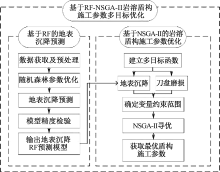
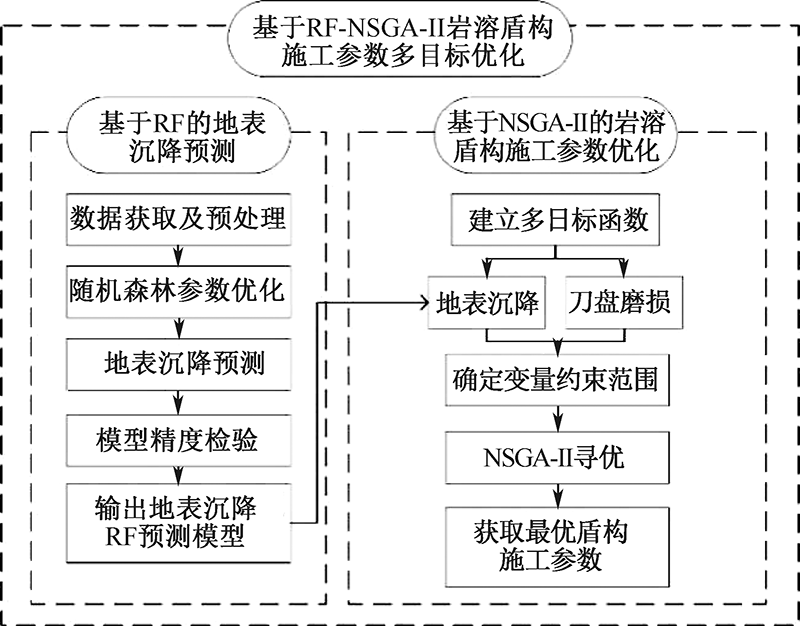
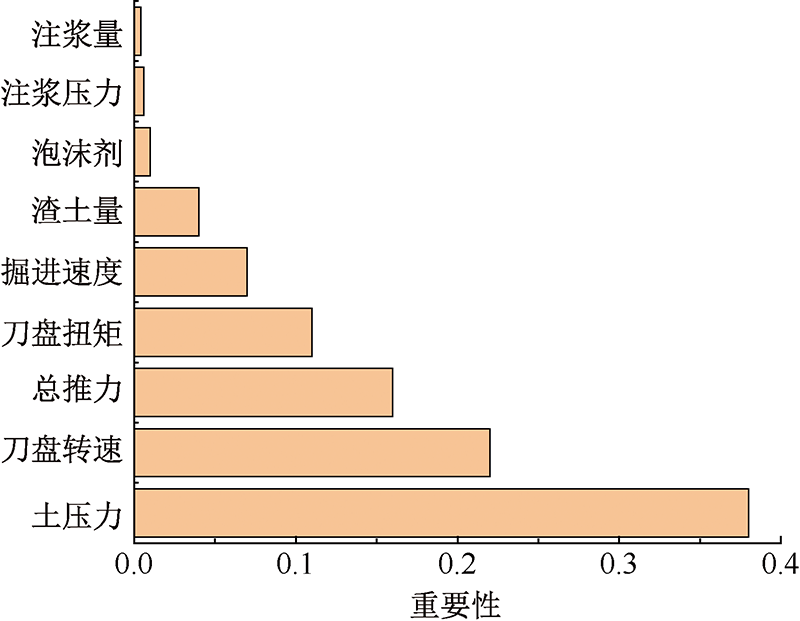
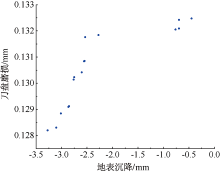
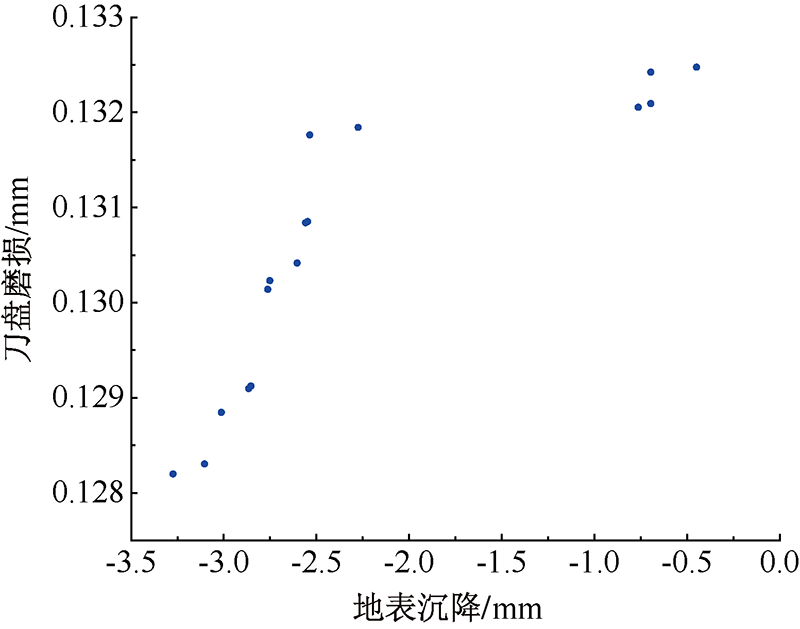
| [1] |
王军武, 胡蝶, 吴寒, 等. 小直径深层排水隧道盾构施工安全风险评价[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2020, 30(6): 113-120.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2020.06.017
|
|
WANG Junwu, HU Die, WU Han, et al. Risk assessment in construction of small-diameter deep drainage tunnel[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2020, 30(6): 113-120.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2020.06.017
|
| [2] |
冯欢欢, 王树英, 杨露伟, 等. 复杂地质条件下TBM刀具失效形式及原因分析与应对措施[J]. 隧道建设:中英文, 2022, 42(1):130-136.
|
|
FENG Huanhuan, WANG Shuying, YANG Luwei, et al. Forms and causes of failure in tunnel boring machine cutters under complex geological conditions and corresponding countermeasures[J]. Tunnel Construction, 2022, 42(1): 130-136.
|
| [3] |
OCAK I, SEKER S E. Calculation of surface settlements caused by EPBM tunneling using artificial neural network, SVM, and Gaussian processes[J]. Environmental Earth Sciences, 2013, 70(3): 1 263-1 276.
|
| [4] |
