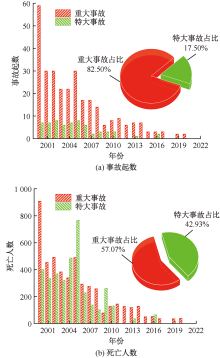
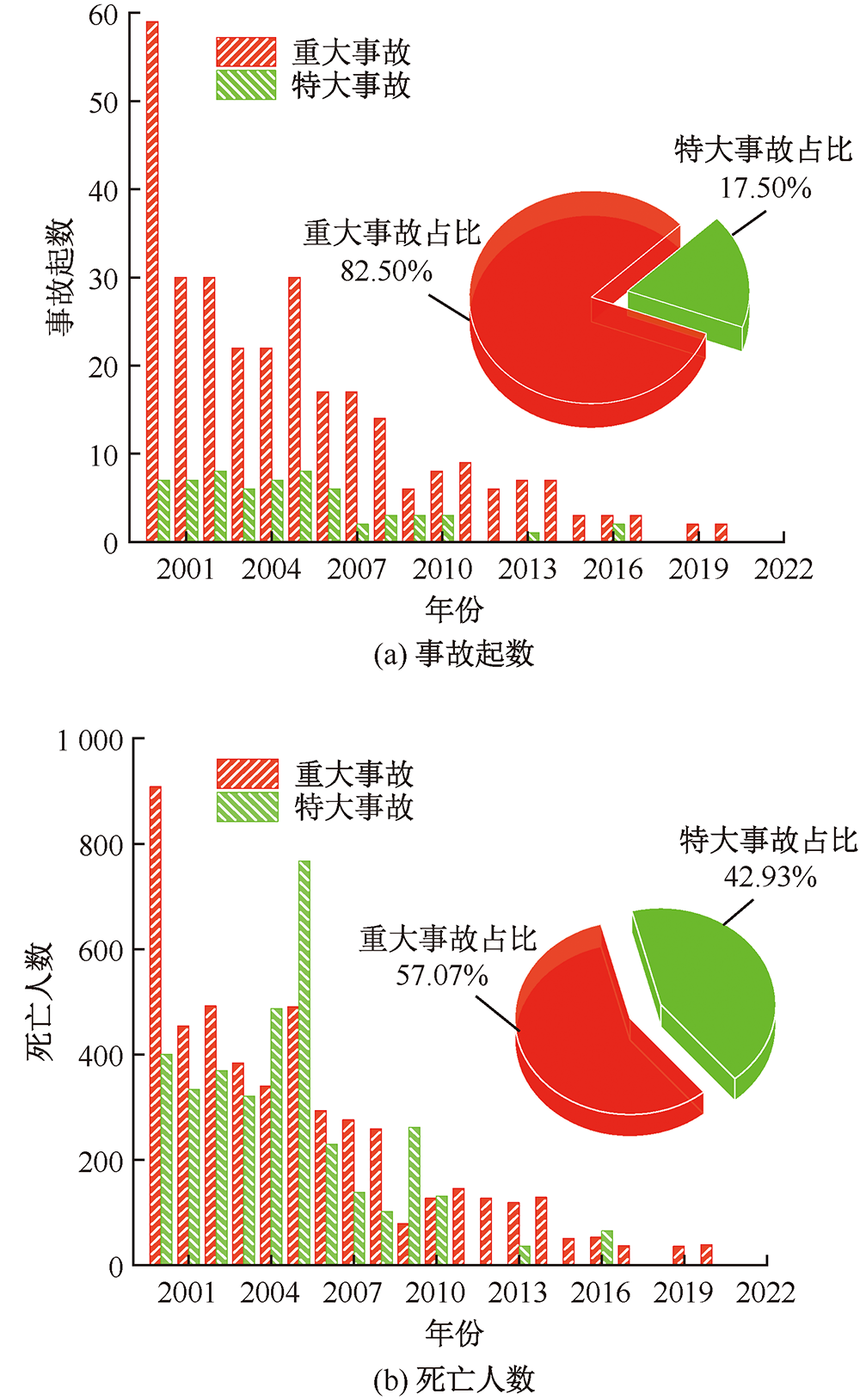
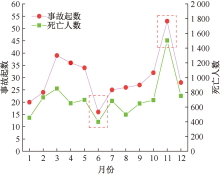
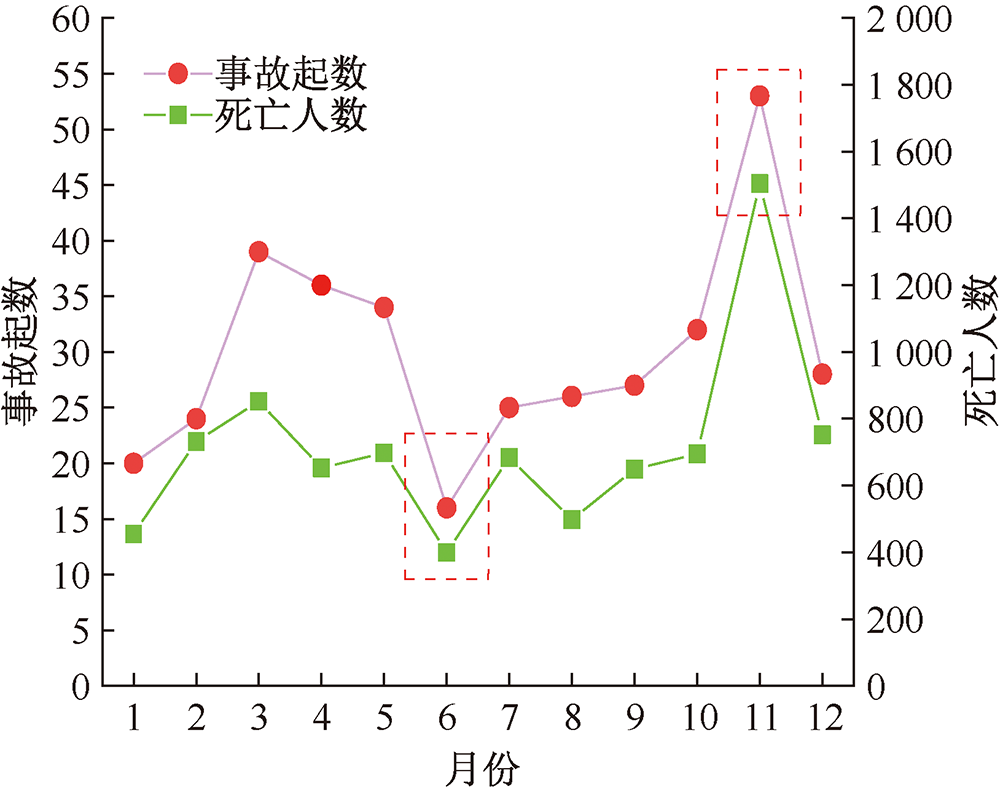
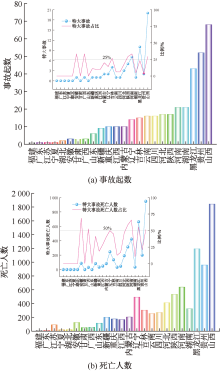
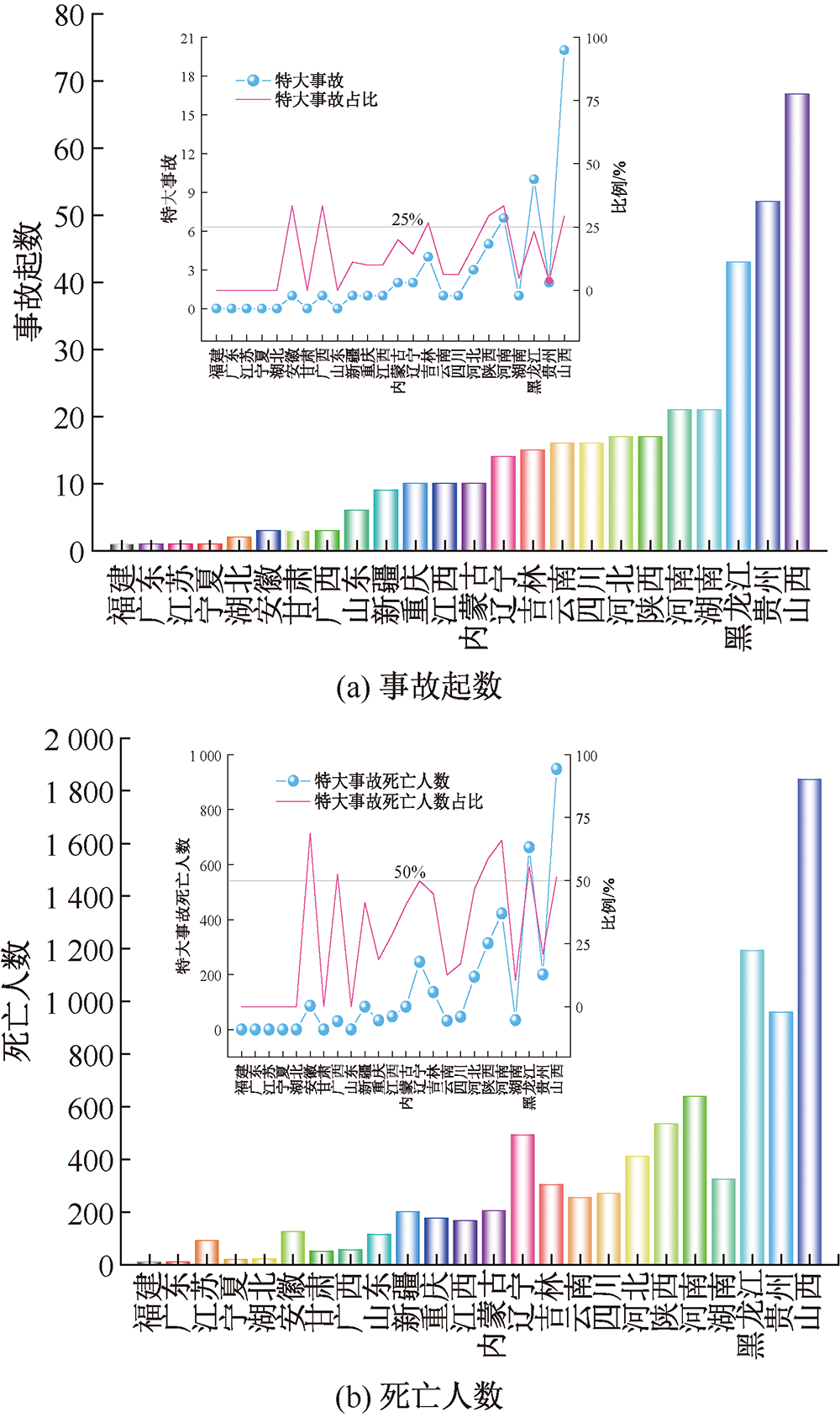
