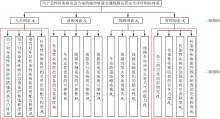
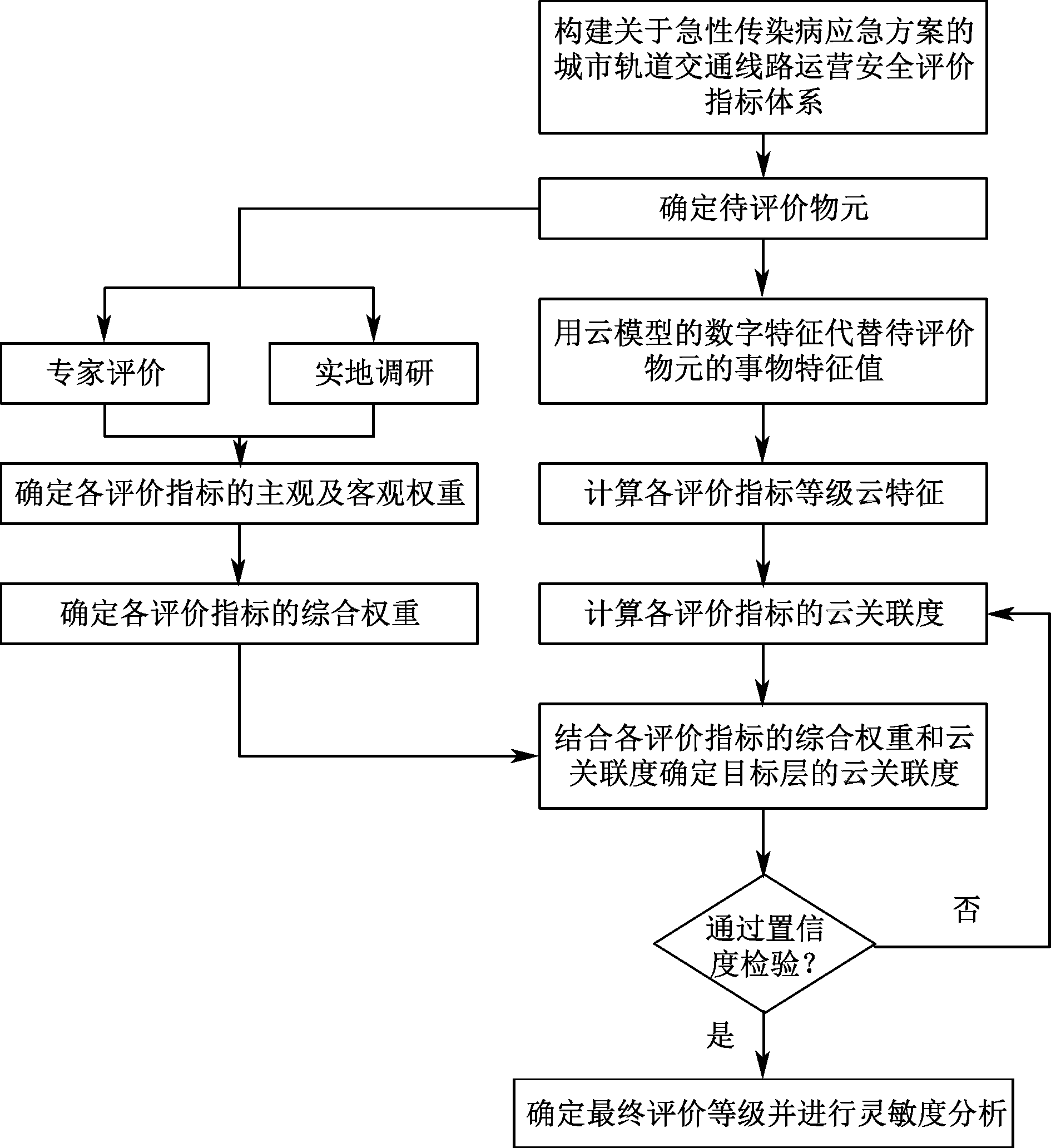
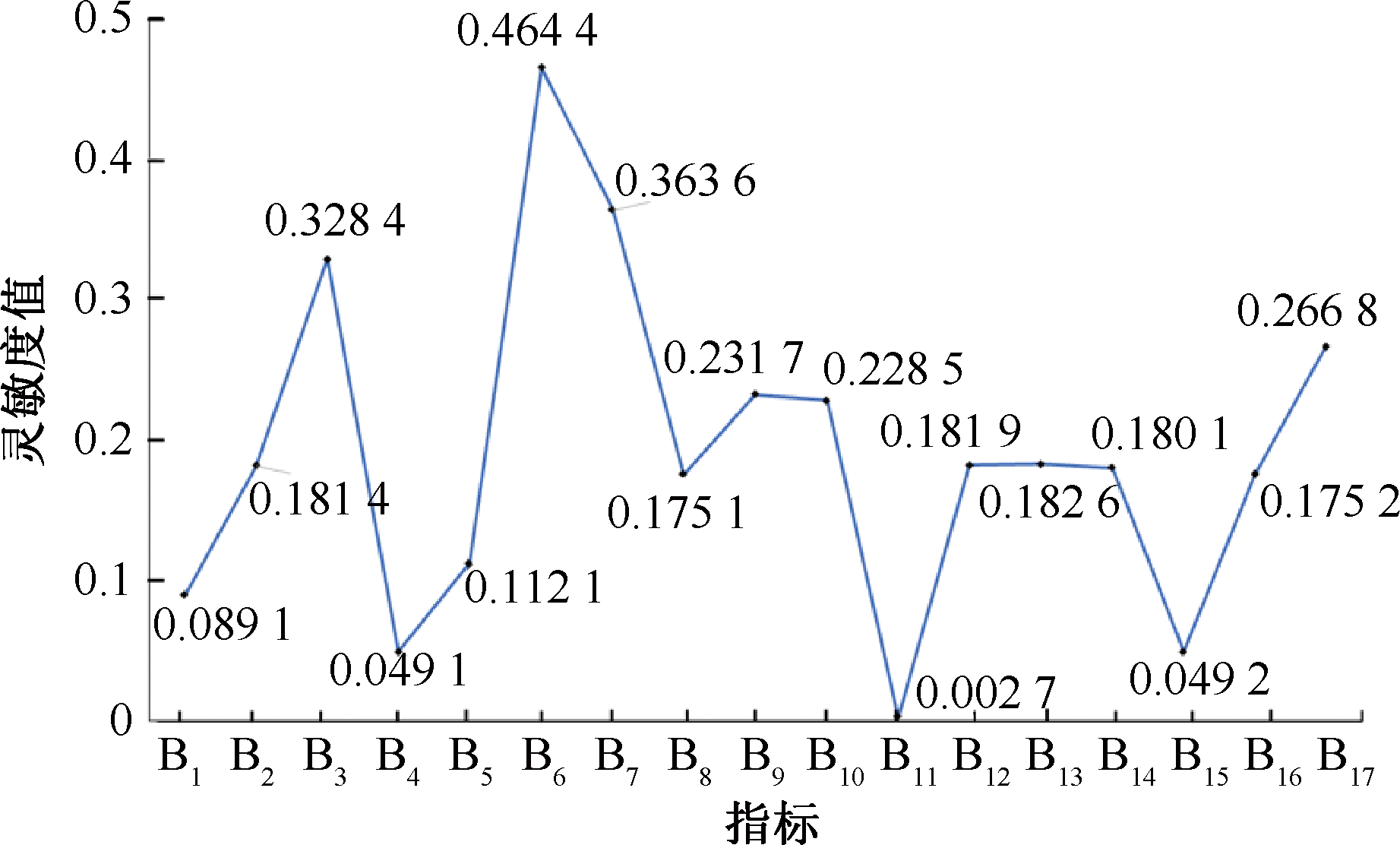
| [1] |
苏旭明, 王艳辉, 祝凌曦. 改进的故障模式及影响分析在城市轨道交通运营安全评价中的应用[J]. 城市轨道交通研究, 2011, 14(5):65-69.
|
|
SU Xuming, WANG Yanhui, ZHU Lingxi. Safety evaluation of urban rail transit operation based on improved fault model and effect analysis[J]. Urban Mass Transit, 2011, 14(5):65-69.
|
| [2] |
王艳辉, 黄雅坤, 李曼. 基于组合赋权方法的城轨线路运营安全评价[J]. 同济大学学报:自然科学版, 2013, 41(8):1243-1248.
|
|
WANG Yanhui, HUANG Yakun, LI Man. Evaluation of urban rail transit line operational safety based on combination weighting method[J]. Journal of Tongji University:Natural Science, 2013, 41(8):1243-1248.
|
| [3] |
姜林林. 基于BP神经网络的城市轨道交通运营安全评价与设计[D]. 大连: 大连交通大学, 2014.
|
|
JIANG Linlin. Urban rail transit operation safety evaluation and design based on BP neural network[D]. Dalian: Dalian Jiaotong University, 2014.
|
| [4] |
黎新华, 李俊辉. 基于DEMATEL和ISM融合的城市轨道交通车站运营安全评价方法研究[J]. 铁道运输与经济, 2018, 40(7):116-121.
|
|
LI Xinhua, LI Junhui. A study on an assessment system on safe operation of urban rail stations based on DEMATEL and ISM[J]. Railway Transport and Economy, 2018, 40(7):116-121.
|
| [5] |
鹿颖. 基于风险矩阵法的城市轨道交通运营安全评价研究[D]. 长春: 吉林大学, 2019.
|
|
LU Ying. Research on safety evaluation of urban rail transit operation based on risk matrix method[D]. Changchun: Jilin University, 2019.
