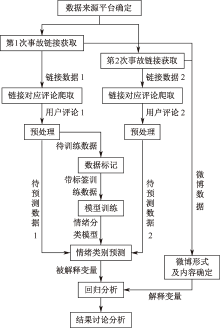
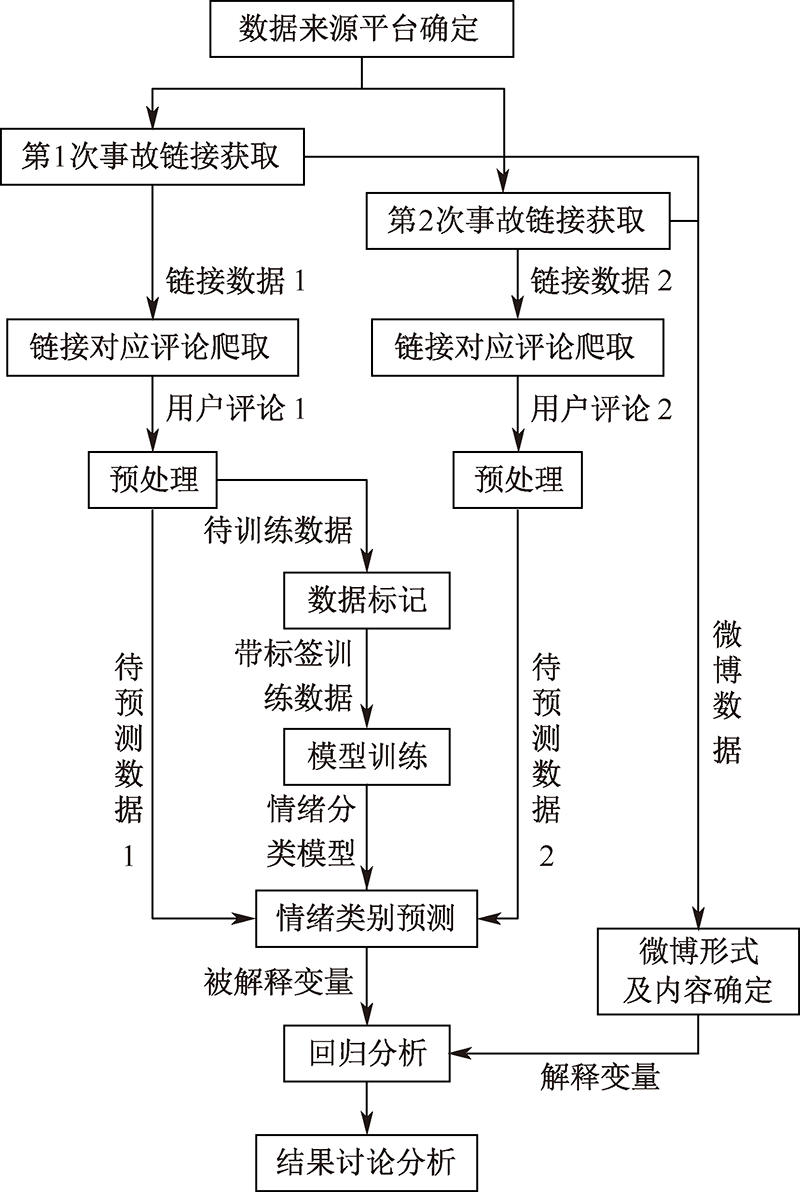
| [1] |
国家统计局. 中华人民共和国2020年国民经济和社会发展统计公报[J]. 中国统计, 2021(3):8-22.
|
| [2] |
陈伟珂, 王炳淳. 基于SEM的地铁施工不安全行为与认知关系的研究[J]. 中国安全生产科学技术, 2015, 11(3):154-160.
|
|
CHEN Weike, WANG Bingchun. Study on relationship between unsafe behaviors and cognition in subway construction based on SEM[J]. Journal of Safety Science and Technology, 2015, 11(3):154-160.
