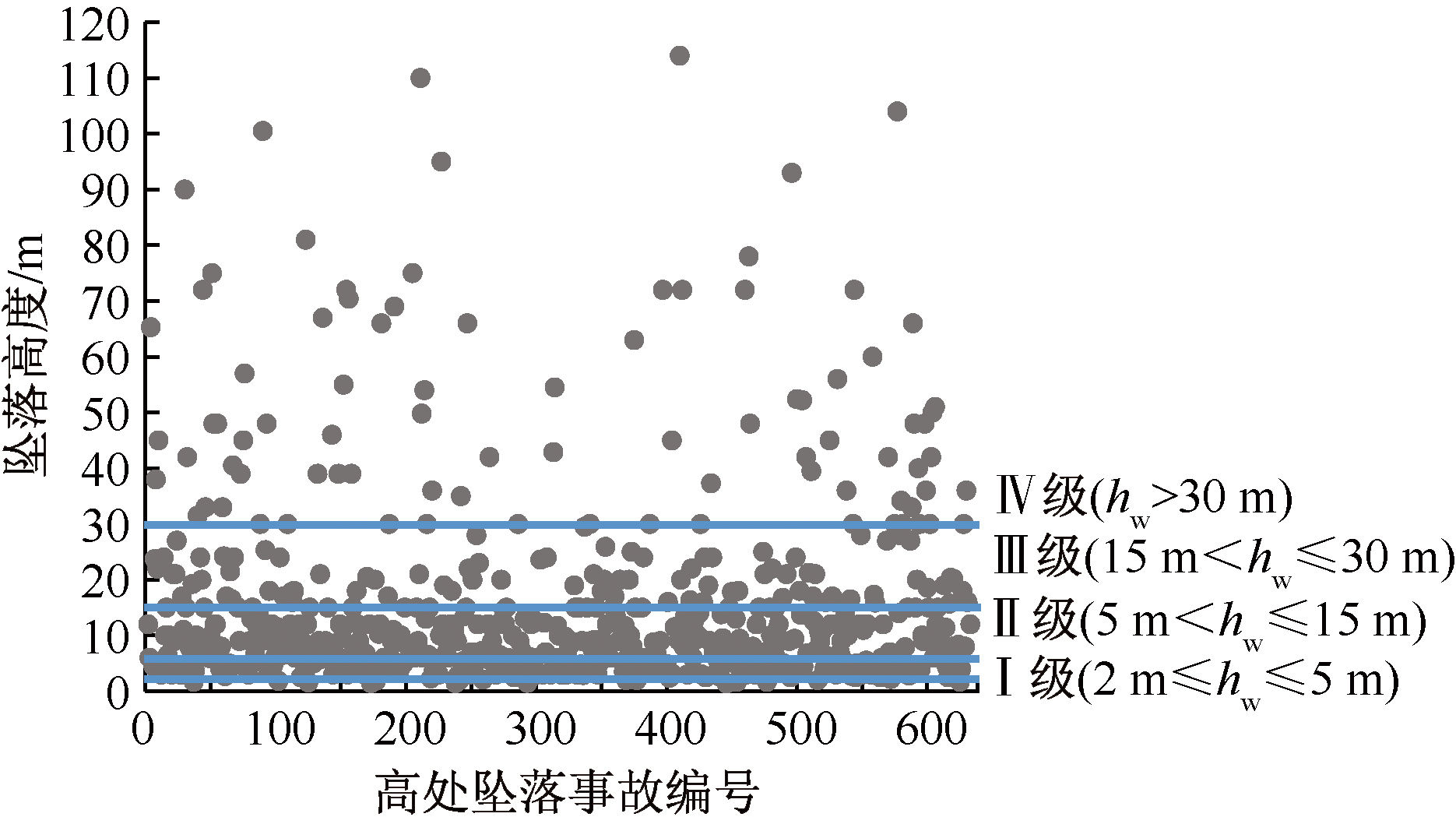
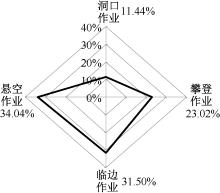
