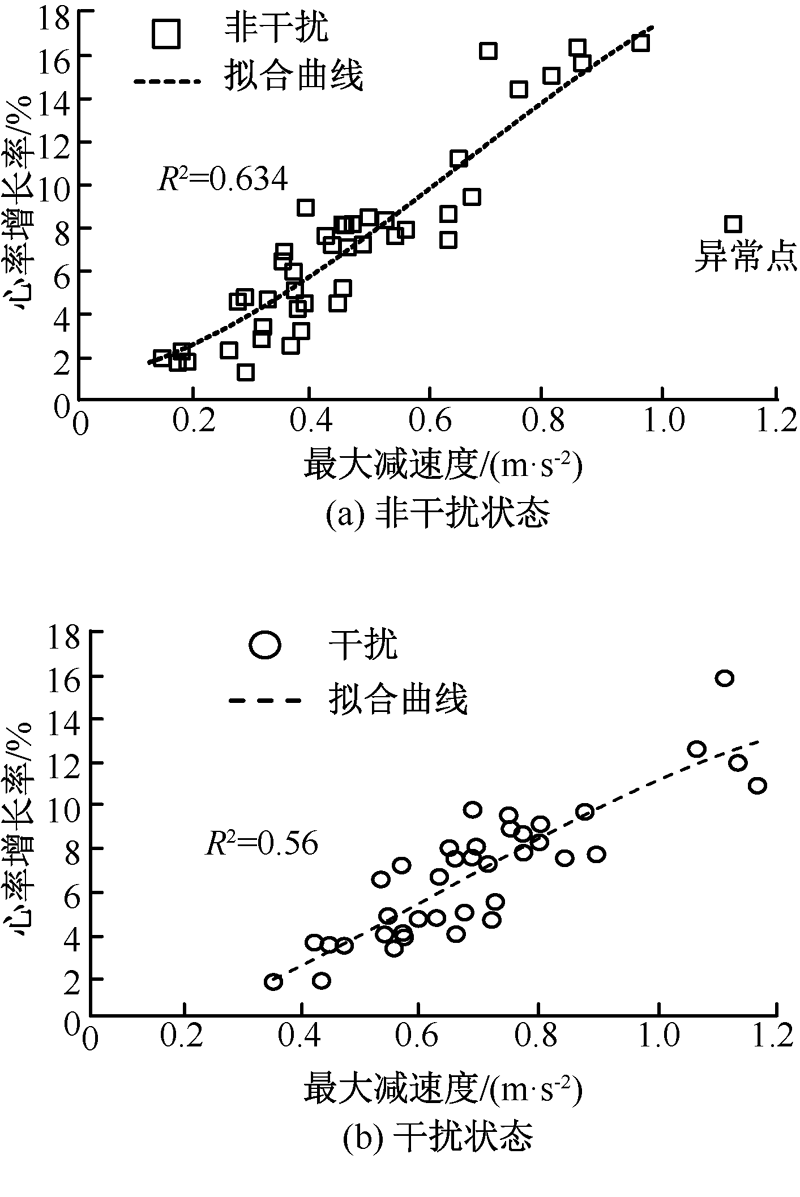
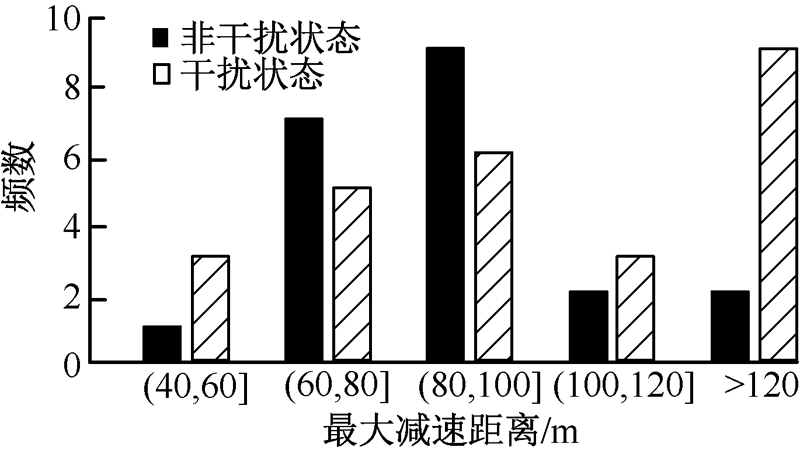
| [1] |
刘建蓓, 马小龙, 张志伟, 等. 基于心电分析的青藏高原驾驶人疲劳特性[J]. 交通运输工程学报, 2016, 16 (4):151-158.
