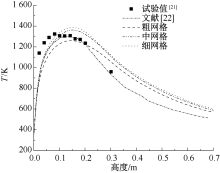
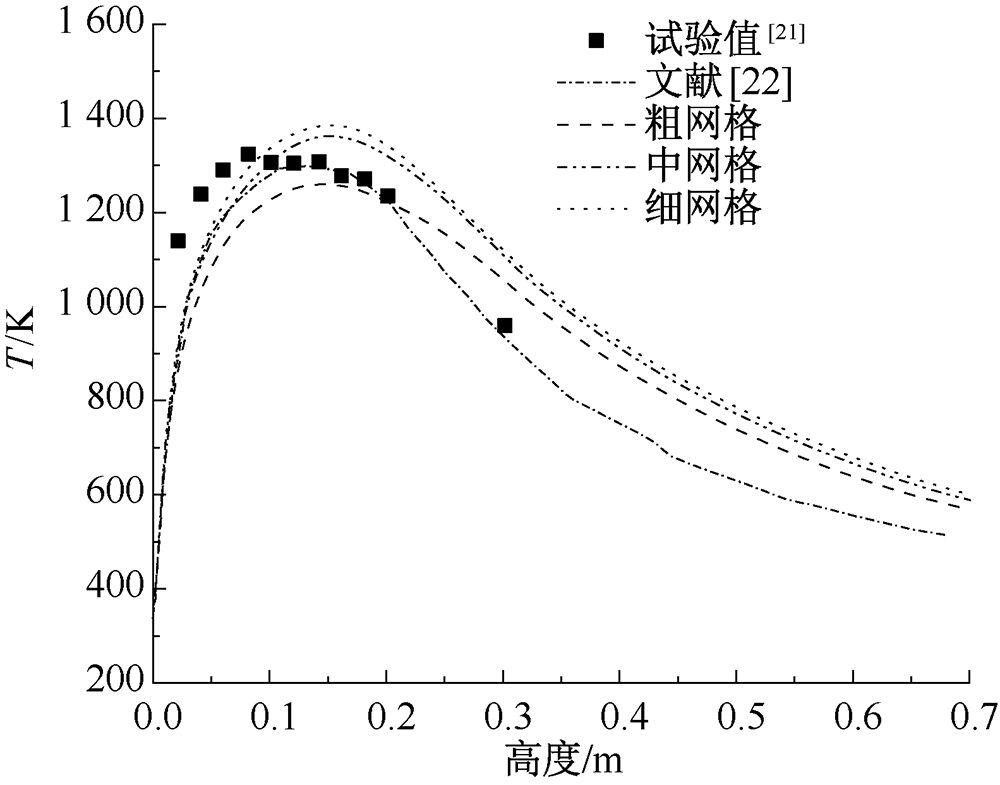
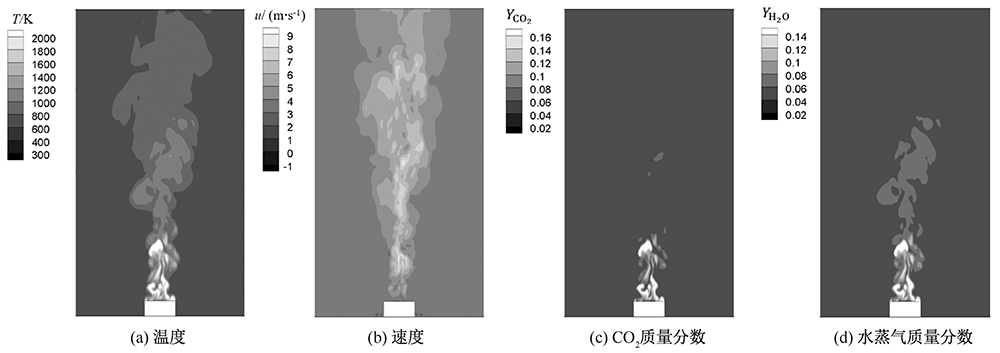
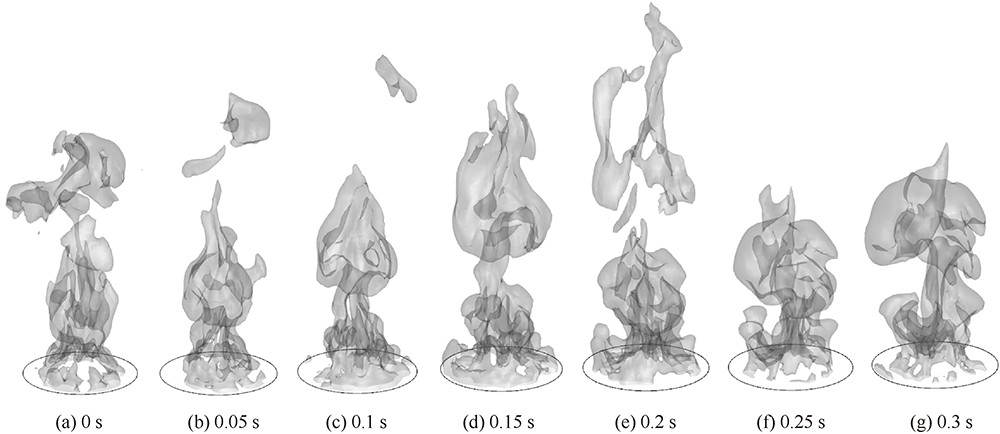
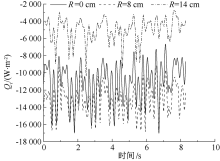
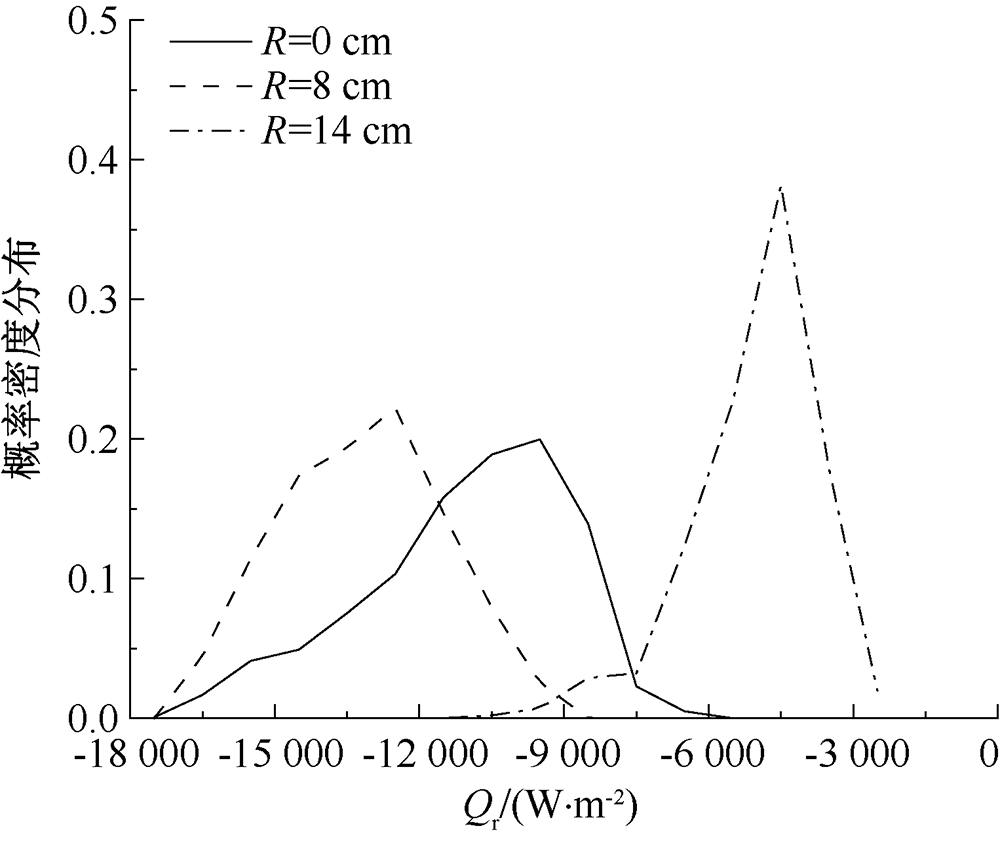
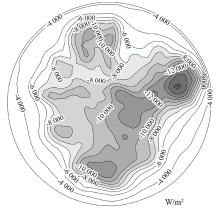
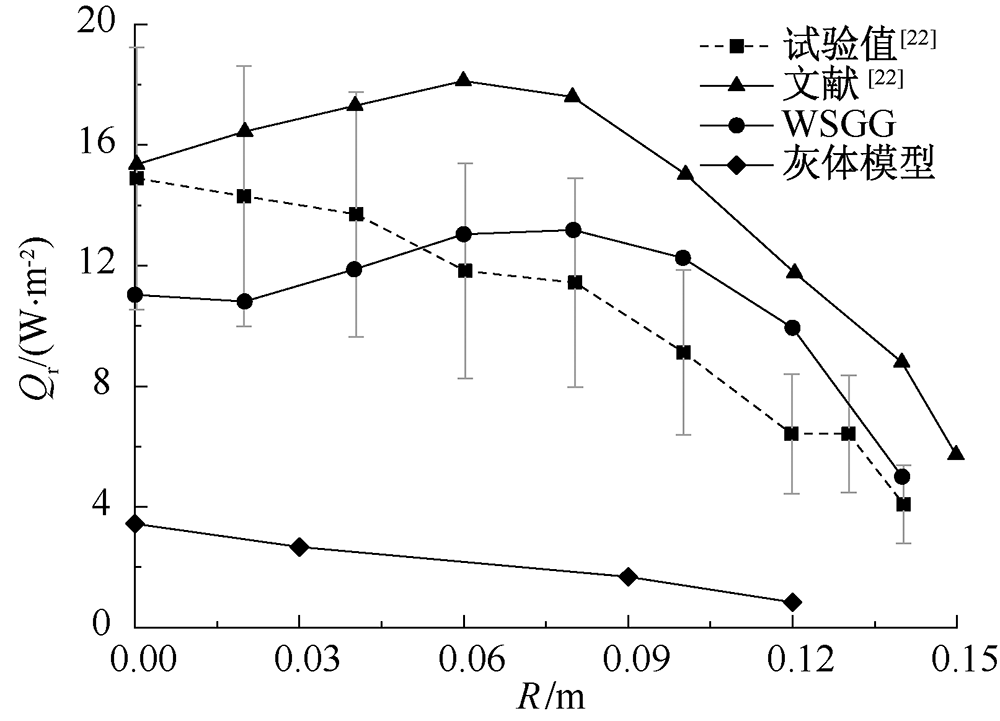
| [1] |
黄勇, 张红伟, 申荣艳, 等. 抑爆柴油池火燃烧特性试验研究[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2019, 29(8): 55-60.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2019.08.009
|
|
HUANG Yong, ZHANG Hongwei, SHEN Rongyan, et al. Experimental study on pool fire combustion characteristics of explosion suppression diesel fuel[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2019, 29(8): 55-60.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2019.08.009
