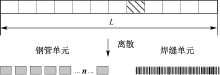
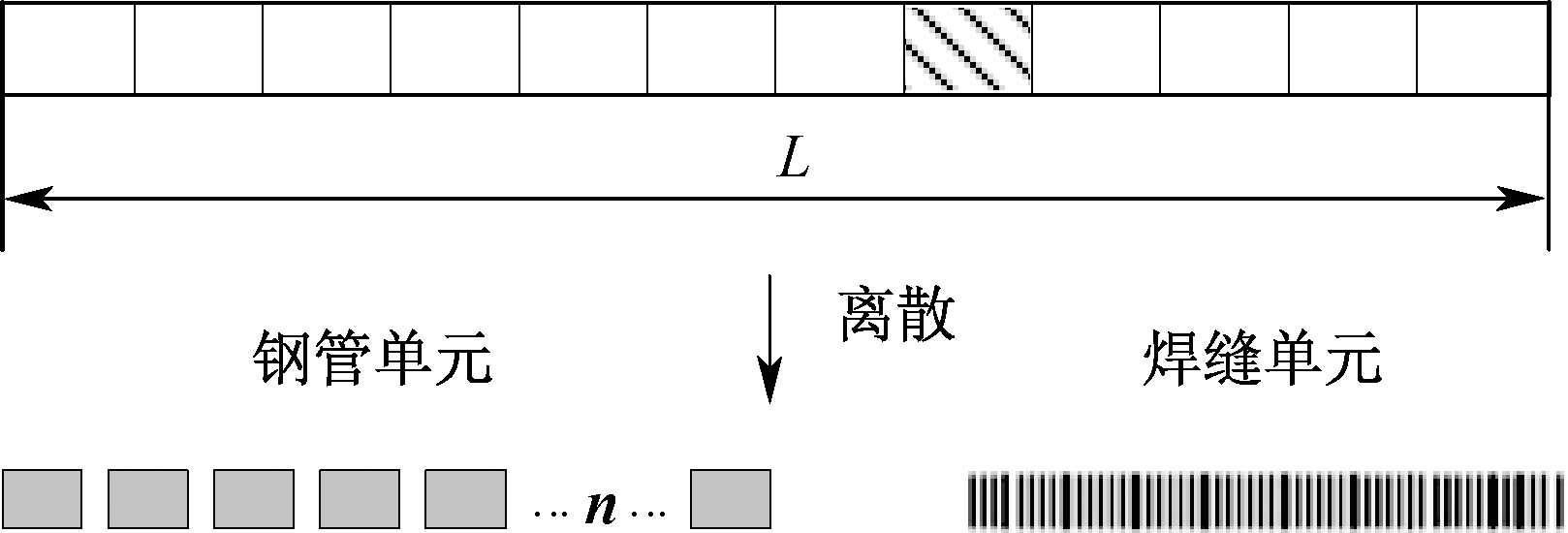
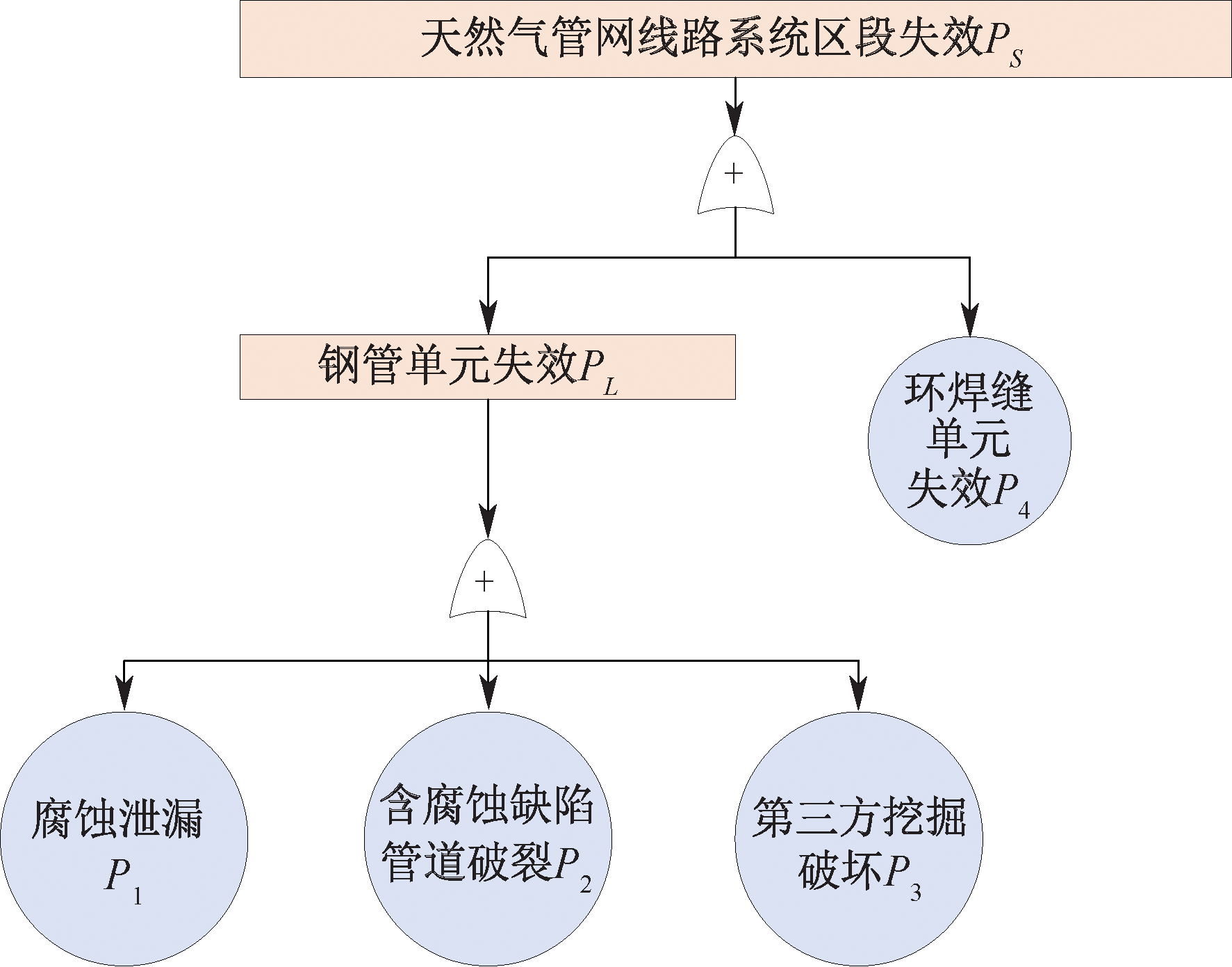
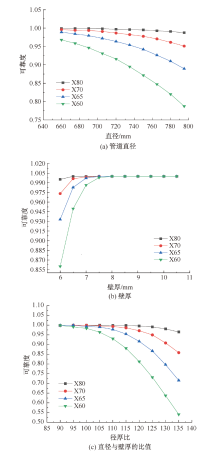
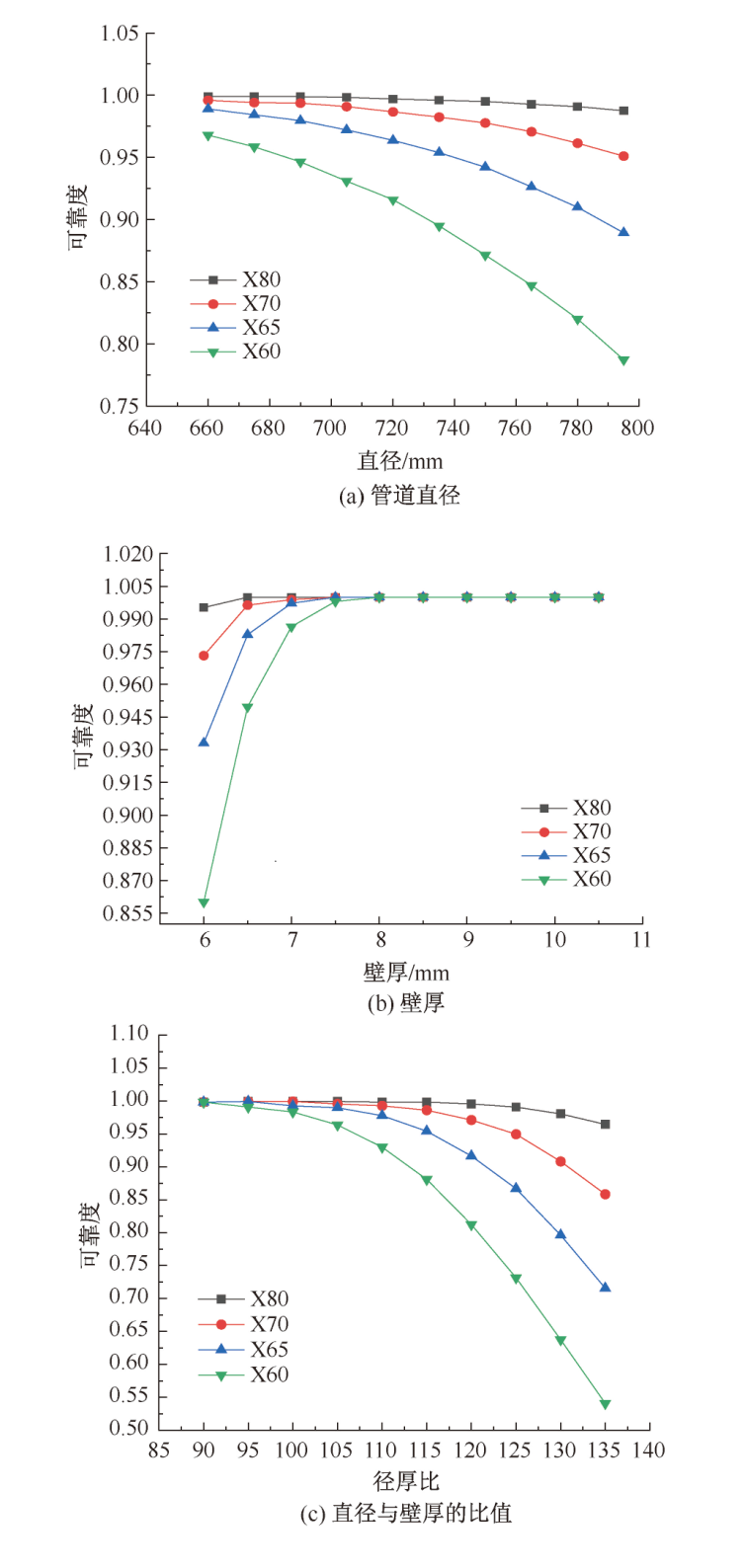
| [1] |
宫运华, 张喆, 范志炜. 油气管道事故原因分类模型及其社会网络分析[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2024, 34(9):34-40.
|
|
GONG Yunhua, ZHANG Zhe, FAN Zhiwei. Classification model of oil and gas pipeline accidents causes and its social network analysis[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2024, 34(9):34-40.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2024.09.1353
|
| [2] |
王海燕, 任帅, 孙东旭. 含腐蚀缺陷油气管道剩余强度的评价方法对比[J]. 腐蚀与防护, 2025, 46(2):80-88,94.
|
|
