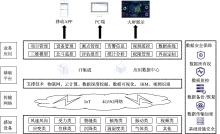
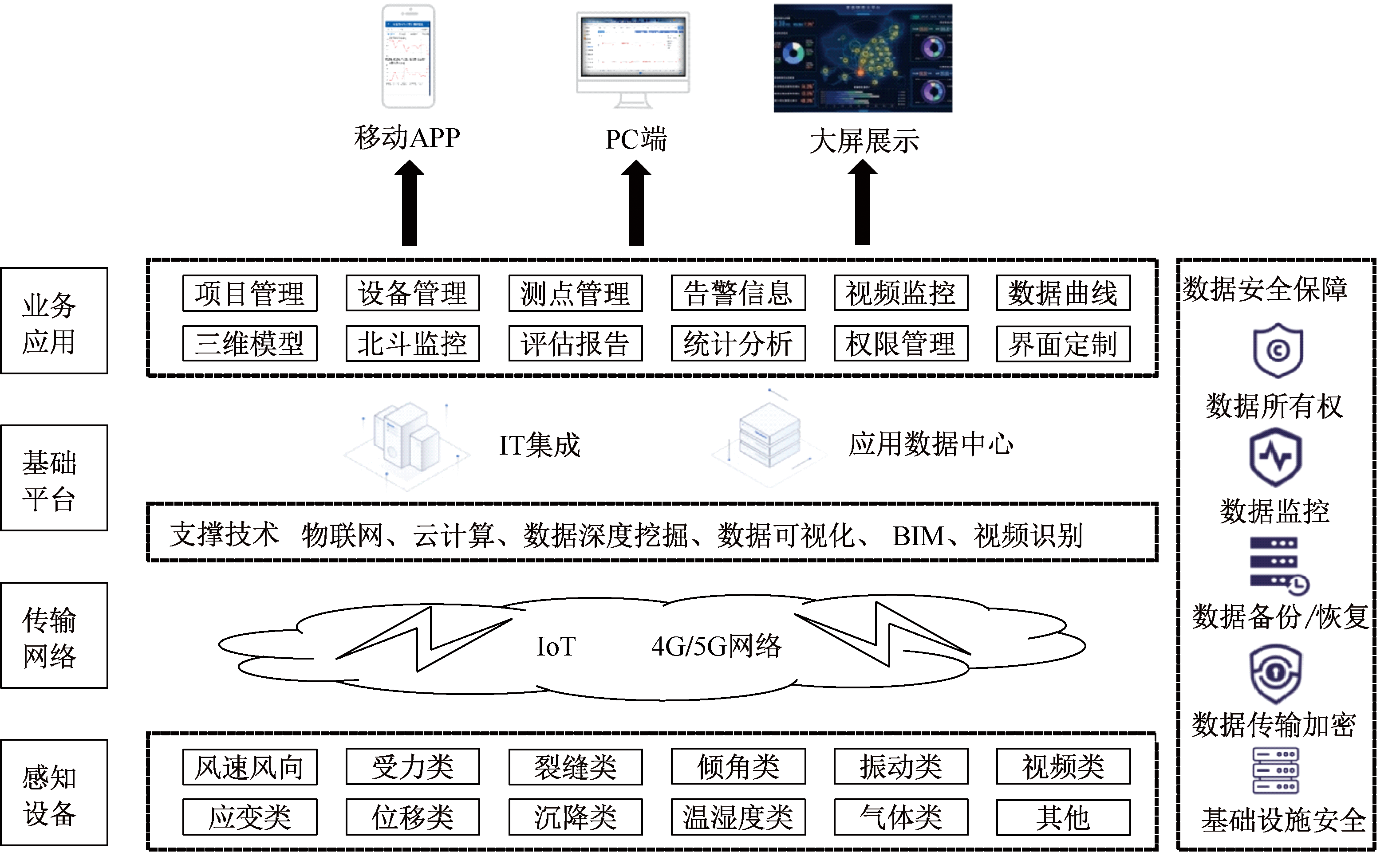
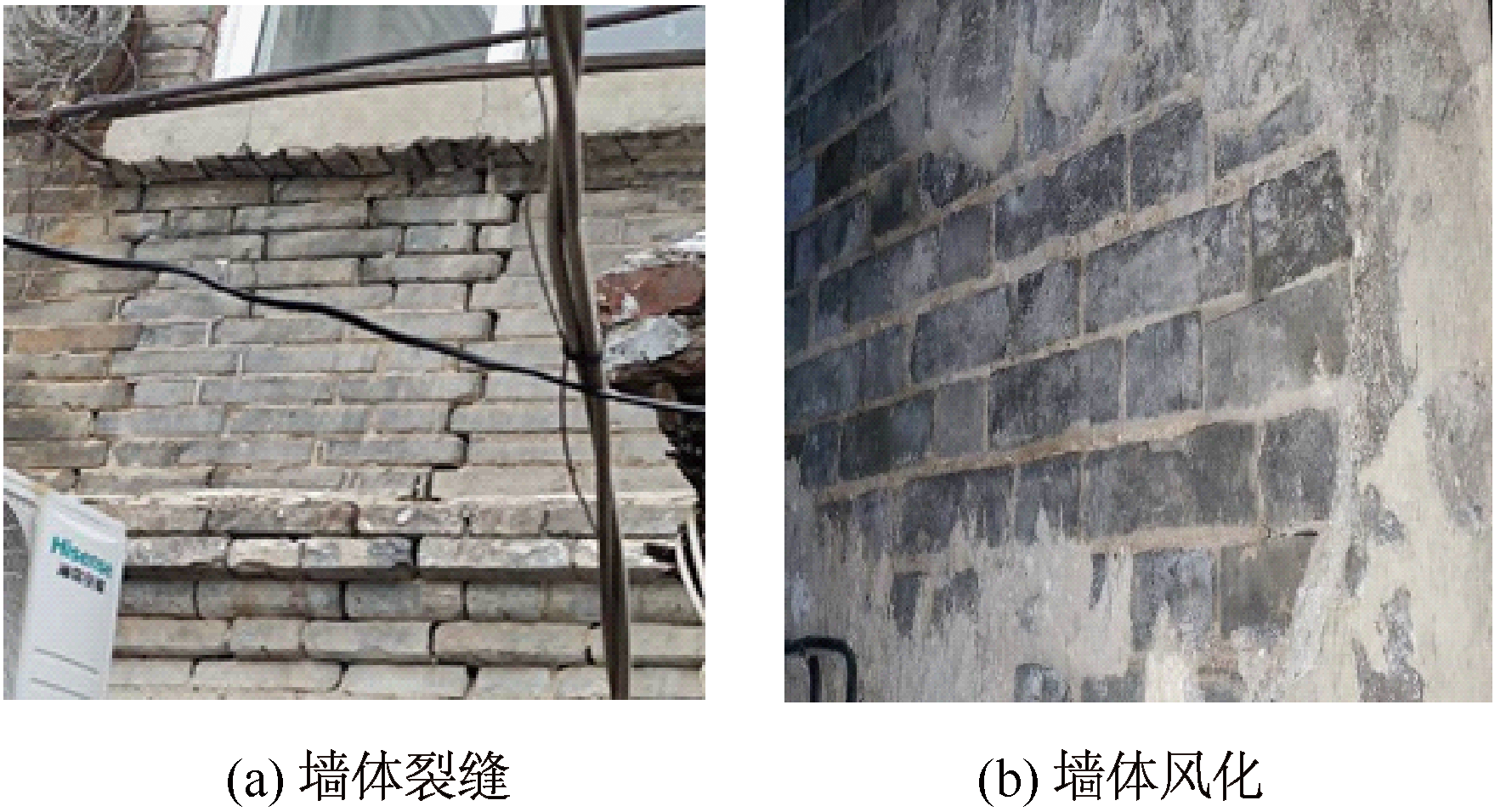
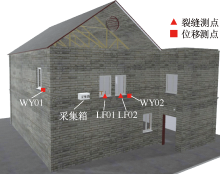
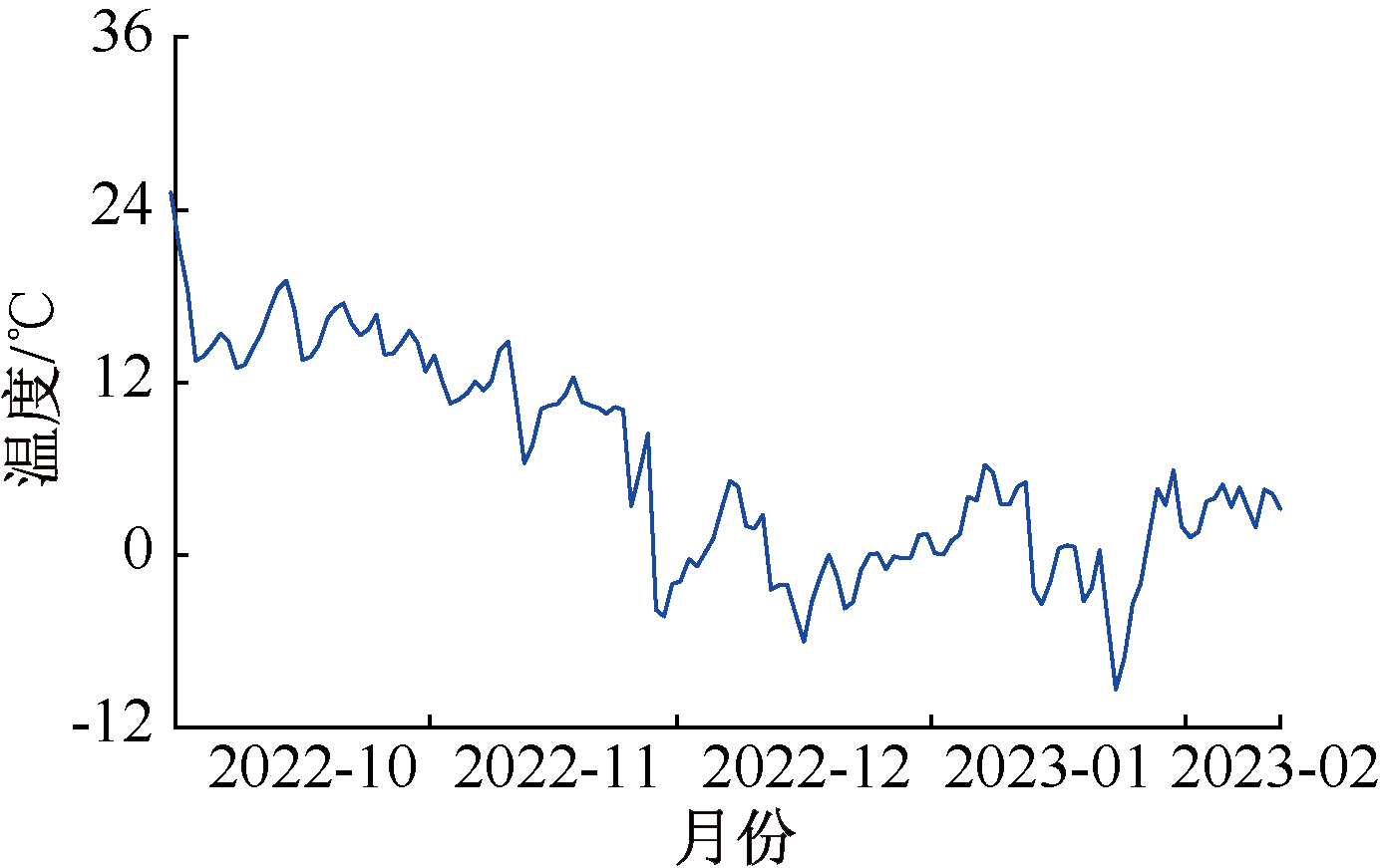
