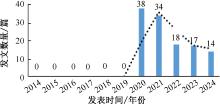
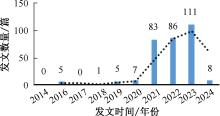
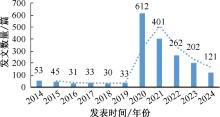
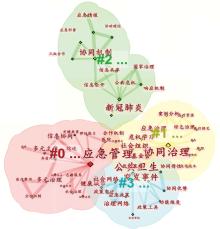
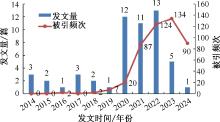
| [1] |
王小理. 生物安全时代:新生物科技变革与国家安全治理[J]. 国际安全研究, 2020, 38(4):109-135,159-160.
|
|
WANG Xiaoli. The age of biosecurity: new biotechnology revolution and national biosecurity governance[J]. Journal of International Security Studies, 2020, 38(4): 109-135, 159-160.
|
| [2] |
司林波, 裴索亚. 国家生物安全风险防控和治理的影响因素与政策启示:基于扎根理论的政策文本研究[J]. 中共天津市委党校学报, 2021, 23(3):61-71.
|
|
SI Linbo, PEI Suoya. The influencing factors and policy enlightenment of national biosecurity risk control and governance:research on policy text based on grounded theory[J]. Journal of the Party School of Tianjin Committee of the CPC, 2021, 23(3): 61-71.
|
| [3] |
章楚加. 生物安全风险协同共治范式的建构逻辑与规范内涵:基于《生物安全法》评述视角[J]. 青海社会科学, 2021(5):154-161.
|
|
ZHANG Chujia. Construction logic and normative connotation of collaborative governance paradigm for biosecurity risks:a review perspective based on the biosecurity law[J]. Qinghai Social Sciences, 2021(5): 154-161.
|
| [4] |
赫尔曼·哈肯[德]. 协同学-大自然构成的奥秘[M]. 凌复华,译. 上海: 上海译文出版社, 2005:15-75.
|
|
HAKEN H. Synergetics: the secret of nature's structure[M]. LING Fuhua,Translated. Shanghai: Shanghai Translation Publishing House, 2005:15-75.
|
| [5] |
SCHNEIDER S K. Governmental response to disasters:the conflict between bureaucratic procedures and emergent norms[J]. Public Administration Review, 1992, 52(2):135-145.
doi: 10.2307/976467
|
| [6] |
郭景涛. 城市群重大公共安全事件应急指挥协同研究[D]. 武汉: 华中科技大学, 2016.
|
|
GUO Jingtao. The optimization study on cooperative relationship of emergency command for major emergency of urban agglomeration safety incidents in urban agglomerations[D]. Wuhan: Huazhong University of Science and Technology, 2016.
|
| [7] |
刘楠, 侯林. 协同视角下地方政府应对突发公共卫生事件治理研究[J]. 国际公关, 2024(2):101-103.
|
|
LIU Nan, HOU Lin. Governance of local governments in responding to public health emergencies from a collaborative perspective[J]. International Public Relations, 2024(2): 101-103.
|
| [8] |
李维安, 孟乾坤, 刘昱沛, 等. 公共卫生危机应急协同治理:基于火神山医院和红十字会的案例分析[J]. 工程管理科技前沿, 2024, 43(3):8-17.
|
|
LI Weian, MENG Qiankun, LIU Yupei, et al. Emergency collaborative governance of public health crisis:a case study of Huoshenshan hospital and the Red Cross[J]. Frontiers of Science and Technology of Engineering Management, 2024, 43(3): 8-17.
|
| [9] |
THOMPSON D, MCCUAIG J, WILKES B. 跨部门合作原则及特点[C]. 环境治理跨部门合作研讨会论文集, 2007:17-24.
|
|
THOMPSON D, MCCUAIG J, WILKES B. Principles and characteristics of cross-sectoral collaboration[C]. Proceedings of the Symposium on Cross-sectoral Collaboration in Environmental Governance, 2007:17-24.
|
| [10] |
EISINGER P. Imperfect federalism: the intergovernmental partnership for homeland security[J]. Public Administration Review, 2010, 66(4):537-545.
doi: 10.1111/puar.2006.66.issue-4
|
| [11] |
李安楠, 邓修权, 赵秋红. 分形视角下的非常规突发事件应急组织动态重构:以8·12天津港爆炸事件为例[J]. 管理评论, 2016, 28(8):193-206.
