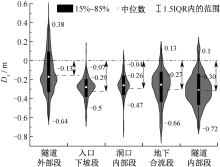
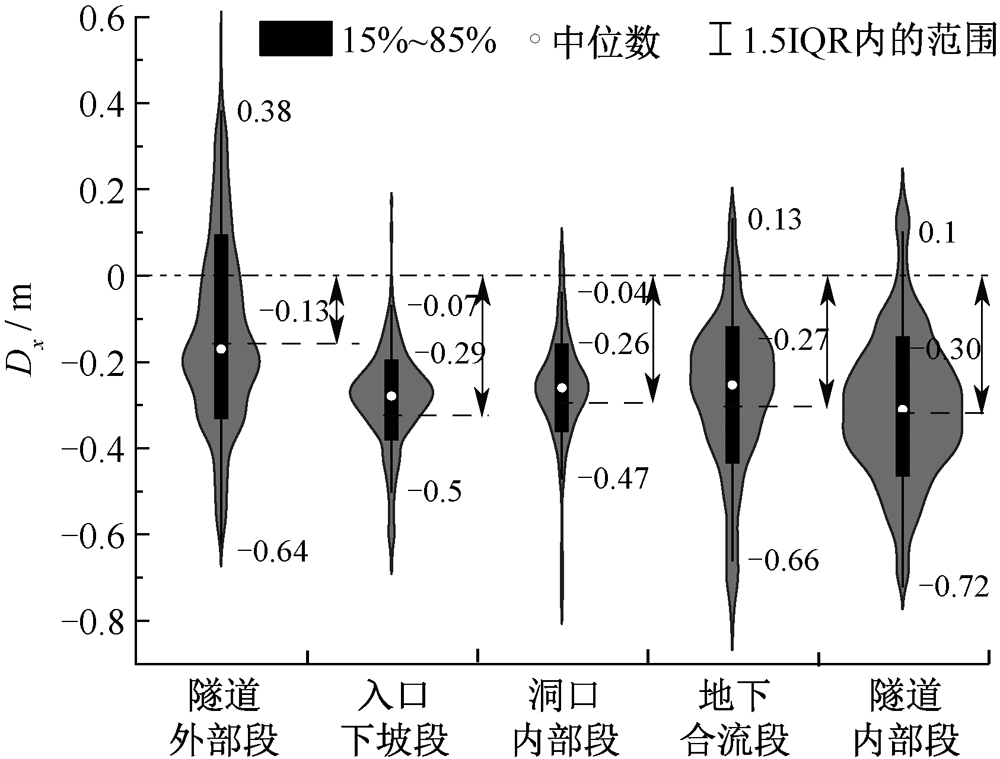
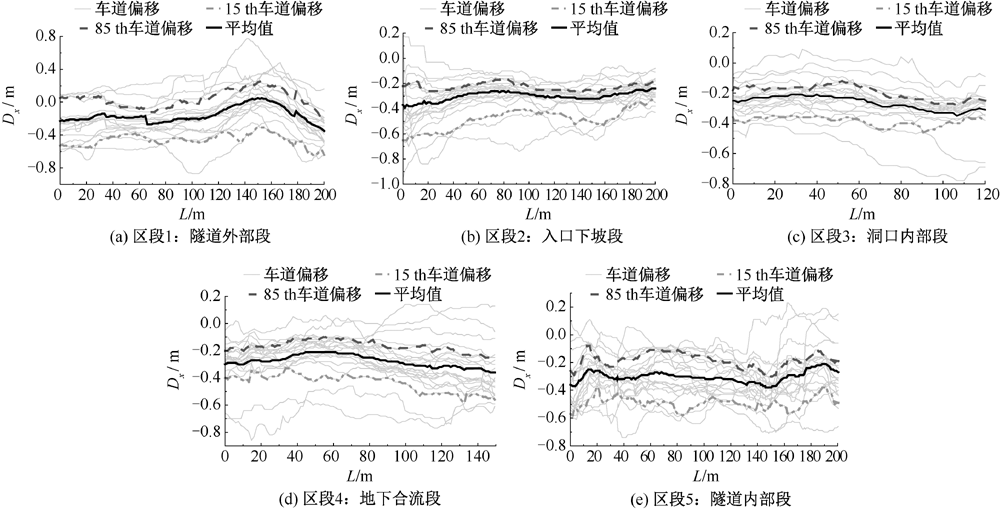
| [1] |
WANG Xuesong, AZATI Y, QUDDUS M, et al. Statistical analysis of traffic crashes on mountainous freeway tunnel sections[J]. Transportation Research Record, 2023, 2678(2):1-10.
|
| [2] |
王萌, 毛琰, 狄胜德, 等. 城市地下道路分合流区变速车道长度研究[J]. 公路交通科技, 2020, 37(1): 104-114.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-0268.2020.01.013
|
|
WANG Meng, MAO Yan, DI Shengde, et al. Study on length of speed-change lane in diverging and merging areas of urban underground road[J]. Journal of Highway and Transportation and Research and Development, 2020, 37(1): 104-114.
