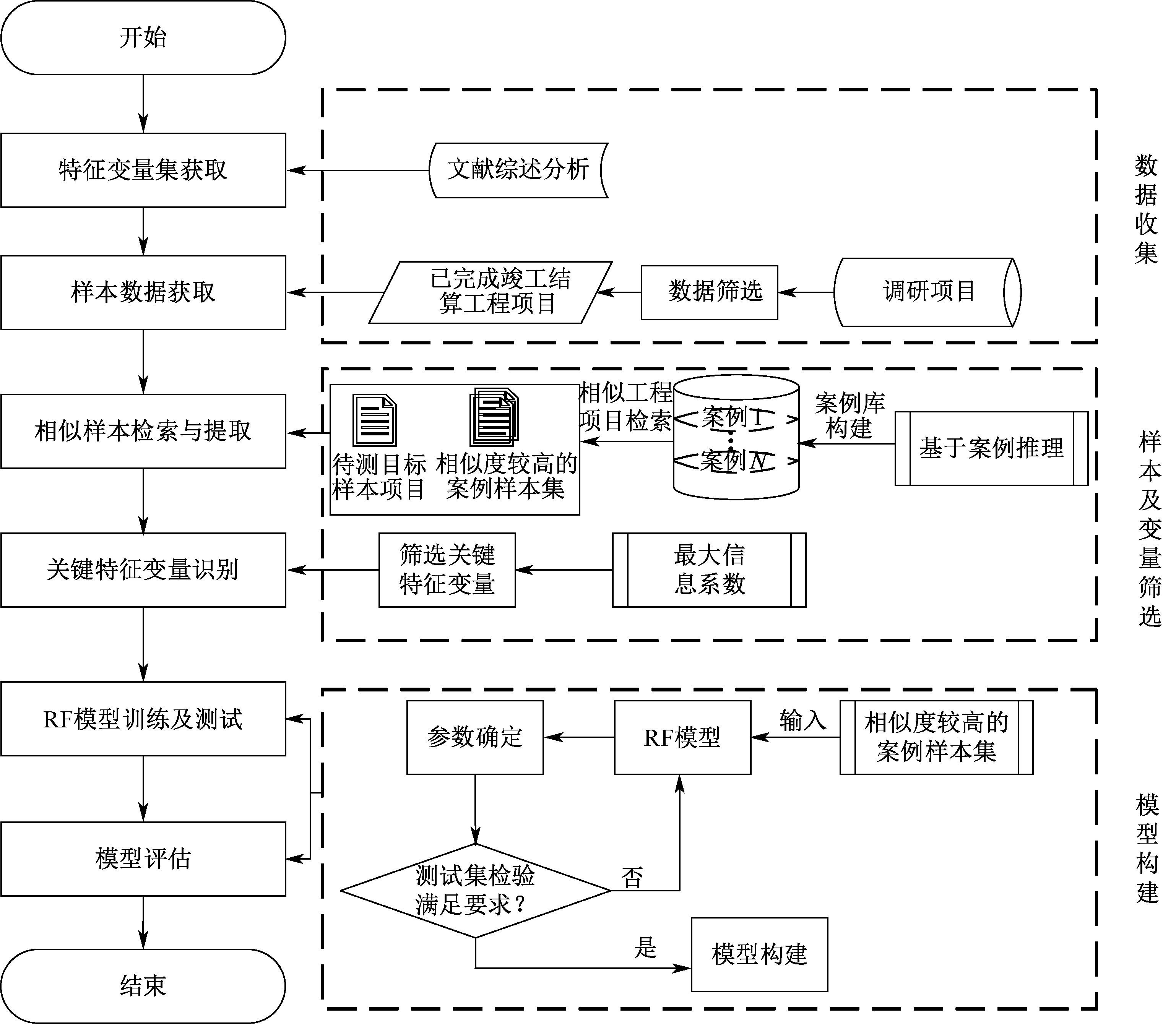
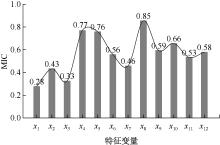
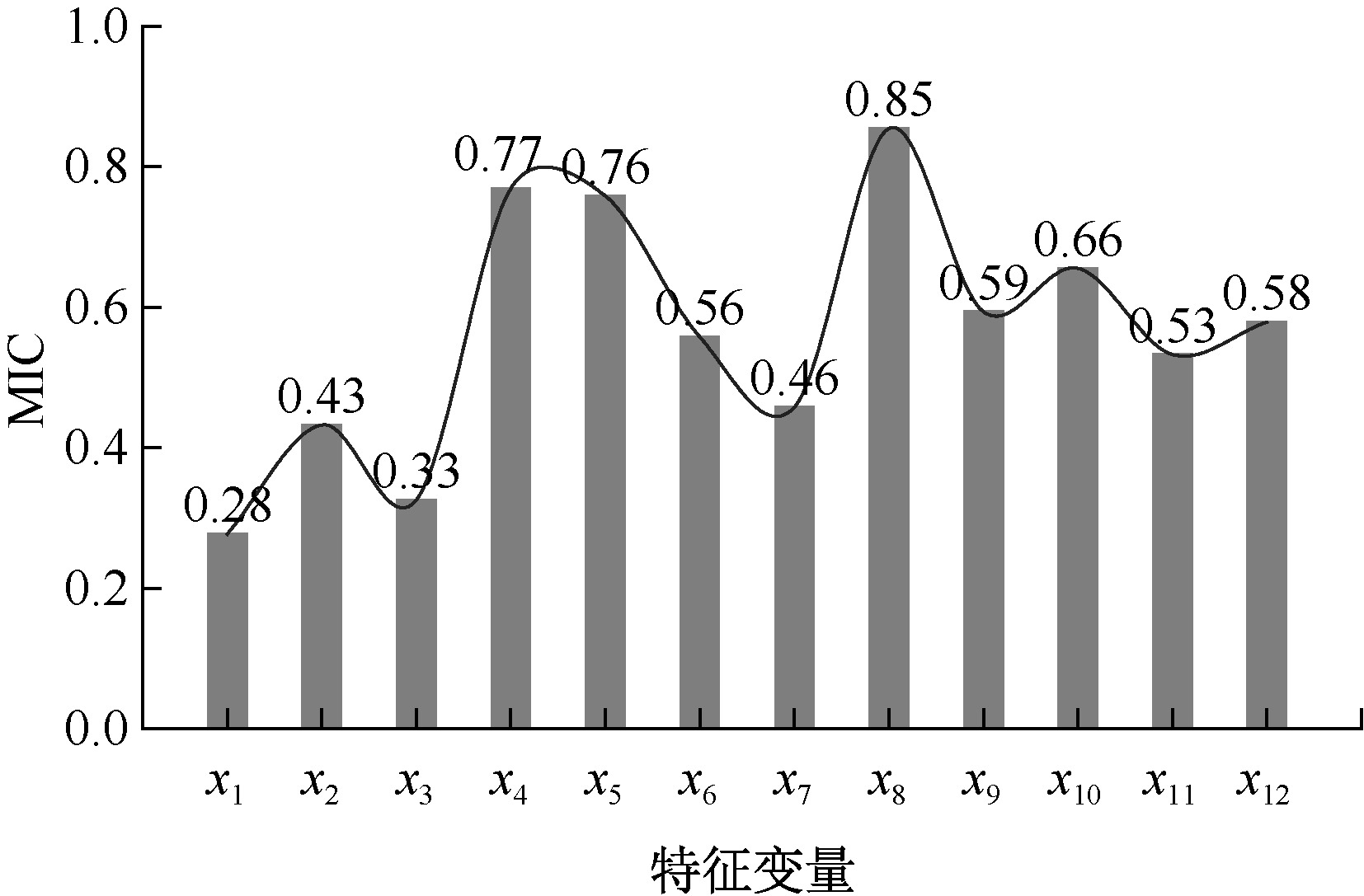
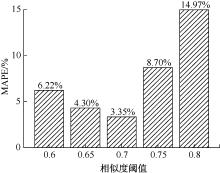
| [1] |
郑文博. 国内外建筑工程安全管理主要成就: 基于安全事故、安全管理制度及相关文献的研究[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2022, 32(10):8-17.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2022.10.1932
|
|
ZHENG Wenbo. Main achievements of construction engineering safety management: review of safety accidents, safety management system, and relevant literature[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2022, 32(10):8-17.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2022.10.1932
|
| [2] |
李秀云, 杨高升, 李杰. 最优安全文明施工措施费费率计取模型的构建与应用[J]. 中国安全生产科学技术, 2013, 9(10):147-151.
|
|
LI Xiuyun, YANG Gaosheng, LI Jie. Establishment and application of accrual model about optimal safe and civilized construction measures fee rate[J]. Journal of Safety Science and Technology, 2023, 9(10):174-151.
|
| [3] |
GURCANLI G E, BILIR S, SEVIM M. Activity based risk assessment and safety cost estimation for residential building construction projects[J]. Safety Science, 2015, 80: 1-12.
doi: 10.1016/j.ssci.2015.07.002
|
| [4] |
BELAY A M, TORP O, THODESEN C, et al. A framework for organizing a resilient cost benefit analysis for construction projects[J]. Procedia Engineering, 2016, 145: 1169-1176.