|
| [2] |
陈福真, 张明广, 王妍, 等. 罐区池火灾多米诺效应试验研究[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2017, 27(11): 31-36.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2017.11.006
|
|
CHEN Fuzhen, ZHANG Mingguang, WANG Yan, et al. Experimental study on domino effect in pool fire in tank farm[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2017, 27(11): 31-36.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2017.11.006
|
| [3] |
侯志强, 陈梓松. 多米诺效应对港口油品储罐事故概率的影响[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2020, 30(9): 59-65.
|
|
HOU Zhiqiang, CHEN Zisong. Influence of domino effect on accident probability of oil storage tanks in ports[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2020, 30(9): 59-65.
|
| [4] |
庄磊, 陈国庆, 孙志友, 等. 大型油罐火灾的热辐射危害特性[J]. 安全与环境学报, 2008, 8(4): 110-114.
|
|
ZHUANG Lei, CHEN Guoqing, SUN Zhiyou, et al. On the damage study of the thermal radiation of the large oil-tank fire accidents[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2008, 8(4): 110-114.
|
| [5] |
傅智敏, 黄晓哲, 李元梅. 烃类池火灾热辐射量化分析模型探讨[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2010, 20(8): 65-70.
|
|
FU Zhimin, HUANG Xiaozhe, LI Yuanmei. Discussion on thermal radiation flux model for hydrocarbon pool fires[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2010, 20(8): 65-70.
|
| [6] |
魏东, 杨君涛, 董希琳. 着火油罐稳定燃烧时的辐射热分布[J]. 热科学与技术, 2005, 4(3): 241-245.
|
|
WEI Dong, YANG Juntao, DONG Xilin. Thermal radiation distribution of steady burning of oil tank[J]. Journal of Thermal Science and Technology, 2005, 4(3): 241-245.