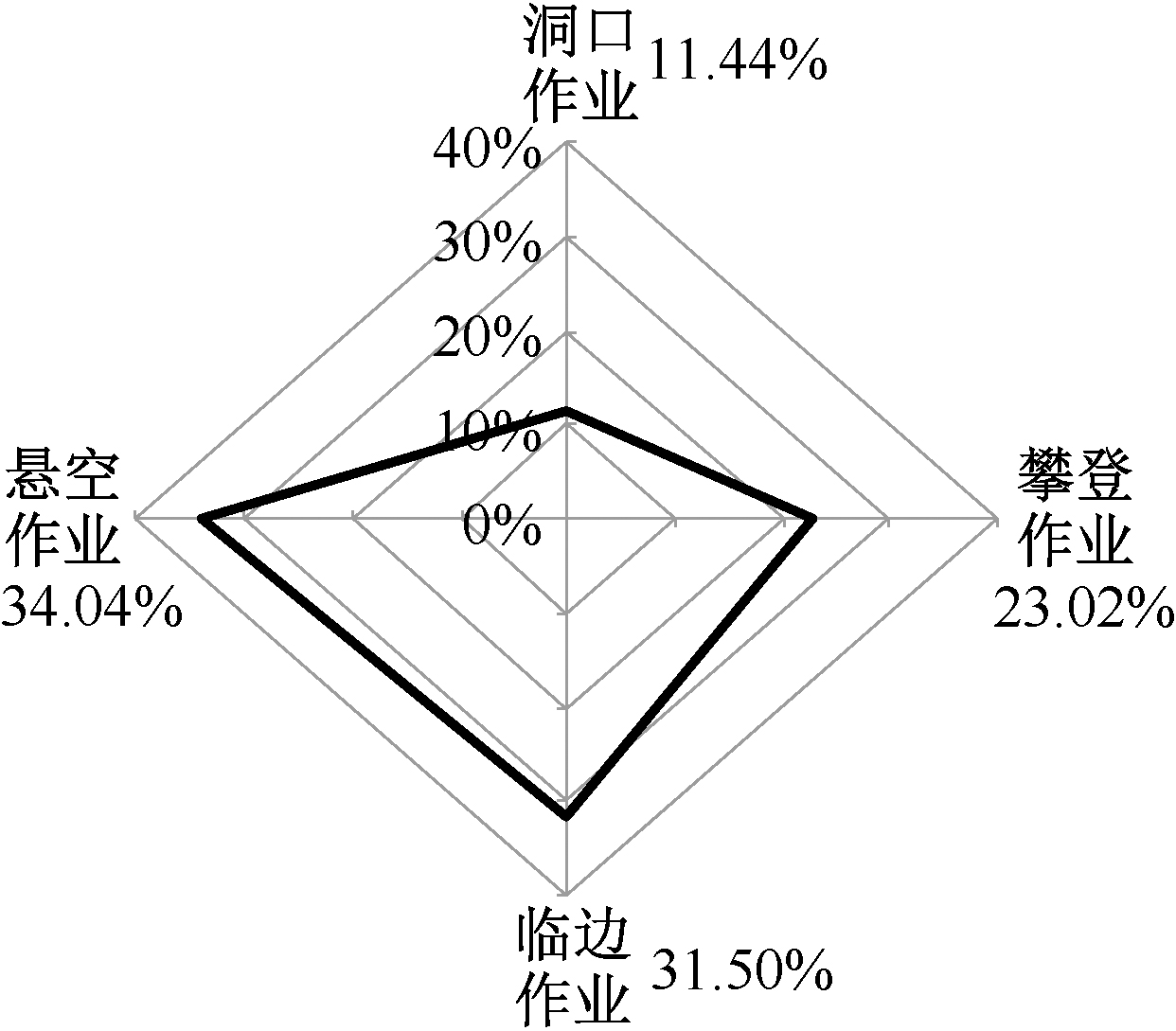
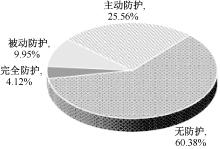
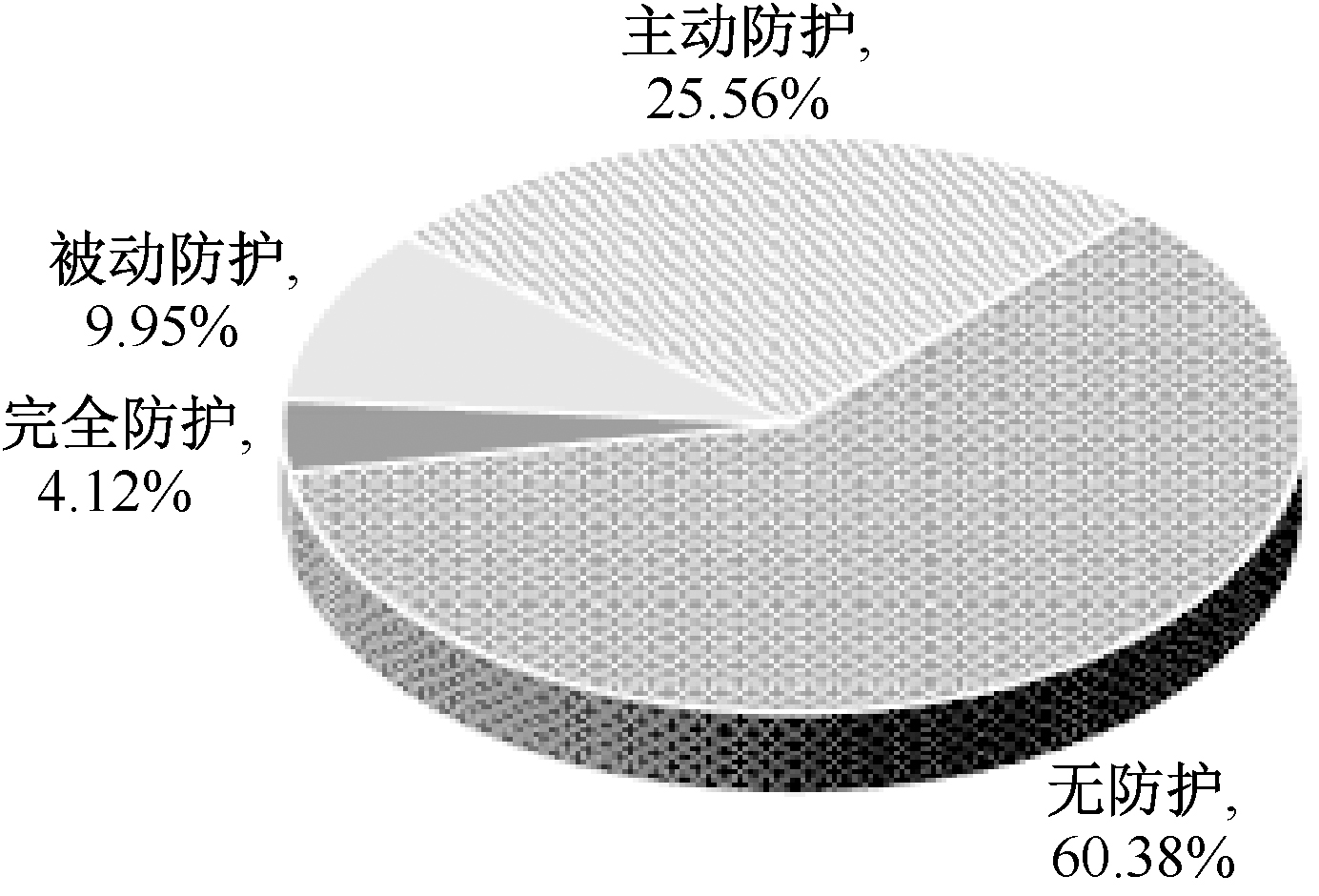
