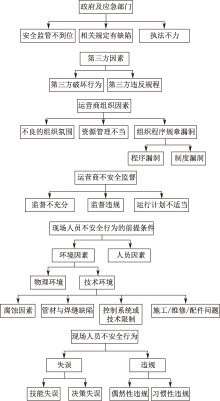
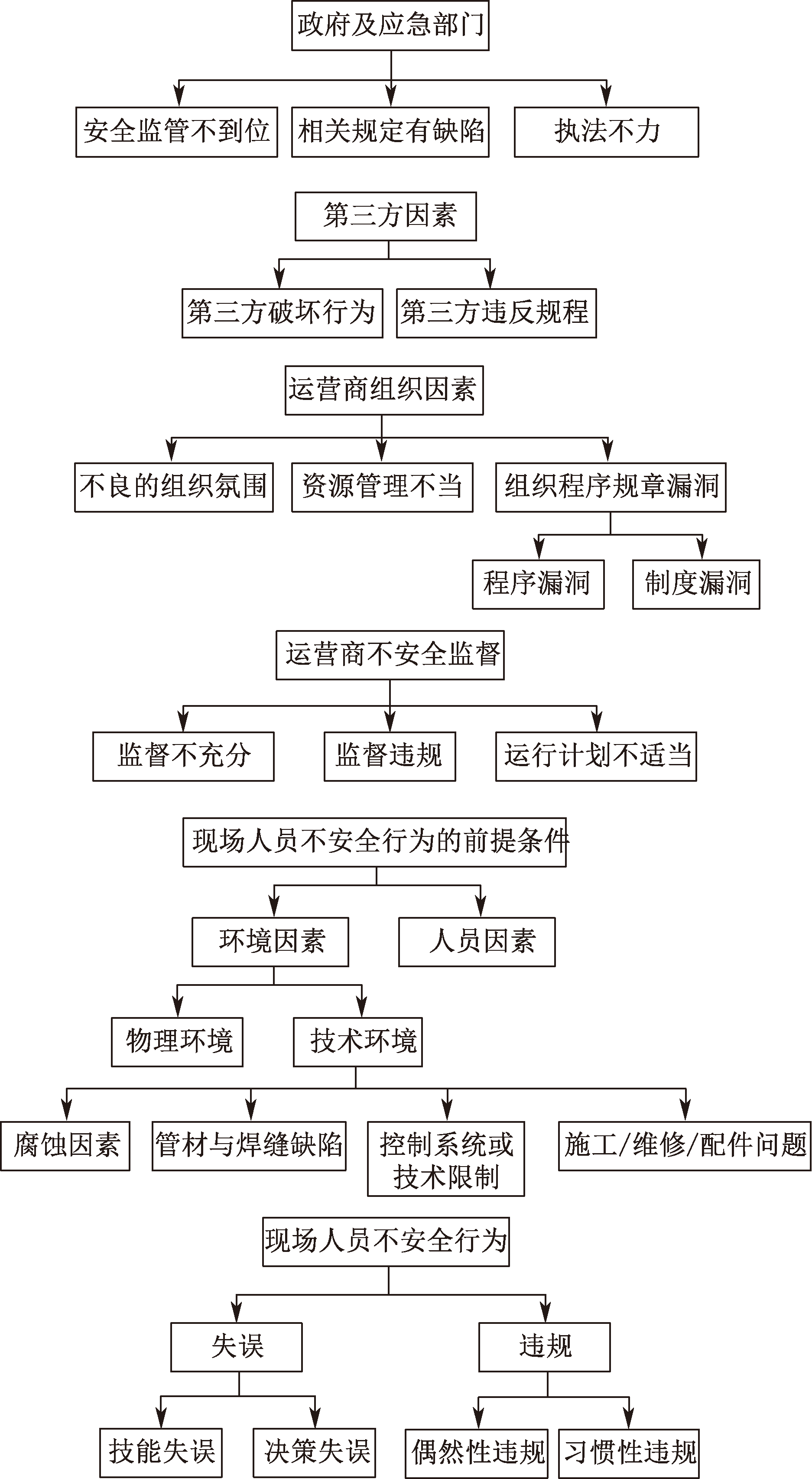
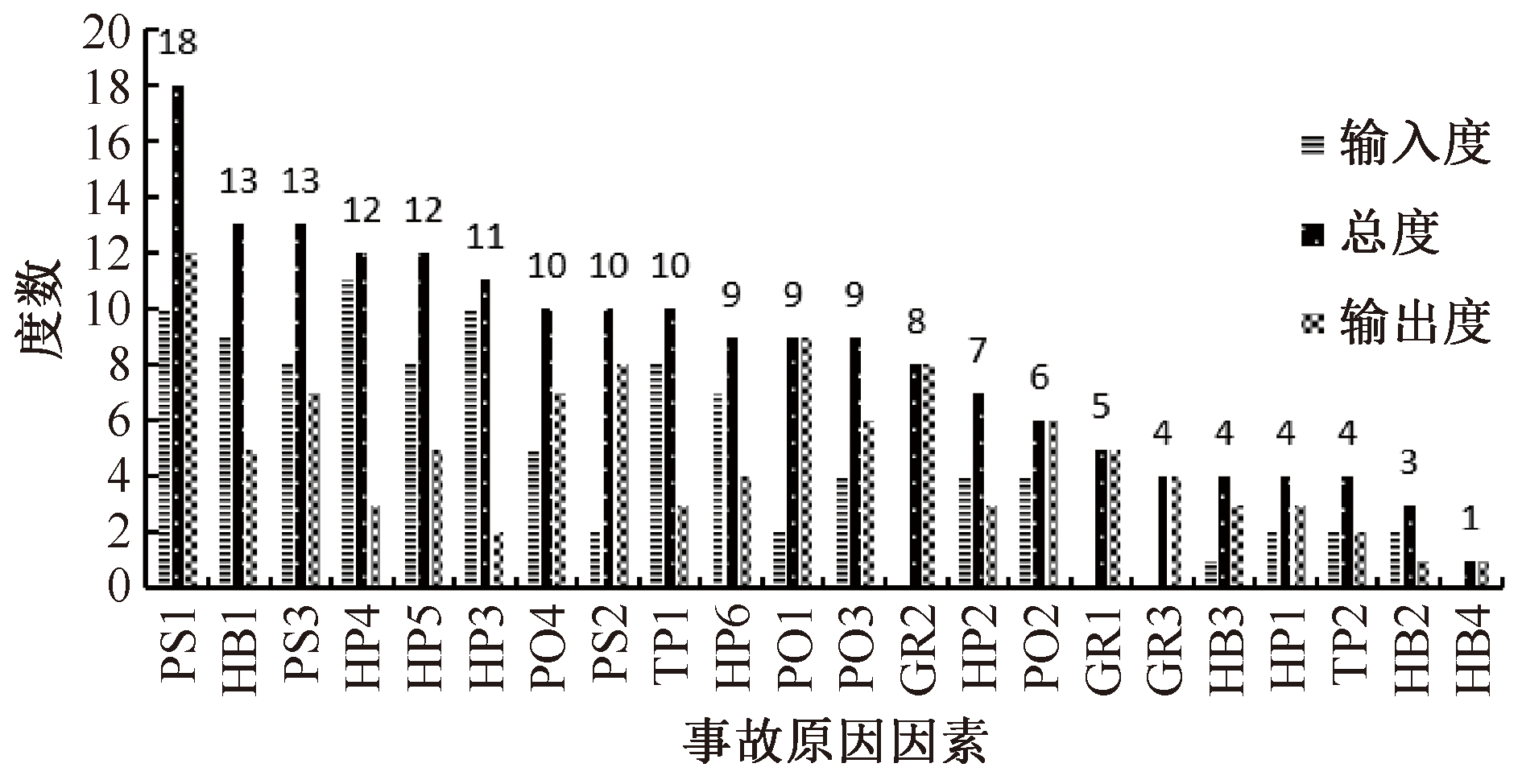
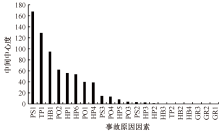
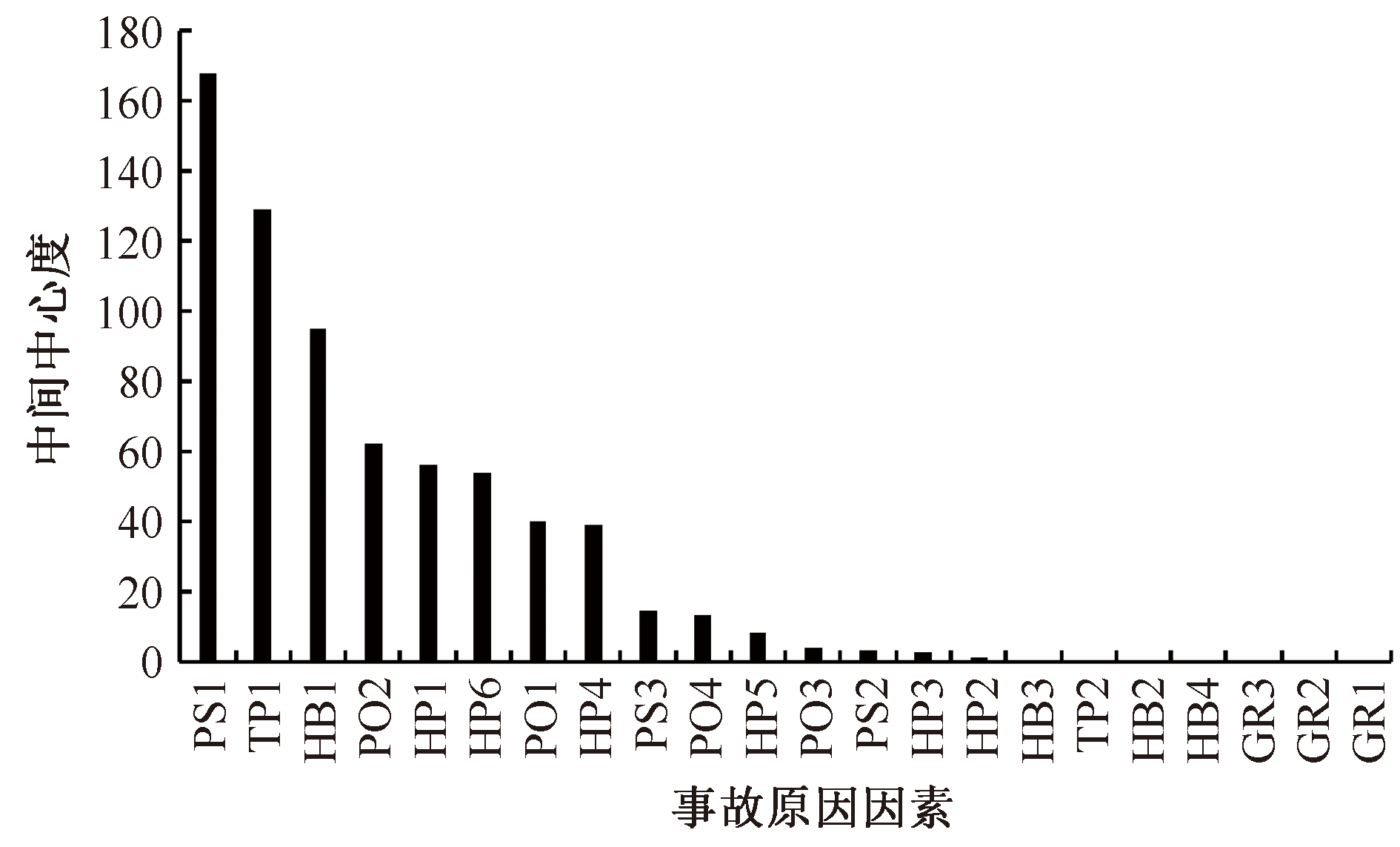
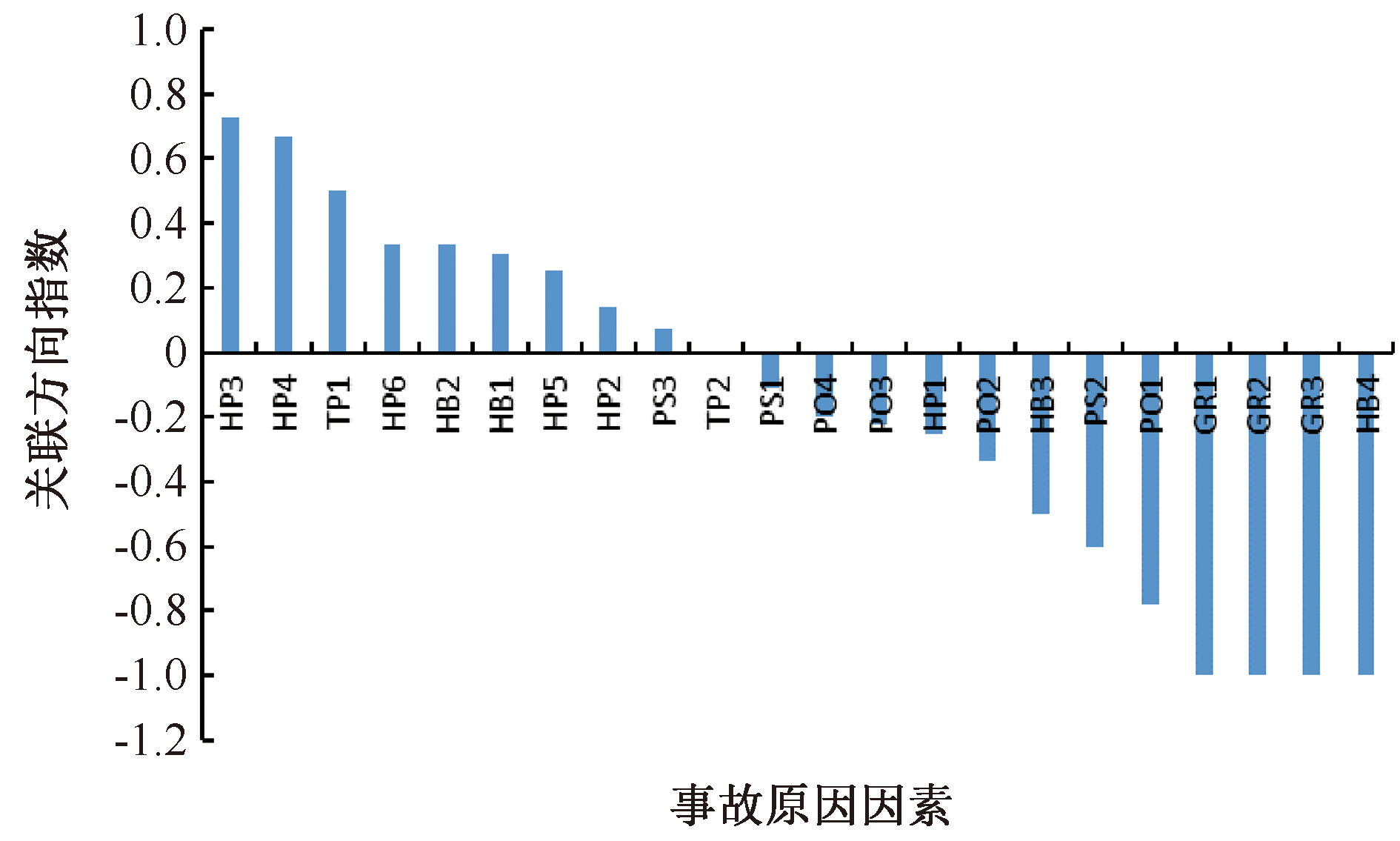
| [1] |
狄彦, 帅健, 王晓霖, 等. 油气管道事故原因分析及分类方法研究[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2013, 23(7): 109-115.
|
|
DI Yan, SHUAI Jian, WANG Xiaolin, et al. Study on methods for classifying oil and gas pipeline incidents[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2013, 23(7): 109-115.
