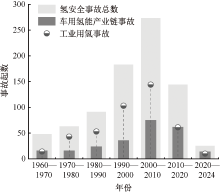
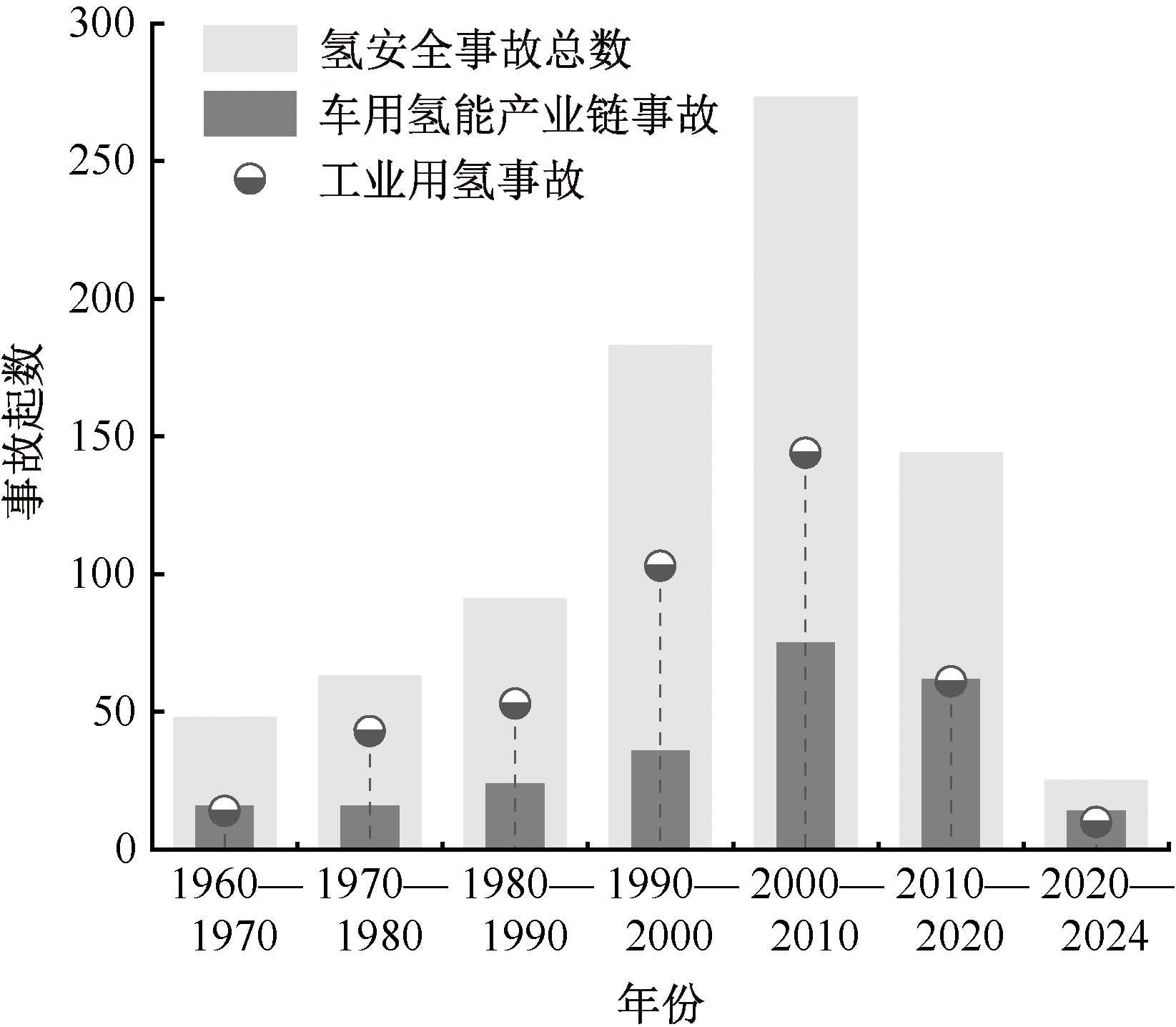
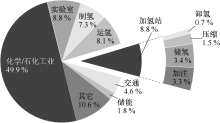
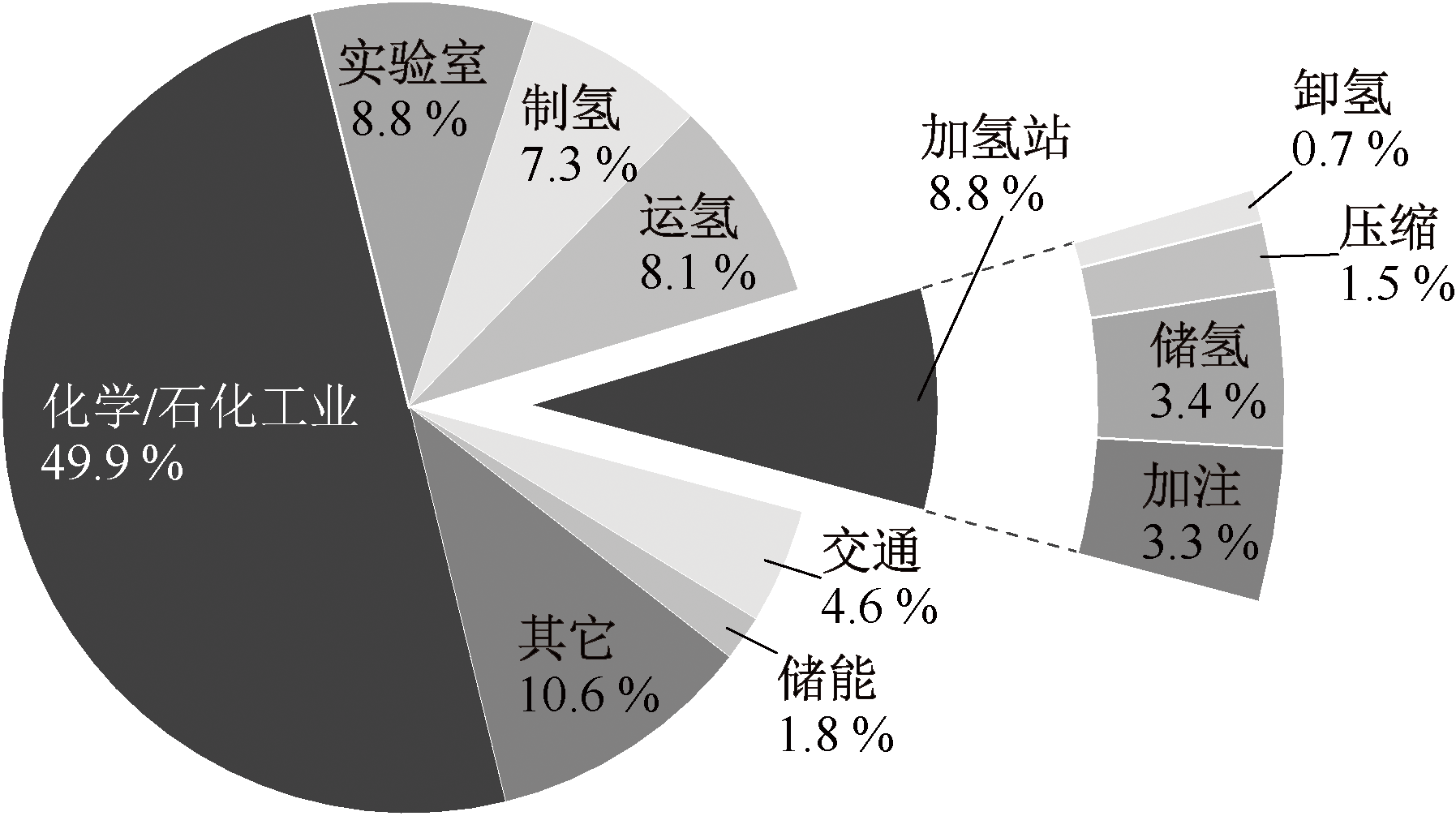
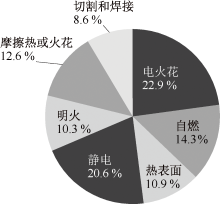