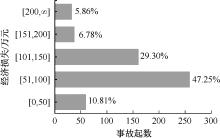
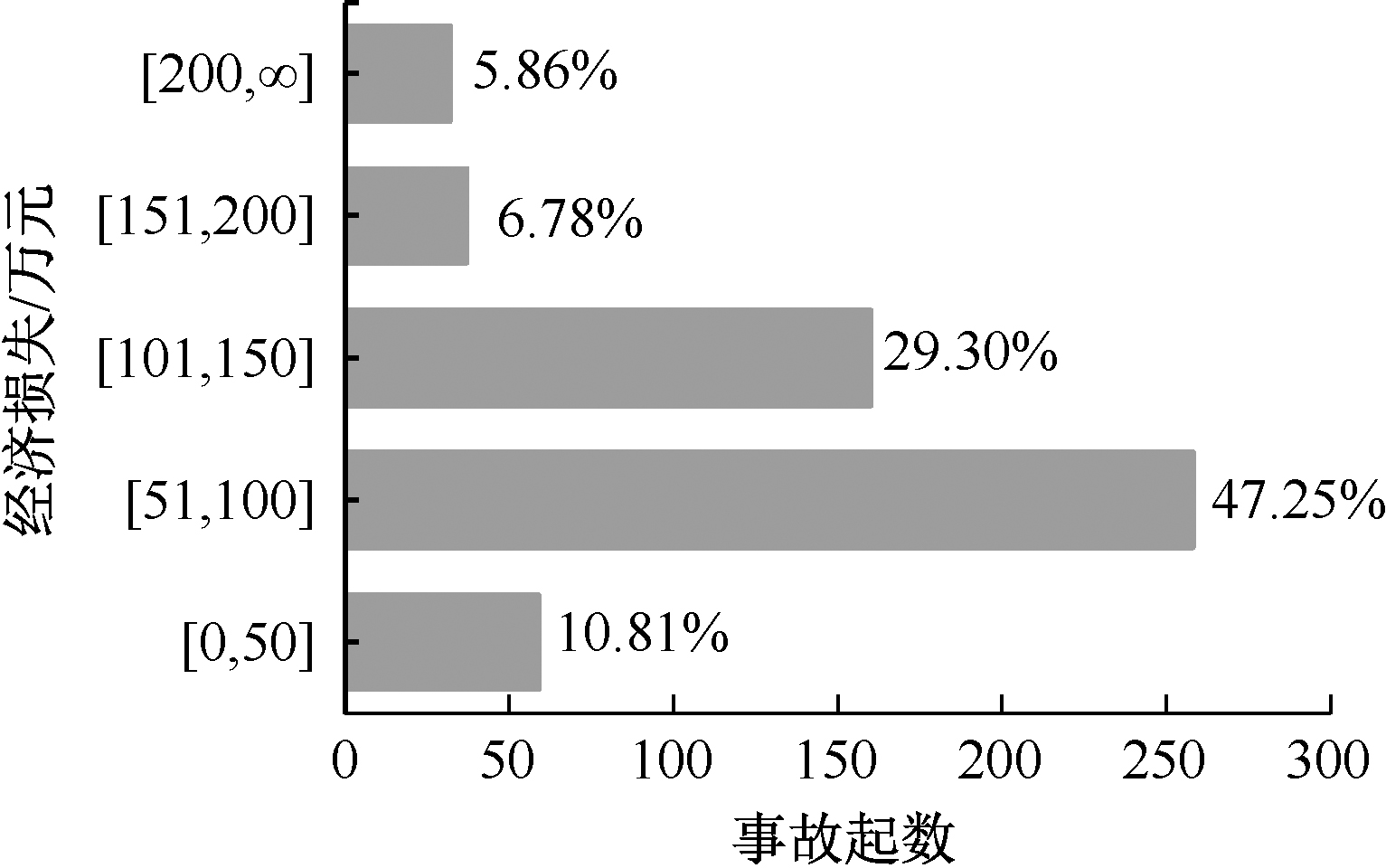
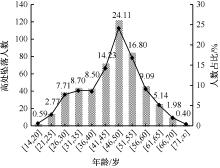
| [1] |
常理. 决不能只重发展不顾安全[N]. 经济日报, 2020-04-29(5).
