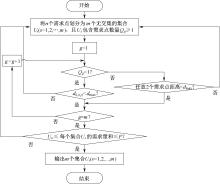
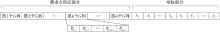
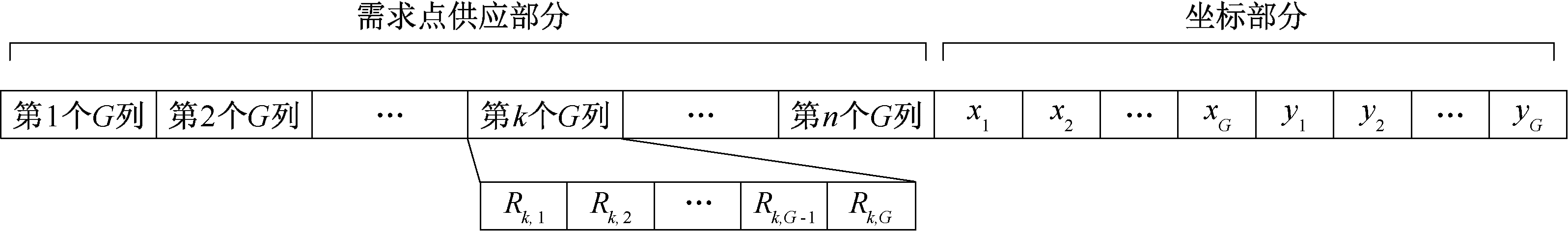
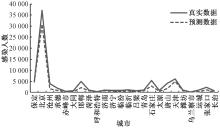
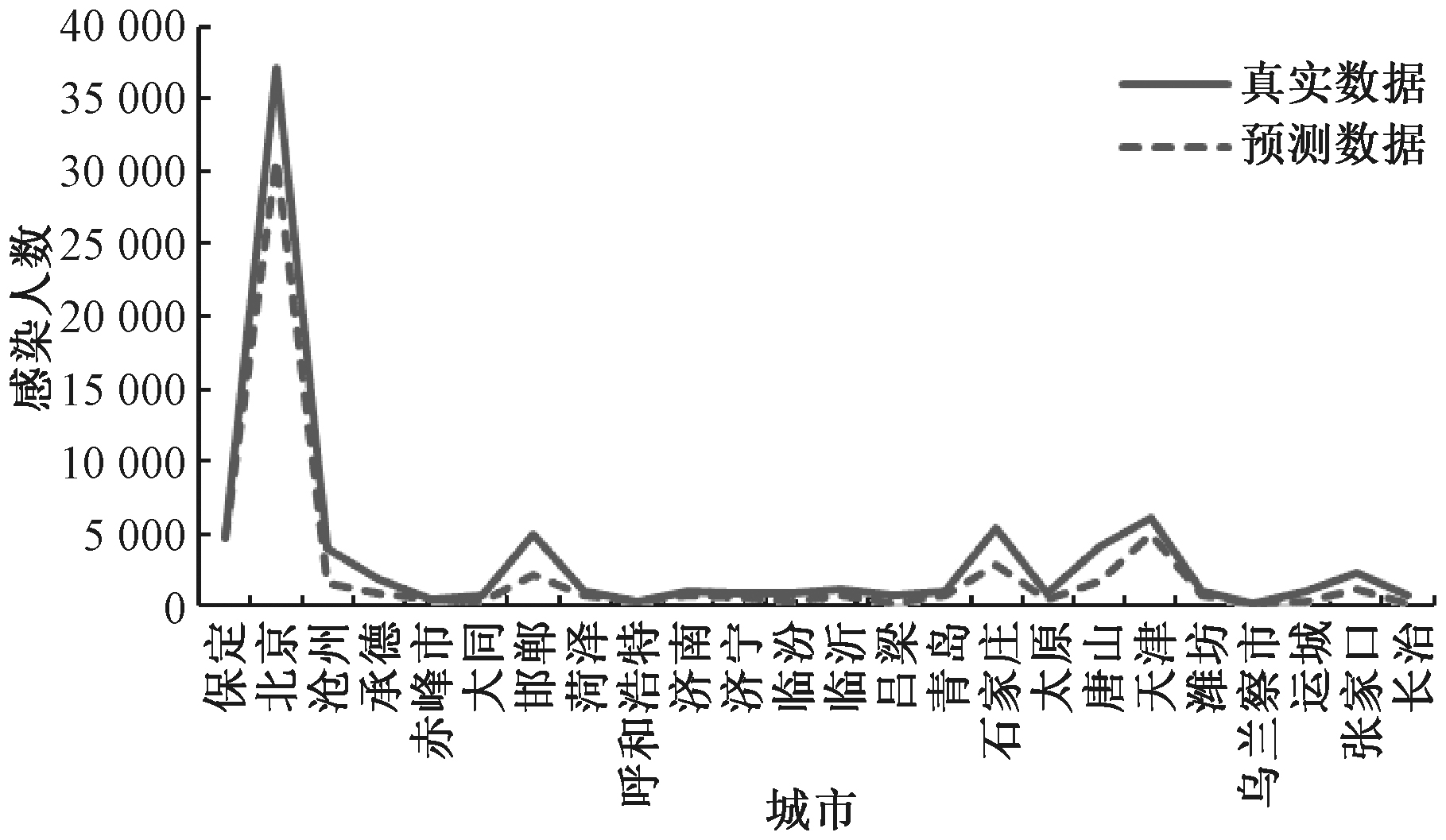
| [1] |
杨广映, 门金坤, 蒋鹏, 等. 基于二型模糊集理论的应急设施选址方法[J]. 大连理工大学学报, 2020, 60(6):654-662.
|
|
YANG Gangying, MEN Jinkun, JIANG Peng, et al. Emergency facility location method based on type-2 fuzzy set theory[J]. Journal of Dalian University of Technology, 2020, 60(6):654-662.
|
| [2] |
周宇阳, 张惠珍, 马良. 求解应急医疗设施分层递进式选址问题的改进免疫算法[J]. 运筹学学报, 2021, 25(2):15-34.
|
|
ZHOU Yuyang, ZHANG Huizhen, MA Liang. An improved immune algorithm for solving hierarchical and progressive location problem of emergency medical facilities[J]. Chinese Journal of Operation Research, 2021, 25(2):15-34.
|
| [3] |
纪颖, 严梦凡, 刘臣. 新冠肺炎疫情下应急医疗点的选址鲁棒配置研究[J]. 安全与环境学报, 2023, 23(1):193-204.
|
|
JI Ying, YAN Mengfan, LIU Chen. Research on robust location allocation of emergency medical points in COVID-19[J]. Journal of Safety and Environment, 2023, 23(1):193-204.
|
| [4] |
陈刚, 付江月. 灾后不确定需求下应急医疗移动医院鲁棒选址问题研究[J]. 中国管理科学, 2021, 29(9):213-223.
|
|