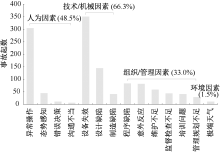
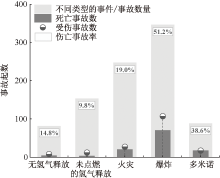
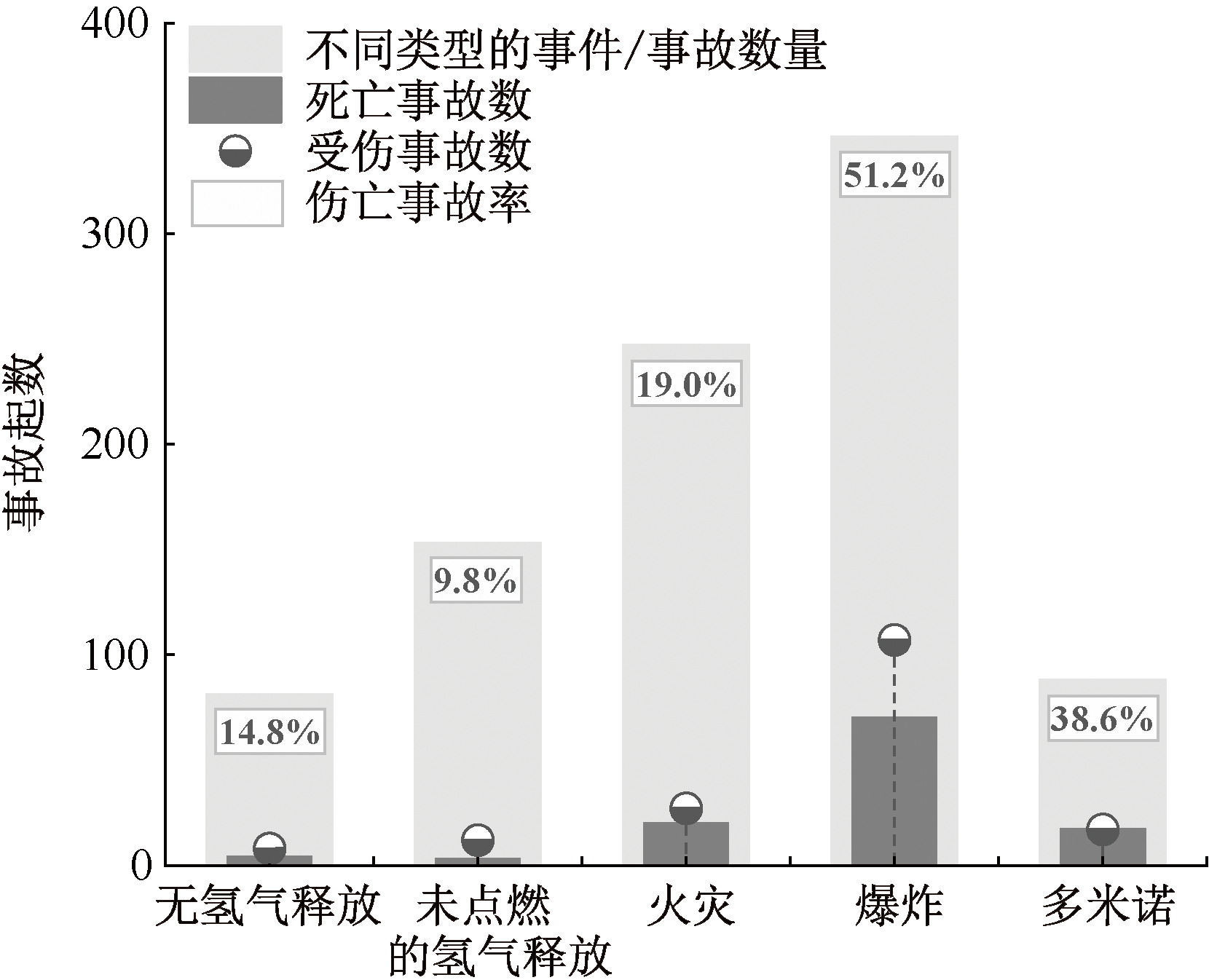
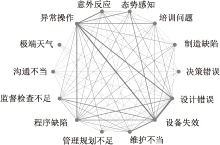
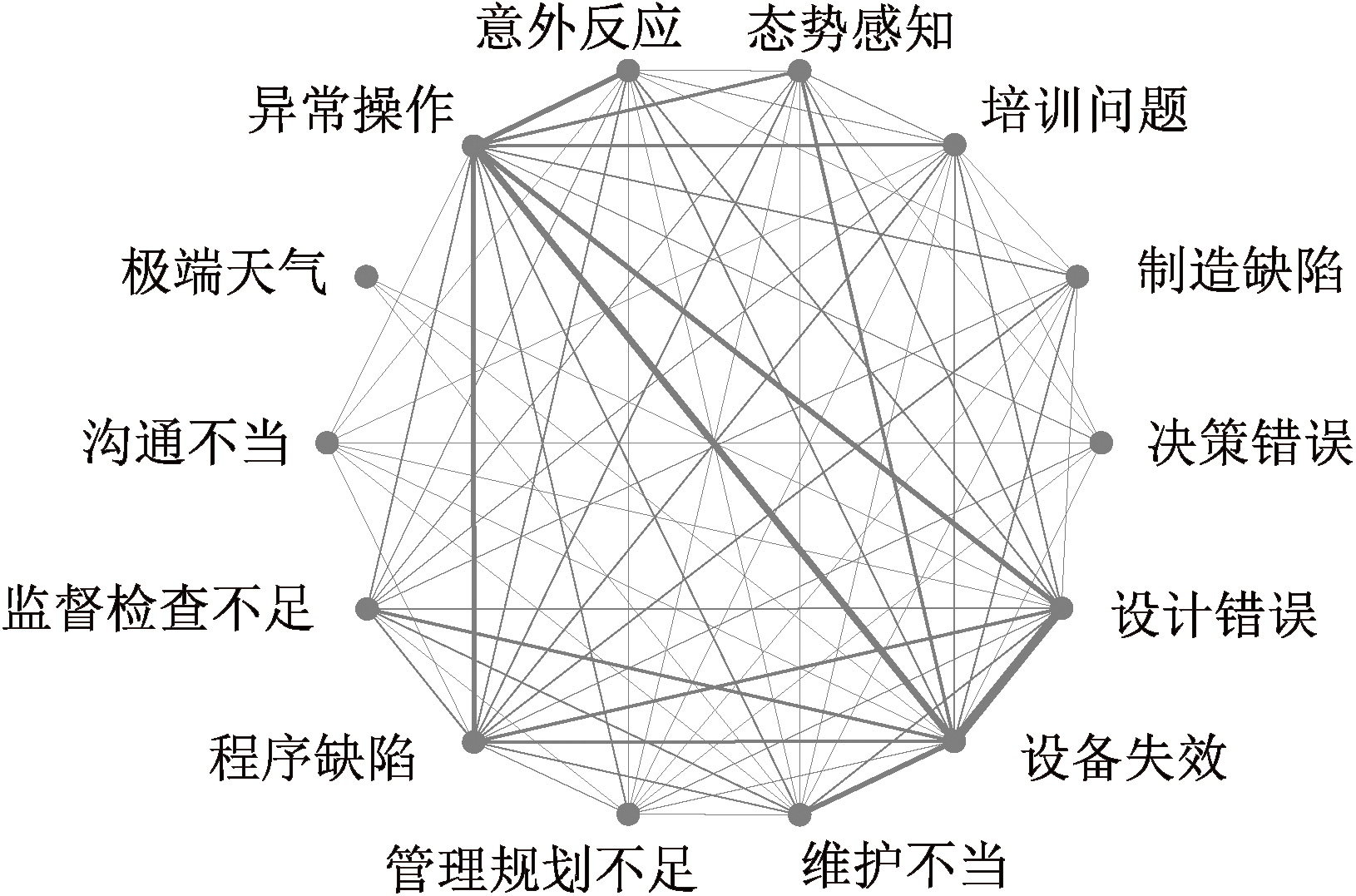
