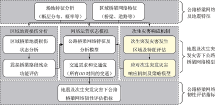
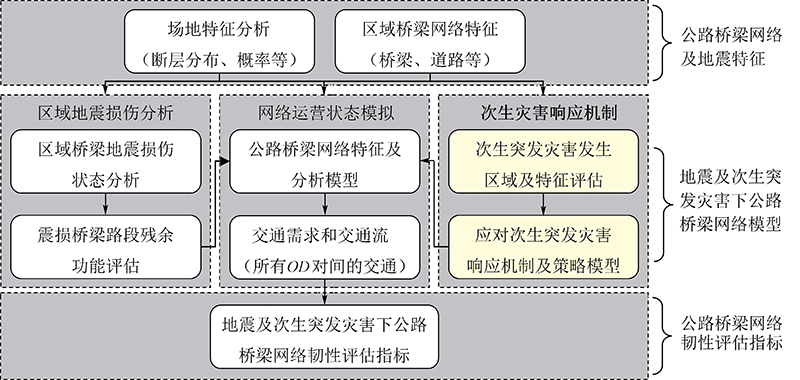
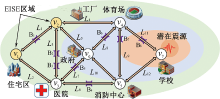
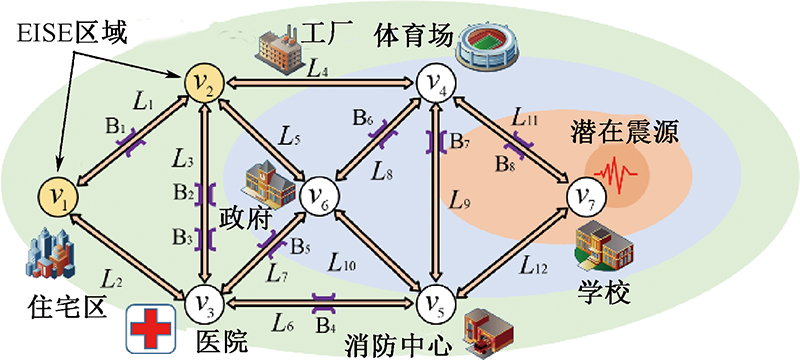
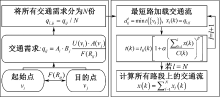
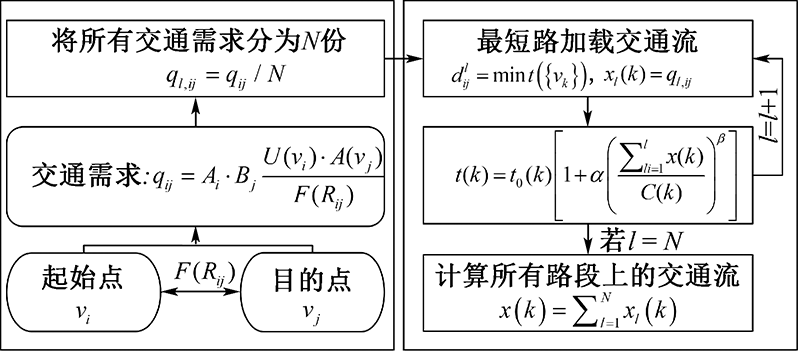