|
| [6] |
任刚, 陈佳洁, 高瑾瑶, 等. 基于改进可拓物元法的地铁车站运营安全评价方法[J]. 城市轨道交通研究, 2020, 23(3):136-139.
|
|
REN Gang, CHEN Jiajie, GAO Jinyao, et al. Safety assessment of metro station operation based on improved extension and matter element method[J]. Urban Mass Transit, 2020, 23(3):136-139.
|
| [7] |
WU Huawen, ZHEN Jin, ZHANG Jing. Urban rail transit operation safety evaluation based on an improved CRITIC method and cloud model[J]. Journal of Rail Transport Planning & Management, 2020, 16:1002-1006.
|
| [8] |
张渺. G1-EW组合赋权云模型下地铁运营安全风险评价[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2022, 32(6):163-170.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2022.06.0947
|
|
ZHANG Miao. Risk assessment of metro operation based on G1-EW combination weighting cloud model[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2022, 32(6):163-170.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2022.06.0947
|
| [9] |
GB50157—2013,地铁设计规范[S].
|
|
GB50157-2013, Code for design metro[S].
|
| [10] |
李国良, 王磊, 杨晓严, 等. 我国交通基础设施发展水平比较研究[J]. 公路交通科技, 2021, 38(11):97-105.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-0268.2021.11.012
|
|
LI Guoliang, WANG Lei, YANG Xiaoyan, et al. Comparative study on development level of transport infrastructure in China[J]. Journal of Highway and Transportation Research and Development, 2021, 38(11):97-105.
|