|
| [2] |
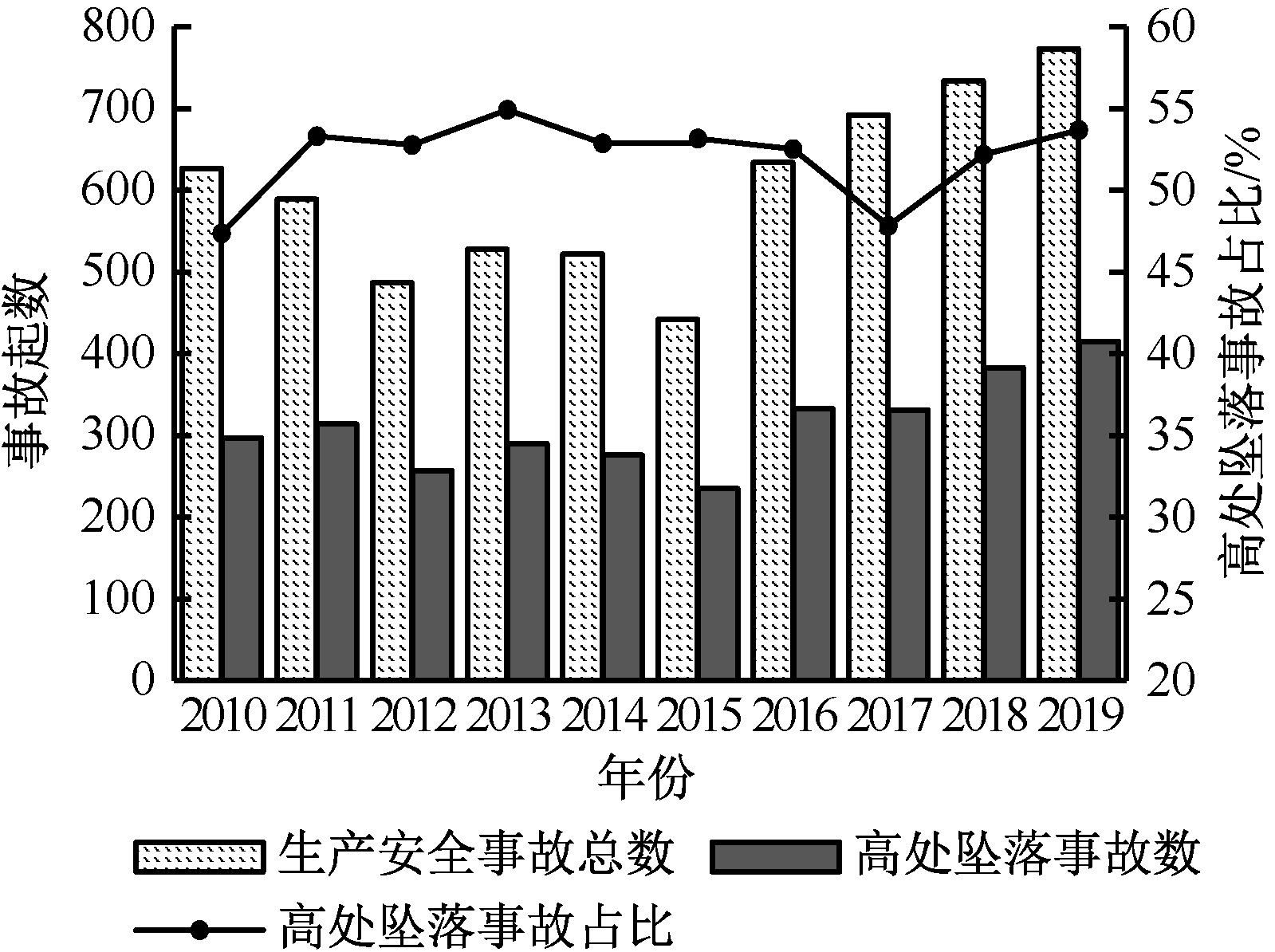
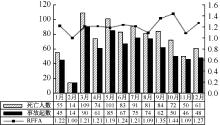
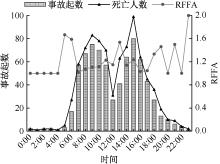
中华人民共和国住房和城乡建设部. 住房城乡建设部关于2019年房屋市政工程生产安全事故情况的通报[EB/OL].[2020-06-19].
|
| [3] |
马彬, 陈立道, 姜敏. 建筑施工高处坠落事故研究[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2004, 4(9):108-112.
|
|
MA Bin, CHEN Lidao, JIANG Min. Study on falling accidents in construction industry[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2004, 14(9):108-112.
|
| [4] |
黄国耀, 许江, 车轫. 重庆市建筑业高处坠落事故调查分析[J]. 中国安全生产科学技术, 2007, 3(1):54-57.
|
|
HUANG Guoyao, XU Jiang, CHE Ren, et al. Investigation and analysis on falling accidents of construction area in Chongqing[J]. Journal of Safety Science and Technology, 2007, 3(1):54-57.
|
| [5] |
张明轩, 朱月娇, 翟玉杰, 等. 建筑工程高处坠落事故的故障树分析方法研究[J]. 煤炭工程, 2008, 40(2):112-114.
|
|
ZHANG Mingxuan, ZHU Yuejiao, ZHAI Yujie, et al. Research on fault tree analysis method for fall accidents in construction engineering[J]. Coal Engineering, 2008, 40(2):112-114.
|
| [6] |
邓航, 庞奇志, 朱德英, 等. 建筑施工高处坠落事故分析及预防对策[J]. 工业安全与环保, 2010, 36(4):57-59.
