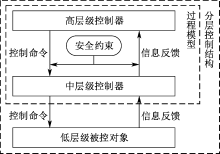
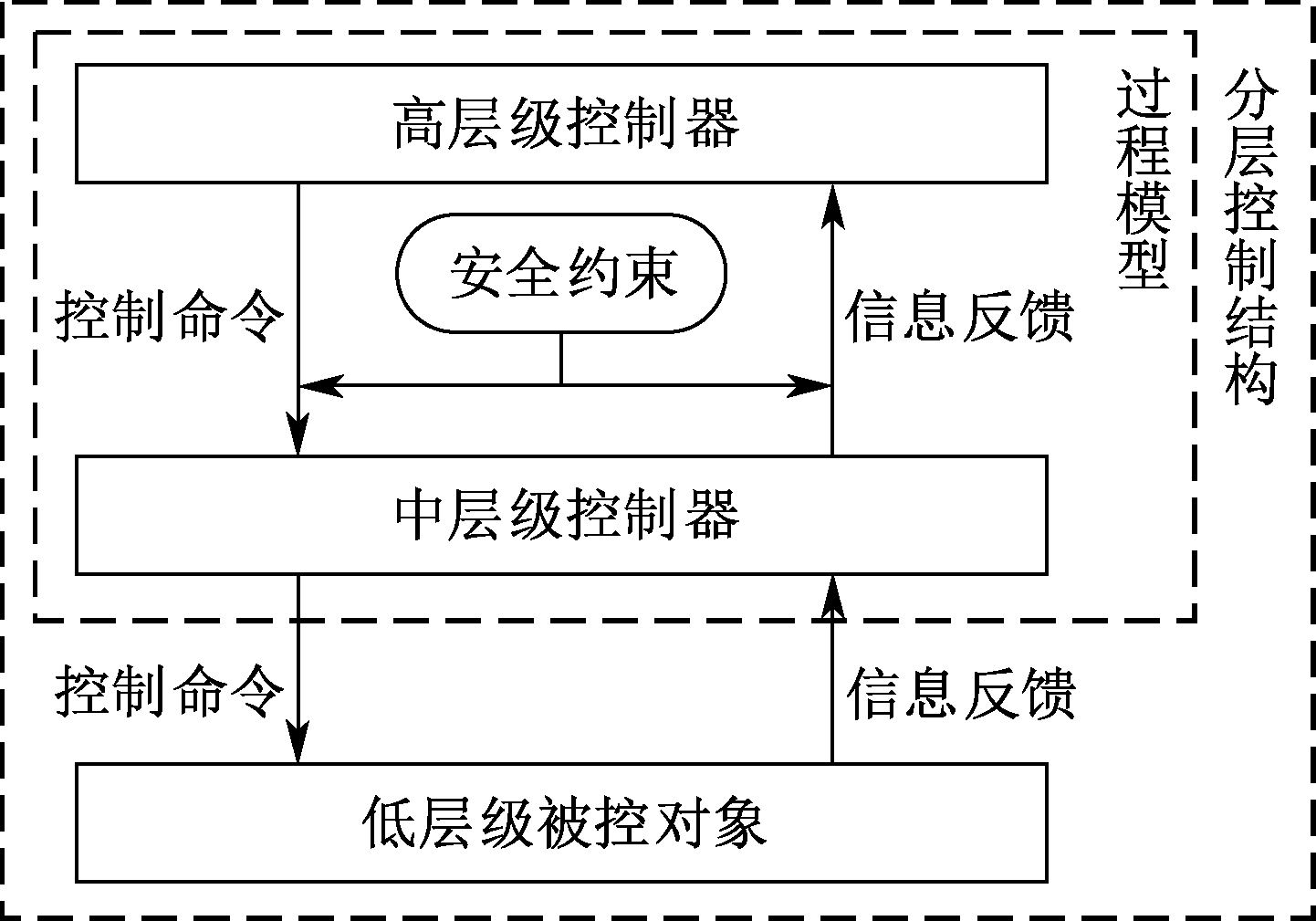
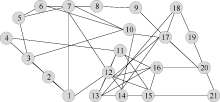
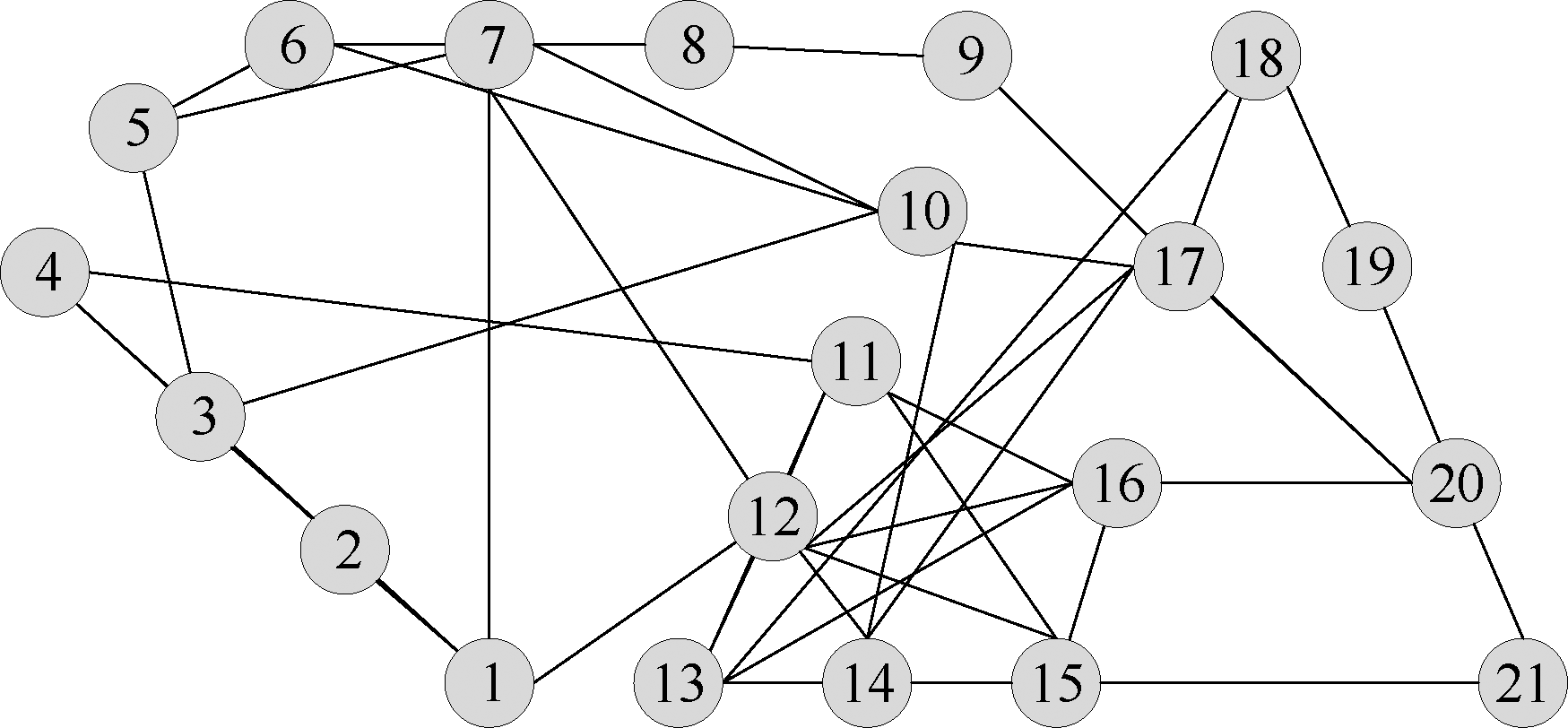
| [1] |
晏鸿, 杨明, 李佳琪, 等. 我国越野跑赛事发展的回顾反思与展望:兼论甘肃白银黄河石林越野赛事件的赛事组织[J]. 南京体育学院学报, 2021, 20(7): 61-70.
|
|
YAN Hong, YANG Ming, LI Jiaqi, et al. Review, reflection and prospect of cross country race development in China:on the event organization of Gansu Baiyin Huanghe Shilin cross country event[J]. Press of NanJing Sport Institute, 2021, 20(7): 61-70.
|
| [2] |
EMERY P. Past, present, future major sport event management practice: the practitioner perspective[J]. Sport Management Review, 2010, 13(2): 158-170.
|
| [3] |
席永涛, 张靓, 付姗姗, 等. 基于SFN-SD的北极冰区船舶航行风险传递路径研究[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2023, 33(4): 52-60.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2023.04.0840
|
|
XI Yongtao, ZHANG Liang, FU Shanshan, et al. Research on risk transfer path of ship navigation in Arctic waters based on SFN and SD[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2023, 33(4): 52-60.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2023.04.0840
|
| [4] |
ZHANG Yuexia, PAN Daiwei. Layered SIRS model of information spread in complex networks[J]. Applied Mathematics and Computation, 2021, 411: DOI: 10.1016/j.amc.2021.126524.
|
| [5] |
杨琳, 周炬诺. 复杂工程项目风险传递机理[J]. 科技管理研究, 2021, 41(16): 209-217.
|
|
YANG Lin, ZHOU Junuo. Risk transfer mechanism of complex engineering projects[J]. Science and Technology Management Research, 2021, 41(16): 209-217.
|
| [6] |
LEVESON N G. Applying systems thinking to analyze and learn from events[J]. Safety Science, 2011, 49(1): 55-64.