CHEN Gang, FU Jiangyue. Emergency medical mobile hospital robust location problem in post-disaster under demand[J]. Chinese Journal of Management Science, 2021, 29(9):213-223.
|
| [5] |
于冬梅, 高雷阜, 赵世杰. 考虑共享不确定因素的应急设施最大覆盖选址模型[J]. 运筹与管理, 2020, 29(12):43-50.
doi: 10.12005/orms.2020.0312
|
|
YU Dongmei, GAO Leifu, ZHAO Shijie, A maximum covering location model for emergency facility considering shared uncertainties[J]. Operations Research and Management Science, 2020, 29(12):43-50.
doi: 10.12005/orms.2020.0312
|
| [6] |
张鑫, 高淑春. 需求不确定下的应急物资储备库选址模型研究[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2017, 27(2): 169-174.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2017.02.030
|
|
ZHANG Xin, GAO Shuchun. Research on location model of emergency supplies repository under demand uncertainty[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2017, 27(2): 169-174.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2017.02.030
|
| [7] |
王惠珠, 周建勤. 基于不确定需求的铁路救援基地选址问题研究[J]. 北京交通大学学报:社会科学版, 2020, 19(3):100-107.
|
|
WANG Huizhu, ZHOU Jianqin. Location planning of railway rescue centers based on uncertain demand[J]. Journal of Beijing Jiaotong University:Social Sciences Edition, 2020, 19(3):100-107.