CHEN Renpeng, ZHANG Ping, WU Huaina, et al. Prediction of shield tunneling-induced ground settlement using machine learning techniques[J]. Frontiers of Structural and Civil Engineering, 2019, 13(6): 1363-1 378.
doi: 10.1007/s11709-019-0561-3
|
| [5] |
王鹏. 基于机器学习的地铁隧道施工扰动控制研究[J]. 现代隧道技术, 2019, 56(增2): 368-373.
|
|
WANG Peng. Control of construction disturbance induced by shield tunnelling based on machine learning[J]. Modern Tunnelling Technology, 2019, 56(S2): 368-373.
|
| [6] |
石超, 薛皓文, 丁小彬. 基于BP神经网络的硬岩地层盾构滚刀磨损预测[J]. 现代隧道技术, 2020, 57(增1): 217-225.
|
|
SHI Chao, XUE Haowen, DING Xiaobin. Prediction of cutter wear of shield machine in hard rock stratum based on BP neural network[J]. Modern Tunnelling Technology, 2020, 57(S1): 217-225.
|
| [7] |
REN Dongjie, SHEN Shuilong, ARUL A, et al. Prediction model of TBM disc cutter wear during tunnelling in heterogeneous ground[J]. Rock Mechanics and Rock Engineering, 2018, 51(11): 3599-3611.
doi: 10.1007/s00603-018-1549-3
|
| [8] |
陈焱, 王宇皓, 方勇, 等. 砂性地层土压平衡盾构切刀磨损室内试验研究[J]. 现代隧道技术, 2021, 58(5): 159-166.
|
|
CHEN Yan, WANG Yuhao, FANG Yong, et al. Laboratory experimental study on the wear of EPB shield cutting tools in sandy stratum[J]. Modern Tunnelling Technology, 2021, 58(5):159-166.
