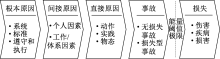
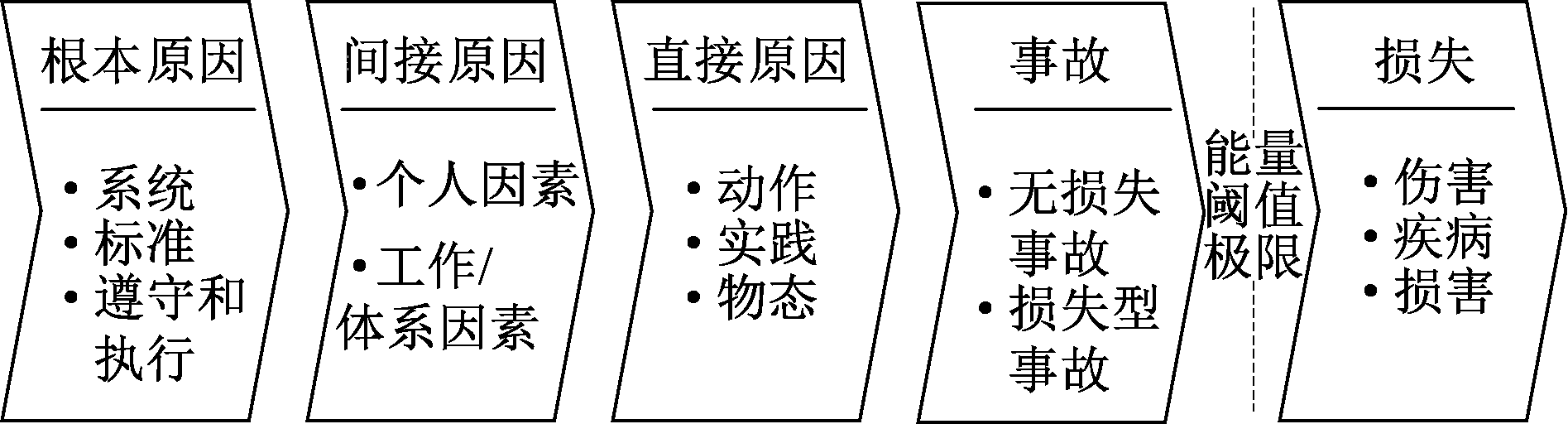
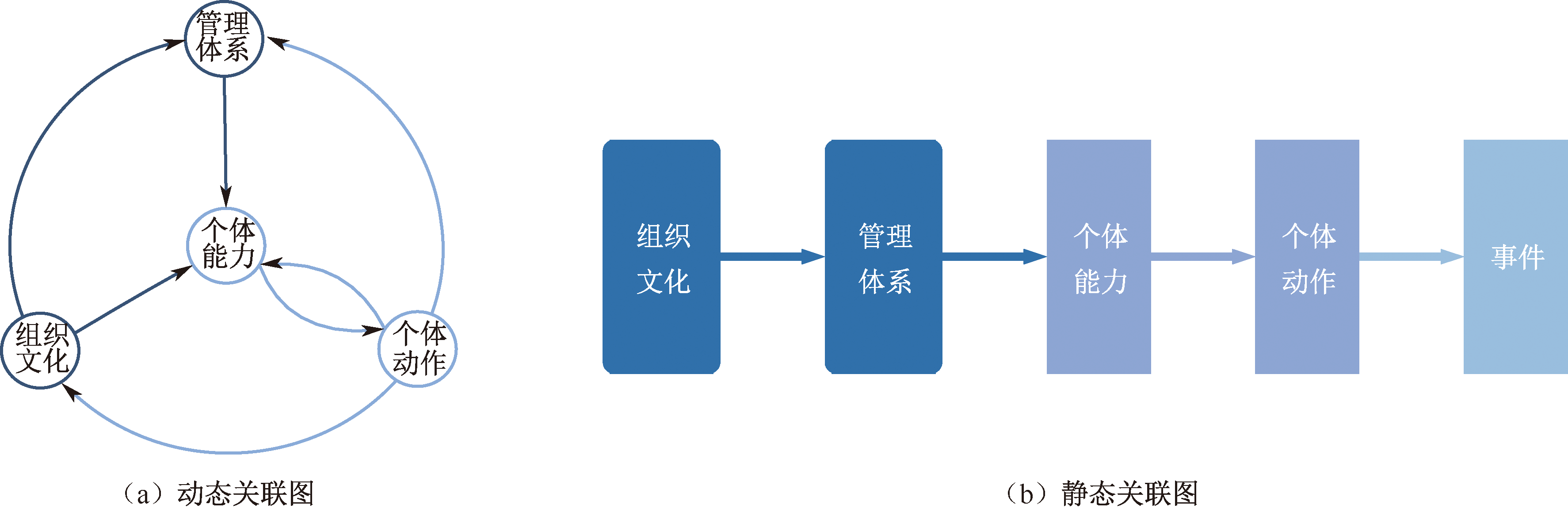
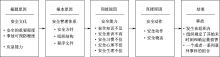
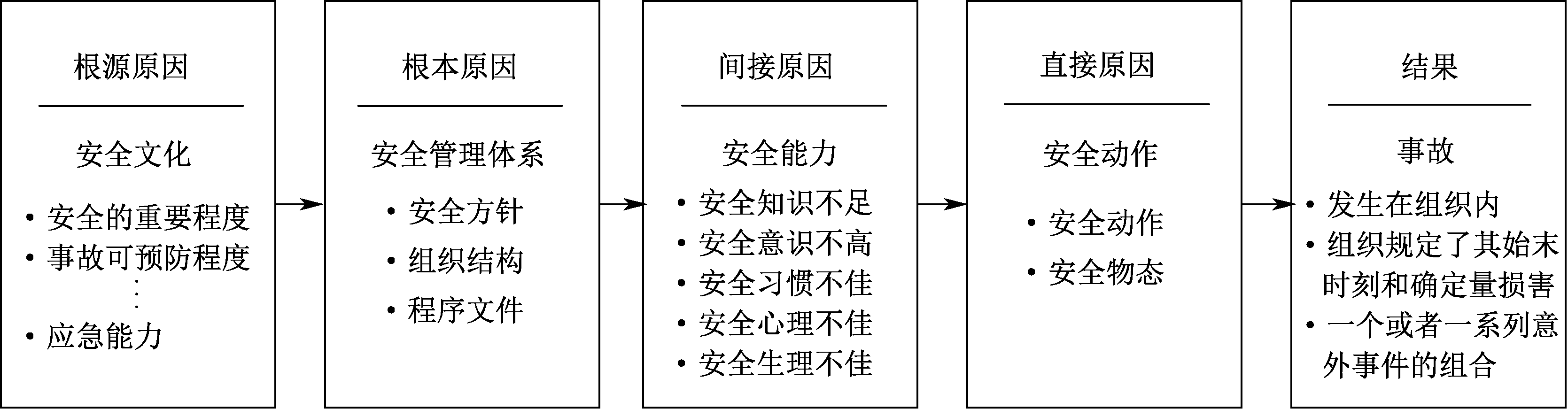
| [1] |
FU Gui, XIE Xuecai, JIA Qingsong, et al. The development history of accident causation models in the past 100 years: 24Model, a more modern accident causation model[J]. Process Safety and Environmental Protection, 2020, 134:47-82.
doi: 10.1016/j.psep.2019.11.027
|
| [2] |
HEINRICH W H. Industrial accident prevention[M]. New York: McGraw Hill Book Company, 1941:13-20.
|
| [3] |
BIRD F E, GERMAIN G L. Practical loss control leadership[M]. Loganville: International Loss Control Institute, 1986:1-10.
|
| [4] |
AMYOTTEE P R, OEHMEN A M. Application of a loss causation model to the Westray mine explosion[J]. Chemical Engineering Research & Design, 2002, 80(1):55-59.
|
| [5] |
李杰, 伊宏艳, 李乃文. 我国事故致因研究团队与热点主题研究[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2022, 32(7):20-27.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2022.07.1965
|
|
LI Jie, YI Hongyan, LI Naiwen. Investigation on research team and hot topics of accident causation in China[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2022, 32(7):20-27.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2022.07.1965
|
| [6] |
傅贵, 陈奕燃, 许素睿, 等. 事故致因“2-4”模型的内涵解析及第6版的研究[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2022, 32(1):12-19.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2022.01.002
|
|
