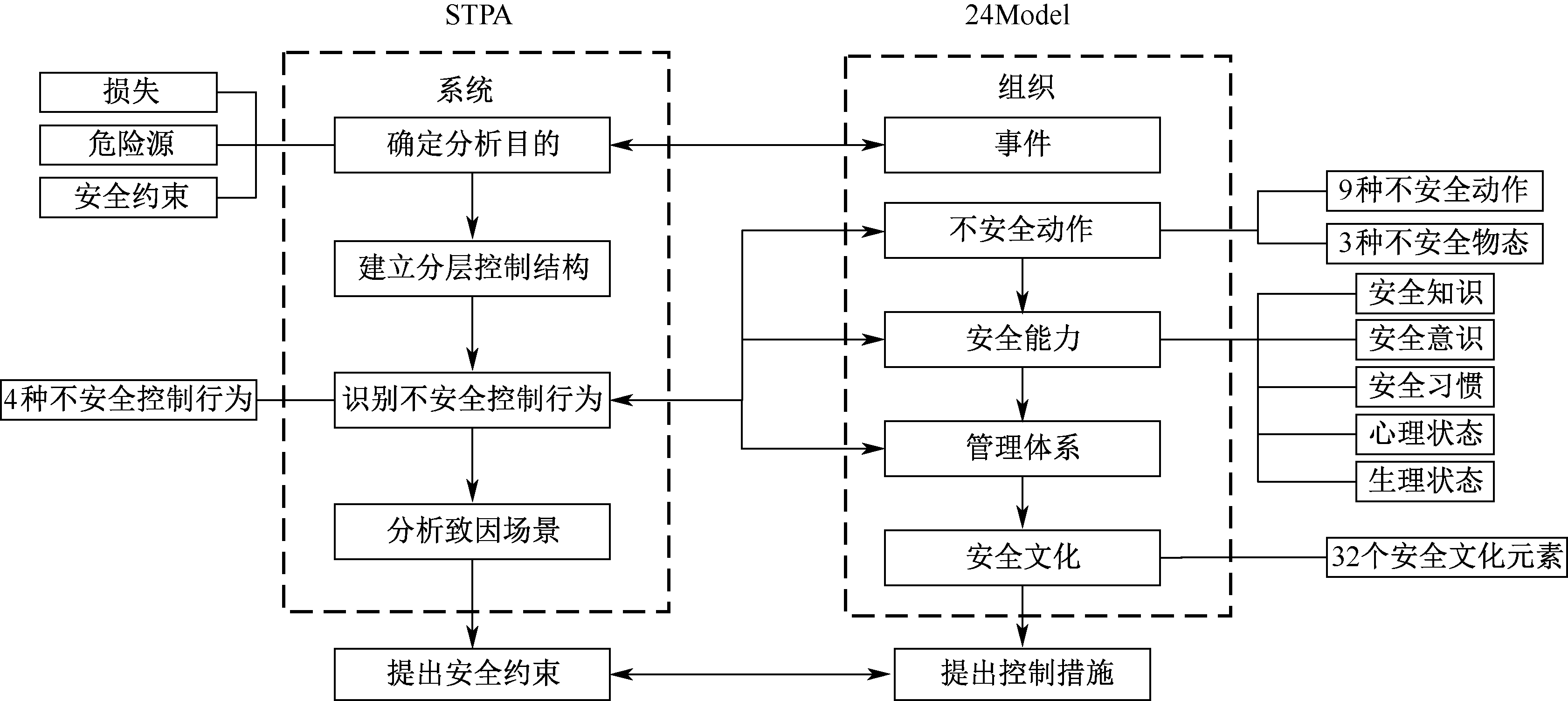
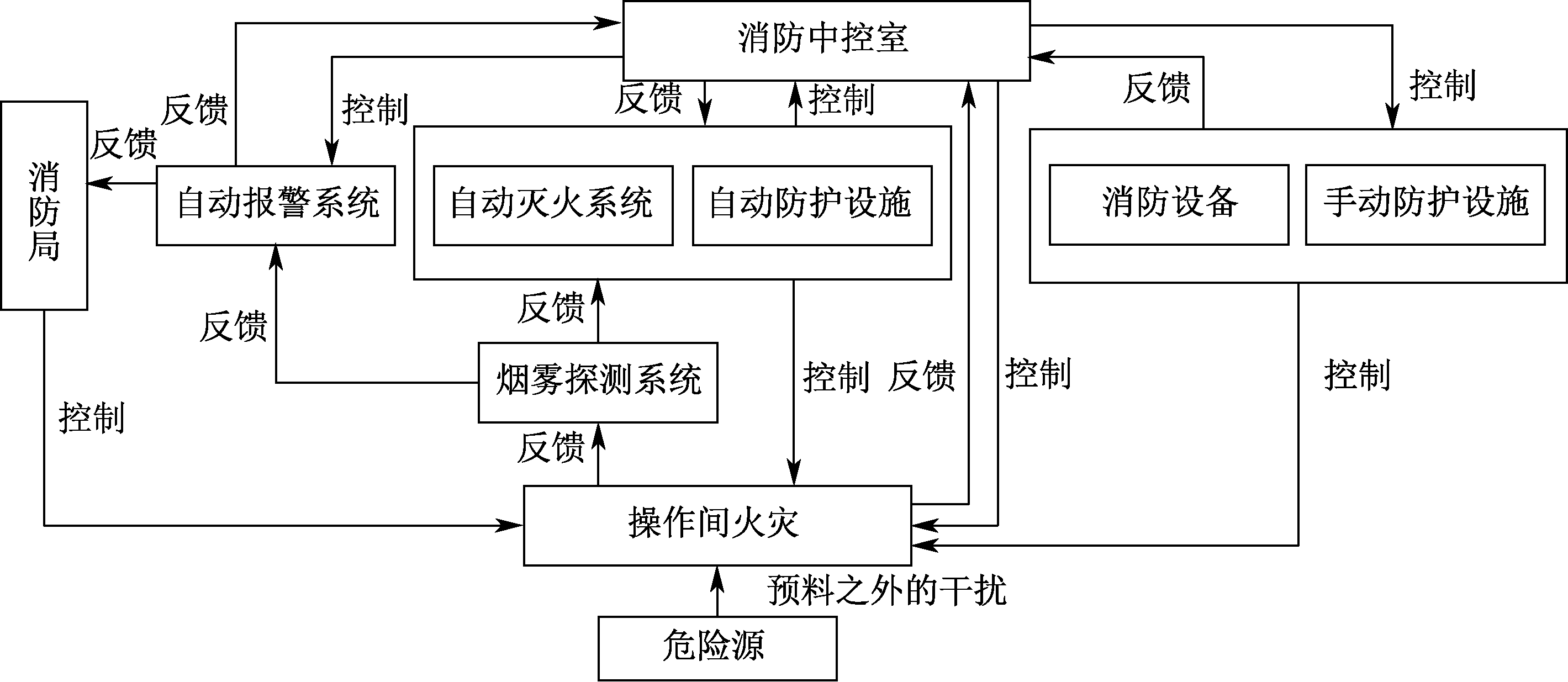
| [1] |
傅贵, 郭孝臣. 事故致因理论的研究与应用简评[J]. 安全, 2019, 40(9): 1-5.
|
|
FU Gui, GUO Xiaochen. A brief review on the study and application of accident causation theory[J]. Safety & Security, 2019, 40(9): 1-5.
|
| [2] |
许娜. 系统论事故致因理论及其应用[J]. 价值工程, 2018, 37(33): 208-209.
|
|
XU Na. Systemic accident-causing theory and its application[J]. Value Engineering, 2018, 37(33): 208-209.