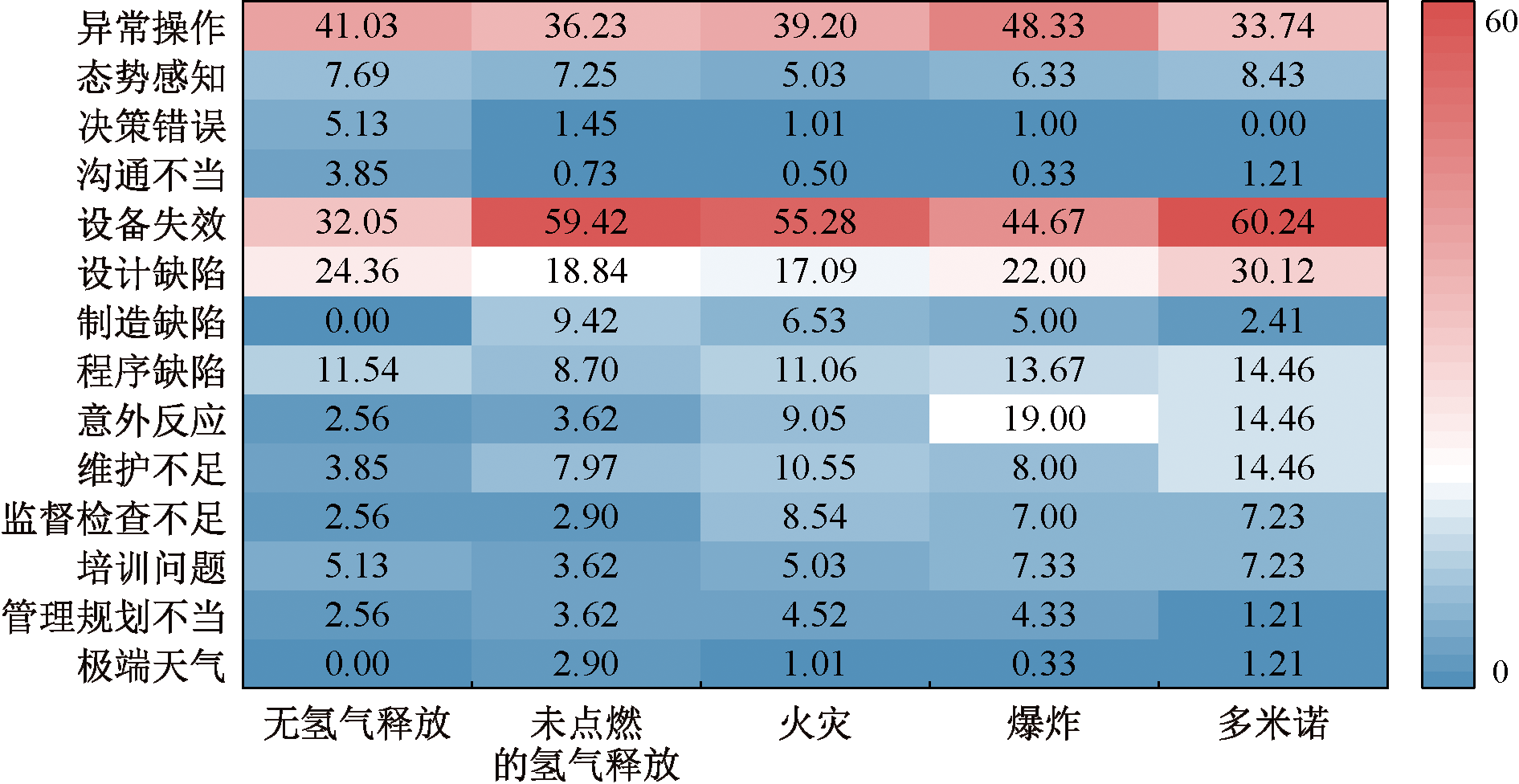
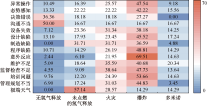
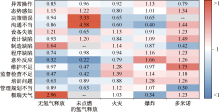
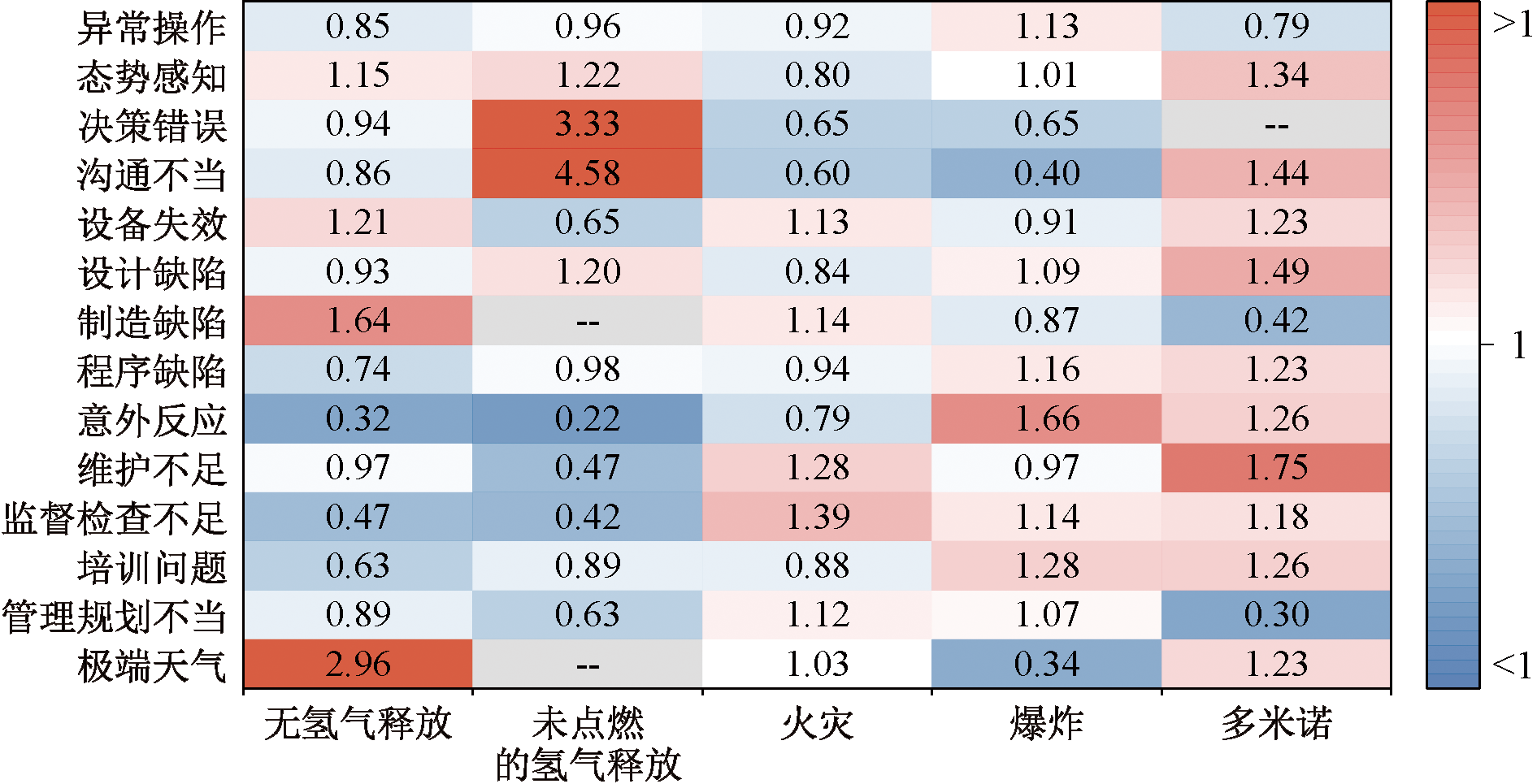
| [1] |
中国化学品安全协会. 韩国江原道一工厂氢气爆炸致2人死亡[EB/OL].(2019-05-24). https://www.chemicalsafety.org.cn/article/we07q275qggnmxod.
|
| [2] |
氢启未来,美国加氢站再次爆炸,60间房屋被毁!氢燃料安全再敲警钟[EB/OL].(2021-01-20). https://h2weilai.com/cms/index/shows/catid/29/id/962.html.
|
| [3] |
KIRCHSTEIGER C, ARELLANO A V, FUNNEMARK E. Towards establishing an international hydrogen incidents and accidents database (HIAD)[J]. Journal of Loss Prevention in the Process Industries, 2007, 20(1): 98-107.
|
| [4] |
Pacific Northwest National Laboratory, Department of energy. Hydrogen tools[EB/OL].(2019-02-23). https://h2tools.org/lessons?search_api_fulltext=.
