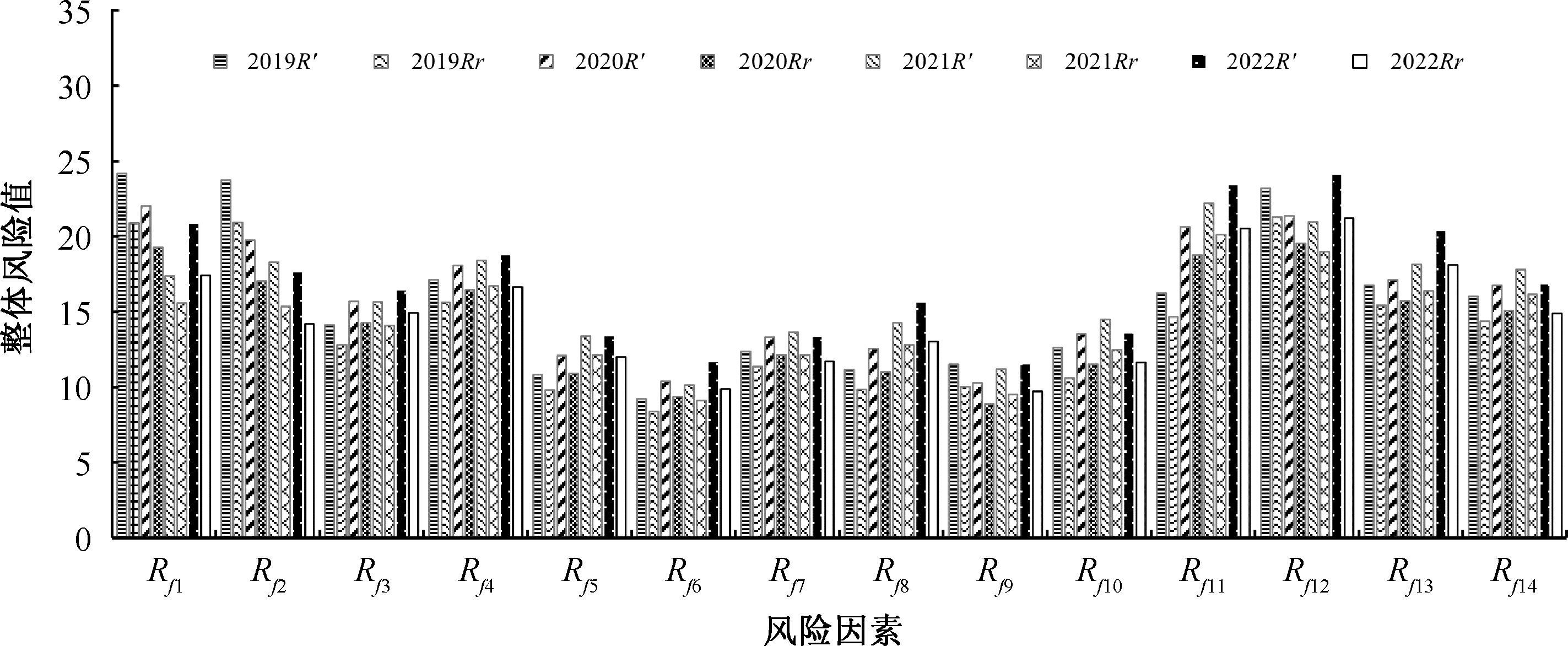
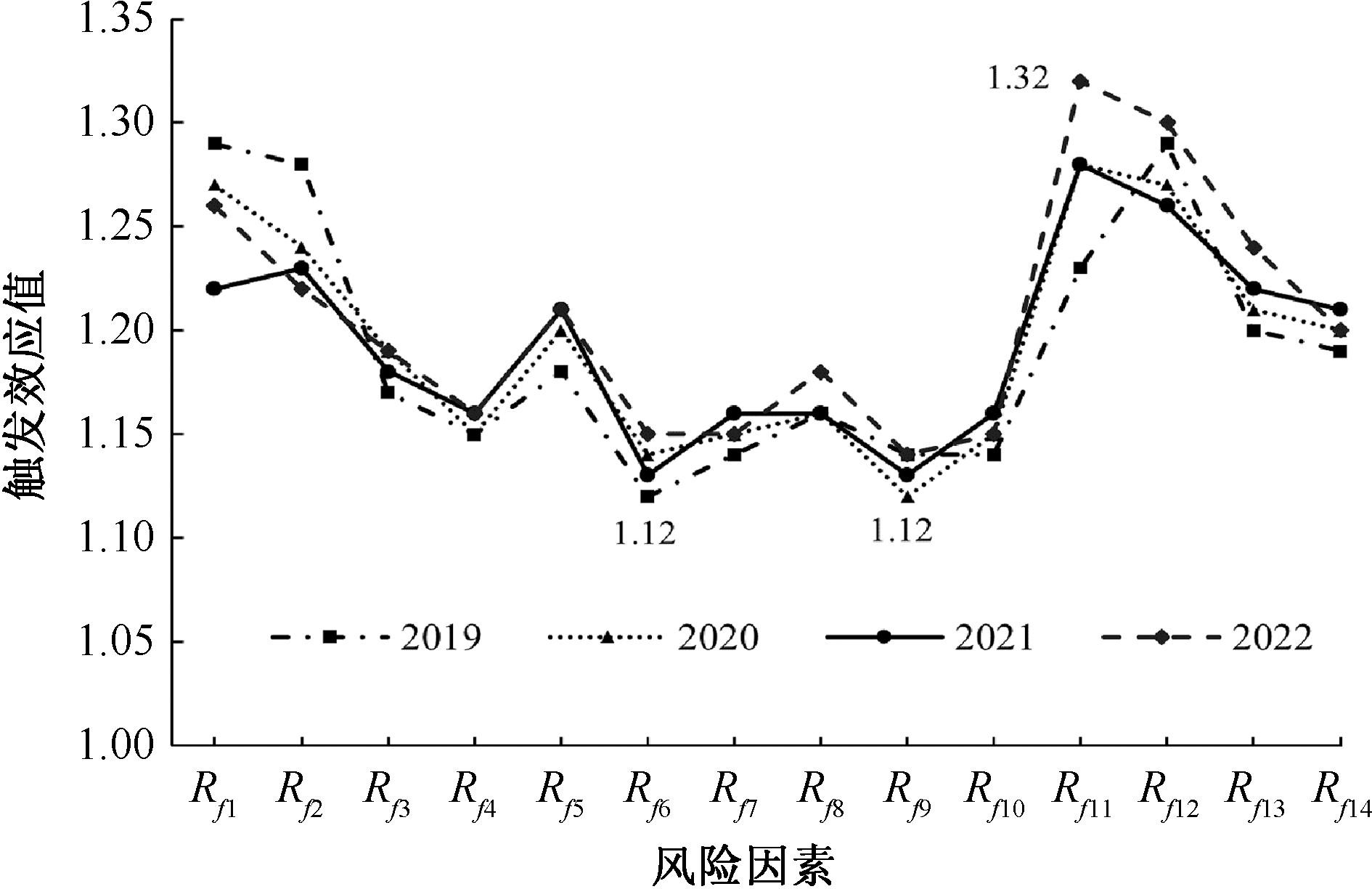
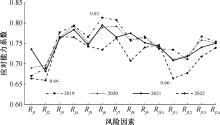
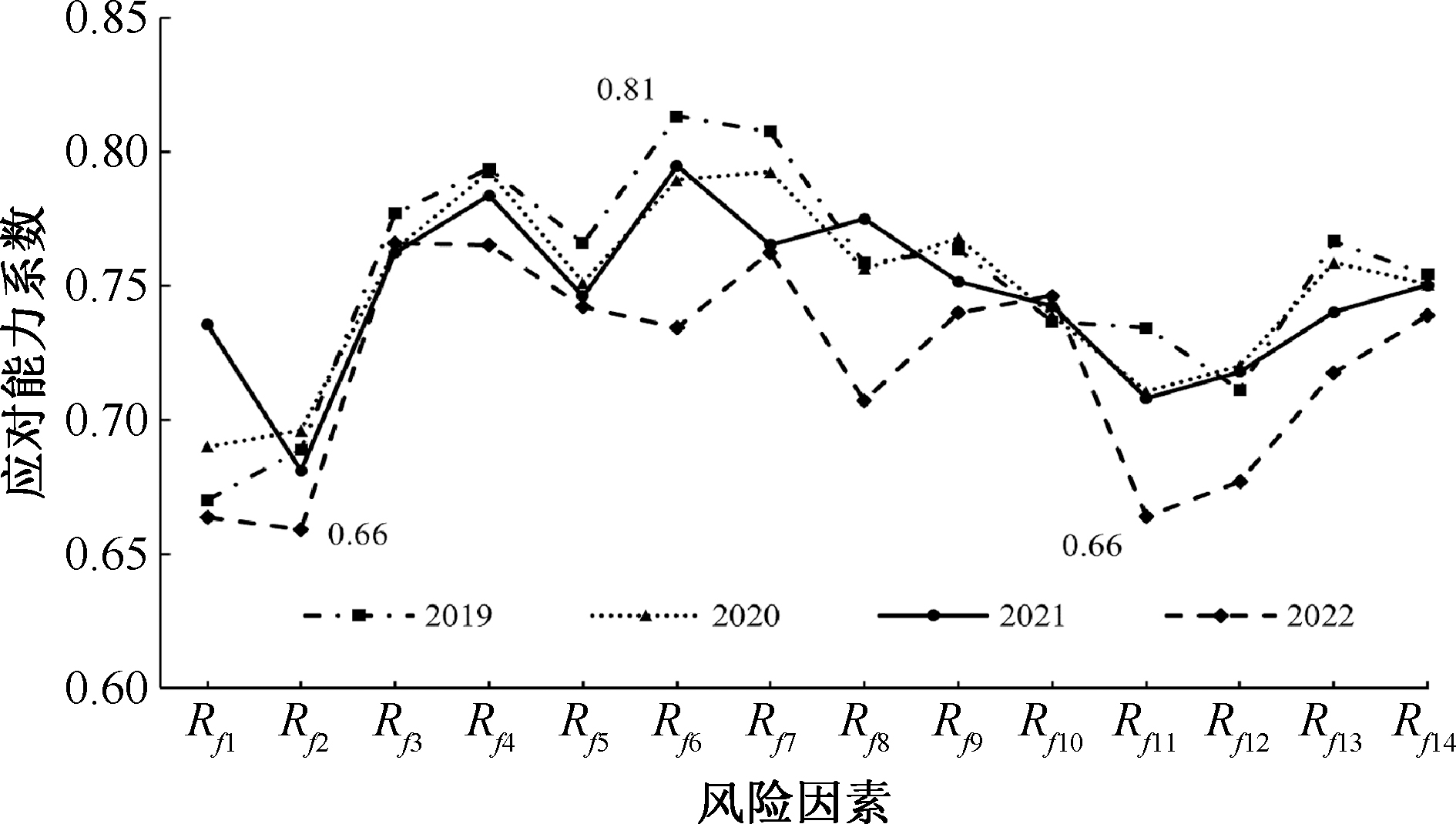
| [1] |
晏然. 健全国家物资储备体系[J]. 红旗文稿, 2020(9):27-29.
|
| [2] |
魏宇琪, 杨敏, 梁樑. 基于需求预测和模块化的应急物资库库联动方法研究[J]. 中国管理科学, 2019, 27(6):123-135.
|
|
WEI Yuqi, YANG Min, LIANG Liang. Research on the linkage method of relief materials warehouse based on demand forecasting and modularization[J]. Chinese Journal of Management Science, 2019, 27(6):123-135.
|
| [3] |
HOFSTRA N, PETKOVA B, DULLAERT W, et al. Assessing and facilitating warehouse safety[J]. Safety Science, 2018, 105(5):134-148.
|
| [4] |
DE KOSTER R B M, STAM D, BALK B M. Accidents happen: the influence of safety-specific transformational leadership, safety consciousness, and hazard reducing systems on warehouse accidents[J]. Journal of Operations Management, 2011, 29(7/8):753-765.
|
| [5] |
ZHAN Xuegang, WU Wei, SHEN Leidi, et al. Industrial internet of things and unsupervised deep learning enabled real-time occupational safety monitoring in cold storage warehouse[J]. Safety Science, 2022, 152(8):1-9.
|
| [6] |
WINKELHAUS S, GROSSE E H. Logistics 4.0: a systematic review towards a new logistics system[J]. International Journal of Production Research, 2020, 58(1):18-43.
|
| [7] |
LYU Chen, WU Zongzhi, LIU Zegong, et al. The multi-level comprehensive safety evaluation for chemical production instalment based on the method that combines grey-clustering and EAHP[J]. International Journal of Disaster Risk Reduction, 2017, 21(1):243-250.