|
|
LI Annan, DENG Xiuquan, ZHAO Qiuhong. Unconventional emergency organizational dynamic reconstruction based on fractal:8.12 Tianjin explosions case study[J]. Management Review, 2016, 28(8): 193-206.
|
| [12] |
KOLIBA C J, MILLS R M, ZIA A. Accountability in governance networks: an assessment of public, private, and nonprofit emergency management practices following hurricane katrina[J]. Public Administration Review, 2011, 71(2):210-220.
doi: 10.1111/puar.2011.71.issue-2
|
| [13] |
柯小玲, 刘正娟, 郭海湘, 等. 基于三方演化博弈的突发公共卫生事件应急响应及仿真研究[J]. 运筹学报, 2024, 28(1):57-76.
|
|
KE Xiaoling, LIU Zhengjuan, GUO Haixiang, et al. Emergency response and simulation research for public health emergencies based on tripartite evolutionary game[J]. Journal of Operations Research Society of China, 2024, 28(1): 57-76.
|
| [14] |
薛澜, 彭宗超, 钟开斌, 等. 中国公共卫生应急指挥体系探析[J]. 中国工程科学, 2021, 23(5):1-8.
doi: 10.15302/J-SSCAE-2021.05.001
|
|
XUE Lan, PENG Zongchao, ZHONG Kaibin, et al. Public health emergency command system of china[J]. Strategic Study of Chinese Academy of Engineering, 2021, 23(5): 1-8.
|
| [15] |
张海波, 童星. 中国应急管理效能的生成机制[J]. 中国社会科学, 2022(4):64-82,205-206.
|
|
ZHANG Haibo, TONG Xing. The generative mechanisms for the effectiveness of emergency management in China[J]. Social Sciences in China, 2022(4): 64-82,205-206.
|
| [16] |
WAUGH W L, STREIB G. Collaboration and leadership for effective emergency management[J]. Public Administration Review, 2006, 66(S1):131-140.
doi: 10.1111/puar.2006.66.issue-s1
|
| [17] |
KAPUCU N, HU Q. Understanding multiplexity of collaborative emergency management networks[J]. American Review of Public Administration, 2016, 46(4):399-417.
doi: 10.1177/0275074014555645
|
| [18] |
KAPUCU N, GARAYEV V. Designing,manging, and sustaining functionally collaborative emergency management networks[J]. American Review of Public Administration, 2013, 43(3):312-330.
doi: 10.1177/0275074012444719
|
| [19] |
NOHRSTEDT D. Expaining mobilization and performance of collaborations in routine emergency management[J]. Administration & Society, 2016, 48(2):135-162.
|
| [20] |
CIGLER B A. Hurricane Katrina: two intergovernmental challenges[J]. The Public Manager, 2007, 35(4):3-7.
|
| [21] |
CAIN E B, GERBER R E, HUI I. The challenge of externally generated collaborative governance: california's attempt at regional water management[J]. The American Review of Public Administration, 2020, 50(4/5):428-437.
doi: 10.1177/0275074020908578
|
| [22] |
杨舒雨, 谭爽. 突发公共卫生事件沟通困境与破解之道:博弈理论视角[J]. 青岛医药卫生, 2024, 56(2):141-144.
|
|
YANG Shuyu, TAN Shuang. Communication dilemma of public health emergencies and the way to crack it-game theory perspective[J]. Qingdao Medical Journal, 2024, 56(2): 141-144.
|
| [23] |
NOHRSTEDT D. Does adaptive capacity influence service delivery? evidence from swedish emergency management collaborations[J]. Public Management Review, 2015, 17(5):718-735.
doi: 10.1080/14719037.2013.848921
|
| [24] |
LUBELL M, MEWHIRTER M J, BERARDO R, et al. Transaction costs and the perceived effectiveness of complex institutional systems[J]. Public Administration Review, 2017, 77(5):668-680.
doi: 10.1111/puar.2017.77.issue-5
|
| [25] |
仝鹏. 健全地方政府应急管理的协同体系机制研究[J]. 中国管理信息化, 2016, 19(22):176-177.
|
|
TONG Peng. Research on improving collaborative system mechanism of local government emergency management[J]. China Management Informationization, 2016, 19(22): 176-177.