WANG Haiyan, REN Shuai, SUN Dongxu. Comparison of evaluation methods for residual strength of oil and gas pipeline with corrosion defects[J]. Corrosion and Protection, 2025, 46(2):80-88,94.
|
| [3] |
骆正山, 毕傲睿. 腐蚀管道寿命可靠性的步降应力加速试验研究[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2017, 27(1):59-64.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2017.01.011
|
|
LUO Zhengshan, BI Aorui. Research on reliability of corroded pipelines based on step-down-stress accelerated life testing[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2017, 27(1):59-64.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2017.01.011
|
| [4] |
任伟, 帅健. 管道环焊缝可靠性的参数统计分布研究[J]. 石油科学通报, 2016, 1(3):484-492.
|
|
REN Wei, SHUAI Jian. Research into the statistical distribution of reliability parameters for girth welds on pipelines[J]. Petroleum Science Bulletin, 2016, 1(3):484-492.
|
| [5] |
王旭, 帅健, 张圣柱, 等. 基于应变的高钢级管道环焊接头失效评定方法[J]. 天然气工业, 2023, 43(2):121-130.
|
|
WANG Xu, SHUAI Jian, ZHANG Shengzhu, et al. A strain based failure assessment method for girth welded joints in high grade steel line pipes[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2023, 43(2):121-130.
|
| [6] |
ABYANI M, BAHAARI M. A new approach for finite element based reliability evaluation of offshore corroded pipelines[J]. International Journal of Pressure Vessels and Piping, 2021,193: DOI: 10.1016/J.IJPVP.2021.104449.
|
| [7] |
ABDELMOETY K, KAINAT M, YOOSEF-GHODSI N, et al. Strain-based reliability analysis of dented pipelines using a response surface method[J]. Journal of Pipeline Science and Engineering, 2022, 2(1):29-38.