|
| [3] |
LI Hujun, CHEN Huihua, ZHAO Zhengyu, et al. Tunnel construction workers' cognitive biases and unsafe behaviors: the mediating effects of risk perceptions[J]. Advances in Civil Engineering, 2020, 2020: 1-10.
|
| [4] |
叶贵, 越宏哲, 冯新怡, 等. 建筑工人不安全行为的认知失效致因仿真研究[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2020, 30(11): 6-12.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn 1003-3033.2020.11.002
|
|
YE Gui, YUE Hongzhe, FENG Xinyi, et al. Simulation study on causes of cognitive failure of construction workers' unsafe behavior[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2020, 30(11): 6-12.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn 1003-3033.2020.11.002
|
| [5] |
郭进平, 王朵. 基于乐观偏差的人车交互行为影响研究[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2020, 30(10): 34-40.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn 1003-3033.2020.10.005
|
|
GUO Jinping, WANG Duo. Influence study on pedestrian-vehicle interaction behaviors based on optimistic bias[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2020, 30(10): 34-40.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn 1003-3033.2020.10.005
|
| [6] |
LUO Xiaochun, LI Heng, HUANG Ting, et al. A field experiment of workers' responses to proximity warnings of static safety hazards on construction sites[J]. Safety Science, 2016, 84:216-224.
doi: 10.1016/j.ssci.2015.12.026
|
| [7] |
ZHAO Dong, MCCOY A P, KLEINER B M, et al. Stakeholder perceptions of risk in construction[J]. Safety Science, 2016, 82:111-119.
pmid: 26441481
|
| [8] |
刘素霞, 朱雨晴, 梅强. 损失认知、 安全态度与企业安全生产行为关系研究[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2017, 27(10):123-129.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2017.10.021
|
|
LIU Suxia, ZHU Yuqing, MEI Qiang. Relationships between perception of loss, safety attitude and enterprises' work safety behavior[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2017, 27(10):123-129.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2017.10.021
|
| [9] |
韩豫, 尹贞贞, 刘嘉伦, 等. 建筑工人的危险认知偏差特性及成因[J]. 土木工程与管理学报, 2019, 36(5):56-61.
|
|
HAN Yu, YIN Zhenzhen, LIU Jialun, et al. Characteristics and causes of hazard cognitive bias of construction workers[J]. Journal of Civil Engineering and Management, 2019, 36(5):56-61.
|
| [10] |
CHANDON P, MORWITZ V G, REINARTZ W J. Do intentions really predict behavior? self-generated validity effects in survey research[J]. Journal of Marketing, 2005, 69(2):1-14.
|
| [11] |
LI Qiang, XIA Menglin, GUO Xiaona, et al. Spatial characteristics and influencing factors of risk perception of haze in China: the case study of publishing online comments about haze news on sina[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2021, 785(2): DOI: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.147236.
doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.147236
|
| [12] |
GENG Shuolin, ZHOU Qi, LI Mingjie, et al. Spatial-temporal differences in disaster perception and response among new media users and the influence factors: a case study of the Shouguang flood in Shandong province[J]. Natural Hazards, 2021, 105(6): 1-22.
doi: 10.1007/s11069-020-04112-7
|
| [13] |
王炼, 贾建民. 突发性灾害事件风险感知的动态特征:来自网络搜索的证据[J]. 管理评论, 2014, 26(5):169-176.
|
|
WANG Lian, JIA Jianmin. Risk perception dynamics in unexpected disaster events: evidence from online search[J]. Management Review, 2014, 26(5):169-176.
|
| [14] |
LERNER J S, LI Ye, VALDESOLO P, et al. Emotion and decision making[J]. Annual Review of Neuroscience, 2015, 66(1): 799-823.
|
| [15] |
ERTEN J G, TOPOLINSKI S. Shades of surprise: assessing surprise as a function of degree of deviance and expectation constraints[J]. Cognition, 2019, 192: DOI: 10.1016/j.cognition.2019.05.023.
doi: 10.1016/j.cognition.2019.05.023
|
| [16] |
REISENZEIN R, HORSTMANN G, SCHÜTZWOHL A. The cognitive-volutionary model of surprise: a review of the evidence[J]. Topics in Cognitive Science, 2017, 11(1):1-25.