|
| [26] |
KAPUCU N, AUGUSTIN M E, GARAYEV V. Interstate partnerships in emergency management: emergency management assistance compact in response to catastrophic disasters[J]. Public Administration Review, 2009, 69(2):297-313.
doi: 10.1111/puar.2009.69.issue-2
|
| [27] |
SORENSEN E, TORFING J. Enhancing collaborative innovation in the public sector[J]. Administration & Society, 2011, 43(8):842-868.
|
| [28] |
赵林度, 杨世才. 基于Multi_Agent的城际灾害应急管理信息和资源协同机制研究[J]. 灾害学, 2009, 24(1):139-143.
|
|
ZHAO Lindu, YANG Shicai. Information and resources synergetic mechanism of inter-city disaster emergency management based on multi-agent systems[J]. Journal of Catastrophology, 2009, 24(1): 139-143.
|
| [29] |
刘洪渭, 张朋柱, 李树荣, 等. 突发公共事件的决策网络及其协同决策分类[J]. 上海管理科学, 2011, 33(1):89-93.
|
|
LIU Hongwei, ZHANG Pengzhu, LI Shurong, et al. Research on decision network and coordination decision classification[J]. Shanghai Management Science, 2011, 33(1): 89-93.
|
| [30] |
关雷, 佟士祺, 颜华琨, 等. 基于群体网络计划的应急协同决策方法[J]. 大连海事大学学报, 2012, 38(3):73-76.
|
|
GUAN Lei, TONG Shiqi, YAN Huakun, et al. Emergency collaborative decision-making method based on group network planning[J]. Journal of Dalian Maritime University, 2012, 38(3): 73-76.
|
| [31] |
宋艳, 王博石. 我国地震灾害应急协同决策系统可靠性建模与仿真[J]. 自然灾害学报, 2014, 23(3):171-180.
|
|
SONG Yan, WANG Boshi. Modeling and simulaton of reliability of earthquake disaster emergency coordination decision-making system in China[J]. Journal of Natural Disasters, 2014, 23(3): 171-180.
|
| [32] |
和媛媛, 巩在武. 考虑协同网络信息的非常规突发事件应急多指标决策模型[J]. 统计与决策, 2015 (23):75-77.
|
|
HE Yuanyuan, GONG Zaiwu. Emergency multi-criteria decision-making model for unconventional emergencies considering collaborative network information[J]. Statistics and Decision, 2015 (23): 75-77.
|
| [33] |
陈兴, 王勇, 吴凌云, 等. 多阶段多目标多部门应急决策模型[J]. 系统工程理论与实践, 2010, 30(11):1977-1985.
doi: 10.12011/1000-6788(2010)11-1977
|
|
CHEN Xing, WANG Yong, WU Lingyun, et al. Emergency decision model with multiple stages, multiple objectives, and multidivisional cooperation[J]. Systems Engineering-Theory & Practice, 2010, 30(11): 1977-1985.
|
| [34] |
范一大, 王磊, 李素菊. 重大自然灾害空间信息协同服务机制研究[J]. 遥感学报, 2011, 15(5):1053-1064.
|
|
FAN Yida, WANG Lei, LI Suju. A study on the construction of a spatial information cooperative service mechanism for emergency disaster applications[J]. Journal of Remote Sensing, 2011, 15(5): 1053-1064.
|
| [35] |
辛禾, 王齐龙, 何璞玉, 等. 基于神经网络模型的电网企业应急协同管控机制研究[J]. 陕西电力, 2015, 43(8):1-5, 21.
|
|
XIN He, WANG Qilong, HE Puyu, et al. Study on collaborative mechanism of grid enterprise emergency management based on neural network model[J]. Shaanxi Electric Power, 2015, 43(8): 1-5, 21.
|
| [36] |
李安楠, 邓修权, 赵秋红. 分形视角下的非常规突发事件应急协同组织[J]. 系统工程理论与实践, 2017, 37(4):937-948.
doi: 10.12011/1000-6788(2017)04-0937-12
|
|
LI Annan, DENG Xiuquan, ZHAO Qiuhong. Unconventional emergency coordinated organization based on fractal[J]. Systems Engineering-Theory & Practice, 2017, 37(4): 937-948.
|
| [37] |
李秋霞. 城市突发公共卫生事件经济影响与应急处置机制研究[D]. 北京: 中国社会科学院大学, 2021.