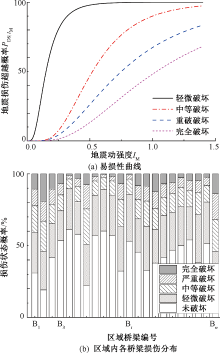
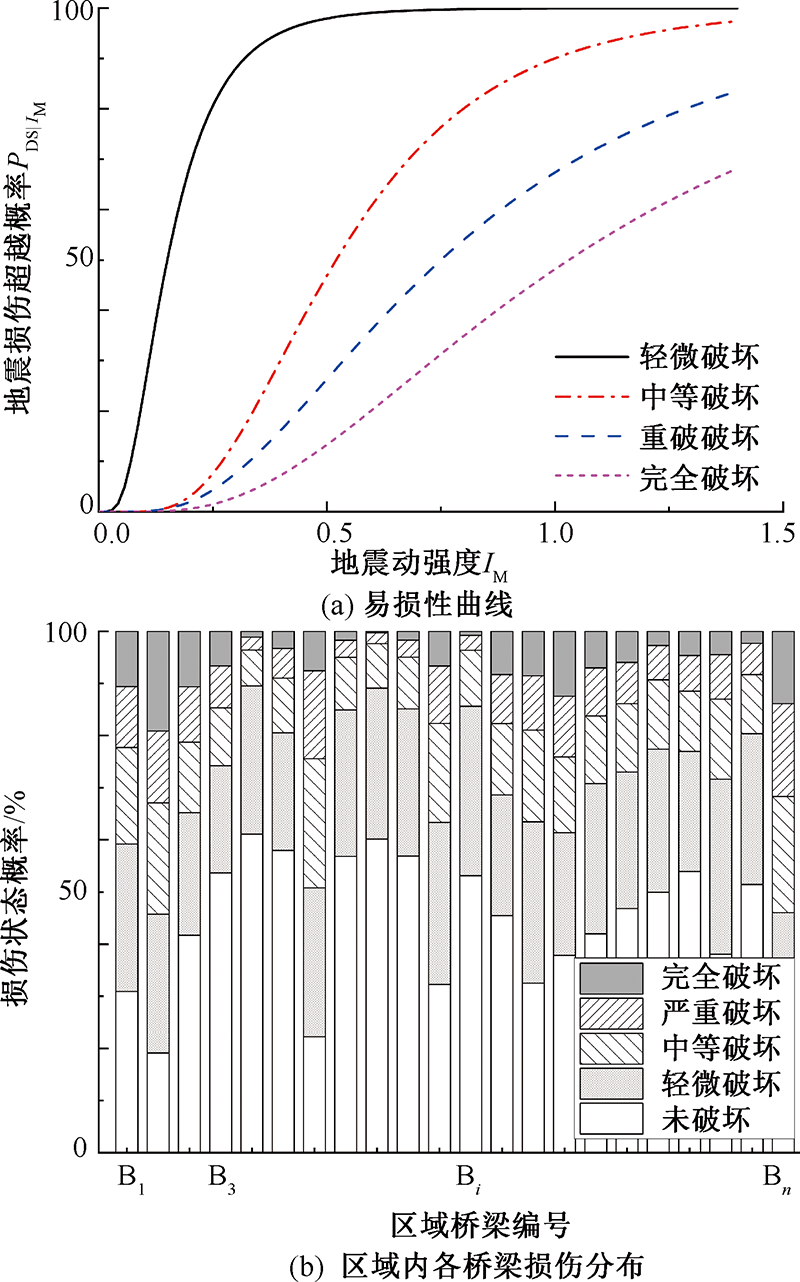
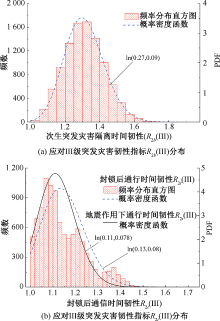
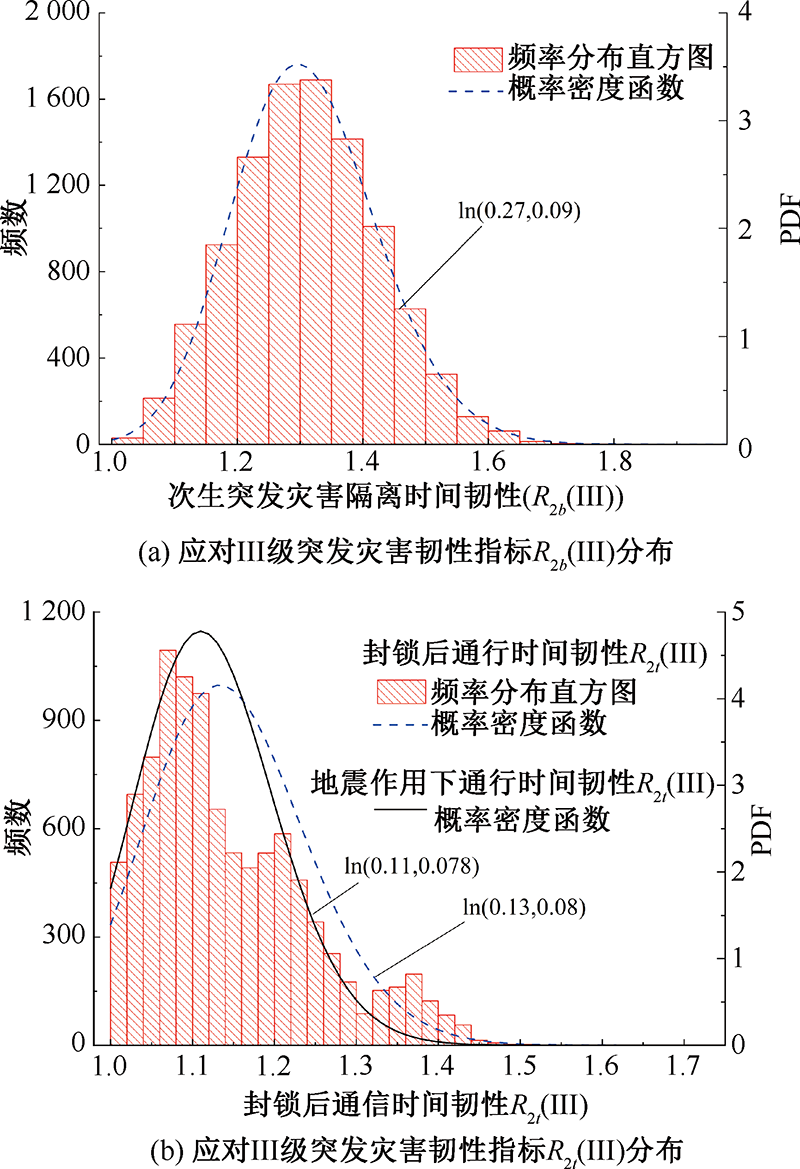
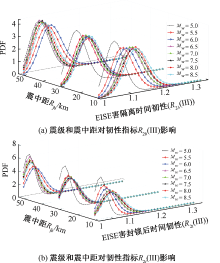
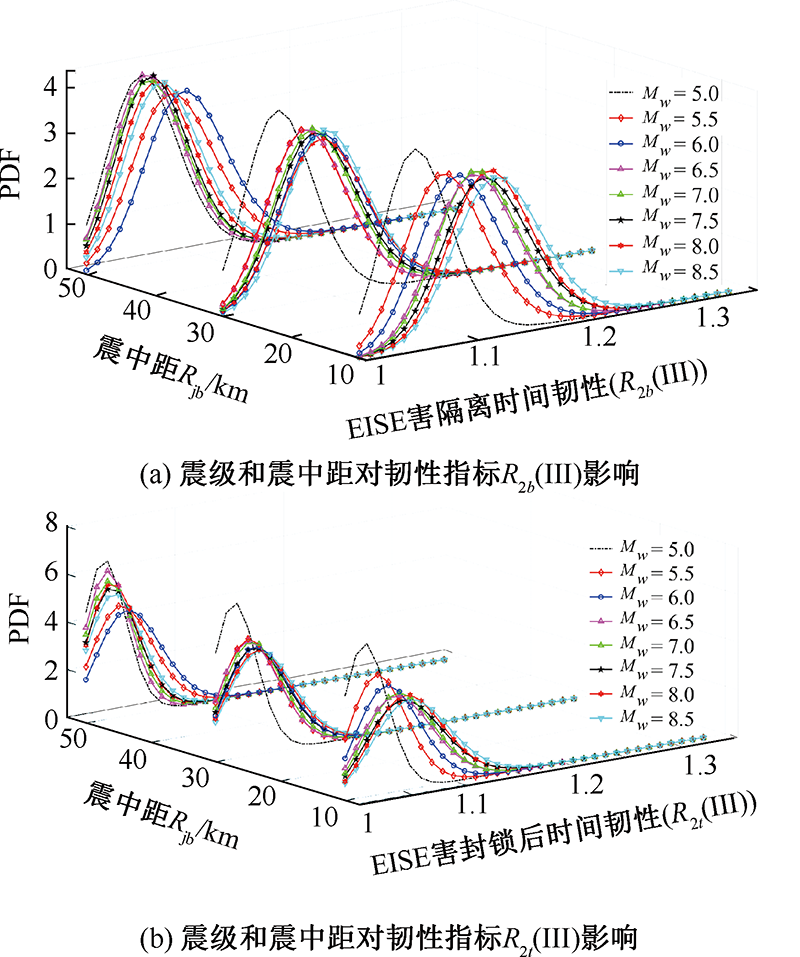
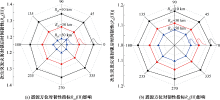
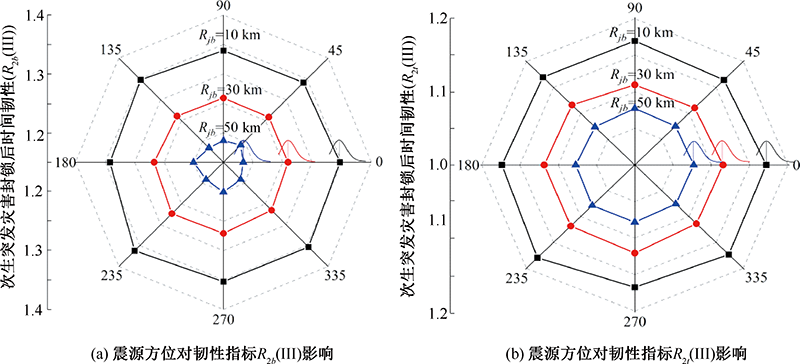
| [1] |
YAMAZAKI F, MURAO O. Vulnerability functions for Japanese buildings based on damage data from the 1995 Kobe Earthquake[C]. Implications of Recent Earthquakes on Seismic Risk, 2000:91-102.
