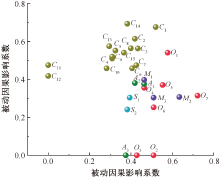
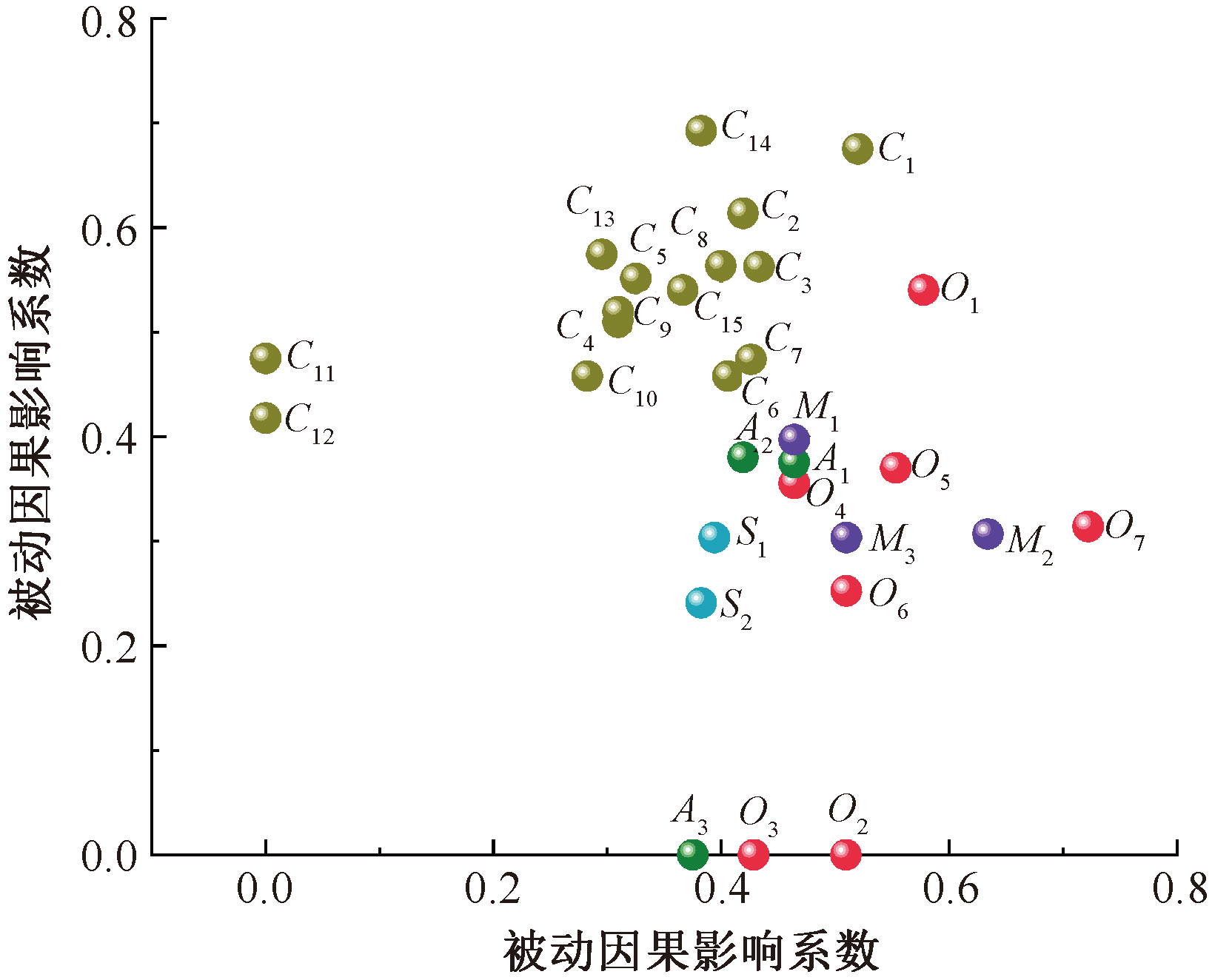
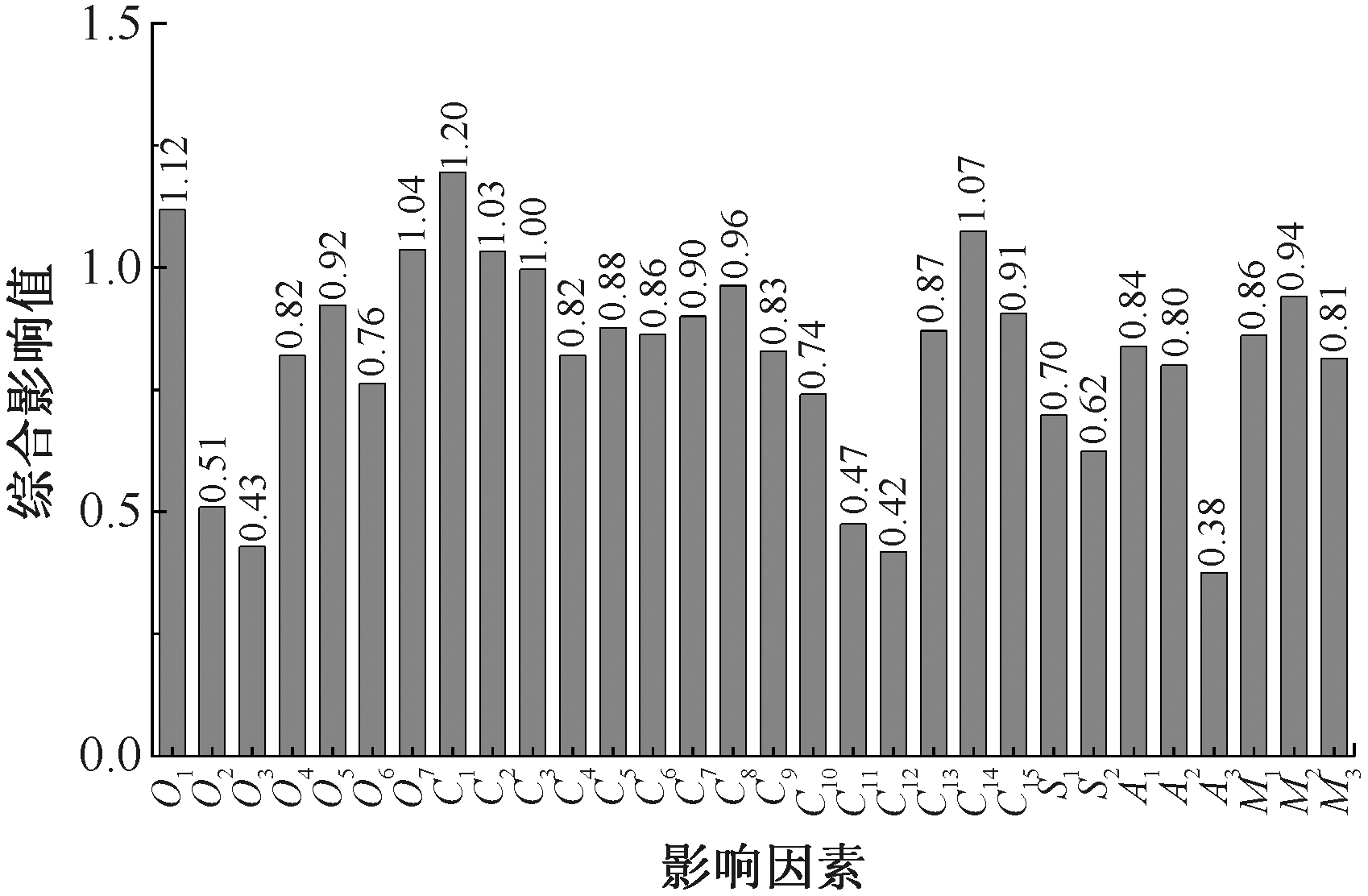
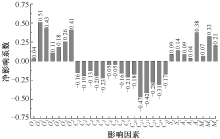
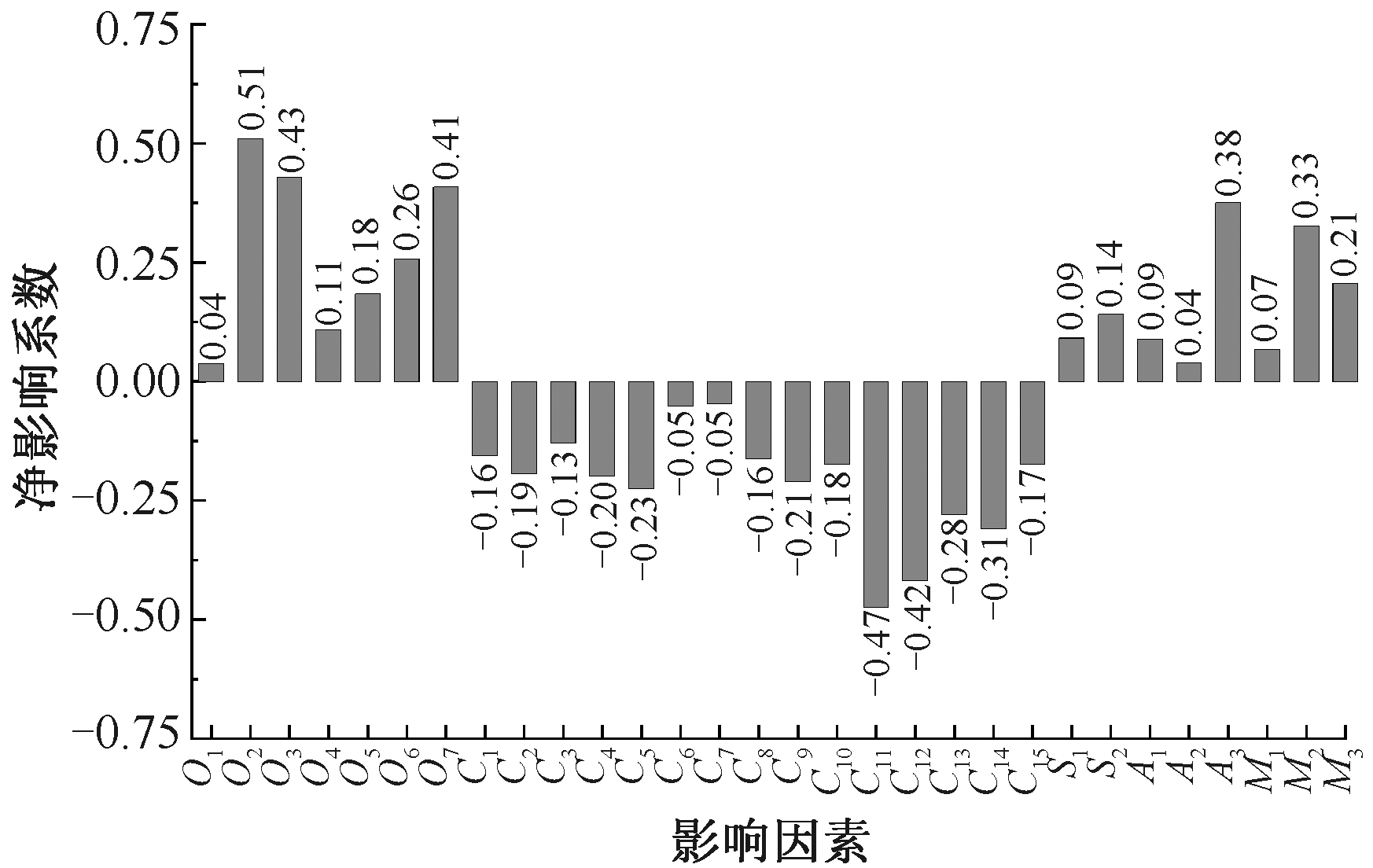
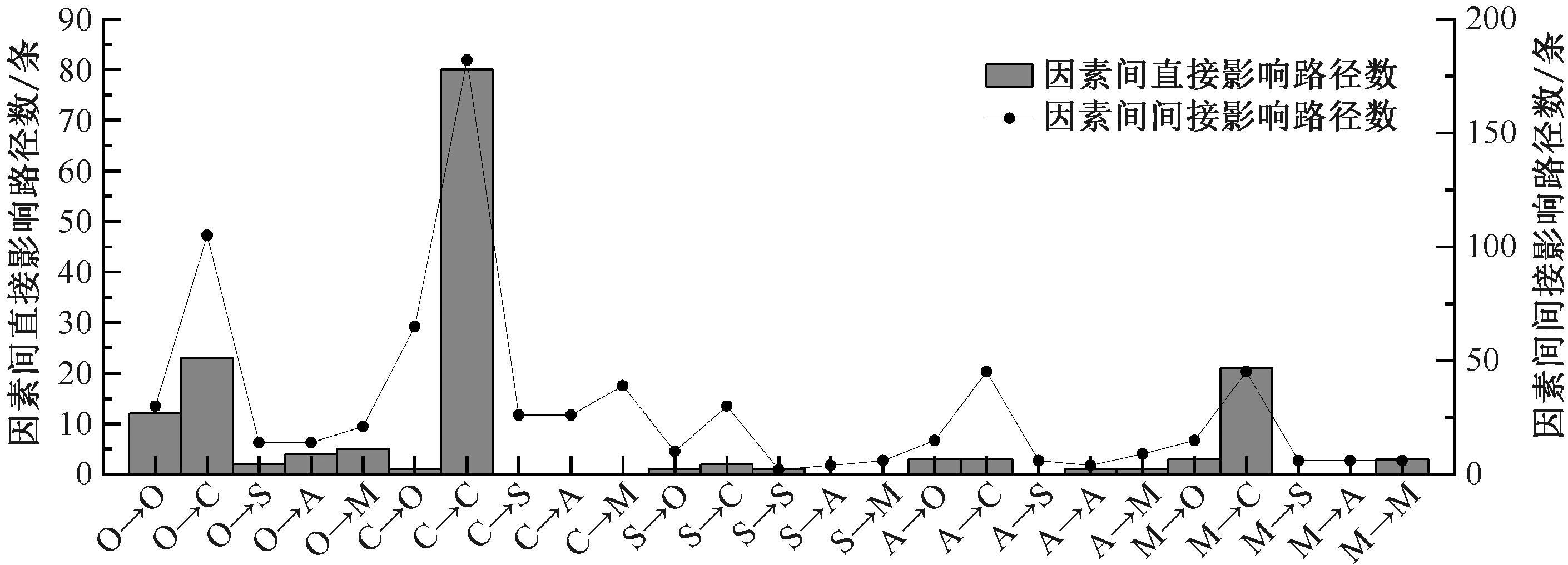
| [1] |
王园园. 建设工程各方主体安全行为相互关系及安全责任界定研究[D]. 北京: 首都经济贸易大学, 2017.
|
|
WANG Yuanyuan. The relationship and safety liability among the participants of construction projects[D]. Beijing: Capital University of Economics and Business, 2017.
|
| [2] |
李陶然. 多方参与的建筑安全管理体系研究[D]. 重庆: 重庆大学, 2012.
|
|