doi: 10.1016/j.proeng.2016.04.151
|
| [5] |
LEE J, JEONG J, SOH J, et al. Quantitative analysis of the accident prevention costs in Korean construction projects[J]. Buildings, 2022, 12(10): DOI: 10.3390/BUILDINGS12101536.
|
| [6] |
KETABI A B, HERAVI G. Developing a framework for evaluating construction project safety levels and optimal cost allocation to safety influential factors[J]. Engineering, Construction and Architectural Management, 2022, 29(2): 643-668.
doi: 10.1108/ECAM-07-2020-0536
|
| [7] |
陈伟, 周曼, 叶家军, 等. 建筑工程安全施工费费率测算的PSO-BP模型研究[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2016, 26(5):146-151.
|
|
CHEN Wei, ZHOU Man, YE Jiajun, et al. PSO-BP modeling research on fee rate measurement of construction project safe construction cost[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2016, 26(5):146-151.
|
| [8] |
陈伟, 杨主张, 容思思, 等. 地铁安全文明施工费费率标准动态测算研究[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2018, 28(4):145-150.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2018.04.025
|
|
CHEN Wei, YANG Zhuzhang, RONG Sisi, et al. Dynamic calculation method of safety-civilized measure cost rate of subway project[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2018, 28(4):145-150.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2018.04.025
|
| [9] |
张舒, 代涵, 史秀志, 等. 基于PSO-RF的建筑安全文明施工费费率预测[J]. 安全与环境学报, 2022, 22(2):844-850.
|
|
ZHANG Shu, DAI Han, SHI Xiuzhi, et al. Prediction of fee rate for safety-civilized construction cost based on PSO-RF model[J]. Journal of Safety and Environment, 2022, 22(2):844-850.
|
| [10] |
杨文臣, 周燕宁, 田毕江, 等. 基于聚类分析和SVM的二级公路交通事故严重度预测[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2022, 32(5):163-169.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2022.05.1263
|
|
YANG Wenchen, ZHOU Yanning, TIAN Bijiang, et al. Traffic accident severity prediction for secondary highways based on cluster analysis and SVM model[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2022, 32(5):163-169.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2022.05.1263
|
| [11] |
KARABADJI N E I, KORBA A A, ASSI A, et al. Accuracy and diversity-aware multi-objective approach for random forest construction[J]. Expert Systems with Applications, 2023,225: DOI: 10.1016/J.ESWA.2023.120138.
|
| [12] |
赖成光, 陈晓宏, 赵仕威, 等. 基于随机森林的洪灾风险评价模型及其应用[J]. 水利学报, 2015, 46(1):58-66.
|
|
LAI Chengguang, CHEN Xiaohong, ZHAO Shiwei, et al. A flood risk assessment model based on random forest and its application[J]. Journal of Hydraulic Engineering, 2015, 46(1):58-66.
|
| [13] |
SPEISER J L, MILLER M E, TOOZE J, et al. A comparison of random forest variable selection methods for classification prediction modeling[J]. Expert Systems with Applications, 2019, 134: 93-101.
doi: 10.1016/j.eswa.2019.05.028
pmid: 32968335
|
| [14] |
XIAO Xue, SKITMORE M, YAO Weixin, et al. Improving robustness of case-based reasoning for early-stage construction cost estimation[J]. Automation in Construction, 2023, 151:DOI: 10.1016/j.autcon.2023.104777.
|
| [15] |
RESHEF D N, RESHEF Y A, FINUCANE H K, et al. Detecting novel associations in large data sets[J]. Science, 2011, 334(6062): 1518-1524.
doi: 10.1126/science.1205438
pmid: 22174245
|
| [16] |
罗为检. 应用最大信息系数和支持向量机估测森林蓄积量[J]. 东北林业大学学报, 2022, 50(1):40-45.
|
|
LUO Weijian. Forest volume estimation using maximum information coefficient and support vector machine[J]. Journal of Northeast Forestry University, 2022, 50(1):40-45.
|
| [17] |
BREIMAN L. Random forests[J]. Machine Learning, 2001, 45: 5-32.
doi: 10.1023/A:1010933404324
|
| [18] |
温博文, 董文瀚, 解武杰, 等. 基于改进网格搜索算法的随机森林参数优化[J]. 计算机工程与应用, 2018, 54(10):154-157.
doi: 10.3778/j.issn.1002-8331.1612-0328
|
|
WEN Bowen, DONG Wenhan, XIE Wujie, et al. Parameter optimization method for random forest based on improved grid search algorithm[J]. Computer Engineering and Applications, 2018, 54(10):154-157.
doi: 10.3778/j.issn.1002-8331.1612-0328
|