|
| [8] |
CEDILLO-CAMPOS M G, CEDILLO-CAMPOS H O. w@reRISK method: security risk level classification of stock keeping units in a warehouse[J]. Safety Science, 2015, 79(11):358-368.
|
| [9] |
SHARIFF A M, LEONG C T. Inherent risk assessment: a new concept to evaluate risk in preliminary design stage[J]. Process Safety and Environmental Protection, 2009, 87(6):371-376.
|
| [10] |
陈国华, 李佳玲, 陈学希, 等. 灾害链网络下城市区域安全风险评估模型[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2022, 32(11):146-153.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2022.11.2043
|
|
CHEN Guohua, LI Jialing, CHEN Xuexi, et al. A safety risk assessment model of urban areas under disaster chain network[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2022, 32(11):146-153.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2022.11.2043
|
| [11] |
王刚, 商荦真, 刘学麟, 等. 采用AHP-熵权法的巷道启封中毒窒息致因研究[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2021, 31(7):187-192.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn 1003-3033.2021.07.026
|
|
WANG Gang, SHANG Luozhen, LIU Xuelin, et al. Study on causes of poisoning and asphyxiation in roadway opening by AHP-entropy weight method[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2021, 31(7):187-192.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn 1003-3033.2021.07.026
|
| [12] |
PURDY G. ISO 31000: 2009—setting a new standard for risk management[J]. Risk Analysis: An International Journal, 2010, 30(6):881-886.
|
| [13] |
FRAZIER T G, WOOD E X, PETERSON A G. Residual risk in public health and disaster management[J]. Applied Geography, 2020, 125(12):1-11.
|
| [14] |
WU Jinru, CHEN Xiaolong, LU Jianzhong. Assessment of long and short-term flood risk using the multi-criteria analysis model with the AHP-Entropy method in Poyang Lake basin[J]. International Journal of Disaster Risk Reduction, 2022, 75(9):1-17.
|
| [15] |
GILL J C, MALAMUD B D. Hazard interactions and interaction networks (cascades) within multi-hazard methodologies[J]. Earth System Dynamics, 2016, 7(3):659-679.
|
| [16] |
蒲宇, 冯晨鹏, 丁晶晶, 等. 应急物资储备综合评价指标体系构建研究[J]. 科技促进发展, 2018, 14(5):417-425.
|
|
PU Yu, FENG Chenpeng, DING Jingjing, et al. Study on establishment of the index system for emergency material reserve comprehensive evaluation[J]. Science & Technology for Development, 2018, 14(5):417-425.
|
| [17] |
LI Yang, WANG Hao, BAI Ke, et al. Dynamic intelligent risk assessment of hazardous chemical warehouse fire based on electrostatic discharge method and improved support vector machine[J]. Process Safety and Environmental Protection, 2021, 145(1):425-434.
|
| [18] |
SEGUÍ X, DARBRA R M, VÍLCHEZ J A, et al. Methodology for the quantification of toxic dispersions originated in warehouse fires and its application to the QRA in Catalonia (Spain)[J]. Journal of Loss Prevention in the Process Industries, 2014, 32(6):404-414.
|
| [19] |
刘婷, 张越, 周建波. 新时代国家战略物资储备体系的发展与展望[J]. 宏观经济管理, 2022(12):75-82.
|
|
LIU Ting, ZHANG Yue, ZHOU Jianbo. The development and outlook of the China's national system of strategic supplies in the new era[J]. Macroeconomic Management, 2022(12):75-82.
|
| [20] |
樊亚静. 某基层储备仓库仓储安全管理研究[D]. 北京: 北京交通大学, 2015.
|
|
FAN Yajing. Research on security management of a reserve warehouse[D]. Beijing: Beijing Jiaotong University, 2015.
|
| [21] |
卢艺. 加快健全我国国家物资储备体系[J]. 宏观经济管理, 2020(11):51-56.
|
|
LU Yi. Move faster to improve China's national system of material reserves[J]. Macroeconomic Management, 2020(11):51-56.
|
| [22] |
白文志. 国家物资储备仓库安防信息化系统建设研究[D]. 天津: 天津大学, 2019.
|
|
BAI Wenzhi. Research on reform of security system of national material reserve warehouse[D]. Tianjin: Tianjin University, 2019.
|