|
| [2] |
LEVESON N. A new accident model for engineering safer systems[J]. Safety Science, 2004, 42(4), 237-270.
|
| [3] |
赵挺生, 胡俊杰, 师玉栋, 等. 塔吊安装与拆卸作业安全性分析[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2021, 31(10): 32-38.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2021.10.005
|
|
ZHAO Tingsheng, HU Junjie, SHI Yudong, et al. Safety analysis on tower crane installation and dismantling[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2021, 31(10): 32-38.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2021.10.005
|
| [4] |
吴海涛, 黎双喜. 高铁应急调度STAMP/STPA安全性分析[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2021, 31(6): 113-120.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn 1003-3033.2021.06.015
|
|
WU Haitao, LI Shuangxi. High-speed railway emergency dispatching safety analysis based on STAMP/STPA[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2021, 31(6): 113-120.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn 1003-3033.2021.06.015
|
| [5] |
王瑛, 孙贇, 李超, 等. 基于STAMP模型的军机飞行训练安全性分析[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2018, 28(9): 68-73.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2018.09.012
|
|
WANG Ying, SUN Yun, LI Chao, et al. Analysis of military aircraft flight training safety based on STAMP model[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2018, 28(9):68-73.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2018.09.012
|
| [6] |
QIAO Wanguan, CHEN Xue, XIA Wenxin. STAMP-based causal analysis of the coal mine major accident: from the perspective of safety process[J]. Energy Reports, 2021, 7(S7): 116-124.