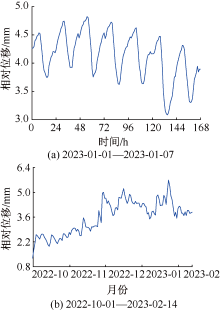
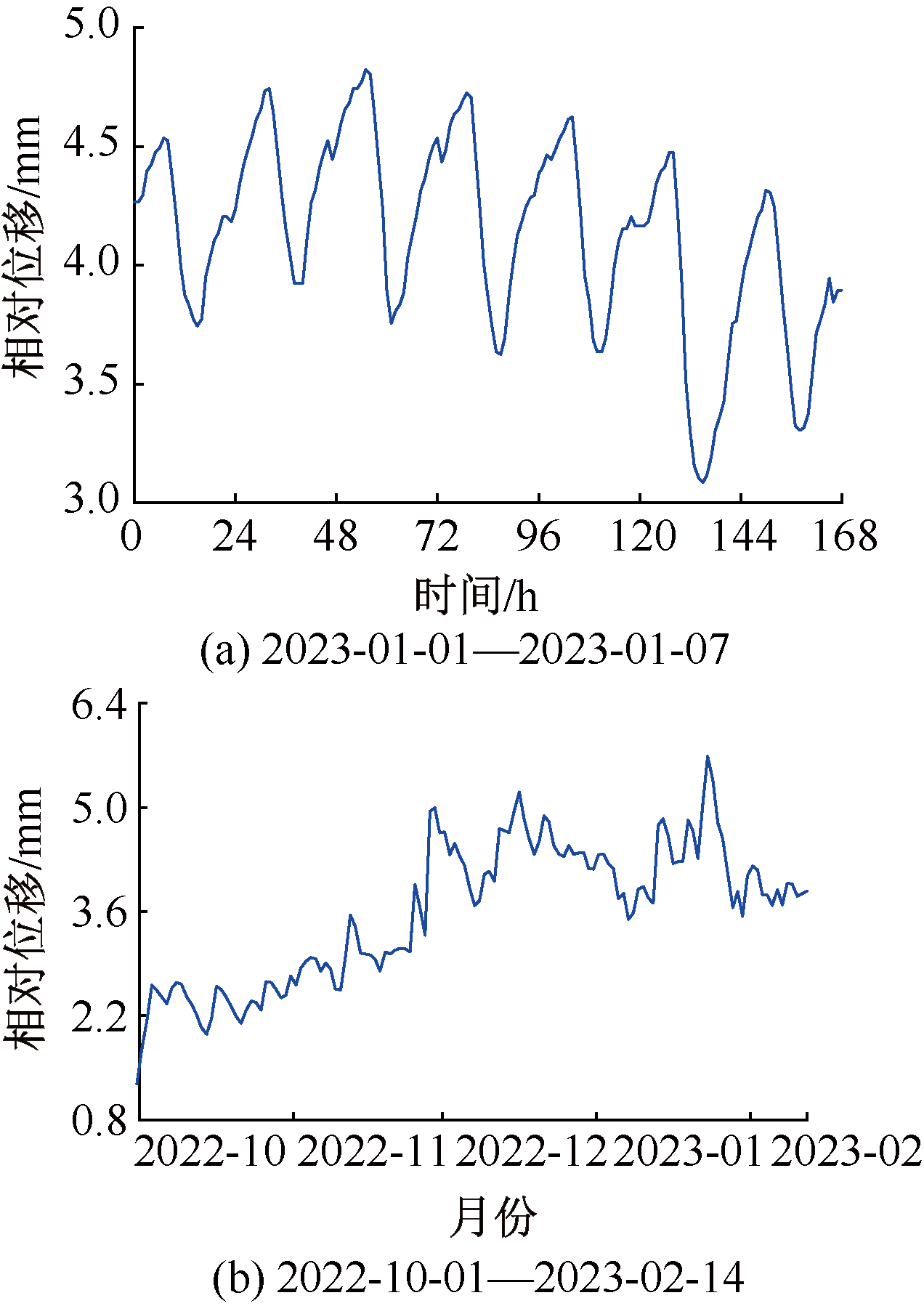
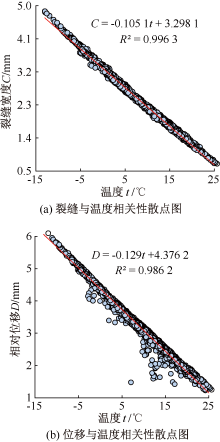
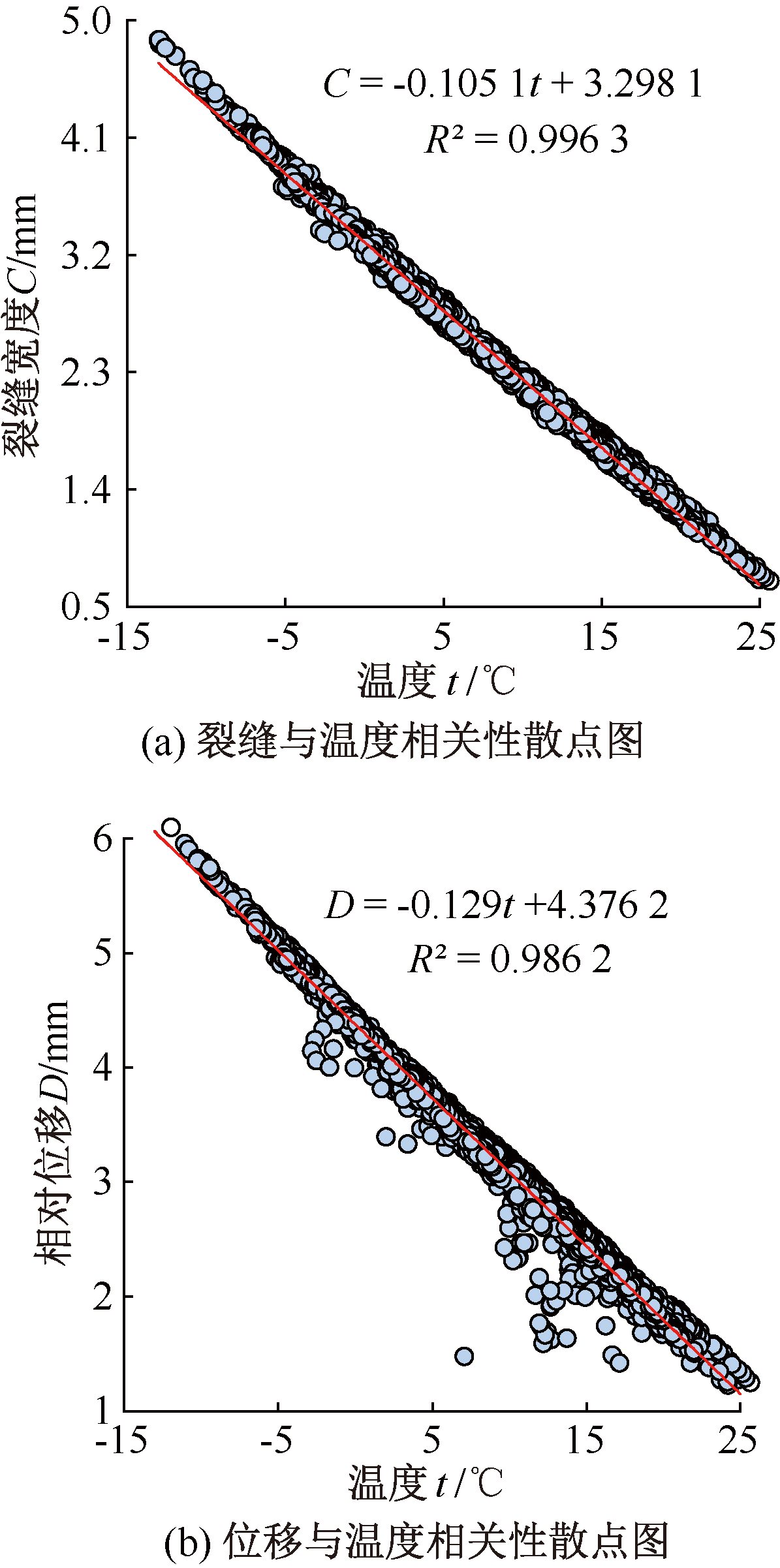
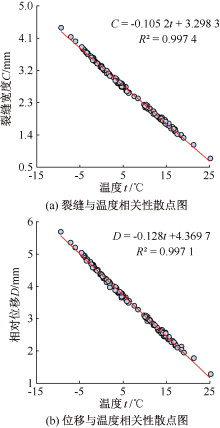
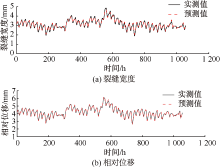
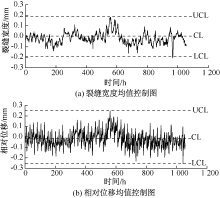
| [1] |
徐建, 梁建国, 石柳, 等. 我国砌体结构发展的若干问题探讨[J]. 建筑结构, 2016, 46(15): 91-97.
|
|
XU Jian, LIANG Jianguo, SHI Liu, et al. Discussion on some problems of development of masonry structures in China[J]. Building Structure, 2016, 46(15): 91-97.
|
| [2] |
阮超, 张延军, 李胡爽, 等. 武汉大东湖城市污水深隧结构健康监测系统研究[J]. 中国给水排水, 2021, 37(20): 126-132.
|
|
YUAN Chao, ZHANG Yanjun, LI Hushuang, et al. Research on structure health monitoring system of dadonghu urban sewage deep tunnel in Wuhan[J]. China Water and Wastewater, 2021, 37(20): 126-132.
|
| [3] |
轩慎青, 陈良超, 方舟, 等. 大跨度空间网格结构健康监测系统设计及应用[J]. 北京化工大学学报:自然科学版, 2022, 49(5): 108-116.
