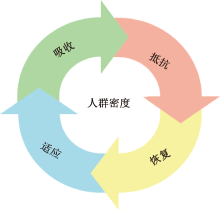
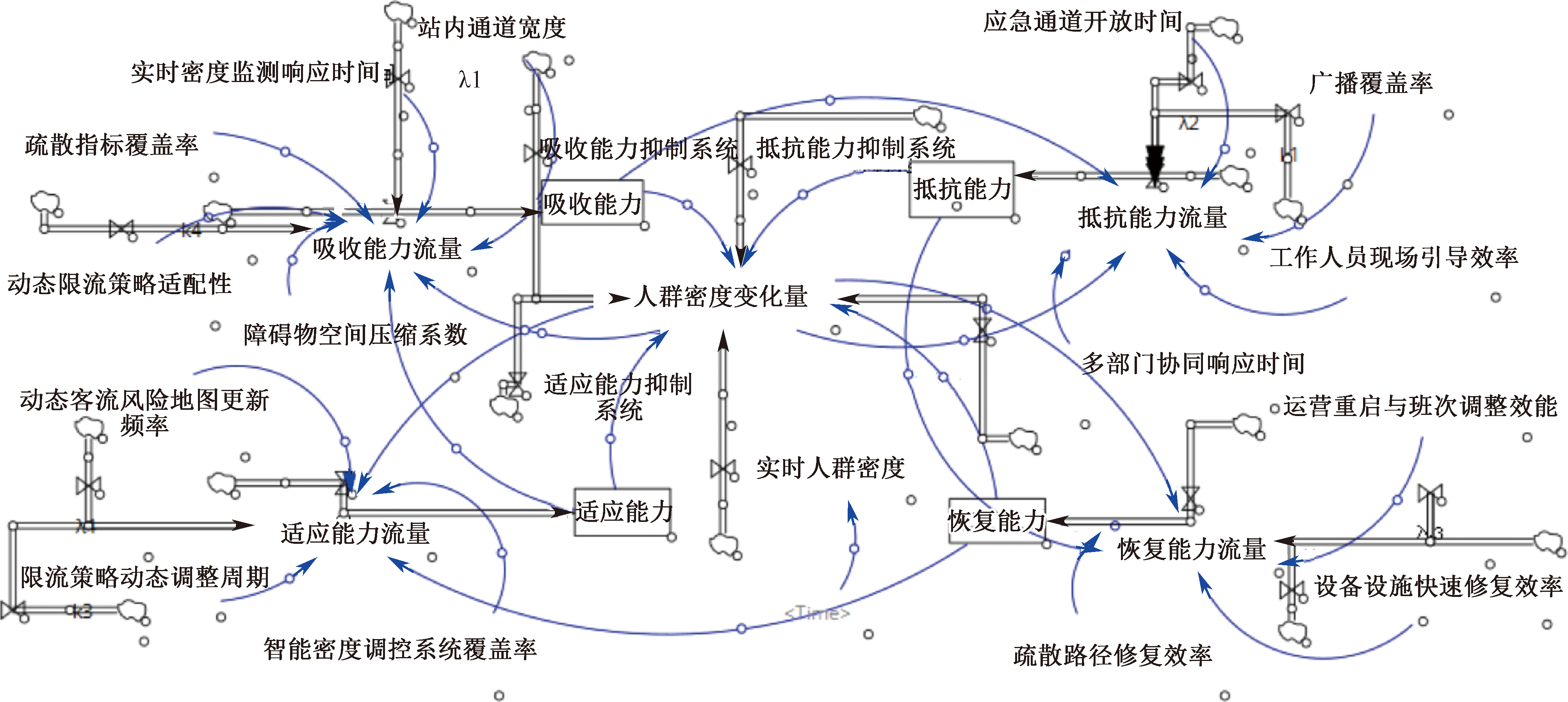
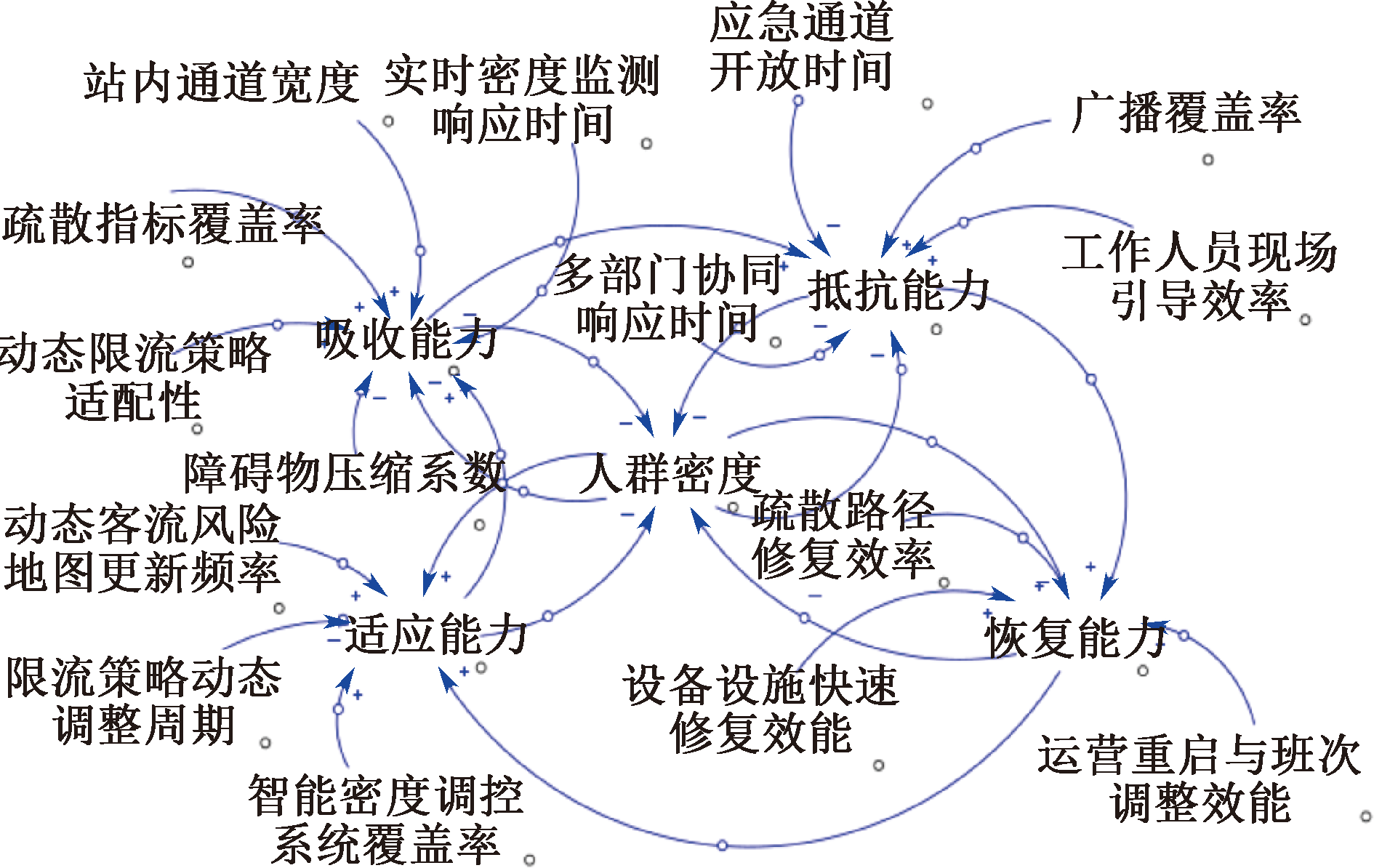
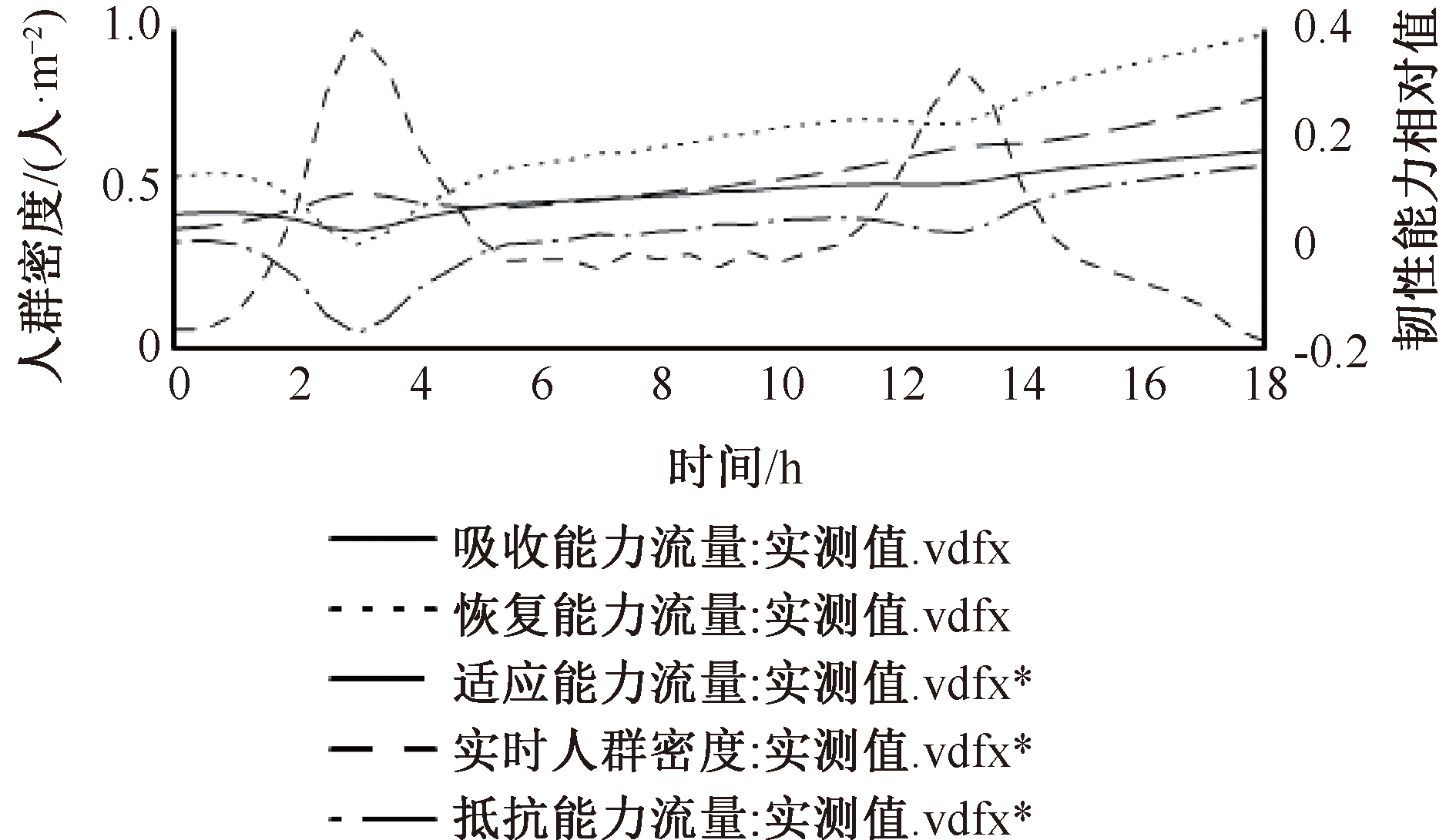
| [1] |
交通运输部. 2024年城市轨道交通运营数据速报[EB/OL].(2025-01-15). https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/qgwtz21W4LZfpHDX3JFlWQ.
|
| [2] |
张立茂, 刘梦洁, 吴贤国, 等. 基于DEA的地铁站拥挤踩踏风险分析[J]. 土木工程与管理学报, 2014, 31(4):76-82.
|
|
ZHANG Limao, LIU Mengjie, WU Xianguo, et al. Risk analysis of crowded stampede accident in subway stations based on DEA method[J]. Journal of Civil Engineering and Management, 2014, 31(4):76-82.