|
|
DENG Hang, PANG Qizhi, ZHU Deying, et al. Analysis and countermeasures about falling accidents of architecture construction[J]. Industrial Safety and Environmental Protection, 2010, 36(4):57-59.
|
| [7] |
徐影, 杨高升, 夏柠萍, 等. 基于FTA-Reason的施工作业高空坠落风险预控研究[J]. 中国安全生产科学技术, 2015, 11(7):171-177.
|
|
XU Ying, YANG Gaosheng, XIA Ningping, et al. Study on pre-control of high falling risk in construction operation based on FTA-Reason model[J]. Journal of Safety Science and Technology, 2015, 11(7):171-177.
|
| [8] |
赵金娜, 郭进平, 侯东升, 等. 基于AHP的高处坠落事故脆性分析[J]. 中国安全生产科学技术, 2009, 5(5):204-208.
|
|
ZHAO Jinna, GUO Jinping, HOU Dongsheng, et al. Analysis of brittleness of falling accident based on analytic hierarchy process[J]. Journal of Safety Science and Technology, 2009, 5(5):204-208.
|
| [9] |
施式亮, 刘勇, 李润求, 等. 基于AHP-Fuzzy的高处坠落危险性评价研究[J]. 中国安全生产科学技术, 2011, 7(2):132-137.
|
|
SHI Shiliang, LIU Yong, LI Runqiu, et al. Research and application on risk assessment of high falling based on AHP[J]. Journal of Safety Science and Technology, 2011, 7(2):132-137.