|
| [7] |
张媛媛, 黄有波, 吕淑然. 矩形泄漏孔水平喷射火热辐射研究[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2017, 27(6): 73-78.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2017.06.013
|
|
ZHANG Yuanyuan, HUANG Youbo, LYU Shuran. Study on thermal radiation of horizontally oriented rectangular source fuel jet fire[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2017, 27(6): 73-78.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2017.06.013
|
| [8] |
刘全义, 朱博, 邓力, 等. 低压环境下不同直径油池火特征参量研究[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2021, 31(4): 105-110.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2021.04.014
|
|
LIU Quanyi, ZHU Bo, DENG Li, et al. Study on characteristic parameters of oil pool fire of different diameters in low pressure environment[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2021, 31(4): 105-110.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2021.04.014
|
| [9] |
王坚, 王伟, 杨锐, 等. 高高原机场油池火燃烧特性研究[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2017, 27(10): 62-67.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2017.10.011
|
|
WANG Jian, WANG Wei, YANG Rui, et al. High plateau airport pool fire combustion characteristic research[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2017, 27(10): 62-67.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2017.10.011
|
| [10] |
JI Jie, GONG Changzhiu, WAN Huaxian, et al. Prediction of thermal radiation received by vertical targets based on two-dimensional flame shape from rectangular n-heptane pool fires with different aspect ratios[J]. Energy, 2019, 185: 644-652.
doi: 10.1016/j.energy.2019.07.083
|
| [11] |
LIU Jiahao, ZHOU Zhihui. Examination of radiative fraction of small-scale pool fires at reduced pressure environments[J]. Fire Safety Journal, 2019, 110: DOI: 10.1016/j.firesaf.2019.102894.
doi: 10.1016/j.firesaf.2019.102894
|
| [12] |
GUO Qi, ROOT K J, CARLTON A, et al. Framework for rapid prediction of fire-induced heat flux on concrete tunnel liners with curved ceilings[J]. Fire Safety Journal, 2019, 109: DOI: 10.1016/j.firesaf.2019.102866.
doi: 10.1016/j.firesaf.2019.102866
|
| [13] |
SHI Congling, LIU Wei, HONG Wenjie, et al. A modified thermal radiation model with multiple factors for investigating temperature rise around pool fire[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2019, 379: DOI: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2019.120801.
doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2019.120801
|
| [14] |
MA Li, NMIRA F, CONSALVI J L. Large Eddy Simulation of medium-scale methanol pool fires-effects of pool boundary conditions[J]. Combustion and Flame, 2020, 222: 336-354.
doi: 10.1016/j.combustflame.2020.09.007
|
| [15] |
WU Bifen, ROY S P, ZHAO Xinyu. Detailed modeling of a small-scale turbulent pool fire[J]. Combustion and Flame, 2020, 214: 224-237.
doi: 10.1016/j.combustflame.2019.12.034
|
| [16] |
XU Rui, LE V M, MARCHAND A, et al. Simulations of the coupling between combustion and radiation in a turbulent line fire using an unsteady flamelet model[J]. Fire Safety Journal, 2021, 120: DOI: 10.1016/j.fresaf.2020.103101.
doi: 10.1016/j.fresaf.2020.103101
|
| [17] |
FRAGA G C, COELHO P J, FRANÇA F H R. Assessing individual time-averaged emission and absorption correlations for large-scale turbulent pool fires[J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2021, 165: DOI: 10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2020.120665.
doi: 10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2020.120665
|
| [18] |
CHU Huaqiang, LIU Fengshan, ZHOU Huaichun. Calculations of gas radiation heat transfer in a two-dimensional rectangular enclosure using the line-by-line approach and the statistical narrow-band correlated-k model[J]. International Journal of Thermal Sciences, 2012, 59: 66-74.
doi: 10.1016/j.ijthermalsci.2012.04.003
|
| [19] |
MARAGKOS G, BEJI T, MERCI B. Towards predictive simulations of gaseous pool fires[J]. Proceedings of the Combustion Institute, 2019, 37(3): 3927-3934.
doi: 10.1016/j.proci.2018.05.162
|
| [20] |
VERMESI I, DIDOMIZIO M J, RICHTER F, et al. Pyrolysis and spontaneous ignition of wood under transient irradiation: experiments and a-priori predictions[J]. Fire Safety Journal, 2017, 91: 218-225.
doi: 10.1016/j.firesaf.2017.03.081
|
| [21] |
HOWELL J R, MENGUC M P, SIEGEL R. Thermal radiation heat transfer, 5th edition[M]. Boca Raton: CRC Press, 2010: 619-710.
|
| [22] |
AHMED M, TROUVE A. Large eddy simulation of the unstable flame structure and gas-to-liquid thermal feedback in a medium-scale methanol pool fire[J]. Combustion and Flame, 2021, 225: 237-254.
doi: 10.1016/j.combustflame.2020.10.055
|