|
| [3] |
焦方通, 杜志刚, 王首硕, 等. 城市水下特长隧道弯道驾驶人扫视行为研究[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2019, 29(7): 104-109.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2019.07.017
|
|
JIAO Fangtong, DU Zhigang, WANG Shoushuo, et al. Research on saccade behavior of drivers in extra-long urban underwater tunnel curves[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2019, 29(7): 104-109.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2019.07.017
|
| [4] |
LIU Shuo, WANG Junhua, FU Ting. Effects of lane width, lane position and edge shoulder width on driving behavior in underground urban expressways: a driving simulator study[J]. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 2016, 13(10): DOI: 10.3390/IJERPH13101010.
|
| [5] |
FENG Zhongxiang, YANG Miaomiao, DU Yingjie, et al. Effects of the spatial structure conditions of urban underpass tunnels' longitudinal section on drivers' physiological and behavioral comfort[J]. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 2021, 18(20): DOI: 10.3390/ijerph182010992.
|
| [6] |
焦方通, 杜志刚, 王首硕, 等. 城市水下特长隧道出入口视觉及舒适性研究[J]. 中国公路学报, 2020, 33(6): 147-156.
doi: 10.19721/j.cnki.1001-7372.2020.06.014
|
|
JIAO Fangtong, DU Zhigang, WANG Shoushuo, et al. Visual characteristic and comfort at the entrance and exit of theextra long urban underwater tunnel[J]. China Journal of Highway and Transport, 2020, 33(6): 147-156.
doi: 10.19721/j.cnki.1001-7372.2020.06.014
|
| [7] |
WANG Xuesong, LIU Qian, GUO Feng, et al. Causation analysis of crashes and near crashes using naturalistic driving data[J]. Accident Analysis & Prevention, 2022, 177: DOI: 10. 1016/J. AAP. 2022. 106821.
|
| [8] |
MILLER E E, BOYLE L N. Driver behavior in road tunnels: association with driver stress and performance[J]. Transportation Research Record, 2015, 2518(1): 60-67.
|
| [9] |
PERVEZ A, HUANG Helai, HAN Chunyang, et al. Revisiting freeway single tunnel crash characteristics analysis: a six-zone analytic approach[J]. Accident Analysis & Prevention, 2020, 142: DOI: 10. 1016/J. AAP. 2020. 105542.
|
| [10] |
GUO Tangyi, PAN Shu, SHAO Fei, et al. Drivers' fixation transfer characteristics in urban tunnels[J]. Journal of Southeast University: English Edition, 2021, 37(3): 325-331.
|
| [11] |
乔建刚, 杨程, 陈彦欣. 基于驾驶员心率和速度差的高速公路纵坡度研究[J]. 中国安全生产科学技术, 2022, 18(5): 216-221.
|
|
QIAO Jian'gang, YANG Cheng, CHEN Yanxin, et al. Research on longitudinal slope of expressway based on driver's heart rate and speed difference[J]. Journal of Safety Science and Technology, 2022, 18(5): 216-221.
|
| [12] |
SHAO Xiaojun, CHEN Feng, MA Xiaoxiang, et al. The impact of lighting and longitudinal slope on driver behaviour in underwater tunnels: a simulator study[J]. Tunnelling and Underground Space Technology, 2022, 122: DOI: 10.1016/J.TUST.2022.104367.
|
| [13] |
YAN Guanfeng, WANG Mingnian, QIN Pengcheng, et al. Comparative study on drivers' eye movement characteristics and psycho-physiological reactions at tunnel entrances in plain and high-altitude areas: a pilot study[J]. Tunnelling and Underground Space Technology, 2022, 122: DOI: 10.1016/J.TUST.2022.104370.
|
| [14] |
MA Zhaoyou, FANG Shouen, LIU Shuo, et al. Analysis of the relationship between the number of traffic accidents and the traffic flow & section location in extralong tunnel[J]. Engineering, 2020, 12(2): 71-81.
|
| [15] |
MEHRI A, ALIABADI M, GOLMOHAMMADI R, et al. An empirical investigation of disability glare and visibility level during driving inside very long road tunnels: a case study[J]. Tunnelling and Underground Space Technology, 2022, 125: DOI: 10.1016/J.TUST.2022.104496.
|
| [16] |
徐宇, 郑晅, 李雪, 等. 隧道遮光棚不舒适眩光定量评价方法研究[J]. 现代隧道技术, 2020, 57(1): 120-124.
|
|
XU Yu, ZHENG Xuan, LI Xue, et al. Quantitative study on the discomfort glare of the road tunnel sunshades[J]. Modern Tunnelling Technology, 2020, 57(1): 120-124.
|
| [17] |
王首硕, 杜志刚, 冯守中, 等. 高速公路隧道入口区域视线诱导系统有效性研究[J]. 交通运输工程学报, 2021, 21(2): 267-277.
|
|
WANG Shoushuo, DU Zhigang, FENG Shouzhong, et al. Research on effectiveness of visual guiding system in entrance zone of freeway tunnel[J]. Journal of Traffic and Transportation Engineering, 2021, 21(2): 267-277.
|