|
| [9] |
曾铁梅, 王金峰, 吴贤国, 等. 盾构下穿既有隧道位移控制施工参数多目标优化[J]. 铁道标准设计, 2022, 66(2):98-104.
|
|
ZENG Tiemei, WANG Jinfeng, WU Xianguo, et al. Multi-objective optimization of displacement of shield tunneling underpass existing tunnel based on GA-LSSVM combining NSGA-II[J]. Rallway Standard Design, 2022, 66(2):98-104.
|
| [10] |
BREIMAN L. Random forests[J]. Machine Learning, 2001, 45(1): 5-32.
doi: 10.1023/A:1010933404324
|
| [11] |
张新生, 蔡宝泉. 基于改进随机森林模型的海底管道腐蚀预测[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2021, 31(8): 69-74.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2021.08.010
|
|
ZHANG Xinsheng, CAI Baoquan. Corrosion prediction of submarine pipelines based on improved random forest model[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2021, 31(8):69-74.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2021.08.010
|
| [12] |
SRINIVAS N, DEB K, ROY P K, et al. Comparative study of vector evaluated GA and NSGA applied to multiobjective optimization[C]. Proceedings of the Symposium on Genetic Algorithms, 1995: 83-90.
|
| [13] |
DEB K, AGRAWAL S, PRATAP A, et al. A fast elitist non-dominated sorting genetic algorithm for multi-objective optimization: NSGA-II[C]. International Conference on Parallel Problem Solving From Nature, 2000: 849-858.
|
| [14] |
LIU Xuxuan, XU Sheng, HUANG Yueyang. Optimal control for earth pressure balance of shield machine based on action-dependent heuristic dynamic programming[J]. ISA Transactions, 2019, 94: 28-35.
doi: 10.1016/j.isatra.2019.04.007
|
| [15] |
BOUAYAD D, TUNNELLING F E J, TECHNOLOGY U S. Modeling the relationship between ground surface settlements induced by shield tunneling and the operational and geological parameters based on the hybrid PCA/ANFIS method[J]. Tunnelling and Underground Space Technology, 2017, 68: 142-152.
doi: 10.1016/j.tust.2017.03.011
|
| [16] |
邓立营, 刘春光, 党军锋. 盾构机刀盘扭矩及盾体推力计算方法研究[J]. 矿山机械, 2010, 38(17): 13-16.
|
|
DENG Liying, LIU Chunguang, DANG Junfeng. Research on method of calculating torque of cutter head of shield machine and thrust of shield[J]. Mining Machine, 2010, 38(17): 13-16.
|
| [17] |
KIM D, PHAM K, PARK S, et al. Determination of effective parameters on surface settlement during shield TBM[J]. Geomechanics and Engineering, 2020, 21(2): 153-164.
|
| [18] |
吕乾乾. 地铁盾构隧道同步注浆施工对地层沉降影响的预测分析[D]. 天津: 天津大学, 2012.
|
|
LYU Qianqian. Prediction and analysis of influence on stratum settlement of subway shield tunnel construction with synchronous grouting[D]. Tianjin: Tianjin University, 2012.
|
| [19] |
陶冶. 基于SVM的盾构刀盘能耗预测分析[D]. 武汉: 华中科技大学, 2017.
|
|
TAO Ye. Prediction and analysis of energy consumption of shield cutter based on SVM[D]. Wuhan: Huazhong University of Science and Technology, 2017.
|
| [20] |
张垚. 土压平衡盾构机掘进系统能耗优化控制[D]. 抚顺: 辽宁石油化工大学, 2019.
|
|
ZHANG Yao. Optimization control of energy consumption in tunneling system of earth pressure balance shield tunneling machine[D]. Fushun: Liaoning University of Petrochemical Technology, 2019.
|
| [21] |
GAO Minyu, ZHANG Ning, SHEN Shuilong, et al. Real-time dynamic earth-pressure regulation model for shield tunneling by integrating gru deep learning method with ga optimization[J]. Ieee Access, 2020, 8: 64 310-64 323.
|