|
| [3] |
LEVESON N. A new accident model for engineering safer systems[J]. Safety Science, 2004, 42(4):237-270.
doi: 10.1016/S0925-7535(03)00047-X
|
| [4] |
LEVESON N. A new approach to hazard analysis for complex systems[C]. Proceedings of International Conference of the System Safety Society, 2003:1-12.
|
| [5] |
傅贵, 陈奕燃, 许素睿, 等. 事故致因“2-4”模型的内涵解析及第6版的研究[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2022, 32(1): 12-19.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2022.01.002
|
|
FU Gui, CHEN Yiran, XU Surui, et al. Detailed explanations of 24Model and development of its 6th version[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2022, 32 (1): 12-19.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2022.01.002
|
| [6] |
李杰, 伊宏艳, 李乃文. 我国事故致因研究团队与热点主题研究[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2022, 32(7): 20-27.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2022.07.1965
|
|
LI Jie, YI Hongyan, LI Naiwen. Investigation on research team and hot topics of accident causation in China[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2022, 32 (7): 20-27.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2022.07.1965
|
| [7] |
马海涛. 自动车道保持系统人机交互安全分析与评价[D]. 长春: 吉林大学, 2020.
|
|
MA Haitao. Safety analysis and evaluation of human-machine interaction of automated lane keeping system[D]. Changchun: Jilin University, 2020.
|
| [8] |
吴康. 机载安全关键软件模型验证技术研究[D]. 天津: 中国民航大学, 2020.
|
|
WU Kang. Research on airborne safety critical software model varication technology[D]. Tianjin: Civil Aviation University of China, 2020.
|
| [9] |
宋晗炜. 基于设备状态信息的FAO系统运行风险态势评估[D]. 北京: 北京交通大学, 2021.
|
|
SONG Hanwei. Risk situation assessment of FAO system operation based on equipment status[D]. Beijing: Beijing Jiaotong University, 2021.
|
| [10] |
鲁征, 傅贵. 安全管理学及其试验设计研究[J]. 安全与环境学报, 2016, 16(4): 225-231.
|
|
LU Zheng, FU Gui. On the safety management theory and the design for the corresponding experiments[J]. Journal of Safety and Environment, 2016, 16(4): 225-231.
|
| [11] |
闫锋, 徐文韬. 基于STPA的FADEC系统TLD安全性方法研究[J]. 西安航空学院学报, 2022, 40(5): 22-26.
|
|
YAN Feng, XU Wentao. Research on TLD safety method of FADEC system based on STPA[J]. Journal of Xi'an Aeronautical Institute, 2022, 40(5): 22-26.
|
| [12] |
杨晓强, 贺非, 贺强, 等. 基于形式化STPA的机务维修模块分析[J]. 滨州学院学报, 2021, 37(4): 12-19.
|
|
YANG Xiaoqiang, HE Fei, HE Qiang, et al. Analysis of maintenance module based on formal STPA method[J]. Journal of Binzhou University, 2021, 37(4): 12-19.
|
| [13] |
卢志友, 张亚强, 艾留阳. 24Model模型在危化品事故分析中的应用探讨[J]. 化工安全与环境, 2022, 35(4): 17-21.
|
| [14] |
李明海, 常通, 杨一帆. 基于24Model的非煤矿山事故分析[J]. 工业安全与环保, 2022, 48(9): 69-73.
|
|
LI Minghai, CHANG Tong, YANG Yifan. Analysis of non-coal mine accidents based on 24Model and grey correlation degree[J]. Industrial Safety and Environmental Protection, 2022, 48(9): 69-73.
|
| [15] |
朱明昌, 黄立文, 谢澄, 等. 基于STAMP/STPA的LNG船对船过驳系统安全性分析[J]. 交通信息与安全, 2021, 39(6): 44-53.