|
| [8] |
王东营, 陈小平, 刘权, 等. 基于改进的云模型-FMEA的油气管道风险排序[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2024, 34(5):61-68.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2024.05.1069
|
|
WANG Dongying, CHEN Xiaoping, LlU Quan, et al. Risk ranking of oil and gas pipeline based on improved cloud model-FMEA[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2024, 34(5):61-68.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2024.05.1069
|
| [9] |
CALEYO F, VALOR A, ALFONSO L, et al. Bayesian analysis of external corrosion data of non-piggable underground pipelines[J]. Corrosion Science, 2015, 90: 33-45.
|
| [10] |
LEIRA B, NAESS A, NAESS O. Reliability analysis of corroding pipelines by enhanced Monte Carlo simulation[J]. International Journal of Pressure Vessels and Piping, 2016,144:11-17.
|
| [11] |
LIU Aihua, CHEN Ke, HUANG Xiaofei, et al. Dynamic risk assessment model of buried gas pipelines based on system dynamics[J]. Reliability Engineering & System Safety, 2021, 208: DOI: 10.1016/J.RESS.2020.107326.
|
| [12] |
AULIA T, SRIRAMULA S. Dynamic reliability model for subsea pipeline risk assessment due to third-party interference[J]. Journal of Pipeline Science and Engineering, 2021, 1(3): 277-289.
|
| [13] |
ZHENG Qian, ABDELMOETY K, LI Yong, et al. Reliability analysis of intact and defected pipes for internal pressure related limit states specified in CSA Z622:19[J]. International Journal of Pressure Vessels and Piping, 2021,192: DOI: 10.1016/J.IJPVP.2021.104411.
|
| [14] |
韩冰, 季蓓蕾, 付强, 等. 含体积型缺陷集输管道剩余强度评价方法适用性[J]. 腐蚀与防护, 2025, 46(3):91-98.
|
|
HAN Bing, JI Beilei, FU Qiang, et al. Applicability of residual strength evaluation method for gathering and transportation pipelines with volume defects[J]. Corrosion and Protection, 2025, 46(3):91-98.
|
| [15] |
ASME B31G-2009, Manual for determining the remaining strength of corroded pipelines[S].
|
| [16] |
BS 7910-2019, Guide to methods for assessing the acceptability of flaws in metallic structures[S].
|
| [17] |
张强, 杨玉锋, 郑洪龙, 等. 第三方挖掘作用下管道可靠性评估研究[J]. 中国安全生产科学技术, 2017, 13(2):143-147.
|
|
ZHANG Qiang, YANG Yufeng, ZHENG Honglong, et al. Study on reliability evaluation of pipeline under the effect of third-party excavation[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2017, 13(2):143-147.
|
| [18] |
WALODDI W. A statistical distribution function of wide applicability[J]. Journal of Applied Mechanics. 1951,18: 293-297.
|
| [19] |
EZMAREH Z, YARI G. Statistical inference of stress-strength reliability of gompertz distribution under type II censoring. advances in mathematical physics[J]. Advances in Mathematical Physics, 2022: DOI: 10.1155/2022/2129677.
|
| [20] |
温轶群, 段富海. 一种基于GO法的多态反馈系统选择性维修模型[J]. 大连理工大学学报, 2023, 63(5):501-508.
|
|
WEN Yiqun, DUAN Fuhai. A selective maintenance model for polymorphic feedback system based on GO methodology[J]. Journal of Dalian University of Technology, 2023, 63(5):501-508.
|
| [21] |
NAZEMI N, DAS S. Behavior of X60 line pipe subjected to axial and lateral deformations[J]. Journal of Pressure Vessel Technology, 2010, 132(3): DOI: 10.1115/1.4001426.
|
| [22] |
杨玉锋, 葛新东, 郑洪龙, 等. 第三方损坏对管道可靠性的影响规律[J]. 油气储运, 2017, 36(8):903-909.
|
|
YANG Yufeng, GE Xindong, ZHENG Honglong, et al. Influence laws of third party damage on pipeline reliability[J]. Oil and Gas Storage and Transportation, 2017, 36(8):903-909.
|
| [23] |
郭庆, 翟红波, 刘永寿. 考虑动态腐蚀的输流管道时变共振可靠性及灵敏度分析[J]. 兵器装备工程学报, 2024, 45(1):166-172, 216.
|
|
GUO Qing, ZHAI Hongbo, LIU Yongshou. Time-variant resonance reliability and sensitivity analysis of pipes conveying fluid considering dynamic corrosion[J]. Journal of Ordnance Equipment Engineering, 2024, 45(1):166-172, 216.
|