FU Gui, CHEN Yiran, XU Surui, et al. Detailed explanations of 24Model and development of its 6th version[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2022, 32(1):12-19.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2022.01.002
|
| [7] |
OBP. Terms and definitions[EB/OL]. [2023-01-29]. https://www.iso.org/obp.
|
| [8] |
GB/T 33000—2016, 企业安全生产标准化基本规范[S].
|
|
GB/T 33000-2016, Guideline of China occupational safety and health management system[S].
|
| [9] |
袁晨辉, 傅贵. 不安全动作定义的研究[J]. 安全, 2021, 42(7):50-55.
|
|
YUAN Chenhui, FU Gui. Research on the definition of unsafe act[J]. Safety & Security, 2021, 42(7):50-55.
|
| [10] |
ROWEN A, GRABOWSKI M, RUSSELL D W. The impact of work demands and operational tempo on safety culture, motivation and perceived performance in safety critical systems[J]. Safety Science, 2022,155:DOI: 10.1016/j.ssci.2022.105861.
|
| [11] |
ISO. What is a management system?[EB/OL]. [2023-01-30]. https://www.iso.org/management-system-standards.html.
|
| [12] |
JOOMA Z, HUTCHINGS J, HOAGLAND H. The development of questions to determine the effectiveness of the incident investigation process for electrical incidents[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industry Applications, 2015, 51(5):4245-4254.
doi: 10.1109/TIA.2015.2431645
|
| [13] |
SURAJI A, DUFF A R, PECKITT S J. Development of causal model of construction accident causation[J]. Journal of Construction Engineering and Management, 2001, 127(4):337-344.
doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9364(2001)127:4(337)
|