|
| [7] |
吴海涛, 黎双喜. 高铁应急调度STAMP/STPA安全性分析[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2021, 31(6): 113-120.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn 1003-3033.2021.06.015
|
|
WU Haitao, LI Shuangxi. High-speed railway emergency dispatching safety analysis based on STAMP/STPA[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2021, 31(6): 113-120.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn 1003-3033.2021.06.015
|
| [8] |
LI Chunguang, LIAO Xiaofeng, WU Zhongfu, et al. Complex functional networks[J]. Mathematics and Computers in Simulation, 2001, 57(6): 355-365.
|
| [9] |
曾小康, 冯阳, 赖文庆, 等. 基于AHP-熵权法的城市燃气管道风险评价[J]. 中国安全生产科学技术, 2021, 17(5): 130-135.
|
|
ZENG Xiaokang, FENG Yang, LAI Wenqing, et al. Risk assessment of urban gas pipeline based on AHP and entropy weight method[J]. Journal of Safety Science and Technology, 2021, 17(5): 130-135.
|
| [10] |
李华, 郭皓杰, 谢辉, 等. 基于信息熵的森林火灾应急指挥信息传递分析[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2023, 33(1): 80-87.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2023.01.2359
|
|
LI Hua, GUO Haojie, XIE Hui, et al. Information transmission analysis of forest fire emergency command based on information entropy[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2023, 33(1): 80-87.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2023.01.2359
|
| [11] |
徐曼, 鲁富荣, 马国帅, 等. 基于信息传播影响因素的边重要性度量方法[J]. 计算机工程与科学, 2020, 42(1): 55-63.
|
|
XU Man, LU Furong, MA Guoshuai, et al. An edge importance measurement method based on information dissemination characteristics[J]. Computer Engineering and Science, 2020, 42(1): 55-63.
|