|
|
ZHU Mingchang, HUANG Liwen, XIE Cheng, et al. A safety analysis of LNG ship-to-ship transfer system based on a STAMP/STPA model[J]. Journal of Transport Information and Safety, 2021, 39 (6): 44-53.
|
| [16] |
LEVESON N, THOMAS J P. STPA handbook[Z]. 2018.
|
| [17] |
李耀华, 高源. 基于STPA-ANP模型的民机系统安全性分析[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 2022, 44(9): 2986-2994.
|
|
LI Yaohua, GAO Yuan. Safety analysis of civil aircraft system based on STPA-ANP model[J]. System Engineering and Electronics, 2022, 44(9): 2986-2994.
|
| [18] |
秦楠, 马亮, 黄锐. 基于STPA的潜艇鱼雷发射控制系统安全性分析[J]. 系统工程理论与实践, 2019, 39(12): 3208-3216.
doi: 10.12011/1000-6788-2019-0541-09
|
|
QIN Nan, MA Liang, HUANG Rui. Safety analysis for Submarine torpedo launch control system based on STPA[J]. Systems Engineering-Theory & Practice, 2019, 39 (12): 3208-3216.
|
| [19] |
ISO. Online browsing platform[EB/OL]. (2021-09-13).www.iso.org/obp.
|
| [20] |
ALLISON C K, REVELL K M, SEARS R, et al. Systems theoretic accident model and process (STAMP) safety modelling applied to an aircraft rapid decompression event[J]. Safety Science, 2017, 98: 159-166.
doi: 10.1016/j.ssci.2017.06.011
|
| [21] |
傅贵, 樊运晓, 佟瑞鹏, 等. 通用事故原因分析方法(第4版)[J]. 事故预防学报, 2016, 2(1): 7-12.
|
|
FU GUI, FAN Yunxiao, TONG Ruipeng, et al. A universal methodology for the causation analysis of accidents(4th Edition)[J]. Journal of Accident Prevention, 2016, 2 (1): 7-12.
|
| [22] |
童文清, 傅贵, 解学才, 等. 我国煤矿安全文化建设现状研究:来自60家煤矿的证据[J]. 中国安全生产科学技术, 2020, 16(12): 85-91.
|
|
TONG Wenqing, FU Gui, XIE Xuecai, et al. Research on construction status of coal mine safety culture in China: evidence from 60 coal mines[J]. Journal of Safety Science and Technology, 2020, 16(12): 85-91.
|
| [23] |
史思杨. 基于MB-STPA的飞机刹车系统安全性分析方法研究[D]. 天津: 中国民航大学, 2020.
|
|
SHI Siyang. Research on safety analysis method of aircraft brake system based on MB-STPA[D]. Tianjin: Civil Aviation University of China, 2020.
|
| [24] |
焦宇, 陈曦, 李新, 等. 基于24Model-5Why的航运企业安全文化薄弱环节研究[J]. 安全与环境学报, 2023, 23(4): 1185-1193.
|
|
JIAO Yu, CHEN Xi, LI Xin, et al. Research on the weaknesses of safety culture in shipping companies based on 24Model-5Why[J]. Journal of Safety and Environment, 2023, 23(4): 1185-1193.
|
| [25] |
上半年消防救援队伍日均接处警创新高[EB/OL]. (2022-07-25).https://www.119.gov.cn/gk/sjtj/2022/30512.shtml.
|
| [26] |
宋炜, 傅贵. 电动车火灾事故原因及预防措施分析[J]. 安全, 2022, 43(3): 39-45.
|
|
SONG Wei, FU Gui. Analysis on the causes and preventive measures of electric vehicle fire accidents[J]. Safety & Security, 2022, 43(3): 39-45.
|
| [27] |
北京市应急管理局. 北京市安全生产监督管理局关于石景山区喜隆多购物广场“10.11”较大火灾事故的通报[EB/OL].(2014-04-25).https://ehsgy.blog.ehs.cn/article-17160-1.html
|