|
| [8] |
张忠义, 宋英华, 王喆, 等. 多层级防汛应急物资储备库公私协同LAP模型[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2020, 30(5):177-183.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2020.05.027
|
|
ZHANG Zhongyi, SONG Yinghua, WANG Zhe, et al. Public-private collaborative LAP model of multi-tiered flood emergency supplies repositories[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2020, 30(5):177-183.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2020.05.027
|
| [9] |
霍非舟, 董格力, 李墨潇, 等. 考虑需求等级与距离损失联动消防站选址研究[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2022, 32(3):183-193.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2022.03.025
|
|
HUO Feizhou, DONG Geli, LI Moxiao, et al. Study on location selection of linkage fire stations based on demand level and distance loss[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2022, 32(3):183-193.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2022.03.025
|
| [10] |
郑夏, 马良. 应急物资储备中心多目标优化选址的仿真研究[J]. 计算机仿真, 2019, 36(9):473-478.
|
|
ZHENG Xia, MA Liang. Simulation research of emergency materials reserve center multi-objective optimization location[J]. Computer Simulation, 2019, 36(9):473-478.
|
| [11] |
许伦辉, 曹宇超, 林培群. 基于融合免疫优化和遗传算法的多应急物资中心选址与调度[J]. 广西师范大学学报:自然科学版, 2020, 38(6):1-13.
|
|
XU Lunhui, CAO Yuchao, LIN Peiqun. Location and dispatching of multiple emergency materials center based on fusion immune optimization and genetic algorithm[J]. Journal of Guangxi Normal University:Natural Science Edition, 2020, 38(6): 1-13.
|
| [12] |
宋英华, 苏贝贝, 霍非舟, 等. 考虑动态需求的应急物资配送中心快速选址研究[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2019, 29(8):172-177.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2019.08.027
|
|
SONG Yinghua, SU Beibei, HUO Feizhou, et al. Research on rapid location selection of emergency materials distribution center considering dynamic demand[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2019, 29(8):172-177.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2019.08.027
|
| [13] |
孙秉珍, 杨佳楠, 白军成, 等. 充电中断情景下电动汽车充电站两阶段多目标区间选址优化决策[J]. 控制与决策, 2022, 37(4):1005-1014.
|
|
SUN Bingzhen, YANG Jianan, BAl Juncheng, et al. A two-stage multi-objective interval location optimization decision of electric vehicle charging station under charging interruption scenario[J]. Control and Decision, 2022, 37(4):1005-1014.
|
| [14] |
SUN Huali, WANG Yang, ZHANG Jianghua, et al. A robust optimization model for location-transportation problem of disaster casualties with triage and uncertainty[J]. Expert Systems With Applications, 2021, 175: DOI: 10.1016/j.eswa.2021.114867.
doi: 10.1016/j.eswa.2021.114867
|
| [15] |
WANG Jingyuan, WANG Xiaojian, WU Junjie. Inferring metapopulation propagation network for intra-city epidemic control and prevention[C]. 24th ACM SIGKDD International Conference, 2018: 830-838.
|
| [16] |
倪卫红, 陈太. 基于聚类-重心法的应急物流配送中心选址[J]. 南京工业大学学报:自然科学版, 2021, 43(2):255-263.
|
|
NI Weihong, CHEN Tai. Location selection of emergency logistics distribution center based on clustering-center of gravity method[J]. Journal of Nanjing University of Technology: Natural Science Edition, 2021, 43(2):255-263.
|
| [17] |
ALIDAEE B, WANG Haibo, KETHLEY B, et al. A unified view of parallel machine scheduling with interdependent processing rates[J]. Journal of Scheduling, 2019, 22(5): 499-515.
doi: 10.1007/s10951-019-00605-x
|
| [18] |
张惺惺, 吴双胜, 王全意, 等. 北京市2017—2018流行季流感感染率和发病率研究[J]. 国际病毒学杂志, 2019(2):73-76.
|
|
ZHANG Xingxing, WU Shuangsheng, WANG Quanyi, et al. Estimated infection rates and incidence rates of seasonal influenza in Beijing during the 2017-2018 influenza season[J]. International Journal of Virology, 2019(2):73-76.
|
| [19] |
张艳霞, 李进. 基于SIR模型的新冠肺炎疫情传播预测分析[J]. 安徽工业大学学报:自然科学版, 2020, 37(1):94-101.
|
|
ZHANG Yanxia, LI Jin. Prediction and analysis of propagation of novel coronavirus pneumonia epidemic based on SIR model[J]. Journal of Anhui University of Technology: Natural Science Edition, 2020, 37(1):94-101.
|