|
| [2] |
FEMA. Multi-hazard loss estimation methodology: earthquake module technical manual[R]. Washington DC. Federal Emergency Management Agency, 2003.
|
| [3] |
宗亮, 王元清, 杨赛霓, 等. 基于HAZUS平台的中国公路桥梁震害评估模型研究[J]. 土木工程学报, 2014, 47(增1): 263-268.
|
|
ZONG Liang, WANG Yuanqing, YANG Saini, et al. Research on highway bridges seismic damage assessment system for China based on HAZUS[J]. China Civil Engineering Journal, 2014, 47(S1): 263-268.
|
| [4] |
PADGETT J E, DESROCHES R, NILSSON E. Regional seismic risk assessment of bridge network in Charleston, South Carolina[J]. Journal of Earthquake Engineering, 2010, 14(6):918-933.
doi: 10.1080/13632460903447766
|
| [5] |
BANERJEE S, VISHWANATH B S, DEVENDIRAN D K. Multihazard resilience of highway bridges and bridge networks: a review[J]. Structure and Infrastructure Engineering, 2019, 15(12):1694-1714.
doi: 10.1080/15732479.2019.1648526
|
| [6] |
刘伟, 陈科全, 田宗忠, 等. 基于密度熵的道路交通事故影响范围分区模型[J]. 交通运输工程学报, 2019, 19(6): 163-170.
|
|
LIU Wei, CHEN Kequan, TIAN Zongzhong, et al. Partition model of road traffic accident influence area based on density entropy[J]. Journal of Traffic and Transportation Engineering, 2019, 19(6): 163-170.
|
| [7] |
陈旭中. 震后次生灾害下城市交通疏散与救援组织优化仿真[D]. 北京: 北京交通大学, 2020.
|
|
CHEN Xuzhong. Optimization and simulation of urban traffic evacuation and rescue in post earthquake secondary disasters[D]. Beijing: Beijing Jiaotong University, 2020.
|
| [8] |
秦进, 贺钰昕. 定量化交通网络效率评价方法比较[J]. 交通运输工程学报, 2018, 18(2):111-119.
|
|
QIN Jin, HE Yuxin. Evaluation methods comparison of quantitative transportation network efficiency[J]. Journal of Traffic and Transportation Engineering, 2018, 18(2): 111-119.
|
| [9] |
GUO Anxin, LIU Zhenliang, LI Suchao, et al. Seismic performance assessment of highway bridge networks considering post-disaster traffic demand of a transportation system in emergency conditions[J]. Structure and Infrastructure Engineering, 2017, 13(12):1523-1537.
doi: 10.1080/15732479.2017.1299770
|
| [10] |
CIMELLARO G P, REINHORN A M, BRUNEAU M. Framework for analytical quantification of disaster resilience[J]. Engineering Structures, 2010, 32(11):3639-3649.
doi: 10.1016/j.engstruct.2010.08.008
|
| [11] |
BRUNEAU M, CHANG S E, EGUCHI R T, et al. A framework to quantitatively assess and enhance the seismic resilience of communities[J]. Earthquake Spectra, 2003, 19(4):733-752.
doi: 10.1193/1.1623497
|
| [12] |
KILANITIS I, SEXTOS A. Integrated seismic risk and resilience assessment of roadway networks in earthquake prone areas[J]. Bulletin of Earthquake Engineering, 2019, 17(1):181-210.
doi: 10.1007/s10518-018-0457-y
|
| [13] |
FENG Kairui, LI Quanwang, ELLINGWOOD B R. Post-earthquake modelling of transportation networks using an agent-based model[J]. Structure and Infrastructure Engineering, 2020, 16(11):1578-1592.
doi: 10.1080/15732479.2020.1713170
|
| [14] |
MUNTASIR B A H M, SHAHRIA A M. Seismic fragility assessment of highway bridges: a state-of-the-art review[J]. Structure and Infrastructure Engineering, 2015, 11(6):804-832.
doi: 10.1080/15732479.2014.912243
|
| [15] |
NIELSON B G, DESROCHES R. Seismic fragility methodology for highway bridges using a component level approach[J]. Earthquake Engineering & Structural Dynamics, 2007, 36(6):823-839.
|
| [16] |
王建民. 公路桥梁结构运营荷载下安全状态评价方法[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2020, 30(7):48-54.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2020.07.008
|
|
WANG Jianmin. Evaluation method for safety state of highway bridge structure under operation load[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2020, 30(7): 48-54.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2020.07.008
|
| [17] |
BOORE D M, ATKINSON G M. Ground-motion prediction equations for the average horizontal component of PGA, PGV, and 5%-damped PSA at spectral periods between 0.01 s and 10.0 s[J]. Earthquake Spectra, 2008, 24(1):99-138.
doi: 10.1193/1.2830434
|