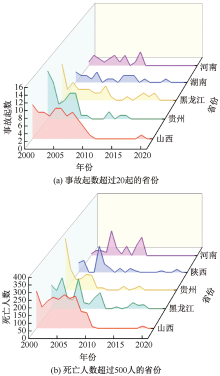
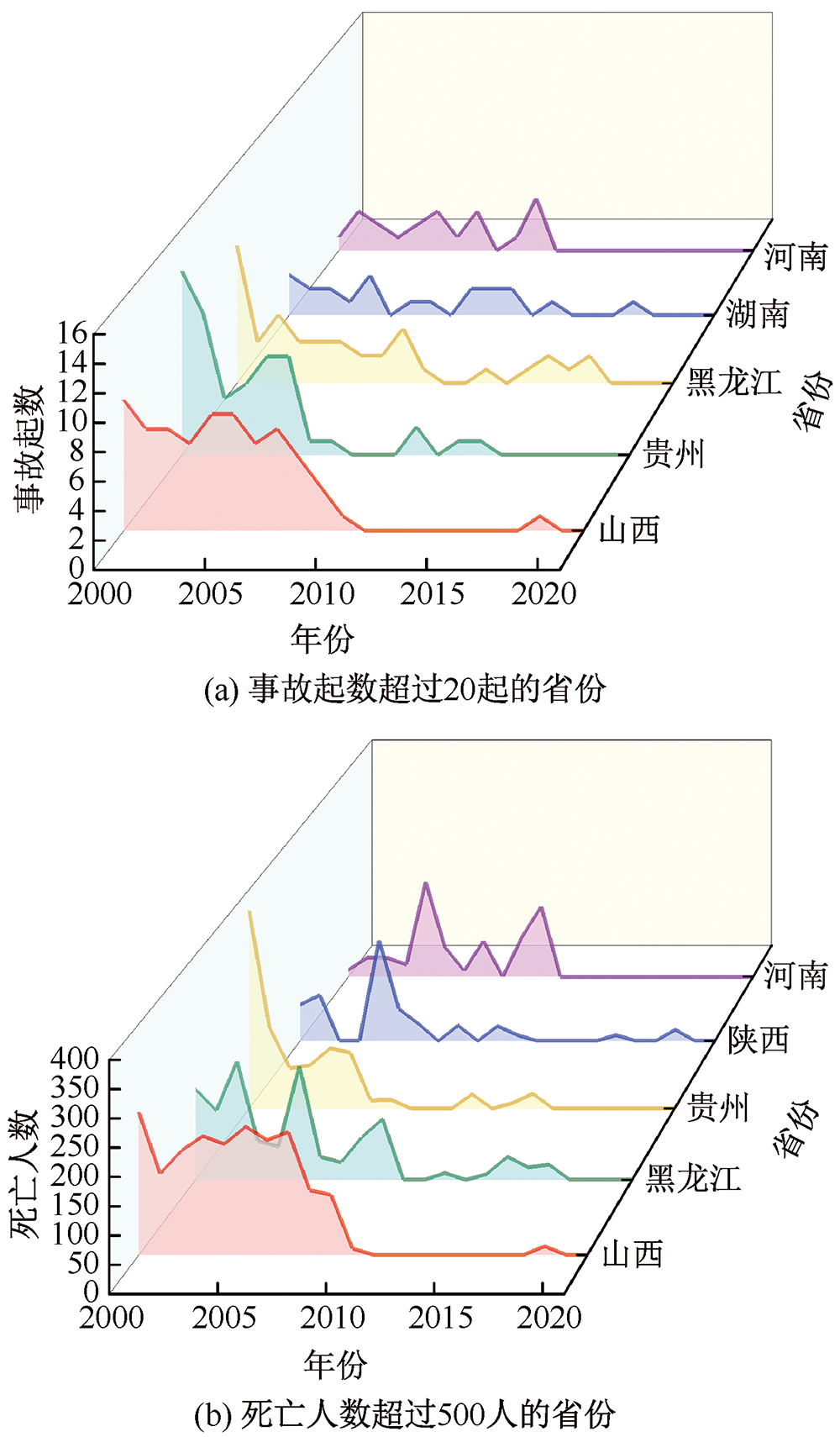
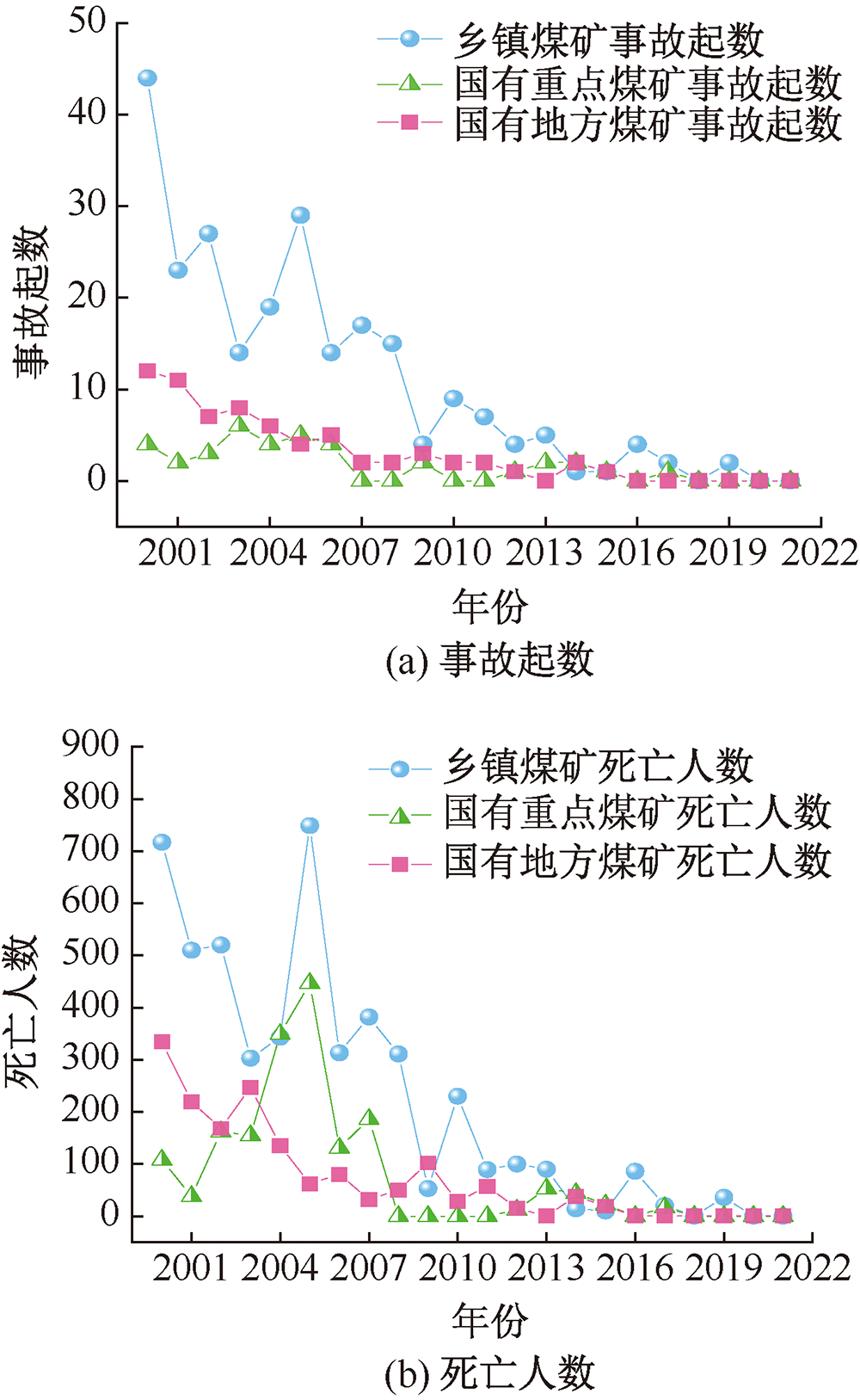
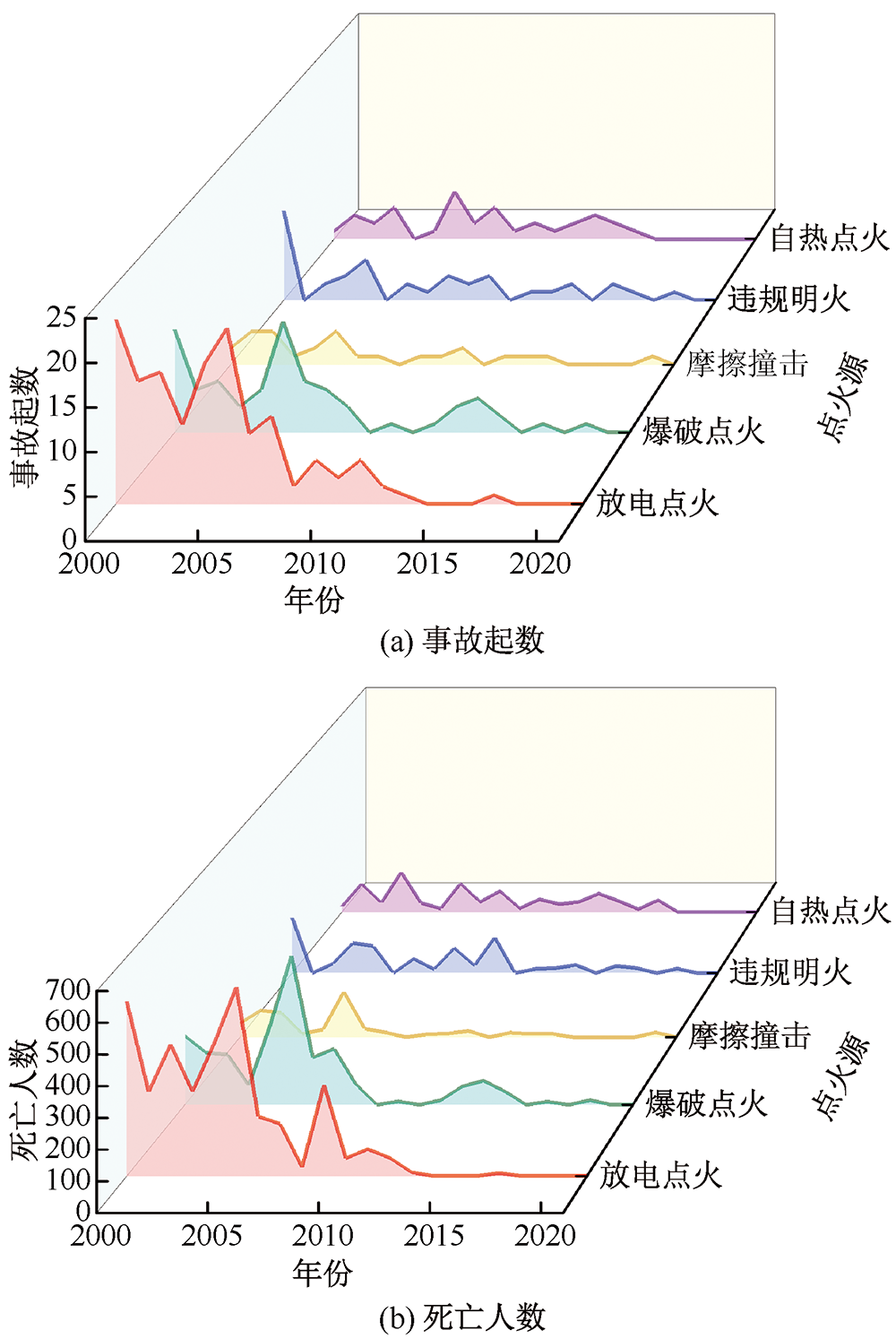
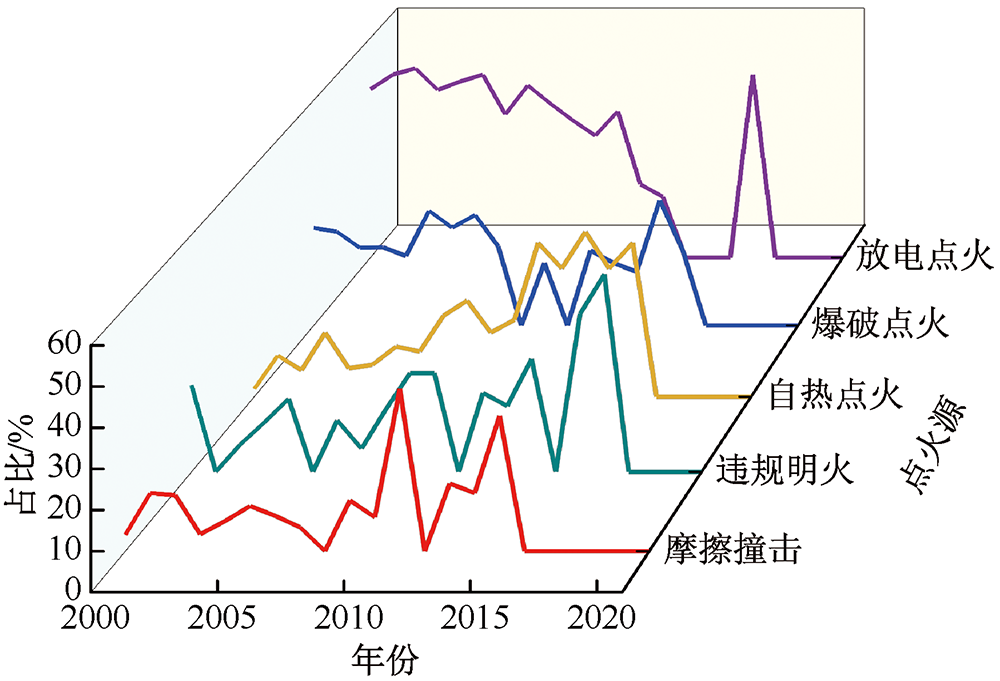
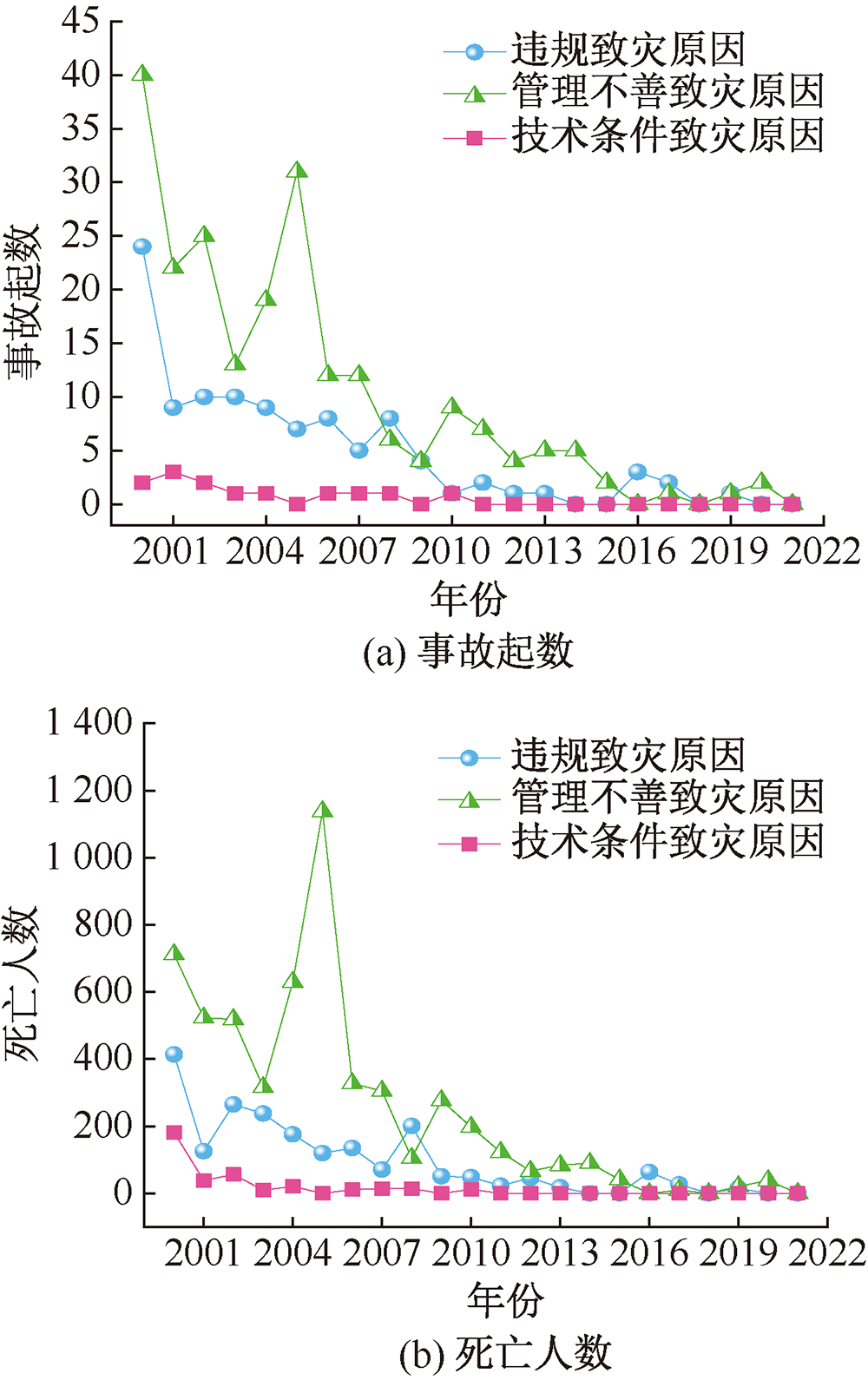
| [1] |
中华人民共和国2021年国民经济和社会发展统计公报[EB/OL]. (2022-02-27). http://www.stats.gov.cn/tjsj/zxfb/202202/t20220227_1827960.html.
|
| [2] |
许素睿. 基于蒙特卡罗法的煤矿工人不安全行为风险评估[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2020, 30(4):172-178.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2020.04.027
|
|
XU Surui. Risk assessment on unsafe behavior of coal miner based on Monte Carlo method[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2020, 30(4):172-178.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2020.04.027
|
| [3] |
王亮, 孙毅民, 褚鹏, 等. 基于时空分布特征的煤层瓦斯测压准确性研究[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2021, 31(2):40-47.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn 1003-3033.2021.02.006
|
|
WANG Liang, SUN Yimin, CHU Peng, et al. Study on accuracy of coal seam gas pressure measurement based on its spatial and temporal distribution characteristics[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2021, 31(2):40-47.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn 1003-3033.2021.02.006
|
| [4] |
李敏. 采空区顶板力—电特征及其点火特性研究[D]. 徐州: 中国矿业大学, 2020.
|
|
LI Min. Study on the mechanical-electrical signature and ignition properties of coal mine goaf roof[D]. Xuzhou: China University of Mining & Technology, 2020.