|
| [7] |
GONG Yunhua, LI Yuntao. STAMP-based causal analysis of China-Donghuang oil transportation pipeline leakage and explosion accident[J]. Journal of Loss Prevention in the Process Industries, 2018, 56: 402-413.
|
| [8] |
CHAUVINA C, LARDJANEB S, MORELA G, et al. Human and organizational factors in maritime accidents: analysis of collisions at sea using HFACS[J]. Accident Analysis and Prevention, 2013, 59: 26-37.
|
| [9] |
李珏, 刘焕. 基于HFACS的施工触电事故致因的关联性分析与干预对策[J]. 长沙理工大学学报:自然科学版, 2019, 16(2): 36-41,48.
|
|
LI Jue, LIU Huan, Association of causes and intervention countermeasures of electric shock accidents based on HFACS[J]. Journal of Changsha University of Science and Technology:Natural Science, 2019, 16(2): 36-41,48.
|
| [10] |
XU Ruihua, LUO Fan, CHEN Gaoming, et al. Application of HFACS and grounded theory for identifying risk factors of air traffic controllers' unsafe acts[J]. International Journal of Industrial Ergonomics, 2021, 86: DOI: 10.1016/j.ergon.2021.103228.
|
| [11] |
KAPTAN M, SARIALIOGLU S, UGURLU O, et al. The evolution of the HFACS method used in analysis of marine accidents: a review[J]. International Journal of Industrial Ergonomics, 2021, 86:DOI: 10.1016/j.ergon.2021.103225.
|
| [12] |
WANG Jing, FAN Yunxiao, GAO Yuan. Revising HFACS for SMEs in the chemical industry: HFACS-CSMEs[J]. Journal of Loss Prevention in the Process Industries, 2020, 65: DOI: 10.1016/j.jlp.2020.104138.
|
| [13] |
李珏, 李佳文. 基于STAMP-HFACS的建筑坍塌事故风险因素分析[J]. 工程管理学报, 2022, 36(5): 148-153.
|
|
LI Jue, LI Jiawen. Risk factors analysis of building collapse accident based on STAMP-HFACS[J]. Journal of Engineering Management, 2022, 36(5): 148-153.
|
| [14] |
LOWER M, MAGOTT J, SKORUOSKI J. A system-theoretic accident model and process with human factors analysis and classification system taxonomy[J]. Safety Science, 2018, 110: 393-410.
|
| [15] |
陈芳, 韩美佳. 空中危险接近事件中的空管风险因素识别[J]. 安全与环境学报, 2021, 21(4): 1583-1591.
|
|
CHEN Fang, HAN Meijia. Risk factors identification of the air traffic control in the near-midair collision[J]. Journal of Safety and Environment, 2021, 21(4): 1583-1591.
|
| [16] |
LI Chenlin, TANG Tao, CHATZIMICHAIKIDOU M M, et al. A hybrid human and organisational analysis method for railway accidents based on STAMP-HFACS and human information processing[J]. Applied Ergonomics, 2019, 79: 122-142.
doi: S0003-6870(18)30742-7
pmid: 30718024
|
| [17] |
韩天园, 田顺, 吕凯光, 等. 基于文本挖掘的重特大交通事故成因网络分析[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2021, 31(9): 150-156.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2021.09.021
|
|
HAN Tianyuan, TIAN Shun, LYU Kaiguang, et al. Network analysis on causes for serious traffic accidents based on textmining[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2021, 31(9): 150-156.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2021.09.021
|
| [18] |
李珏, 王幼芳. 基于文本挖掘的建筑施工高处坠落事故致因网络分析[J]. 安全与环境学报, 2020, 20(4): 1284-1290.
|
|
LI Jue, WANG Youfang. Causation network analysis of the construction falling or collapsing accidents based on the text mining[J]. Journal of Safety and Environment, 2020, 20(4): 1284-1290.
|
| [19] |
贾旭东, 衡量. 扎根理论的“丛林”、过往与进路[J]. 科研管理, 2020, 41(5): 151-163.
|
|
JIA Xudong, HENG Liang. The "jungle",history,and approach road of the grounded theory[J]. Science Research Management, 2020, 41(5): 151-163.
|