doi: 10.1111/tops.12362
|
| [17] |
MAGUIRE P, MOSER P, MAGUIRE R, et al. Seeing patterns in randomness: a computational model of surprise[J]. Topics in Cognitive Science, 2019, 11(1): 103-118.
doi: 10.1111/tops.12345
|
| [18] |
MACEDO L, CARDOSO A. A contrast-based computational model of surprise and its applications[J]. Topics in Cognitive Science, 2019, 11(1): 88-102.
doi: 10.1111/tops.12310
|
| [19] |
MOBBS D, LEDOUX J. The ethological deconstruction of fear(s)[J]. Current Opinion in Behavioral Sciences, 2018, 24: 32-37.
doi: 10.1016/j.cobeha.2018.02.008
|
| [20] |
李华强. 突发性灾害中的公众风险感知与应急管理:基于汶川地震的研究[D]. 成都: 西南交通大学, 2011.
|
|
LI Huaqiang. Risk awareness and emergency management in disastrous events:the case of the Wenchuan earthquake[D]. Chengdu: Southwest Jiaotong University, 2011.
|
| [21] |
ABDULLELAH A, NAHED A, AIED A K, et al. Risk perceptions, fear, depression, anxiety, stress and coping among Saudi nursing students during the COVID-19 pandemic[J]. Journal of Mental Health:Abingdon, England, 2021, 30(2):194-201.
|
| [22] |
CHAPIN J R, PIERCE M. Optimistic bias, sexual assault, and fear[J]. The Journal of general psychology, 2012, 139(1): 19-28.
doi: 10.1080/00221309.2011.635724
|
| [23] |
WAKE S, WORMWOOD J, SATPUTE A B. The influence of fear on risk taking: a meta-analysis[J]. Cognition & Emotion, 2020, 34(6): 1143-1159.
|
| [24] |
DAS S, CHEN M. Yahoo! for amazon: extracting market sentiment from stock message boards[C]. Proceedings of the Asia Pacific Finance Association Annual Conference, 2001:35-43.
|
| [25] |
ZHENG Jianzhong, CHEN Xiaoliang, DU Yajun, et al. Short text sentiment analysis of micro-blog based on BERT[C]. 13th International Conference on Multimedia and Ubiquitous Engineering (MUE)/14th International Conference on Future Information Technology (Future Tech), 2019:390-396.
|
| [26] |
罗俊, 陈黎飞. 基于BERT的不完全数据情感分类[J]. 计算机应用, 2021, 41(1):139-144.
doi: 10.11772/j.issn.1001-9081.2020061066
|
|
LUO Jun, CHEN Lifei. Sentiment classification of incomplete data based on bidirectional encoder representations from transformers[J]. Journal of Computer Applications, 2021, 41(1):139-144.
doi: 10.11772/j.issn.1001-9081.2020061066
|
| [27] |
常城扬, 王晓东, 张胜磊. 基于深度学习方法对特定群体推特的动态政治情感极性分析[J]. 数据分析与知识发现, 2021, 5(3):121-131.
|
|
CHANG Chengyang, WANG Xiaodong, ZHANG Shenglei. Polarity analysis of dynamic political sentiments from tweets with deep learning method[J]. Data Analysis and Knowledge Discovery, 2021, 5(3):121-131.
|
| [28] |
许荣, 赵昶, 常嘉路. 特别重大事故影响个体风险偏好吗?基于中国家庭金融调查的资产配置实证[J]. 保险研究, 2020(12):54-69.
|
|
XU Rong, ZHAO Chang, CHANG Jialu. Do extraordinarily serious accidents affect individuals' risk preference?evidences based on the china household finance survey[J]. Insurance Studies, 2020(12):54-69.
|
| [29] |
余建华, 孙丽. 国外风险认知研究:回顾与前瞻[J]. 灾害学, 2020, 35(1):161-166.
|
|
YU Jianhua, SUN Li. A study of foreign risk perception: retrospect and prediction[J]. Journal of Catastrophology, 2020, 35(1):161-166.
|