|
| [3] |
霍宇芒, 宋守信, 顾一波. 基于组合权重的地铁车站拥挤踩踏事故风险评价[J]. 安全与环境工程, 2016, 23(5):139-143.
|
|
HUO Yumang, SONG Shouxin, GU Yibo. Risk assessment of crowd crushing and trampling accidents in subway stations based on combined weights[J]. Safety and Environmental Engineering, 2016, 23(5):139-143.
|
| [4] |
HELBING D. Traffic and related self-driven many-particle systems[J]. Reviews of Modern Physics, 2001, 73(4): 1 067-1 141.
doi: 10.1103/RevModPhys.73.1067
|
| [5] |
FRUIN J. Pedestrian planning and design[M]. NewYork: Metropolitan Association of Urban Designers and Environmental Planners, 1971:24-27.
|
| [6] |
LU Ying, WANG Jingwen, DAI Weihui, et al. Research on risk factors of human stampede in mass gathering activities considering organizational patterns[J]. Front. Public Health, 2025,13: DOI: 10.3389/fpubh.2025.1555735.
|
| [7] |
王震, 王汉霖. 基于因子分析和熵权-TOPSIS的地铁运营系统韧性评价[J]. 智能城市, 2024, 10(8):73-76.
|
|
WANG Zhen, WANG Hanlin. Resilience evaluation of subway operation systems based on factor analysis and entropy-TOPSIS[J]. Intelligent City, 2024, 10(8): 73-76.
|
| [8] |
YALDA S, BIAL M A, ZHANG Yanjie, et al. Resilience-based strategies for topology enhancement and recovery of metro rail transit networks[J]. Journal of Risk and Uncertainty in Engineering Systems, Part A: Civil Engineering, 2020, 6(2): DOI: 10.1061/ajrua6.0001057.
|
| [9] |
WANG Jiaoe, HUANG Jie, YANG Haoran, et al. Resilience and recovery of public transport use during COVID-19[J]. NPJ Urban Sustain, 2022, 2(1):DOI: 10.1038/s42949-022-00061-1.
|
| [10] |
黄浪, 吴超, 杨冕, 等. 韧性理论在安全科学领域中的应用[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2017, 27(3):1-6.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2017.03.001
|
|
HUANG Lang, WU Chao, YANG Mian, et al. Application of resilience theory in field of safety science[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2017, 27(3): 1-6.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2017.03.001
|
| [11] |
王起全. 地铁拥挤踩踏事故脆弱性区域智能化预警研究[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2018, 28(11):162-167.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2018.11.026
|
|
WANG Qiquan. Research on intelligent early-warning of crowded stampede accidents vulnerabe areas in subway[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2018, 28(11): 162-167.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2018.11.026
|
| [12] |
王起全, 杨鑫刚, 蓝军, 等. 多源流理论视域下的地铁拥挤踩踏事故应急管理策略[J]. 中国安全科学报, 2023, 33(11):181-188.
|
|
WANG Qiquan, YANG Xin'gang, LAN Jun, et al. Emergency management strategy of subway stampede accidents based on multiple-streams theory[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2023, 33(11): 181-188.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2023.11.0792
|
| [13] |
袁欣. 基于仿真优化的地铁站行人踩踏风险控制研究[D]. 武汉: 中南财经政法大学, 2023.
|
|
YUAN Xin. Risk control of pedestrian trampling in subway station based on simulation optimization[D]. Wuhan: Zhongnan University of Economics and Law, 2023.
|
| [14] |
王维莉, 薛雪. 人群聚集场所拥挤踩踏风险评估[J]. 灾害学, 2024, 39(1):146-151,157.
|
|
WANG Weili, XUE Xue. Risk assessment of stampede accident in crowd gathering place[J]. Journal of Catastrophology, 2024, 39(1): 146-151,157.
|
| [15] |
张旭. 城市轨道交通运营系统安全韧性评价[D]. 石家庄: 石家庄铁道大学, 2022.
|
|
ZHANG Xu. Safety resilience evaluation of urban rail transit operation systems[D]. Shijiazhuang: Shijiazhuang Tiedao University, 2022.
|