|
|
XUAN Shenqing, CHEN Liangchao, FANG Zhou, et al. Design and application of a health monitoring system for largespan space grid structures[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Chemical Technology:Natural Science, 2022, 49(5): 108-116.
|
| [4] |
姜锐. 铁路客站结构健康监测应用现状及展望[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2020, 30(增1): 71-76.
|
|
JIANG Rui. Research status and prospect of health monitoring on railway station structures[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2020, 30(S1): 71-76.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2020.S1.014
|
| [5] |
DAL C A, RUSSO S. Evaluation of static and dynamic long-term structural monitoring for monumental masonry structure[J]. Journal of Civil Structural Health Monitoring, 2019, 9(2): 169-182.
|
| [6] |
BARRIAS A, RODRIGUEZ G, CASAS J R, et al. Application of distributed optical fiber sensors for the health monitoring of two real structures in Barcelona[J]. Structure and Infrastructure Engineering, 2018, 14(7): 967-985.
|
| [7] |
BLANCO H, BOFFILL Y, LOMBILLO I, et al. An integrated structural health monitoring system for determining local/global responses of historic masonry buildings[J]. Structural Control and Health Monitoring, 2018, 25(8): DOI: 10.1002/stc.2196.
|
| [8] |
ZINI G, BETTI M, BARTOLI G. A pilot project for the long-term structural health monitoring of historic city gates[J]. Journal of Civil Structural Health Monitoring, 2022, 12(3): 537-556.
|
| [9] |
邢介东. 高铁站房结构健康监测系统设计[J]. 铁道勘察, 2023, 49(2): 124-130,147.
|
|
XING Jiedong. Design and implementation of structural health monitoring system for Jinandong railway station[J]. Railway Investigation and Surveying, 2023, 49(2): 124-130,147.
|
| [10] |
谢全敏, 马伟, 杨文东. 公路隧道结构健康自监测系统设计与实施[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2022, 32(7): 56-62.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2022.07.1444
|
|
XIE Quanmin, MA Wei, YANG Wendong. Design and implementation of SHM system for highway tunels[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2022, 32(7): 56-62.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2022.07.1444
|
| [11] |
李宁, 杜江, 魏建友, 等. 某砖混砌体结构房屋危险性鉴定实例分析[J]. 建筑结构, 2021, 51(增2): 1 416-1 421.
|
|
LI Ning, DU Jiang, WEI Jianyou, et al. Analysis of a case study on the risk appraisal of a brick-concrete structure building[J]. Building Structure, 2021, 51(S2): 1 416-1 421.
|
| [12] |
JGJ 125—2016, 危险房屋鉴定标准[S].
|
|
JGJ 125-2016, Standard of dangerous building appraisal[S].
|
| [13] |
谢扬. 道路工程智能压实数据异常值识别处理方法研究[J]. 市政技术, 2018, 36(5): 17-19.
|
|
XIE Yang. Method research of identification and processing of abnormal value of intelligent compaction data for road engineering[J]. Journal of Municipal Technology, 2018, 36(5): 17-19.
|
| [14] |
任普. 基于大数据的桥梁监测数据清洗方法研究[D]. 南京: 东南大学, 2019.
|
|
REN Pu. Research on the data cleansingmethods for bridge monitoringdata based on big-data platform[D]. Nanjing: Southeast University, 2019.
|
| [15] |
孙延奎. 小波分析及其应用[M]. 北京: 机械工业出版, 2005: 35-46.
|
| [16] |
GB 50292—2015, 民用建筑可靠性鉴定标准[S].
|
|
GB 50292-2015, Standard for appraiser of reliability of civil buildings[S].
|
| [17] |
AKOOND N, PELA L, MOLINS C, et al. Automated data analysis for static structural health monitoring of masonry heritage structures[J]. Structural Control and Health Monitoring, 2020, 27(10): DOI: 10.1002/stc.2581.
|
| [18] |
邓扬, 李爱群, 丁幼亮, 等. 基于长期监测数据的大跨桥梁结构伸缩缝损伤识别[J]. 东南大学学报, 2011, 41(2): 336-341.
|
|
DENG Yang, LI Aiqun, DING Youliang, et al. Damage identification of expansion joints in long span bridge using long-term monitoring data[J]. Journal of Southeast University, 2011, 41(2): 336-341.
|