|
|
LIU Jianbei, MA Xiaolong, ZHANG Zhiwei, et al. Fatigue characteristics of driver in Qinghai-Tibet Plateau based on electrocardiogram analysis[J]. Journal of Traffic and Transportation Engineering, 2016, 16(4): 151-158.
|
| [2] |
林声, 刘建蓓, 阎莹, 等. 基于驾驶负荷的山区高速公路长大下坡路段安全性评价模型[J]. 交通运输工程学报, 2013, 13(6):99-106.
|
|
LIN Sheng, LIU Jianbei, YAN Ying, et al. Safety evaluation model of long-steep downgrade section for montane highway based on driving workload[J]. Journal of Traffic and Transportation Engineering, 2013, 13(6): 99-106.
|
| [3] |
TOZMAN T, MAGDAS E S, MACDOUGALL H G, et al. Understanding the psychophysiology of flow: a driving simulator experiment to investigate the relationship between flow and heart rate variability[J]. Computers in Human Behavior, 2015,52:408-418.
|
| [4] |
李天彪, 艾力·斯木吐拉. 高原公路驾驶员心率变异性试验分析[J]. 科学技术与工程, 2015, 15(19):211-216.
|
|
LI Tianbiao, ELI Ismutulla. Experiment analysis of driver's HRV on plateau highway[J]. Science Technology and Engineering, 2015, 15(19): 211-216.
|
| [5] |
朱兴林, 高超, 艾力·斯木吐拉. 高原公路不同天气状况对驾驶人工作负荷的影响[J]. 科学技术与工程, 2020, 20(20): 8400-8406.
|
|
ZHU Xinglin, GAO Chao, ELI Ismutulla. The influence of different weather conditions on driver's workload on plateau road[J]. Science Technology and Engineering, 2020, 20(20): 8400-8406.
|
| [6] |
陈鹏, 艾力·斯木吐拉. 高原公路驾驶员应激反应能力分析[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2016, 26(4):8-13.
|
|
CHEN Peng, ElI Ismutulla. Analysis of plateau highway driver stress response capability[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2016, 26(4):8-13.
|
| [7] |
胡立伟, 林玉珍. 驾驶人公路驾车过程中主要生理参数变化规律研究[J]. 交通运输系统工程与信息, 2014, 14(1):41-46.
|
|
HU Liwei, LIN Yuzhen. Variation law of driver' s main physiological indicators driving on highway[J]. Journal of Transportation Systems Engineering and Information Technology, 2014, 14(1): 41-46.
|
| [8] |
袁伟, 郭应时, 付锐, 等. 城市道路类型对驾驶人工作负荷的影响[J]. 长安大学学报:自然科学版, 2014, 34(5):95-100.
|
|
YUAN Wei, GUO Yingshi, FU Rui, et al. Influence of urban road section types on drivers' workload[J]. Journal of Chang'an University:Natural Science Edition, 2014, 34(5): 95-100.
|
| [9] |
李显生, 孟凡淞, 郑雪莲, 等. 基于心率变异性的应激场景下驾驶人心理特性分析[J]. 上海交通大学学报, 2018, 52(2):163-168.
|
|
LI Xiansheng, MENG Fansong, ZHENG Xuelian, et al. Psychological characteristics of drivers' in the stress scene based on heart rate variability[J]. Journal of Shanghai Jiaotong University, 2018, 52(2): 163-168.
|
| [10] |
焦方通, 杜志刚, 王首硕, 等. 城市水下特长隧道弯道驾驶人扫视行为研究[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2019, 29(7):104-109.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2019.07.017
|
|
JIAO Fangtong, DU Zhigang, WANG Shoushuo, et al. Research on saccade behavior of drivers in extra-long urban underwater tunnel curves[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2019, 29(7):104-109.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2019.07.017
|
| [11] |
乔建刚, 吴艳霞, 许军. 村镇道路会车特性与驾驶员心生理变化关系研究[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2019, 29(3):8-13.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2019.03.002
|
|
QIAO Jiangang, WU Yanxia, XU Jun. Study on relations between village road vehicles meeting characteristics and driver's psychological physiological state[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2019, 29(3):8-13.
|
| [12] |
GUO Yanyong, SAYEDB T, ESSAB M. Real-time conflict-based Bayesian Tobit models for safety evaluation of signalized intersections[J]. Accident Analysis and Prevention, 2020, 144:DOI:10.1016/j.aap.2020.105660.
|
| [13] |
GUO Yanyong, SAYEDB T, ESSAB M. Drivers' effective decelerating zone in an urban vehicle-Pedestrian conflict situation: observational studies and analyses[J]. Transportation Research Part D, 2019,66:76-84.
|