|
| [5] |
朱云飞, 王德明, 戚绪尧, 等. 1950—2016年我国煤矿特大事故统计分析[J]. 煤矿安全, 2018, 49(10):241-244.
|
|
ZHU Yunfei, WANG Deming, QI Xuyao, et al. Statistics analysis of extra serious coal mine accidents from 1950 to 2016 in China[J]. Safety in Coal Mines, 2018, 49(10):241-244.
|
| [6] |
张津嘉, 许开立, 王贝贝, 等. 特别重大煤矿瓦斯爆炸事故致因分析及管理模式研究[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2016, 26(2):73-78.
|
|
ZHANG Jinjia, XU Kaili, WANG Beibei, et al. Extraordinarily serious gas explosion accidents in coal mines: analysis of causes and research on management mode[J]. China Safety Science Journal. 2016, 26(2):73-78.
|
| [7] |
LI Min, WANG Hetang, WANG Deming, et al. Risk assessment of gas explosion in coal mines based on fuzzy AHP and Bayesian network[J]. Process Safety and Environmental Protection, 2020:DOI: 10.1016/j.psep.2020.01.003.
doi: 10.1016/j.psep.2020.01.003
|
| [8] |
LI Min, WANG Deming, HE Shan. Risk assessment of mine ignition sources using fuzzy Bayesian network[J]. Process Safety and Environmental Protection, 2019:DOI: 10.1016/j.psep.2019.03.029.
doi: 10.1016/j.psep.2019.03.029
|
| [9] |
殷文韬, 傅贵, 袁沙沙, 等. 2001—2012年我国重特大瓦斯爆炸事故特征及发生规律研究[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2013, 23(2):141-147.
|
|
YIN Wentao, FU Gui, YUAN Shasha, et al. Study on basic characteristics and occurrence regularity of major gas explosion accidents in Chinese coal mines during 2001-2012[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2013, 23(2):141-147.
|
| [10] |
李润求, 施式亮, 罗文柯. 煤矿瓦斯爆炸事故特征与耦合规律研究[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2010, 20(2):69-74.
|
|
LI Runqiu, SHI Shiliang, LUO Wenke. Research on cross-coupling characteristics and laws of gas explosion accidents in coal mines[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2010, 20(2):69-74.
|
| [11] |
张慧, 王冬雪, 王启飞. 2005—2016年我国较大及以上煤矿事故特征分析[J]. 安全与环境学报, 2019, 19(5):1847-1852.
|
|
ZHANG Hui, WANG Dongxue, WANG Qifei. Analysis of the characteristic features of major severe coal mining accidents in all over the country in the period of 2005 to 2016[J]. Journal of Safety and Environment, 2019, 19(5):1847-1852.
|
| [12] |
张俊文, 杨虹霞. 2005—2019年我国煤矿重大及以上事故统计分析及安全生产对策研究[J]. 煤矿安全, 2021, 52(12): 261-264.
|
|
ZHANG Junwen, YANG Hongxia. Statistic alanalysis of major and above accidents in coal mines in China from 2005 to 2019 and study on countermeasures for safe production[J]. Safety in Coal Mine, 2021, 52(12):261-264.
|
| [13] |
景国勋, 刘孟霞. 2015—2019年我国煤矿瓦斯事故统计与规律分析[J]. 安全与环境学报, 2022, 22(3):1680-1686.
|
|
JING Guoxun, LIU Mengxia. Statistics and law analysis of coal mine gas accidents in China from 2015 to 2019[J]. Journal of Safety and Environment, 2022, 22(3):1680-1686.
|
| [14] |
景国勋. 2008—2013年我国煤矿瓦斯事故规律分析[J]. 安全与环境学报, 2014, 14(5):353-356.
|
|
JING Guoxun. Law of coal-gas mining accidents in China from 2008 to 2013[J]. Journal of Safety and Environment, 2014, 14(5):353-356.
|
| [15] |
张培森, 牛辉, 朱慧聪, 等. 2019—2020年我国煤矿安全生产形势分析[J]. 煤矿安全, 2021, 52(11):245-249.
|
|
ZHANG Peisen, NIU Hui, ZHU Huicong, et al. Analysis of coal mine safety production situation in China from 2019 to 2020[J]. Safety in Coal Mines, 2021, 52(11):245-249.
|