LI Taoran. Research about multi-side participation of construction safety management system[D]. Chongqing: Chongqing University, 2012.
|
| [3] |
全河, 王孟钧, 马英斌. 规范建筑市场业主行为的思考[J]. 建筑经济, 2006(9): 9-10.
|
|
QUAN He, WANG Mengjun, MA Yingbin. Thoughts on standardizing the behavior of owners in the construction market[J]. Building Economics, 2006 (9): 9-10.
|
| [4] |
TYMVIOS N, GAMBATESE J A. Perceptions about design for construction worker safety: viewpoints from contractors, designers, and university facility owners[J]. Journal of Construction Engineering and Management, 2016, 142(2):DOI: 10.1061/(ASCE)CO.1943-7862.0001165.
|
| [5] |
WU Chunlin, FANG Dongping, LI Nan. Roles of owners' leadership in construction safety:the case of high-speed railway construction projects in China[J]. International Journal of Project Management, 2015, 33(8): 1665-1679.
|
| [6] |
翟伟, 盛智平, 果希光, 等. 雄安新区工程监理区块链管理模式研究与应用[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2021, 31(4): 27-33.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2021.04.004
|
|
ZHAI Wei, SHENG Zhiping, GUO Xiguang, et al. Research on engineering supervision blockchain management pattern in Xiong'an new area and its application[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2021, 31(4): 27-33.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2021.04.004
|
| [7] |
齐建群. 建设五方责任主体常见违规行为及其监管实践与对策[J]. 福建工程学院学报, 2010, 8(增1): 64-66.
|
|
QI Jianqun. Common violations and regulatory practices and countermeasures of the five parties responsible for construction[J]. Journal of Fujian University of Technology, 2010, 8 (S1): 64-66.
|
| [8] |
王伟. 试论建设工程安全生产责任在不同管理模式下的实现路径[J]. 建筑, 2017(9): 24-27.