|
| [10] |
张洪, 宫运华, 傅贵. 基于“2-4”模型的建筑施工高处坠落事故原因分类与统计分析[J]. 中国安全生产科学技术, 2017, 13(9):169-174.
|
|
ZHANG Hong, GONG Yunhua, FU Gui. Causes classification and statistical analysis on falling accidents on construction sites based on “2-4” model[J]. Journal of Safety Science and Technology, 2017, 13(9):169-174.
|
| [11] |
孙世梅, 赵金坤, 傅贵. 基于“2-4”模型的高处坠落事故行为原因研究[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2019, 29(8):23-28.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2019.08.004
|
|
SUN Shimei, ZHAO Jinkun, FU Gui. Study on behavioral causes of falling accidents based on "2-4" model[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2019, 29(8):23-28.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2019.08.004
|
| [12] |
傅贵, 陈奕燃, 许素睿, 等. 事故致因“2-4”模型的内涵解析及第6版的研究[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2022, 32(1):12-19.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2022.01.002
|
|
FU Gui, CHEN Yiran, XU Surui. et al. Detailed explanations of 24Model and development of its 6th version[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2022, 32(1):12-19.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2022.01.002
|
| [13] |
国务院第172次常务会议. 生产安全事故报告和调查处理条例[L]. 2007-06-01.
|
| [14] |
COHEN J. Statistical power analysis for the behavioral sciences[M]. New York: Academic Press, 1977:167-168.
|
| [15] |
李金德, 秦晶. SPSS统计分析与应用[M]. 北京: 清华大学出版社, 2019:155,184-185.
|
| [16] |
SHAO Bo, HU Zhigen, LIU Quan, et al. Fatal accident patterns of building construction activities in China[J]. Safety Science, 2019, 111(1): 253-263.
doi: 10.1016/j.ssci.2018.07.019
|
| [17] |
周建亮, 胡飞翔, 邢艳冬, 等. 工作压力、职业倦怠对建筑工人不安全行为的影响[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2022, 32(11):14-22.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2022.11.2539
|
|
ZHOU Jianliang, HU Feixiang, XING Yandong, et al. Influence of job stress and burnout on unsafe behaviors of construction workers[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2022, 32(11):14-22.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2022.11.2539
|
| [18] |
李大君. “高薪”下的艰辛:建筑工人生存状态调查[J]. 建筑, 2014(4):6-25.
|
| [19] |
GB 50096—2011, 住宅设计规范[S].
|
|
GB 50096-2011, Design code for residential building[S].
|
| [20] |
JGJ 80—2011, 建筑施工高处作业安全技术规范[S].
|
|
JGJ 80-2011, Technical code for safety of working at height of building construction[S].
|
| [21] |
CAMERON I, DUFF R. A technical guide to the selection and use of fall prevention and arrest equipment[M]. Glasgow: HSE Books, 2005: 13-14.
|
| [22] |
HALABI Y, XU Hu, LONG Danbing, et al. Causal factors and risk assessment of fall accidents in the U.S. construction industry: a comprehensive data analysis (2000-2020)[J]. Safety Science, 2022, 146: DOI: org/10.1016/j.ssci.2021.105537.
doi: org/10.1016/j.ssci.2021.105537
|
| [23] |
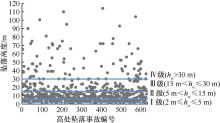
GBT 3608—2008, 高处作业分级[S].
|
|
GBT 3608-2008, Classification of work at heights[S].
|
| [24] |
GB 672119—1986, 企业职工伤亡事故经济损失统计标准[S].
|
|
GB 672119-1986, Statistical standard of economic losses from injury-fatal accidents of enterprise staff and workers[S].
|
| [25] |
国务院第28次常务会议. 建筑工程安全管理条例[L]. 2003-11-24.
|