|
| [5] |
The High Pressure Gas Safety Institute of Japan. 事故信息|高压气体安全协会[EB/OL].(2024-02-28). https://www.khk.or.jp/public_information/incident_investigation/index.html.
|
| [6] |
MIRZA N R, DEGENKOLBE S, WITT W. Analysis of hydrogen incidents to support risk assessment[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2011, 36(18): 12 068-12 077.
|
| [7] |
YANG Fuyuan, WANG Tianze, DENG Xintao, et al. Review on hydrogen safety issues: Incident statistics, hydrogen diffusion, and detonation process[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2021, 46(61): 31 467-31 488.
|
| [8] |
MELIDEO D, WEN J X, MORETTO P. HIAD 2.0-hydrogen incident and accident database[C]. International Conference on Hydrogen Safety, 2019: 209-213.
|
| [9] |
WEN J X, MARONO M, MORETTO P, et al. Statistics, lessons learned and recommendations from analysis of HIAD 2.0 database[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2022, 47(38): 17 082-17 096.
|
| [10] |
|
|
|
| [11] |
王艾迪, 邢莹莹, 张诗雯, 等. 基于关联规则的危险品公路运输事故风险因素研究[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2023, 33(6): 159-165.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2023.06.1618
|
|
WANG Aidi, XING Yingying, ZHANG Shiwen, et al. Research on risk factors of hazardous material highway transport accidents based on association rules[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2023, 33(6): 159-165.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2023.06.1618
|
| [12] |
冯胤伟, 刘正江, 蒋子怡, 等. 基于关联规则挖掘和复杂网络理论的船舶碰撞事故影响因素分析[J]. 大连海事大学学报, 2023, 49(3): 31-44.
|
|
FENG Yinwei, LIU Zhengjiang, JIANG Ziyi, et al. Anaylsis of factors affecting ship collisions based on association rule mining and complex network theory[J]. Journal of Dalian Maritime University, 2023, 49(3): 31-44.
|
| [13] |
况宇琦, 赵挺生, 蒋灵, 等. 塔式起重机事故案例关联规则挖掘与分析[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2021, 31(7): 137-142.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn 1003-3033.2021.07.019
|
|
KUANG Yuqi, ZHAO Tingsheng, JIANG Ling, et al. Mining and analysis of association rules in tower crane accident cases[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2021, 31(7): 137-142.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn 1003-3033.2021.07.019
|
| [14] |
杨利超, 刘敬贤, 刘钊, 等. 价值衰减下水上交通事故致因关联规则挖掘[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2022, 32(10): 127-134.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2022.10.2087
|
|
YANG Lichao, LIU Jingxian, LIU Zhao, et al. Association rules mining of water traffic accidents causation under value attenuation[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2021, 32(10): 127-134.
|
| [15] |
BOCKRIS J O M, LIN G H, PACKHAM N J C. A review of the investigations of the fleischmann-pons phenomena[J]. Fusion Technology, 1990, 18(1): 11-31.
|
| [16] |
YUAN Zhi, KHAKZAD N, KHAN F, et al. Dust explosions: a threat to the process industries[J]. Transactions of The Institution of Chemical Engineers Process Safety Environmental Protection, Part B, 2015, 98: 57-71.
|
| [17] |
NOLAN D P. Handbook of fire and explosion protection engineering principles for oil, gas, chemical, and related facilities:characteristics of hazardous material releases, fires, and explosions[M]. Norwich: William Andrew, 2019: 89-121.
|
| [18] |
Tools h,hydrogen explosion in hydrodesulfurization reactor outlet piping[EB/OL].(2017-09-25). https://h2tools.org/lessons/hydrogen-explosion-hydrodesulfurization-reactor-outlet-piping.
|
| [19] |
RENIERS G, COZZANI V. Domino effects in the process industries: modelling, prevention and managing[M]. Brussels: Newnes, 2013: 176-188.
|
| [20] |
伍星光. 基于安全屏障的油库事故分析和风险评估研究[D]. 北京: 中国石油大学(北京), 2020.
|
|
WU Xingguang. Study on accident analysis and risk assessment for oil depot based on safety barrier[D]. Beijing: China University of Petroleum-Beijing, 2020.
|