|
| [9] |
刘国买, 傅敬宾. 建筑工程安全监管问题与对策研究[J]. 福建建筑, 2017(9): 90-93.
|
|
LIU Guomai, FU Jingbin. Study on problems and countermeasures of construction safety supervision[J]. Fujian Architecture & Construction, 2017 (9): 90-93.
|
| [10] |
周建亮, 方东平, 房继寒. 工程建设安全生产管理的相关主体行为关系模型分析与政策改进[J]. 土木工程学报, 2014, 47(9): 128-134.
|
|
ZHOU Jianliang, FANG Dongping, FANG Jihan. Behavior relationship model and policy improvements related to stakeholder affecting construction safety[J]. Journal of Civil Engineering, 2014, 47 (9): 128-134.
|
| [11] |
WANG Xueqing, XIA Nini, ZHANG Zhitao, et al. Human safety risks and their interactions in China's subways: stakeholder perspectives[J]. Journal of Management in Engineering, 2017, 33(5): DOI: 10.1061/(ASCE)ME.1943-5479.0000544.
|
| [12] |
成连华, 王晨, 李树刚, 等. 基于前景理论的建筑施工安全管理多主体演化博弈研究[J]. 安全与环境学报, 2023, 23(9): 3286-3297.
|
|
CHENG Lianhua, WANG Chen, LI Shugang, et al. Research on multi-agent evolution game of construction safety management based on prospect theory[J]. Journal of Safety and Environment, 2023, 23 (9): 3286-3297.
|
| [13] |
YANG Yang, LI Suzhen, ZHANG Pengcheng. Data-driven accident consequence assessment on urban gas pipeline network based on machine learning[J]. Reliability Engineering & System Safety, 2022, 219: DOI: 10.1016/j.ress.2021.108216.
|
| [14] |
王静. 建筑施工安全管理职责分配的现状和思考研究[J]. 居业, 2022(3): 163-165.
|
|
WANG Jing. Research on the current situation and reflection on the allocation of responsibilities for construction safety management[J]. Create Living, 2022 (3): 163-165.
|
| [15] |
杨轶. 浅谈建设单位在五方责任主体中的地位及项目建设中的作用[J]. 建设监理, 2016(11): 28-30,52.
|
|
YANG Yi. A brief discussion on the position of construction units in the five party responsibility system and their role in project construction[J]. Construction Supervision, 2016 (11): 28-30,52.
|
| [16] |
马秋林. 建设单位在建筑安全生产过程中的责任分析[J]. 建筑安全, 2009, 24(2): 31-33.
|
|
MA Qiulin. Analysis of the responsibilities of construction units in the process of building safety production[J]. Construction Safety, 2009, 24 (2): 31-33.
|
| [17] |
FU Lipeng. Interactions among safety risks in metro deep foundation pit projects: an association rule mining-based modeling framework[J]. Reliability Engineering and System Safety, 2022, 225: DOI: 10.1016/j.ress.2022.108381.
|
| [18] |
张伟, 张潇, 薛楠楠, 等. 塔吊安全事故致因网络模型构建与分析[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2020, 30(12): 1-7.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn 1003-3033.2020.12.001
|
|
ZHANG Wei, ZHANG Xiao, XUE Nannan, et al. Network model establishment and analysis of tower crane safety accident causes[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2020, 30(12): 1-7.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn 1003-3033.2020.12.001
|
| [19] |
刘丹, 朱卫昌, 李墨潇, 等. 利益相关者视角下化工安全关键致因网络分析[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2023, 33(11): 59-66.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2023.11.1087
|
|
LIU Dan, ZHU Weichang, LI Moxiao, et al. Network analysis of chemical safety critical causation from perspective of stakeholders[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2023, 33(11): 59-66.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2023.11.1087
|
| [20] |
HUO Xiaosen, YIN Yuan, JIAO Liudan, et al. A data-driven and knowledge graph-based analysis of the risk hazard coupling mechanism in subway construction accidents[J]. Reliability Engineering & System Safety, 2024, 250: DOI: 10.1016/j.ress.2023.110254.
|
| [21] |
陈大伟. 房屋市政工程施工安全较大及以上事故分析(2020—2022年)[M]. 北京: 中国建筑工业出版社, 2024:2-535.
|