|
|
LI Qiuxia. Research on economic impact and emergency response mechanism of urban public health emergencies[D]. Beijing: University of Chinese Academy of Social Sciences, 2021.
|
| [38] |
高点, 史卢少博, 李婷, 等. 基于SFIC模型的医院突发公共卫生事件多主体协同应对路径研究[J]. 中国医院, 2024, 28(1):23-27.
|
|
GAO Dian, SHI Lushaobo, LI Ting, et al. Research on multi-agent collaborative response path of hospital public health emergencies based on SFIC model[J]. China Hospitals, 2024, 28(1): 23-27.
|
| [39] |
潘潇, 樊博. 应急管理中跨部门协同能力的影响因素研究:以食品药品安全联合监管为实证背景[J]. 软科学, 2014, 28(2):52-55,60.
|
|
PAN Xiao, FAN Bo. Research on cross-agency collaboration in the process of emergency management:employing collaborative supervision on food and medicine as background[J]. Soft Science, 2014, 28(2): 52-55,60.
|
| [40] |
欧阳艳敏. 重大突发公共卫生事件风险预警和控制模型研究[D]. 北京: 北京邮电大学, 2023.
|
|
OUYANG Yanmin. Research on risk-early warning and control models of large-scale public health emergencies[D]. Beijing: Beijing University of Posts and Telecommunications, 2023.
|
| [41] |
刘明, 开吉, 曹杰. 重大突发公共卫生事件防控策略计算实验分析[J]. 系统工程理论与实践, 2024, 44(6):1950-1964.
doi: 10.12011/SETP2023-1459
|
|
LIU Ming, KAI Ji, CAO Jie. Computational experiment analysis of prevention and control strategies for major public health emergencies[J]. Systems Engineering-Theory & Practice, 2024, 44(6): 1950-1964.
|
| [42] |
霍良安, 苏子雯. 突发公共卫生事件中应急医疗物资分配策略研究[J]. 物流科技, 2024, 47(11):1-7.
|
|
HUO Liang'an, SU Ziwen. Research on the distribution strategy of emergency medical supplies under public health emergencies[J]. Logistics Sci-Tech, 2024, 47(11): 1-7.
|
| [43] |
朱华桂, 刘晗. 突发重大公共卫生事件社区与居民演化博弈应急策略研究[J]. 中国应急管理科学, 2024(7):100-117.
|
|
ZHU Huagui, LIU Han. Research on emergency strategy of evolutionary game between community and residents in sudden major public health incidents[J]. China Journal of Emergency Management Science, 2024(7): 100-117.
|
| [44] |
徐明, 钟德寿, 盖赟. 重大疫情防控中政府与公众演化博弈策略分析[J]. 中国社会科学院大学学报, 2022, 42(1):126-141,146.
|
|
XU Ming, ZHONG Deshou, GE Yun. An analysis on the evolutionary game strategies of government and the public in the prevention and control of major pandemic[J]. Journal of University of Chinese Academy of Social Sciences, 2022, 42(1): 126-141, 146.
|
| [45] |
梁雁茹, 刘亦晴. COVID-19疫情下医疗防护用品市场监管演化博弈与稳定性分析[J]. 中国管理科学, 2022, 30(10):85-95.
|
|
LIANG Yanru, LIU Yiqing. The evolutionary game stability of the regulatory mechanism of medical protective equipment market under COVID-19 epidemic[J]. Chinese Journal of Management Science, 2022, 30(10): 85-95.
|
| [46] |
胡欢, 郭晓剑, 梁雁茹. 基于前景理论的重大疫情网络谣言管控三方演化博弈分析[J]. 情报科学, 2021, 39(7):45-53.
|
|
HU Huan, GUO Xiaojian, LIANG Yanru. Game analysis of the three-way evolution of network rumor control under the major epidemic based on prospect theory[J]. Information Science, 2021, 39(7): 45-53.
|
| [47] |
XU Ziqi, CHENG Yukun, YAO Shuailiang. Tripartite evolutionary game model for public health emergencies[J]. Discrete Dynamics in Nature and Society, 2021, 2021:DOI: 10.1155/2021/6693035.
|
| [48] |
YUAN Youwei, DU Lanying, LUO Lanjun, et al. Allocation strategy of medical supplies during a public health emergency: a tripartite evolutionary game perspective[J]. Scientific Reports, 2023, 13(1): DOI: 10.1038/s41598-023-36745-6.
|